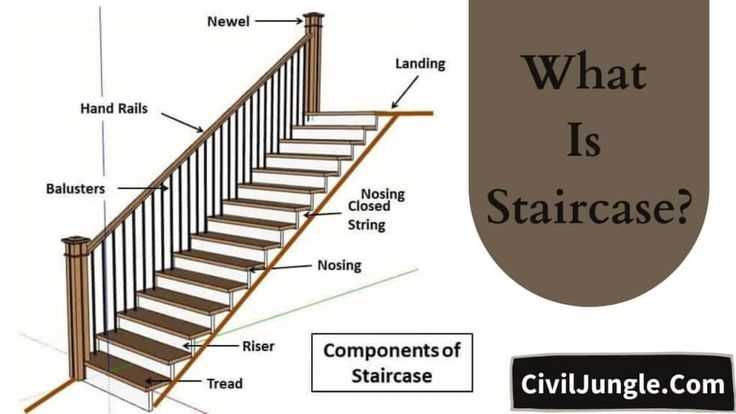
In any architectural endeavor, the interplay of various elements plays a crucial role in ensuring both functionality and aesthetic appeal. When it comes to the vertical transitions within a building, a careful examination of the individual elements reveals their significance in creating a harmonious and safe ascent. Each segment contributes uniquely to the overall experience, influencing not only movement but also the visual flow of the space.
Exploring these essential components allows us to appreciate the intricate design choices that enhance both usability and safety. From the foundational aspects that support weight to the aesthetic features that draw the eye, each aspect serves a purpose that transcends mere practicality. Understanding these elements paves the way for a deeper appreciation of architectural design.
Moreover, the interaction between these various segments is vital for achieving stability and style. The careful selection and arrangement of these components reflect not just functional needs, but also the artistic vision behind the space. This exploration invites us to consider how every detail contributes to the overall narrative of a building’s design, encouraging a comprehensive view of its structure.
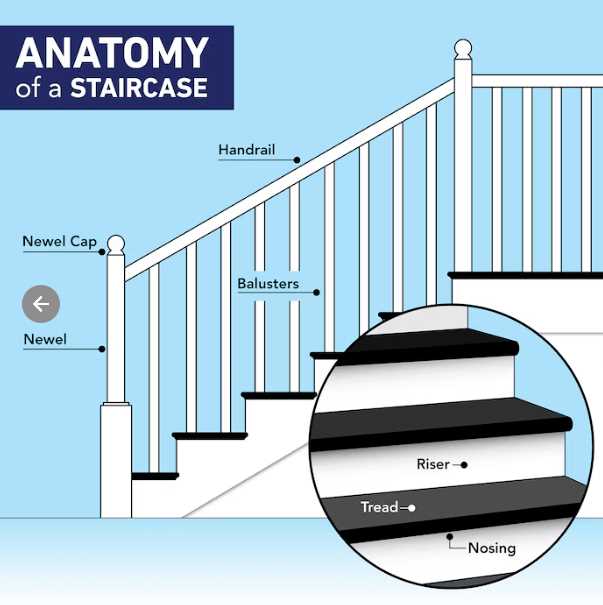
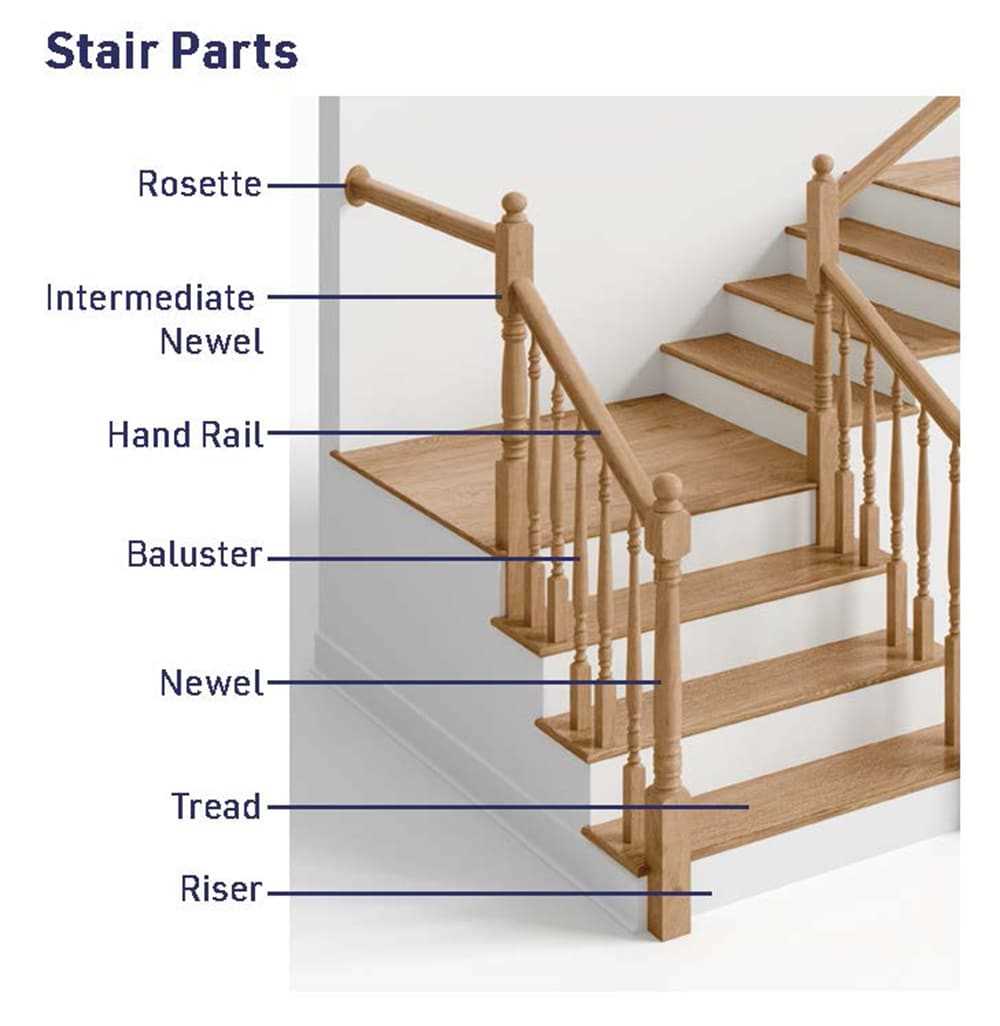
Understanding Staircase Components
The construction of a multi-level structure involves various essential elements that ensure safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Each of these components plays a critical role in facilitating movement between different floors while contributing to the overall design and stability of the framework.
Key Elements of Elevation Structures
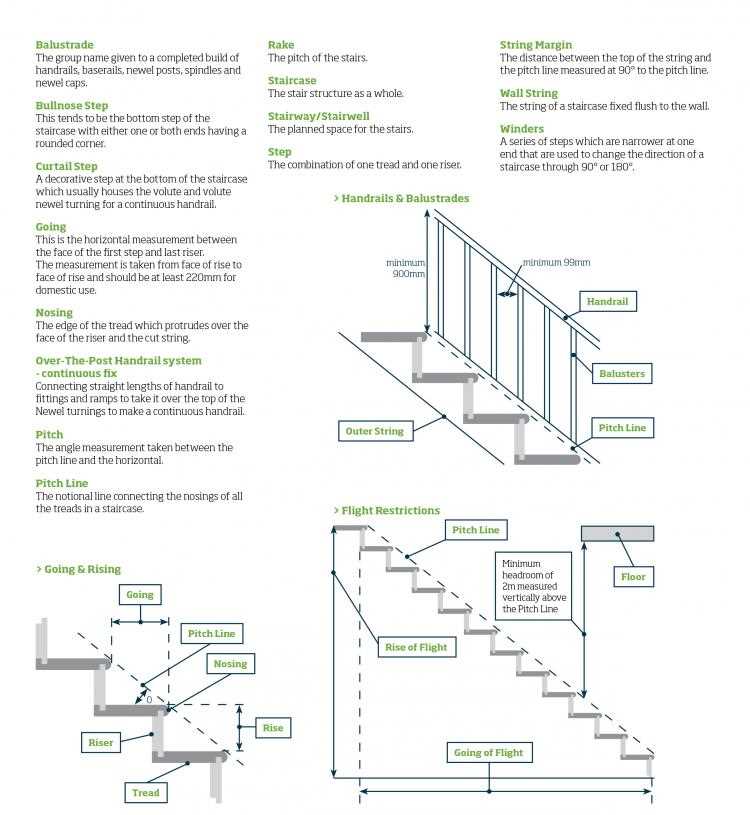
At the heart of every elevation system is the supportive framework, designed to bear the weight and withstand regular usage. Treads provide the surface for stepping, ensuring comfort and traction. In contrast, risers define the height between each level, affecting the overall incline and accessibility.
Enhancements and Safety Features
In addition to the basic elements, various enhancements can be integrated to improve both safety and visual appeal. Handrails are crucial for providing support and security, guiding users along the ascent or descent. Furthermore, balusters serve as protective barriers, preventing accidental falls while adding a decorative touch.
Types of Staircase Designs
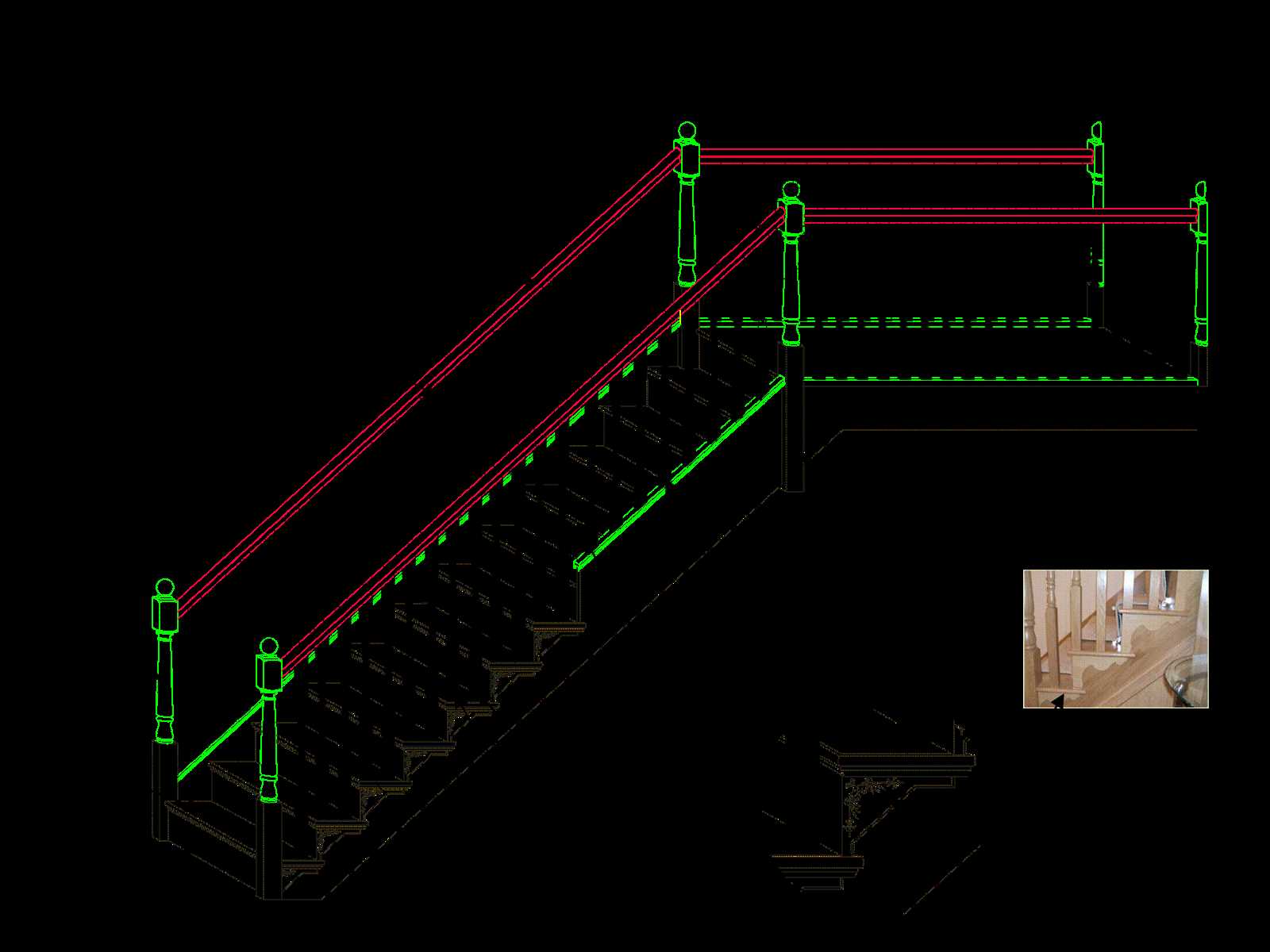
When considering the various approaches to elevation within a structure, it’s essential to explore the diverse styles available. Each design serves a functional purpose while also contributing to the aesthetic appeal of the space. From traditional to contemporary, the selection of form can greatly influence the overall ambiance of an environment.
Traditional Designs
- Straight Steps: The most common type, featuring a direct path between levels.
- Quarter Turn: A simple 90-degree change in direction, often used in corner placements.
- Spiral: Compact and elegant, these designs utilize a circular shape to save space.
Modern Innovations
- Floating: This style creates an illusion of steps suspended in mid-air, emphasizing minimalism.
- Curved: A graceful option that adds fluidity to the overall structure, often serving as a focal point.
- Open Risers: Featuring no backing on steps, this design enhances light flow and visibility.
Ultimately, the choice of elevation style can reflect personal taste while also fulfilling specific spatial requirements. Understanding the characteristics of each approach can assist in making an informed decision for any project.
Materials Used in Stair Construction
The choice of materials for building steps significantly impacts both functionality and aesthetics. Different substances offer unique benefits, contributing to the overall durability, safety, and visual appeal of the structure. Understanding the various options available can aid in making informed decisions for any project.
Common Materials
Wood is a classic choice, providing warmth and elegance, often used in residential settings. Metal, such as steel or aluminum, is favored for its strength and modern appearance, frequently found in commercial environments. Concrete offers exceptional durability and can be molded into various shapes, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Specialty Options
For a more unique look, glass and stone are increasingly popular. Glass adds a contemporary feel, allowing light to pass through, while stone, such as granite or marble, brings a sense of luxury and permanence. Each material can be tailored to meet specific design requirements and functional needs, ensuring the final outcome aligns with the vision of the space.
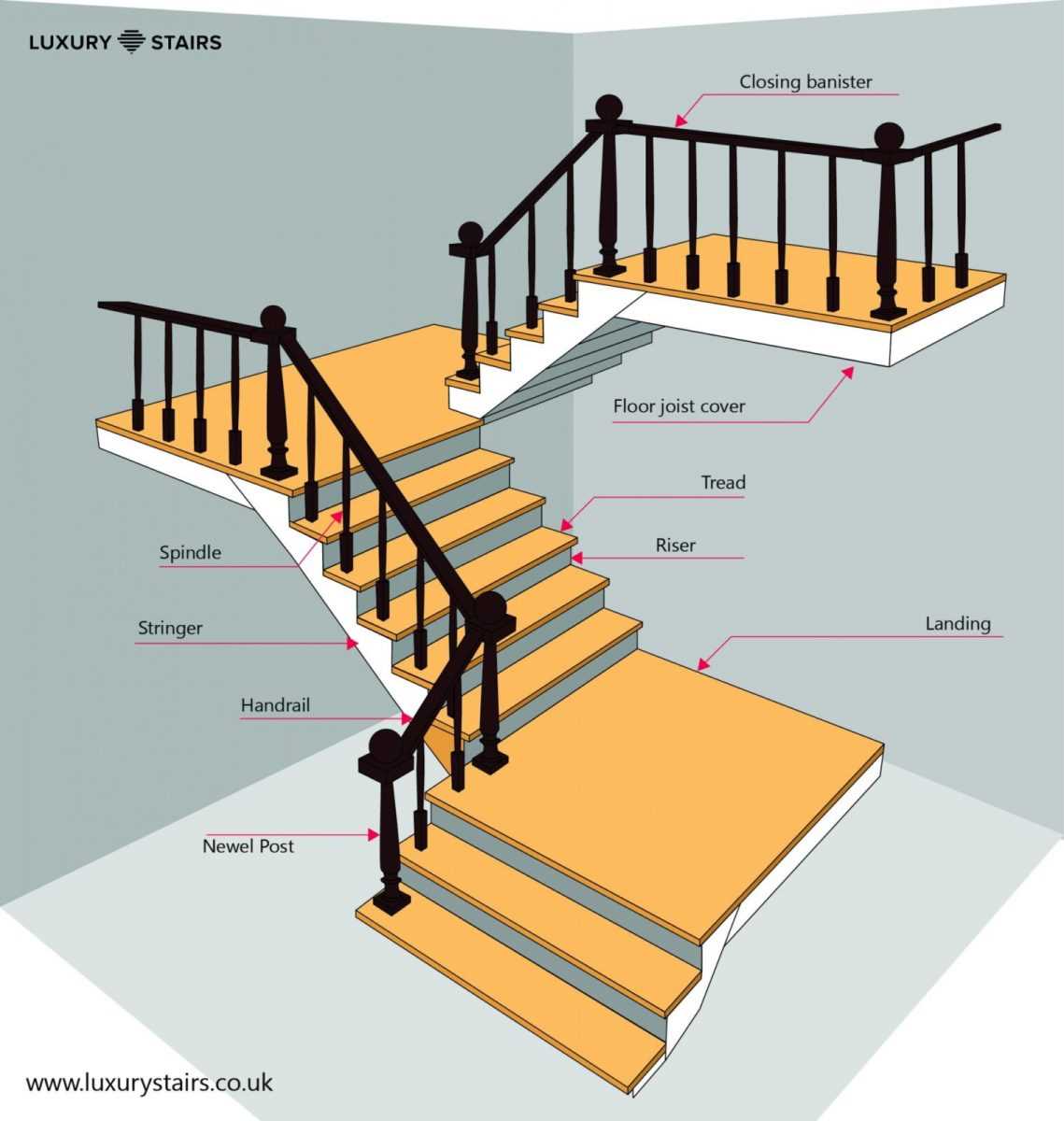
Importance of Handrails and Banisters
Handrails and banisters play a crucial role in ensuring safety and accessibility in elevated structures. They provide support and stability, making it easier for individuals to navigate different levels without the risk of falling. Their presence not only enhances security but also contributes to the overall aesthetic appeal of the environment.
Key benefits of incorporating these elements include:
- Safety: They significantly reduce the risk of accidents, especially for children, the elderly, and those with mobility challenges.
- Support: Users can rely on them for balance, particularly when moving between varying heights.
- Guidance: They help direct movement, providing clear pathways that enhance navigation.
- Aesthetic Value: Well-designed handrails can complement the interior decor and enhance the visual appeal of a space.
- Compliance: Many regulations mandate their installation, ensuring that structures meet safety standards.
In summary, the integration of handrails and banisters is essential for promoting safe movement and adding value to any elevated setting.
Measuring Staircase Dimensions Accurately
Obtaining precise measurements is essential for ensuring safety and functionality in any multi-level structure. Accurate dimensions contribute significantly to the overall design and usability, preventing potential hazards and enhancing aesthetic appeal. This section will explore effective methods for achieving reliable measurements.
First, it’s crucial to gather the right tools, such as a tape measure, level, and square. These instruments provide the accuracy needed for different components. When measuring vertical height, ensure that the tool is held straight to avoid discrepancies. Horizontal distances should be measured at several points to account for any variations.
Additionally, understanding the proper methodology for taking measurements is vital. For instance, when determining the rise and run, it’s important to note the total height and horizontal length to maintain correct proportions. Documenting each measurement clearly will help avoid confusion during the construction or renovation process.
Lastly, consider any building codes or regulations that may dictate specific requirements for dimensions. Compliance with these standards ensures not only safety but also the long-term integrity of the structure. By following these guidelines, you can achieve precise measurements that meet both functional and aesthetic objectives.
Common Safety Standards for Stairs
Ensuring the security of elevated platforms is essential for preventing accidents and injuries. Various guidelines and regulations have been established to promote safe design and usage, addressing both construction and maintenance aspects. Understanding these principles is crucial for architects, builders, and users alike.
- Dimensions: Adhering to specific measurements is vital for safety. The rise and run of steps should be consistent to prevent trips.
- Handrails: The inclusion of sturdy handrails can provide support and stability. Regulations often dictate their height and strength.
- Non-slip Surfaces: Materials used should minimize the risk of slipping, especially in high-traffic areas or locations exposed to moisture.
- Lighting: Adequate illumination is essential. Well-lit pathways help users navigate safely, reducing the likelihood of accidents.
Compliance with these standards not only enhances safety but also fosters a more accessible environment for everyone.
Visualizing Staircase Diagrams Effectively
Effective representation of step-like structures can significantly enhance comprehension and analysis. By utilizing clear visual formats, complex information becomes more digestible, allowing for better retention and understanding. This section delves into various techniques and strategies to optimize the portrayal of such structures.
Here are some key strategies for effective visualization:
- Utilize Consistent Scaling: Maintain uniform dimensions for each level to ensure clarity and coherence.
- Incorporate Color Coding: Use distinct colors to represent different categories or stages, making it easier to differentiate between elements.
- Add Labels: Clearly label each section to provide context and improve navigation through the representation.
- Incorporate Arrows or Lines: Use directional indicators to illustrate progress or relationships between levels.
To further enhance the visual experience, consider the following:
- Integrate Icons: Employ recognizable symbols to convey additional meaning without cluttering the layout.
- Focus on Simplicity: Avoid excessive details that may distract from the main message; less is often more.
- Test Readability: Ensure that your audience can easily interpret the structure by gathering feedback and making necessary adjustments.
By applying these techniques, the visualization of step-like arrangements can become an invaluable tool for communication, analysis, and decision-making. Clear and effective presentations empower users to grasp complex information with ease.
Maintenance Tips for Staircases
Ensuring the longevity and safety of your ascending and descending structures requires regular care and attention. By implementing a few simple practices, you can maintain their functionality and aesthetic appeal, preventing potential hazards and costly repairs.
Regular Inspections
Frequent examinations are crucial to identify wear and tear. Look for any loose components, cracks, or signs of moisture accumulation. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into major concerns.
Cleaning and Safety Measures

Keep surfaces free from debris and spills. Regularly sweeping and mopping will not only enhance appearance but also minimize slip risks. Consider adding non-slip coatings or treads for improved traction, especially in high-traffic areas.
Incorporating these maintenance strategies will ensure your ascending and descending structures remain safe, functional, and visually appealing for years to come.
Innovative Staircase Features to Consider
When designing multi-level spaces, it’s essential to think beyond traditional frameworks. Innovative elements can enhance both functionality and aesthetics, making each ascent not just a necessity but an experience. Integrating modern touches can transform a simple climb into a remarkable journey.
Illuminated Steps: Incorporating lighting into the design can dramatically change the ambiance. LED strips or embedded lights create a striking visual effect while also ensuring safety during low-light conditions.
Material Variety: Experimenting with unconventional materials can add unique character. Combining wood with glass, metal, or stone creates a striking contrast that can elevate the overall design.
Storage Solutions: Creative use of space beneath the elevation can provide practical storage options. Whether it’s built-in cabinets or open shelving, these features maximize utility without compromising style.
Curved Designs: Moving away from straight lines to incorporate curves can soften the appearance. A gently winding ascent can create a flow that enhances movement and adds an organic feel to the environment.
Integrated Seating: Adding seating areas within the structure invites relaxation. Benches or built-in seating can create a functional yet stylish nook that encourages social interaction.
Glass Railings: Using transparent materials for railings can open up spaces and create an illusion of continuity. This approach not only enhances safety but also allows unobstructed views throughout the area.
By considering these innovative elements, designers can create functional and visually appealing transitions that enhance the overall atmosphere of a space.