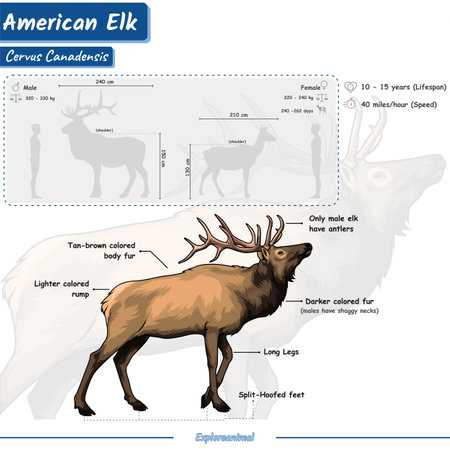
The study of wildlife anatomy provides valuable insights into the various components that make up a creature’s physical structure. This knowledge is essential for wildlife enthusiasts, researchers, and anyone interested in the natural world. By examining the unique characteristics of these organisms, we can appreciate their adaptations and the roles they play within their ecosystems.
Each region of this species contributes to its overall functionality, allowing it to thrive in diverse environments. From locomotion to sensory perception, every segment has evolved to meet specific survival needs. Understanding these features not only enhances our appreciation for nature but also aids in conservation efforts by highlighting the importance of preserving their habitats.
By exploring the intricacies of this well-known animal, we gain a deeper understanding of its behavior and interactions with the surrounding ecosystem. This exploration fosters a connection with wildlife, encouraging respect and protection for these remarkable beings.
Understanding Deer Anatomy
The study of the structure and organization of these graceful creatures provides insight into their physiology and adaptations. Knowledge of their form is essential for various fields, including wildlife management, conservation, and ecological research. Recognizing how their systems operate enhances our understanding of their behavior and habitat needs.
Key components include skeletal frameworks, muscular systems, and vital organs, all of which contribute to their survival and functionality in the wild. Each element plays a distinct role, from mobility to sensory perception, ultimately shaping the overall health and resilience of the species.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Skeletal System | Framework of bones supporting the structure | Provides support, facilitates movement, and protects vital organs |
| Muscular System | Collection of muscles allowing movement | Enables locomotion and various physical activities |
| Circulatory System | Network of blood vessels and heart | Transports oxygen and nutrients throughout the organism |
| Nervous System | System of nerves and brain | Controls bodily functions and processes sensory information |
| Digestive System | Organs involved in food processing | Breaks down food to extract essential nutrients |
Major Organs and Their Functions
The intricate systems within an animal are composed of various essential components that work harmoniously to maintain life. Each crucial organ plays a significant role, contributing to overall health and functionality. Understanding these vital elements provides insight into how living beings operate and adapt to their environments.
The heart serves as the central organ of the circulatory system, pumping blood throughout the organism to deliver oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. The lungs, responsible for respiration, facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, supporting cellular processes. Meanwhile, the liver performs numerous metabolic functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.
The kidneys are vital for maintaining fluid balance and filtering waste from the bloodstream, producing urine as a means of excretion. The stomach and intestines, components of the digestive system, work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate undigested material. Additionally, the brain orchestrates the nervous system, controlling movement, thought processes, and sensory perception, ensuring proper coordination and response to external stimuli.
Each organ, with its specialized function, is essential for the harmonious operation of the entire organism, highlighting the complexity and interdependence of biological systems.
External Features of Deer
The outward characteristics of these elegant creatures play a crucial role in their survival and adaptability in diverse environments. Understanding these traits provides insight into their behavior, ecology, and interaction with their surroundings.
- Antlers: Typically found on males, these unique structures are not only impressive but also serve purposes in mating displays and combat during the breeding season.
- Fur: The coat varies in color and texture, providing effective camouflage against predators. Seasonal changes in fur density and coloration help regulate body temperature.
- Eyes: Positioned on the sides of the head, the large eyes offer a wide field of vision, aiding in predator detection and navigation through their habitat.
- Ears: Highly mobile and sensitive, these features enhance auditory capabilities, allowing them to detect sounds from various directions, crucial for avoiding threats.
Each of these characteristics contributes to the overall adaptability and resilience of the species, making them fascinating subjects for study and observation in the wild.
Musculoskeletal System Overview
The musculoskeletal framework is essential for mobility and support in various species. It encompasses a complex arrangement of structures that work in unison to facilitate movement, provide stability, and protect vital organs. Understanding this intricate system is crucial for comprehending how these creatures navigate their environment and engage in essential activities such as foraging and evasion from predators.
Components of the Framework
This system comprises two main elements: the skeleton and the muscular system. The skeleton consists of bones and cartilage, forming the structural foundation. In contrast, the muscular system, made up of various types of muscles, generates movement by contracting and relaxing. Together, these components allow for a wide range of motions, from running to jumping.
Functions and Importance
The primary functions of this anatomical system include facilitating locomotion, maintaining posture, and enabling complex interactions with the surroundings. Moreover, it plays a pivotal role in supporting overall health and well-being, as the strength and integrity of these components contribute to the organism’s ability to thrive in its habitat. Regular activity is essential for the upkeep of this framework, ensuring that it remains resilient and functional.
Reproductive System Characteristics
The reproductive system of various mammals exhibits fascinating adaptations that facilitate the continuation of the species. Understanding these features reveals crucial insights into their breeding behaviors, hormonal influences, and overall health.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males and females often display distinct physical characteristics, influencing mating strategies and competition.
- Breeding Seasons: Many species have specific mating periods that align with environmental factors, ensuring optimal conditions for offspring survival.
- Gestation Period: The duration of pregnancy varies, impacting the timing of birthing and the care required for the young.
Several notable elements contribute to the reproductive strategies of these mammals:
- Hormonal Regulation: Hormones play a vital role in controlling reproductive cycles and behaviors, influencing factors such as estrus and mating readiness.
- Gestational Care: Maternal behaviors, including nesting and nurturing, are crucial for the healthy development of the offspring.
- Reproductive Organs: Specialized structures are adapted for mating, gestation, and birthing, showcasing a variety of evolutionary adaptations.
Comprehending these reproductive characteristics not only enhances our knowledge of species diversity but also informs conservation efforts aimed at preserving ecosystems and their inhabitants.
Digestive System Components Explained
The digestive system plays a vital role in the overall health and well-being of an animal. This intricate network is responsible for processing food, extracting essential nutrients, and eliminating waste. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system is crucial for comprehending how nourishment is converted into energy and sustenance.
Key Elements of the Digestive Process
At the core of digestion are several key components, each with a distinct function. The process begins in the oral cavity, where food is mechanically broken down and mixed with saliva, containing enzymes that initiate the digestive process. Following this, the esophagus transports the food to the stomach, a muscular organ that further breaks down the contents through a combination of acids and enzymes.
Nutrient Absorption and Waste Elimination
Once food is adequately processed in the stomach, it moves into the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs. The walls of this organ are lined with tiny projections called villi, which facilitate the uptake of nutrients into the bloodstream. After the small intestine, any remaining waste proceeds to the large intestine, where water is reabsorbed, and the remaining material is prepared for excretion.
Nervous System Insights
The complex network responsible for transmitting signals throughout an organism plays a crucial role in its survival and interaction with the environment. Understanding this intricate system reveals how various components work in harmony to facilitate communication, coordination, and response to stimuli.
Structure and Function
The neural network comprises specialized cells that transmit information via electrical impulses. These cells, along with supporting structures, form the backbone of a sophisticated system that governs behavior, movement, and sensory perception. The efficiency of these communications significantly influences the overall functioning of the organism.
Key Components
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Neurons | Transmit signals between different parts of the organism. |
| Glial Cells | Support and protect neurons, ensuring optimal functioning. |
| Synapses | Facilitate communication between neurons through neurotransmitter release. |
| Cerebrum | Involved in higher-order functions such as decision-making and sensory processing. |
| Cerebellum | Coordinates movement and balance, ensuring fluid motor control. |
Adaptations for Survival

In the wild, certain species have evolved unique characteristics that enhance their chances of survival. These modifications allow them to thrive in diverse environments and effectively respond to various challenges, such as predators and changing climates.
Physical features play a crucial role in survival. For instance, strong legs facilitate swift movement, enabling quick escapes from threats. Additionally, a keen sense of hearing allows these creatures to detect sounds from afar, alerting them to potential dangers. The coloration of their fur often blends seamlessly with their surroundings, providing effective camouflage against predators.
Behavioral adaptations also contribute significantly to their survival. For example, many species exhibit social structures that enhance protection through collective vigilance. Furthermore, seasonal migrations or changes in feeding habits reflect their ability to adapt to fluctuating food availability and environmental conditions.
Common Health Issues in Deer
Understanding the prevalent health concerns affecting these graceful mammals is crucial for wildlife management and conservation efforts. Various factors contribute to their well-being, including environmental conditions, nutrition, and disease exposure. Monitoring and addressing these issues can enhance their survival rates and overall population health.
Some common ailments include infections, nutritional deficiencies, and parasites. These issues can lead to severe consequences if not identified and treated promptly. Below is a summary of some typical health challenges faced by these animals.
| Health Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Chronic Wasting Disease | A progressive neurological disorder caused by prions, leading to weight loss, behavioral changes, and eventually death. |
| Hemorrhagic Disease | A viral infection characterized by high fever, swelling, and bleeding, often resulting in sudden death. |
| Foot and Mouth Disease | A highly contagious viral disease that affects the hooves, causing lesions and severe pain. |
| Parasites | Common parasites include ticks, worms, and mites, which can cause anemia, weakness, and decreased reproductive success. |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Lack of essential vitamins and minerals can lead to poor growth, weakened immune systems, and reproductive failures. |