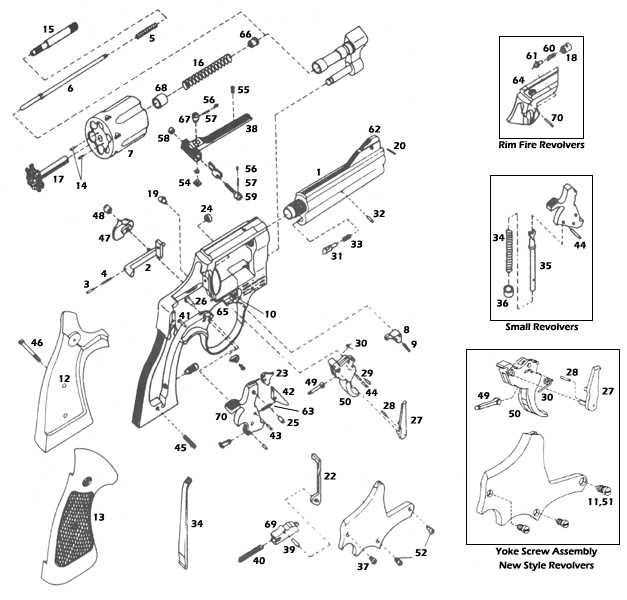
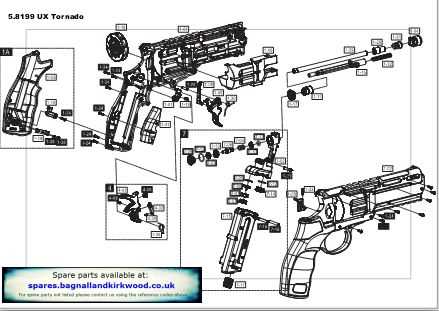
The intricate design of a firearm encompasses various elements that work together to ensure functionality and safety. Each component plays a crucial role, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the mechanism. A comprehensive exploration of these elements reveals the precision involved in their construction and operation.
By examining the structure of a specific type of weapon, enthusiasts and learners can gain insights into how these elements interact. This understanding not only enhances appreciation for the craftsmanship involved but also promotes responsible usage and maintenance. The synergy of these components is vital for both novice users and seasoned experts.
Detailed illustrations and explanations can aid in visualizing the assembly of these features, providing clarity on their respective functions. A thorough grasp of these fundamentals fosters an informed perspective on handling and caring for such mechanisms.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential components that make up the firearm mechanism. By examining the individual elements and their functions, readers will gain a deeper understanding of how this type of weapon operates effectively.
Main Components Overview
Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of the firearm. The following list outlines the primary components:
- Cylinder – Holds the ammunition and rotates to align with the firing mechanism.
- Trigger – Activates the firing mechanism when pulled.
- Hammer – Strikes the firing pin to ignite the cartridge.
- Frame – The main structure that houses all components.
- Sights – Aid in aiming the firearm accurately.
Functionality of Key Elements
Understanding how these parts work together is vital for comprehending the overall operation:
- The cylinder rotates as the trigger is pulled, positioning the next round in line with the firing mechanism.
- The hammer is cocked and released, striking the firing pin to ignite the round.
- Successful ignition sends the projectile down the barrel, resulting in discharge.
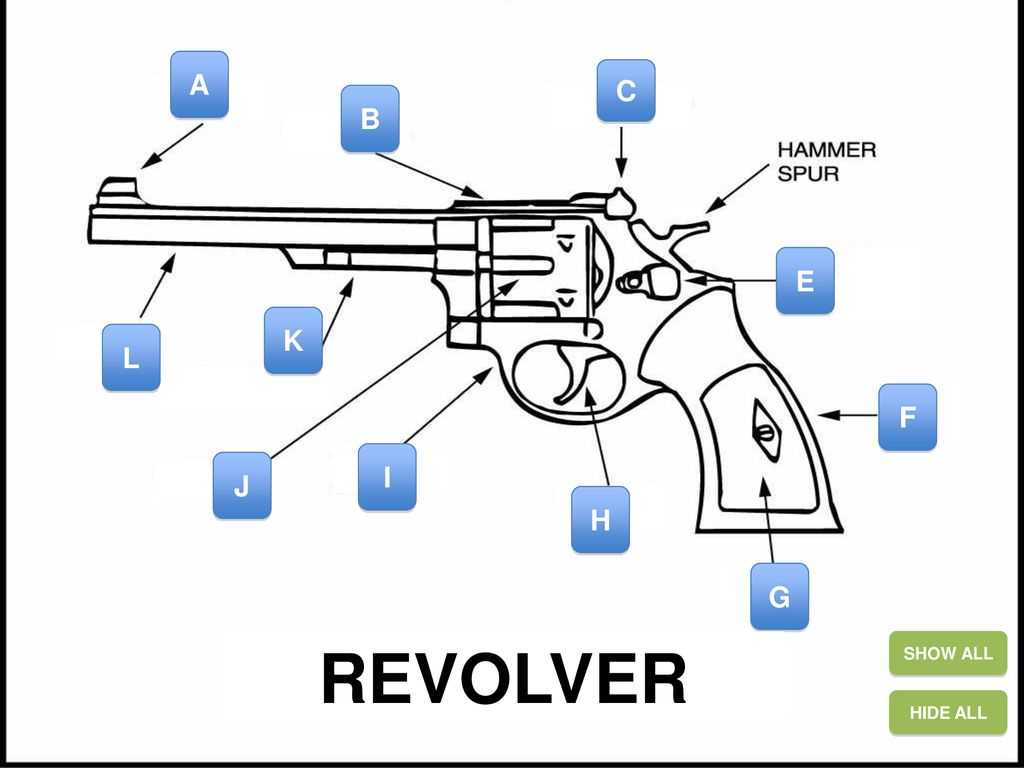
Key Components of a Revolver
The functioning of this type of firearm relies on several essential elements that work together to ensure its operation. Each component plays a critical role in the overall mechanism, contributing to the effectiveness and reliability of the device. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone interested in firearms, whether for practical use, historical knowledge, or design appreciation.
Cylinder: This is a rotating chamber that holds the ammunition. It allows for quick cycling between shots and is fundamental in the loading and firing process.
Trigger: This mechanism is responsible for initiating the firing sequence. When pulled, it engages the hammer or striker, releasing the firing pin to strike the cartridge.
Hammer: This component acts as a striking mechanism that, when cocked and released, strikes the firing pin or cartridge primer, igniting the propellant and firing the projectile.
Frame: The main body of the device houses and supports all other elements. It is designed for strength and durability, allowing for safe handling and operation.
Sights: These are alignment tools that assist the user in aiming at a target. They can vary in style and complexity, impacting accuracy and ease of use.
Functionality of Revolver Parts
The mechanisms within a firearm are designed to work in harmony, ensuring reliability and accuracy during operation. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall effectiveness of the weapon, contributing to its ability to fire projectiles efficiently.
The firing mechanism initiates the discharge of ammunition when the trigger is engaged. This action releases a hammer or striker that impacts the cartridge, igniting the propellant and launching the bullet through the barrel. The rotation system facilitates the sequential alignment of each cartridge with the firing pin, enabling multiple shots without reloading.
The frame serves as the structural foundation, housing various components and providing stability during use. Additionally, the grip allows for comfortable handling, enhancing the user’s control and aim. The barrel is engineered for precision, ensuring that the projectile travels accurately towards its target.
In summary, the intricate interplay of these components underscores the sophistication of the firearm, showcasing a blend of engineering and design aimed at optimal performance.
Types of Revolver Mechanisms
The mechanics behind these firearms play a crucial role in their functionality and reliability. Various designs have emerged over the years, each with unique features that cater to different preferences and operational needs. Understanding these mechanisms can enhance appreciation for their engineering and historical significance.
-
- Single-Action: In this mechanism, the shooter must manually cock the hammer before firing. This design typically allows for a lighter trigger pull, making it suitable for precision shooting.
lessCopy code
- Double-Action: This type allows the user to fire the weapon either by pulling the trigger directly or by first cocking the hammer. This versatility makes it popular among those who prioritize quick operation.
- Double-Action/Single-Action: Combining the features of both previous types, this mechanism offers flexibility. The shooter can choose between a light pull for precision shots or a quicker trigger action for rapid firing.
- Top-Break: This design features a hinge that allows the barrel to swing open for loading and unloading. It provides quick access to the chamber, making it a convenient choice for some users.
- Swing-Out Cylinder: In this system, the cylinder swings outward for easy access to the chambers. This design is prevalent in modern models, as it allows for quicker reloading compared to traditional designs.
Each mechanism has its own advantages and disadvantages, influencing the choice of firearm for various shooting disciplines and preferences. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right model for specific needs.
Revolver Safety Features Explained
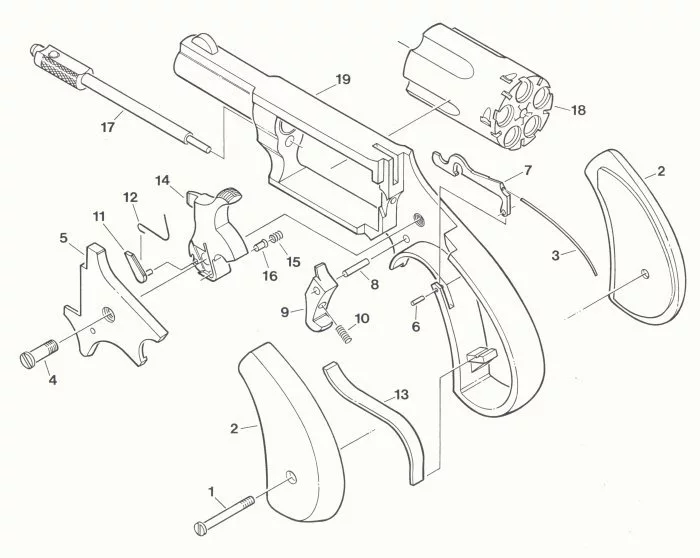
Ensuring user protection while handling firearms is paramount. This section delves into the various mechanisms designed to enhance safety and prevent accidental discharges. Understanding these features is crucial for responsible ownership and use.
Key Safety Mechanisms
- Trigger Safety: A mechanism that prevents the trigger from being pulled unless fully depressed, reducing the risk of unintentional firing.
- Cylinder Lock: A device that secures the cylinder in place, ensuring that it does not rotate unexpectedly when not intended.
- Hammer Block: A safety feature that obstructs the hammer from striking the firing pin unless the trigger is pulled, preventing accidental discharges.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of these safety features are vital. Ensuring that all mechanisms function correctly can significantly reduce the risk of mishaps. Owners should consult professional services for thorough checks to maintain optimal performance.
- Check the trigger mechanism for proper engagement.
- Inspect the cylinder lock for smooth operation.
- Verify the hammer block’s functionality regularly.
Common Materials Used in Revolvers
In the design and construction of firearms, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in determining functionality, durability, and overall performance. Various components are crafted from distinct substances that offer specific advantages, contributing to the effectiveness and reliability of the weapon.
Metals
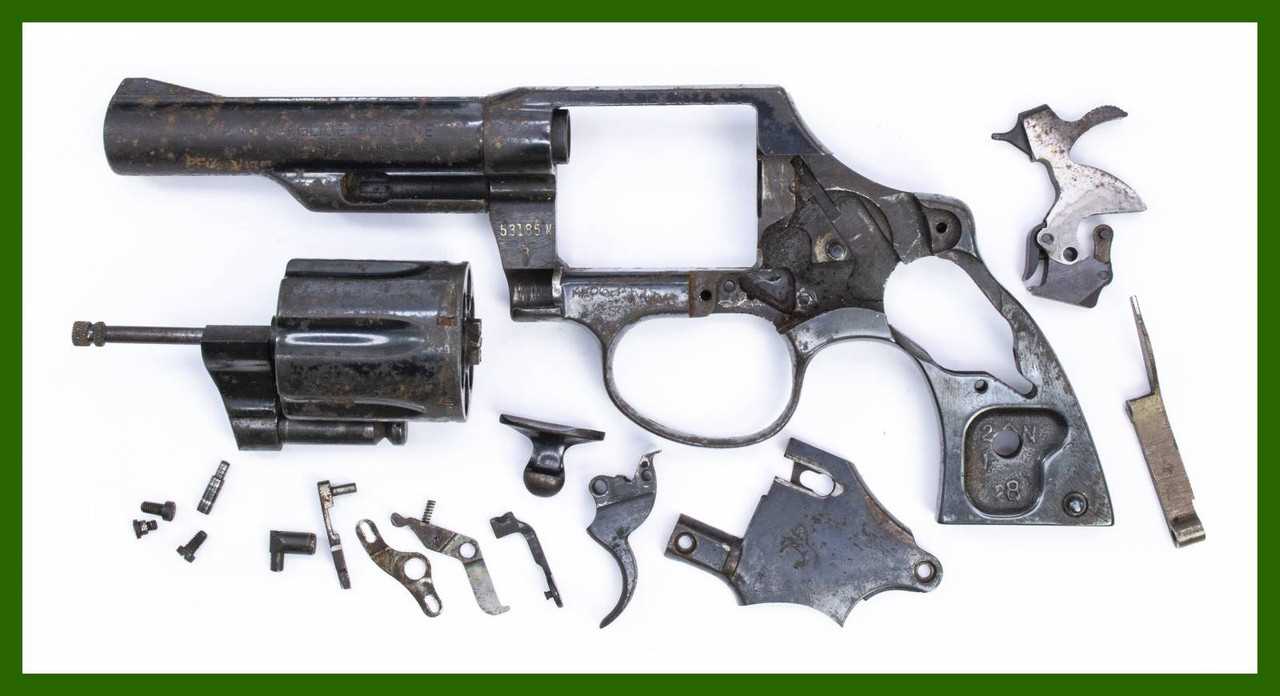

Steel is often the primary choice due to its strength and resilience. High-carbon steel, in particular, provides excellent toughness, making it ideal for critical components that undergo significant stress. In some cases, stainless steel is utilized for its corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity even in challenging conditions.
Polymers
Modern innovations have introduced synthetic materials that enhance the functionality of firearms. Polymer composites are commonly used for grips and frames, offering a lightweight alternative while maintaining durability. These materials are often favored for their ability to absorb shock and provide a comfortable hold.
Maintenance of Revolver Components
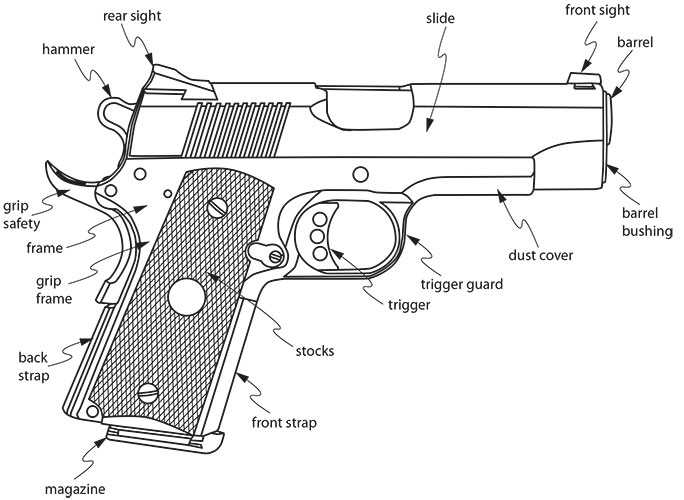
Proper upkeep of firearm elements is crucial for ensuring functionality, reliability, and longevity. Regular attention not only enhances performance but also promotes safety during use. Here are key practices for maintaining these components:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the individual elements frequently to remove residue and dirt that can impede operation.
- Lubrication: Apply suitable lubricants to moving parts to minimize friction and prevent wear.
- Inspection: Routinely check components for signs of damage or wear, addressing any issues promptly.
- Storage: Store the firearm in a dry, secure location to protect it from environmental factors that can cause deterioration.
Following these maintenance practices will help ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the firearm.
Comparing Revolvers with Other Firearms
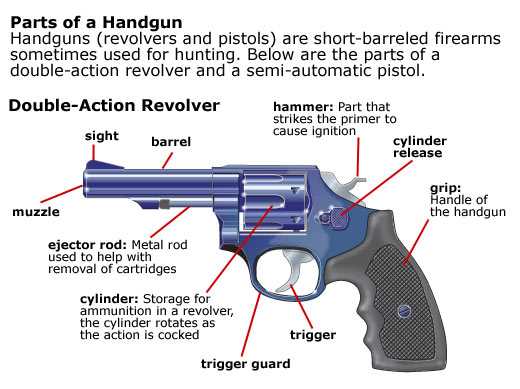
When examining various types of handguns, it is essential to understand the unique characteristics and functionalities that differentiate one design from another. While some models rely on a magazine for ammunition, others utilize a revolving chamber system. This section delves into the distinctions between these firearms, highlighting their advantages and limitations.
One primary difference lies in the mechanism of firing. Traditional handguns often require a specific action to chamber a round, whereas the revolving type offers immediate accessibility to multiple cartridges. This can enhance the speed of engagement in critical situations. Furthermore, the weight and balance of each design contribute to handling and shooting accuracy, with some users preferring the steady grip provided by one type over another.
In terms of ammunition capacity, the revolving design typically accommodates fewer rounds compared to semi-automatic counterparts. This limitation may be a consideration for those seeking higher capacity for competitive shooting or self-defense. However, the reliability of the revolving chamber system can be a significant advantage in environments where maintenance is challenging.
Ultimately, the choice between these types of firearms often depends on individual preferences and intended use. Understanding the inherent differences can guide potential users in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Historical Evolution of Revolver Design
The journey of this innovative firearm has seen remarkable transformations since its inception. Initially designed for simple operation and efficiency, it has evolved into a sophisticated mechanism that balances performance, reliability, and aesthetics. Various cultures and technological advancements have influenced its development, leading to unique designs that cater to different needs and preferences.
Early Innovations
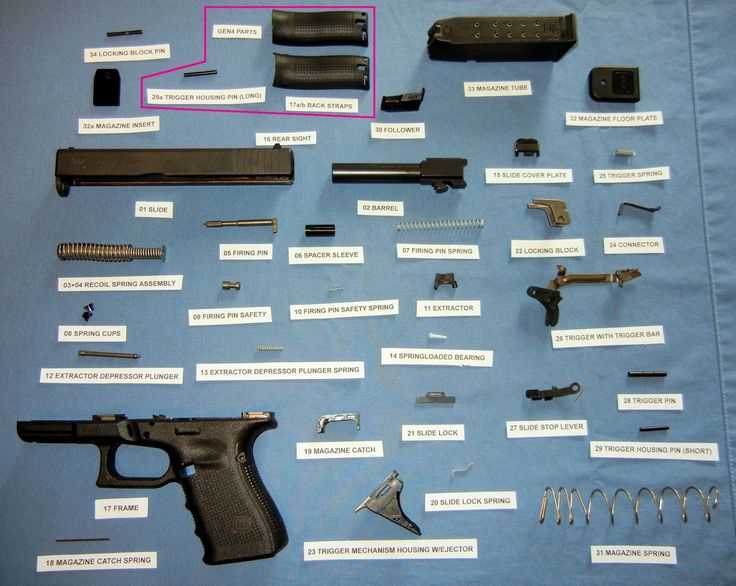

In the early 19th century, the introduction of multi-shot capabilities marked a significant milestone. The first notable designs utilized a rotating cylinder, allowing for rapid firing without the need to reload after each shot. This breakthrough not only enhanced usability but also set the stage for future enhancements in firearm technology.
Modern Advancements
As time progressed, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques further refined the design. Modern iterations incorporate lightweight materials, improved ergonomics, and enhanced safety features, making them more user-friendly. These developments reflect a broader trend in firearm design, emphasizing not only functionality but also user comfort and safety.