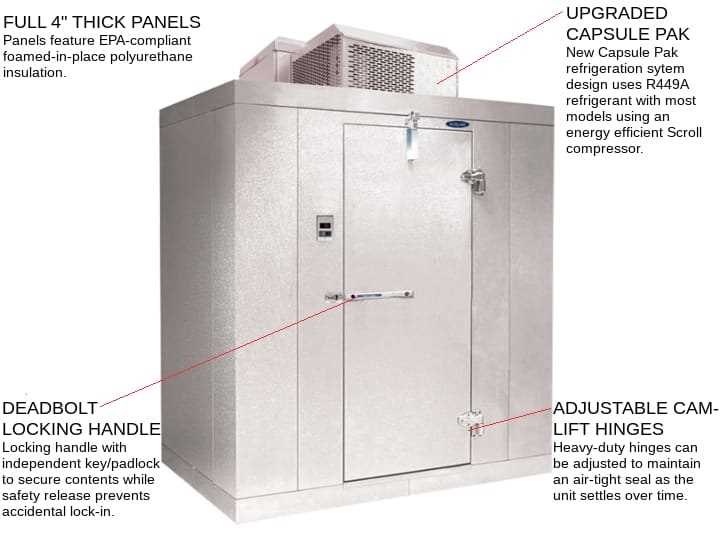
In the realm of temperature management, efficient design is essential for maintaining optimal conditions. Various mechanisms and elements come together to create a seamless environment for preserving perishable goods. This section delves into the intricate workings of these systems, highlighting the significance of each individual component.
Visualizing the arrangement of these critical elements allows for a better grasp of their interdependencies and functions. By examining how these units operate in harmony, one can appreciate the complexities involved in ensuring reliability and efficiency in cooling solutions.
Furthermore, knowledge of specific components enables maintenance personnel to diagnose issues swiftly, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall performance. Understanding these configurations not only aids in troubleshooting but also informs best practices for installation and operation.
Understanding Walk-In Cooler Components
Exploring the intricacies of large refrigeration units reveals a complex interplay of various elements, each contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency. A solid grasp of these essential components is crucial for optimal performance, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Key Elements of Refrigeration Systems
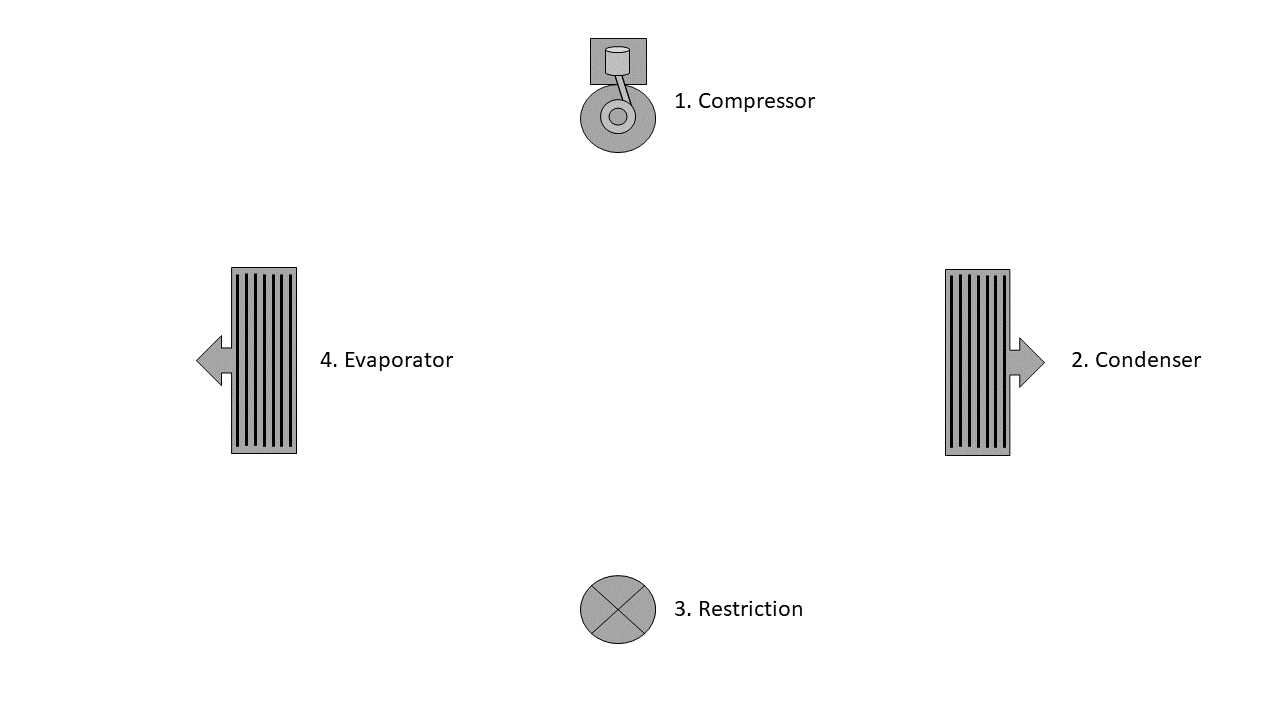
At the heart of these systems lies the compressor, a vital component that circulates refrigerant throughout the unit. This device increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, allowing it to move through the system. Another important part is the evaporator coil, which absorbs heat from the interior space, ensuring the environment remains cool. Additionally, the condenser plays a significant role in releasing heat from the refrigerant, making it an essential part of the cooling cycle.
Supporting Features and Controls
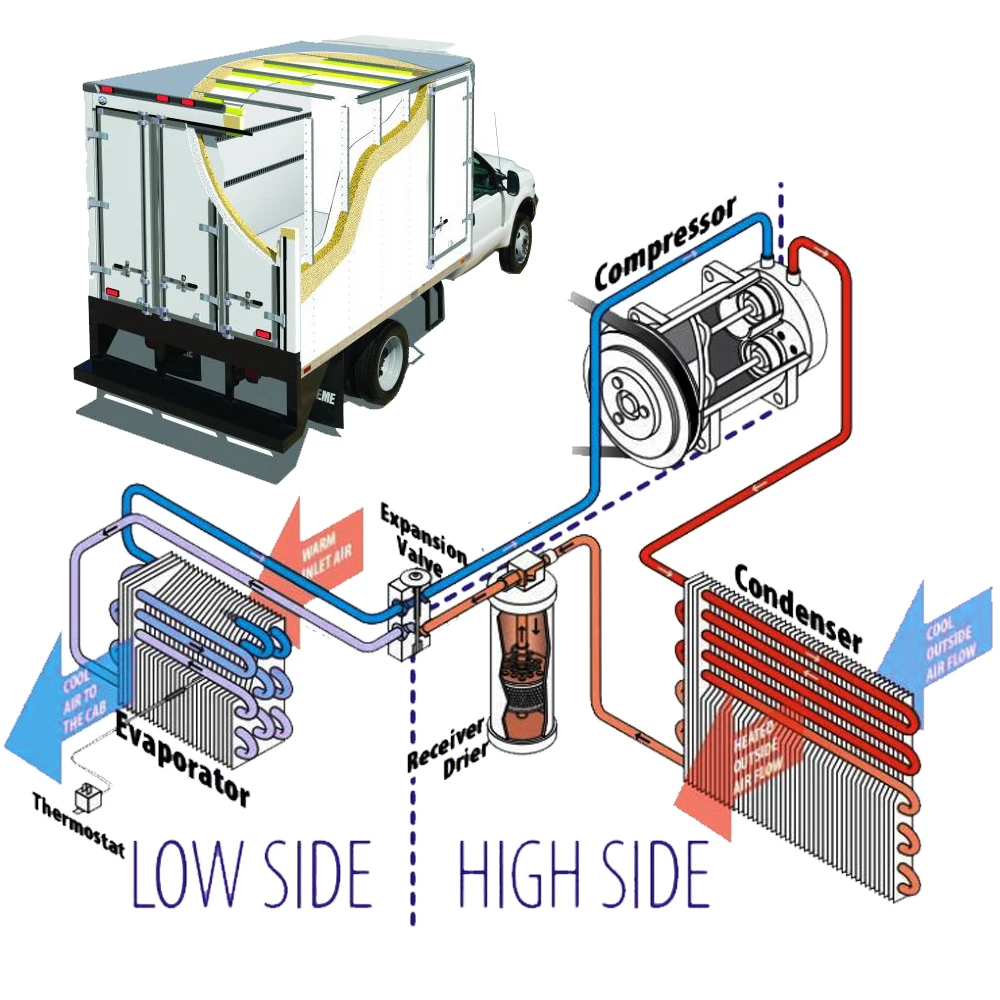
Beyond the primary components, several supporting features enhance functionality. Insulation is critical, as it helps maintain low temperatures by reducing heat transfer. Thermostats and control systems allow for precise temperature regulation, ensuring the environment meets specific storage requirements. Regular checks and maintenance of these elements ensure longevity and efficiency of the entire system.
Key Parts of a Walk-In Cooler
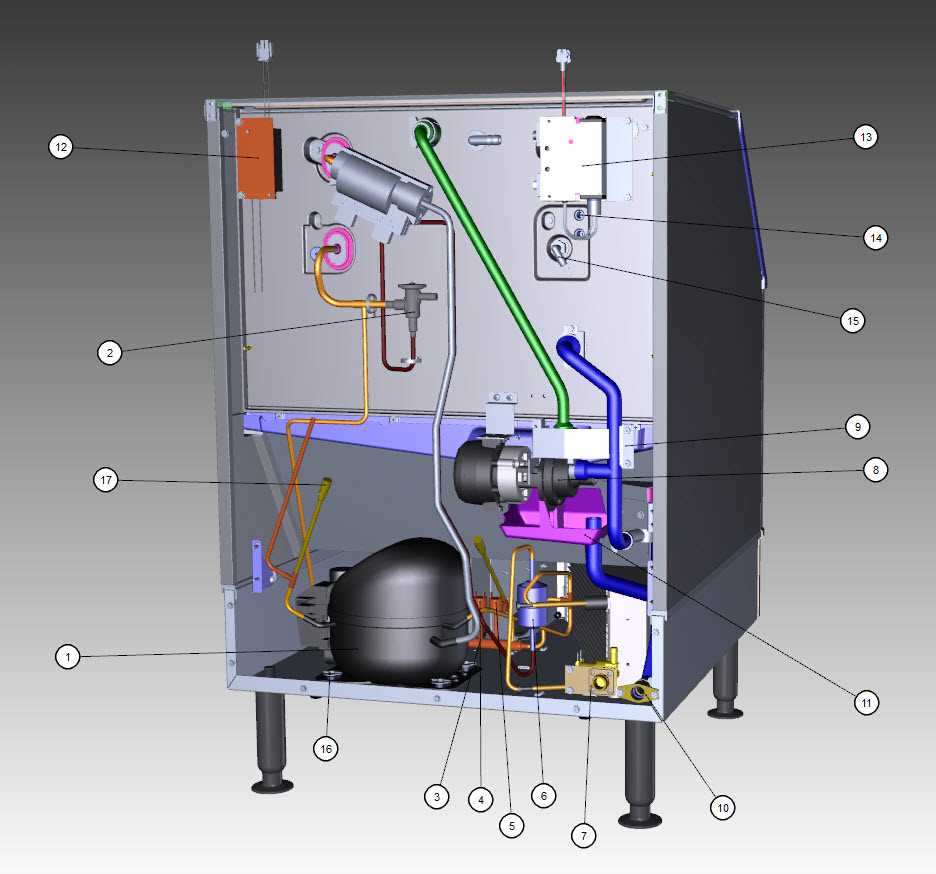
When setting up an industrial refrigeration system for storing perishable items, it’s essential to understand the essential components that contribute to its efficient operation. These systems are complex assemblies, each element playing a specific role in maintaining the ideal environment. In this section, we will examine the key elements involved in keeping the interior temperature consistent and ensuring that the unit functions properly for extended periods.
Refrigeration Unit

At the core of the refrigeration system is the refrigeration unit, which is responsible for maintaining the desired temperature inside the storage space. This unit extracts heat from the enclosed space and expels it outside, ensuring that the environment remains cold enough for product preservation. A well-functioning refrigeration unit is critical for energy efficiency and minimizing operational costs.
Insulated Panels
Another vital component is the insulated panels, which form the structure of the enclosure. These panels are designed to limit heat transfer, maintaining a consistent temperature within the space. The thickness and material of the insulation are critical in determining the effectiveness of the unit. Properly insulated panels reduce the load on the refrigeration unit, leading to lower energy consumption and increased operational efficiency.
Each component plays a specific role, from temperature control to energy management, ensuring that the storage environment is safe and optimal for preserving goods over extended periods.
Importance of Proper Cooling Systems
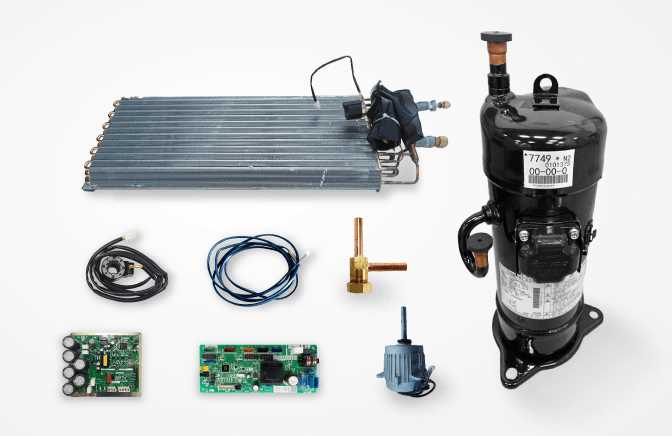

Efficient refrigeration is crucial for preserving products, maintaining safety, and ensuring the optimal functioning of various industries. Without an adequate setup, spoilage, product loss, and increased operational costs can arise. Thus, understanding and maintaining the correct cooling mechanisms is essential for long-term success and smooth operations.
Reliable Temperature Control
The core function of any refrigeration unit is to regulate temperature consistently. Proper temperature management is critical for preserving the quality and integrity of perishable items. In food storage facilities, for instance, temperature fluctuations can lead to spoilage and potential health hazards. In industrial settings, improper cooling can result in malfunctions and downtime, leading to lost productivity.
Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Another significant factor is energy efficiency. A well-designed system not only ensures proper temperature but also minimizes energy consumption. Energy-efficient cooling systems reduce operational costs while also lowering the environmental footprint. Regular maintenance and timely upgrades help in maintaining optimal energy usage and avoiding unnecessary expenses.
In conclusion, the reliability and effectiveness of a cooling system have a direct impact on both operational efficiency and product quality. Whether it is for food storage, industrial purposes, or any other application, investing in a proper refrigeration solution is vital to ensure success.
Common Issues with Walk-In Coolers

In any refrigeration system designed for large-scale storage, maintaining optimal performance is essential. Unfortunately, these units can encounter various challenges over time that may impact their efficiency, temperature control, or energy consumption. Identifying and addressing these problems promptly can prevent costly repairs and downtime. Below are some of the most frequent issues faced by these cooling units, along with their possible causes and solutions.
One of the most common problems is a failure in the cooling cycle. This may result from a malfunction in the compressor, evaporator, or the system’s refrigerant flow. Other issues can arise from poor insulation or faulty door seals, leading to increased energy consumption or compromised temperature control. Regular maintenance checks and prompt repairs are crucial for ensuring the unit remains in good working condition.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent Temperature | Faulty thermostat, blocked air vents | Check thermostat settings and clean air vents |
| Excessive Energy Consumption | Poor door seals, damaged insulation | Replace seals and inspect insulation |
| Unit Running Continuously | Compressor failure, refrigerant leak | Inspect compressor and repair any leaks |
| Frost Build-Up | Defrost timer malfunction, blocked evaporator fan | Repair or replace defrost timer, clean fan |
Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to identify these and other potential issues before they lead to more severe damage. Timely troubleshooting ensures the unit continues to operate efficiently, safeguarding stored products and optimizing energy use.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
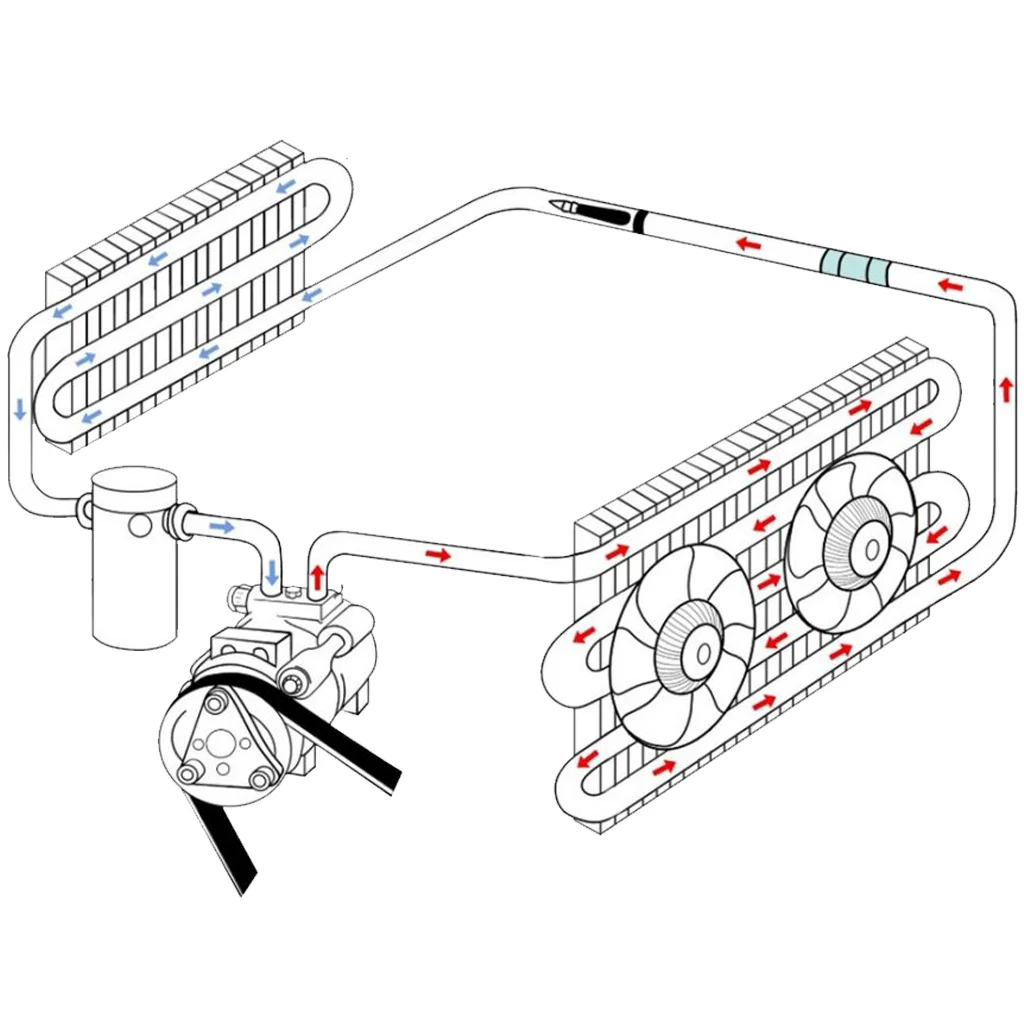
Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring the extended performance and efficiency of your refrigeration unit. Regular care can prevent costly repairs and maintain optimal operation over time. Understanding the key components and their functions helps in addressing potential issues before they become critical failures.
Routine Cleaning and Inspections
Regular cleaning of internal components, such as evaporators and condensers, helps remove dust and debris that can cause system inefficiency. Check for any signs of wear or damage, and replace any deteriorating parts. Cleaning coils and drains can prevent clogging, ensuring the smooth flow of refrigerants and minimizing energy consumption.
Monitor Temperature and Humidity
Maintaining a consistent internal environment is crucial for the longevity of your system. Fluctuating temperatures and humidity levels can strain the mechanical components. Always ensure that the internal temperature is kept within the manufacturer’s recommended range to avoid excessive workload on the unit.
Proactive maintenance is key to preventing unexpected breakdowns. Regular checks and timely part replacements contribute significantly to maintaining operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Refrigerant
When selecting a refrigerant for a temperature-controlled storage unit, it is important to consider several factors that affect both performance and environmental impact. The ideal refrigerant should provide optimal cooling efficiency while being safe for use in specific systems.
- Efficiency: The chosen substance should effectively transfer heat to maintain the desired temperature range without consuming excessive energy.
- Compatibility: Different systems are designed to handle particular types of refrigerants, so compatibility with existing components is crucial.
- Environmental Impact: Choosing a refrigerant with low global warming potential (GWP) and zero ozone depletion potential (ODP) ensures a more eco-friendly solution.
- Regulations: Ensure compliance with local environmental regulations and industry standards to avoid legal issues and penalties.
- Cost: Consider both initial purchase cost and long-term operating expenses, including energy consumption and maintenance requirements.
By carefully evaluating these criteria, you can make an informed decision on the best refrigerant for your system, contributing to its efficiency and sustainability.
Electrical System Overview
The electrical configuration of refrigeration units is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and energy efficiency. This system integrates various components to regulate temperature and maintain optimal performance. Understanding how each part works together is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining consistent functionality.
Main Components
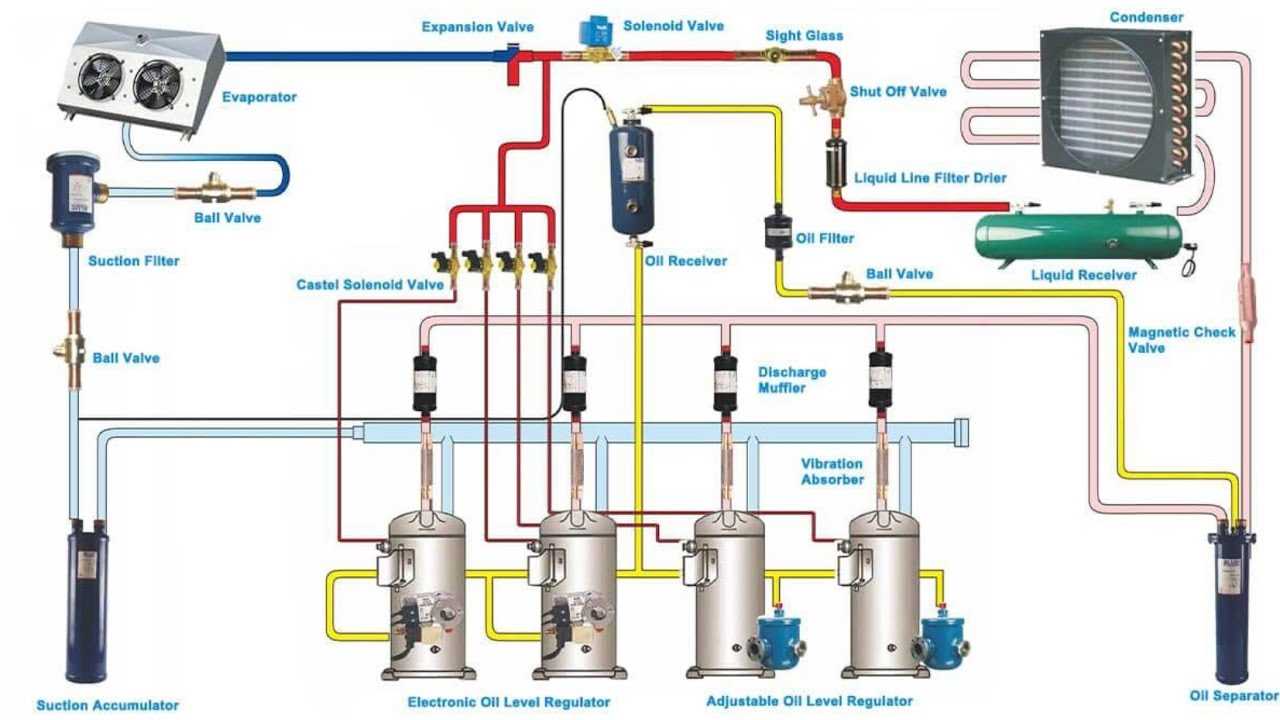
- Power Supply: Provides necessary electrical energy for all components.
- Compressor Motor: Drives the cooling process by circulating refrigerant through the system.
- Evaporator Fan: Ensures proper air circulation and prevents temperature imbalances.
- Thermostat: Monitors and adjusts the internal temperature settings.
Electrical Connections and Safety Features

- Wiring: Connects all electrical components, ensuring efficient energy flow.
- Circuit Breakers: Protect the system from electrical overloads and short circuits.
- Grounding: Prevents electrical hazards by ensuring proper grounding of all components.
Insulation Types and Their Benefits
When it comes to maintaining temperature-controlled environments, choosing the right material for thermal protection is essential. Various options provide different levels of energy efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the benefits of each insulation type can help make an informed decision based on specific needs and usage conditions.
Common Insulation Materials
- Polyurethane Foam: Known for its high thermal resistance and durability, polyurethane foam is commonly used in environments that require excellent temperature control.
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS): Offers strong moisture resistance and a high R-value, making it suitable for areas exposed to humidity or harsh conditions.
- Fiberglass: A cost-effective choice with good thermal properties, often used in a variety of applications for reliable insulation.
- Polyisocyanurate (PIR): Provides superior thermal performance and is often used for its fire-resistant properties, especially in commercial applications.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Specific Needs
- Energy Efficiency: Materials like polyurethane foam and PIR are ideal for environments where energy savings are a priority due to their high insulating values.
- Moisture Control: For areas where moisture might be a concern, XPS is a preferred option as it resists water absorption.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Fiberglass offers a balance between affordability and performance, making it a great choice for standard insulation needs.