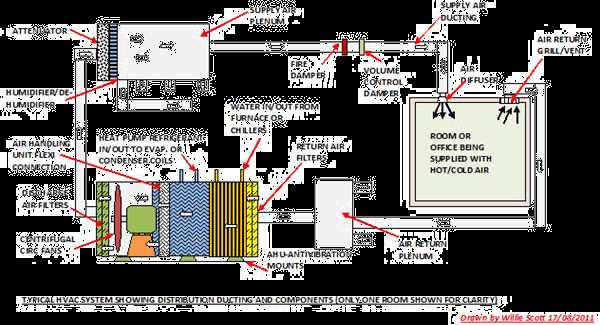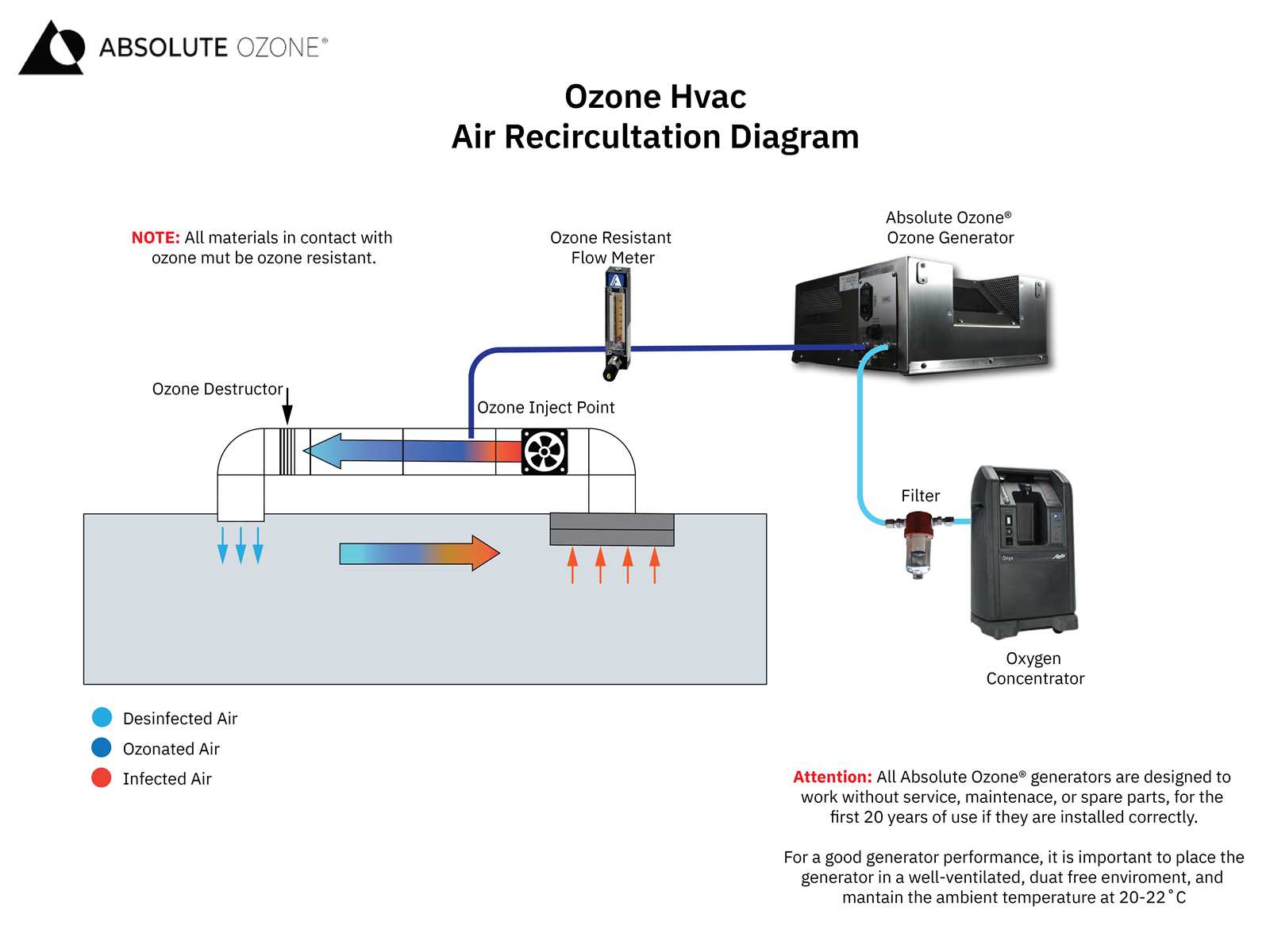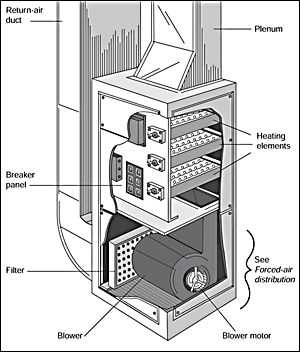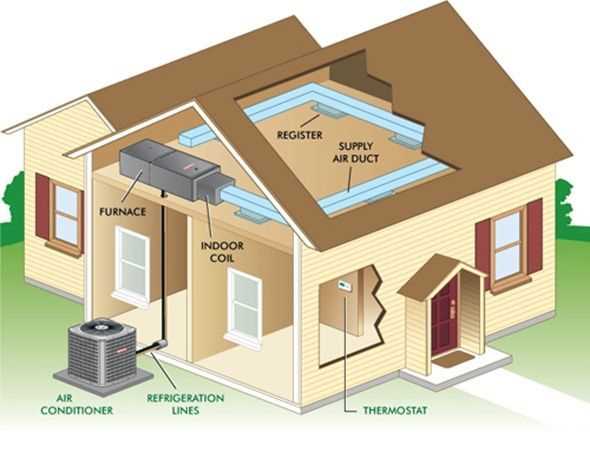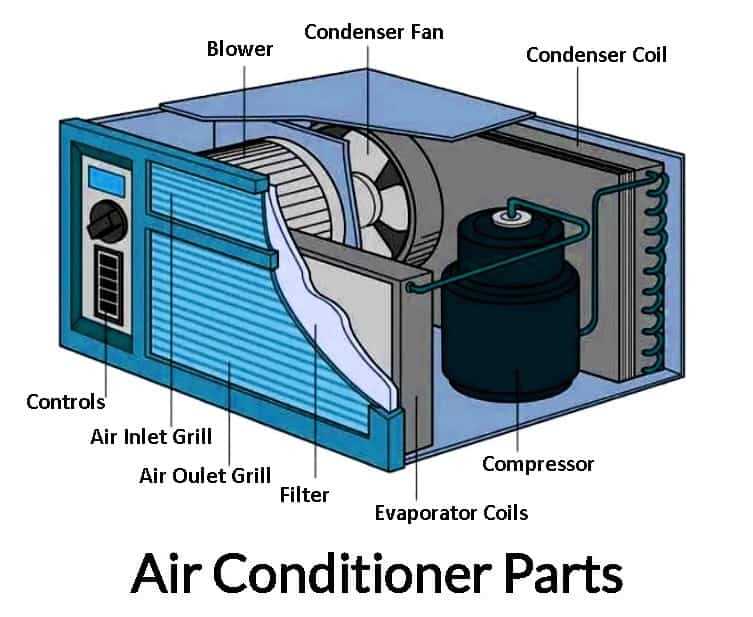
Modern climate regulation systems rely on a range of interconnected elements to manage indoor temperatures and ensure comfort. Each of these components plays a unique role in maintaining the desired environment, working together to deliver efficient performance and energy savings. By examining how these elements operate in unison, we gain a clearer picture of the inner workings of climate control technology.
From the cooling and heating processes to air movement and filtration, various mechanisms collaborate to adjust and maintain optimal conditions. These key elements function in harmony to create a comfortable and healthy indoor atmosphere, tailored to the preferences of the occupants.
Understanding the individual roles and connections between these essential parts offers valuable insights into how this technology optimizes air quality and temperature control. Such knowledge can help in both regular maintenance and the identification of potential issues.
Overview of HVAC System Components
Modern climate control mechanisms rely on several interconnected elements working together to ensure comfort and efficiency. These key elements are responsible for temperature regulation, airflow, and overall indoor environment quality. By understanding the essential components, one can better appreciate how these mechanisms maintain a balanced atmosphere in homes and commercial spaces.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compressor | Pressurizes refrigerant to initiate the cooling process. | ||||||||||||||||
| Evaporator Coil | Absorbs heat from indoor air, cooling the environment. | ||||||||||||||||
| Condenser | Releases absorbed heat to the outside environment. | ||||||||||||||||
| Fan | Circulates air across key elements to e
Heating and Cooling Elements ExplainedThe components responsible for managing indoor temperature focus on providing warmth during colder months and cooling when it’s hot. These elements work together to maintain a balanced and comfortable environment, using different technologies and techniques to regulate the temperature inside buildings. Main Heating Components
Cooling Components
Key Functions of Thermostats in HVACThermostats play a crucial role in regulating indoor temperature by controlling the heating or cooling equipment in residential and commercial spaces. They maintain the desired climate by monitoring environmental conditions and ensuring comfort, efficiency, and energy savings. Temperature RegulationThe primary function of a thermostat is to regulate temperature based on user preferences. It monitors the current room temperature and compares it to the set level, adjusting accordingly to maintain consistent comfort. Energy EfficiencyModern thermostats are designed to optimize energy use. By preventing unnecessary heating or cooling, they help reduce energy consumption, resulting in lower utility bills and environmental impact.
Understanding the Role of CompressorsThe compressor is a vital component that plays a key role in the functionality of various climate control and refrigeration mechanisms. Its primary function revolves around regulating the movement and pressure of gases, which enables the effective transfer of heat. Without this essential unit, the entire cooling or heating process would be hindered, making it difficult to maintain desired temperatures. Through these functions, compressors contribute significantly to maintaining comfortable and controlled environments, ensuring systems run effectively and efficiently. How Air Filters Improve Air Quality
Air filters play a vital role in enhancing the quality of indoor environments by trapping various pollutants and allergens. By effectively removing particles from the air, these components contribute to healthier living spaces, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and promoting overall well-being. Benefits of Clean AirMaintaining clean air within enclosed areas offers several advantages: Types of Air FiltersVarious types of filters are designed to target specific pollutants: By choosing the appropriate filtration methods, individuals can significantly enhance their indoor air quality, leading to a healthier and more pleasant living environment. The Purpose of Blower Motors in HVAC
Blower motors play a crucial role in the efficient functioning of climate control mechanisms. They are responsible for circulating air throughout a space, ensuring a comfortable environment regardless of external conditions. By moving air through various components, these motors help maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels. Air Distribution and ComfortThe primary function of blower motors is to distribute air evenly throughout an area. This circulation enhances comfort by preventing hot or cold spots, allowing for a more consistent atmosphere. A well-functioning blower motor contributes to a balanced climate, making it essential for occupant satisfaction. Energy EfficiencyEfficient blower motors can significantly reduce energy consumption. By optimizing airflow, they allow heating and cooling units to operate more effectively, ultimately leading to lower utility bills. Investing in high-quality motors can enhance the overall performance and longevity of the entire climate control setup. Heat Exchangers and Their ImportanceHeat exchangers play a vital role in transferring thermal energy between different fluids without mixing them. They are essential components in various applications, ensuring efficient energy use and maintaining optimal operating conditions. Understanding their significance can help in appreciating how they enhance performance and efficiency in various environments. Functionality and EfficiencyThese devices work by allowing one fluid to release heat while another absorbs it, facilitating effective energy transfer. This process not only improves overall efficiency but also reduces energy consumption. By optimizing the temperature of working fluids, heat exchangers contribute to cost savings and lower environmental impact. Applications Across Industries
Heat exchangers find applications in numerous fields, including manufacturing, power generation, and heating systems. Their versatility allows them to adapt to different operating conditions, making them crucial for maintaining process reliability and efficiency. From residential heating solutions to large industrial processes, these components are integral to modern energy management. Control Systems for Efficient OperationEffective management of temperature and air quality relies on advanced mechanisms that optimize performance and energy usage. These control solutions play a vital role in ensuring that indoor environments remain comfortable while minimizing resource consumption. Automation and MonitoringAutomated controls enable real-time adjustments based on environmental changes. Sensors monitor conditions such as temperature, humidity, and occupancy, allowing the system to respond dynamically. This level of intelligence ensures that energy is used efficiently, reducing waste and lowering operational costs. Integration of Smart TechnologyThe incorporation of smart technology enhances operational capabilities. Users can manage their environments remotely through applications, enabling personalized settings and schedules. This integration not only promotes convenience but also fosters energy conservation, leading to a sustainable approach to climate control. |