| Component |
Function |
Float Bowl Design and Operation
The float bowl is a critical component in fuel delivery systems, responsible for maintaining a consistent supply of liquid fuel to the mixing chamber. This mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance by regulating the fuel level, thus allowing for efficient combustion and engine functionality. Understanding its design and operation can provide valuable insights into the overall efficiency of the system.
Construction Features
The float bowl typically consists of a chamber designed to hold a specific volume of fuel. Within this chamber, a buoyant device, known as the float, rises and falls with the fuel level. This float is connected to a valve that opens and closes to regulate fuel flow into the mixing area. When the fuel level drops below a certain point, the float descends, opening the valve and allowing more fuel to enter. Conversely, when the level rises, the float ascends, closing the valve to prevent overfilling.
Operational Mechanism
During operation, the float bowl ensures that the fuel remains at an optimal level for effective atomization. This process begins when fuel is drawn from the bowl into the mixing chamber during the intake stroke of the engine. As the engine runs, the float continuously adjusts to maintain the ideal fuel level, responding to fluctuations in demand. This dynamic operation is crucial for achieving the proper air-fuel mixture, which directly influences engine performance, efficiency, and emissions.
Needle Valve and Seat Functionality
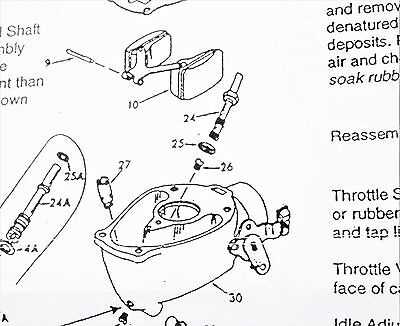
The needle valve and its corresponding seat play a crucial role in regulating the flow of fuel within the engine’s fuel delivery system. This mechanism is vital for maintaining optimal performance by ensuring that the correct amount of fuel enters the combustion chamber at the right time. Understanding how this component operates can help in troubleshooting fuel flow issues and enhancing engine efficiency.
Operation Principles
The needle valve operates by opening and closing in response to pressure changes within the system. When fuel pressure increases, the valve lifts off the seat, allowing fuel to flow through. Conversely, when the pressure decreases, the valve returns to its seated position, halting the flow. This on-off action creates a controlled environment for fuel delivery.
Importance of Proper Functioning
For optimal engine performance, the needle valve and seat must function effectively. Here are some key reasons why their proper operation is essential:
- Fuel Regulation: Ensures a steady and appropriate fuel supply to the engine.
- Preventing Flooding: Stops excessive fuel from entering the combustion chamber, which can lead to flooding and poor performance.
- Efficiency: Contributes to better fuel efficiency by allowing precise control over fuel delivery.
Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are recommended to prevent issues that could compromise the engine’s operation. A malfunctioning needle valve can lead to symptoms such as poor acceleration, stalling, and increased emissions.
Idle Mixture Adjustment Parts
The proper tuning of fuel and air blend during idle conditions is crucial for optimal engine performance. Achieving the right balance ensures smooth operation and can significantly influence efficiency. Various components play a pivotal role in this adjustment, affecting how the mixture is regulated for a steady idle.
Adjustment Screws: These elements allow for fine-tuning of the fuel-air ratio. By turning the screws, users can increase or decrease the amount of fuel entering the system, leading to a richer or leaner mixture, respectively.
Needle Valves: Serving as a control mechanism, these valves help maintain the desired fuel level within the system. Their precise function ensures that the correct volume of fuel is delivered during idle, enhancing engine response.
Mixture Control Mechanism: This assembly regulates the overall blend of fuel and air. By adjusting this mechanism, users can optimize the idle settings, thereby improving engine stability and performance.
Spring Assemblies: These components assist in maintaining tension on the adjustment screws and needles. Proper spring tension is essential for the accurate operation of the mixture control system, ensuring consistent performance over time.
Understanding these elements is vital for anyone looking to maintain or enhance engine functionality. By focusing on the intricate details of each component, users can achieve a well-tuned engine that operates efficiently and reliably.
Common Wear and Replacement Parts
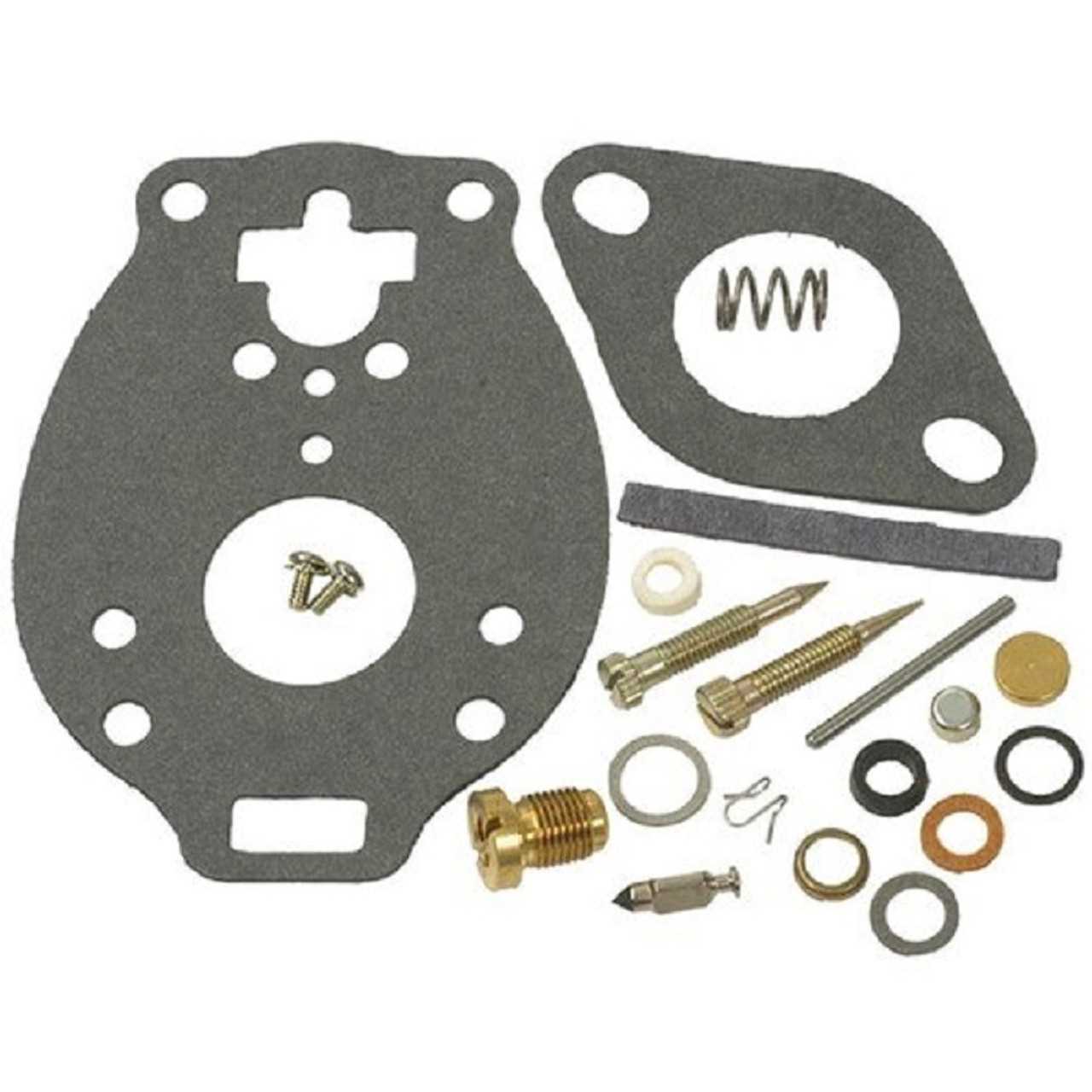

Over time, various components within an engine’s fuel delivery system may experience wear and require replacement to maintain optimal performance. Understanding which elements are most susceptible to deterioration can help ensure your engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Regular inspection and timely substitution of these components can prevent larger issues and extend the lifespan of your machinery.
Key Components Subject to Wear
Several crucial elements may show signs of wear due to continuous use and exposure to fuel and air mixtures. Seals and gaskets are particularly prone to degradation, often leading to air leaks that can affect engine performance. Additionally, float assemblies can become damaged, affecting the fuel level and flow, which can hinder proper engine operation. Regular checks can help identify these issues early.
Replacement Considerations
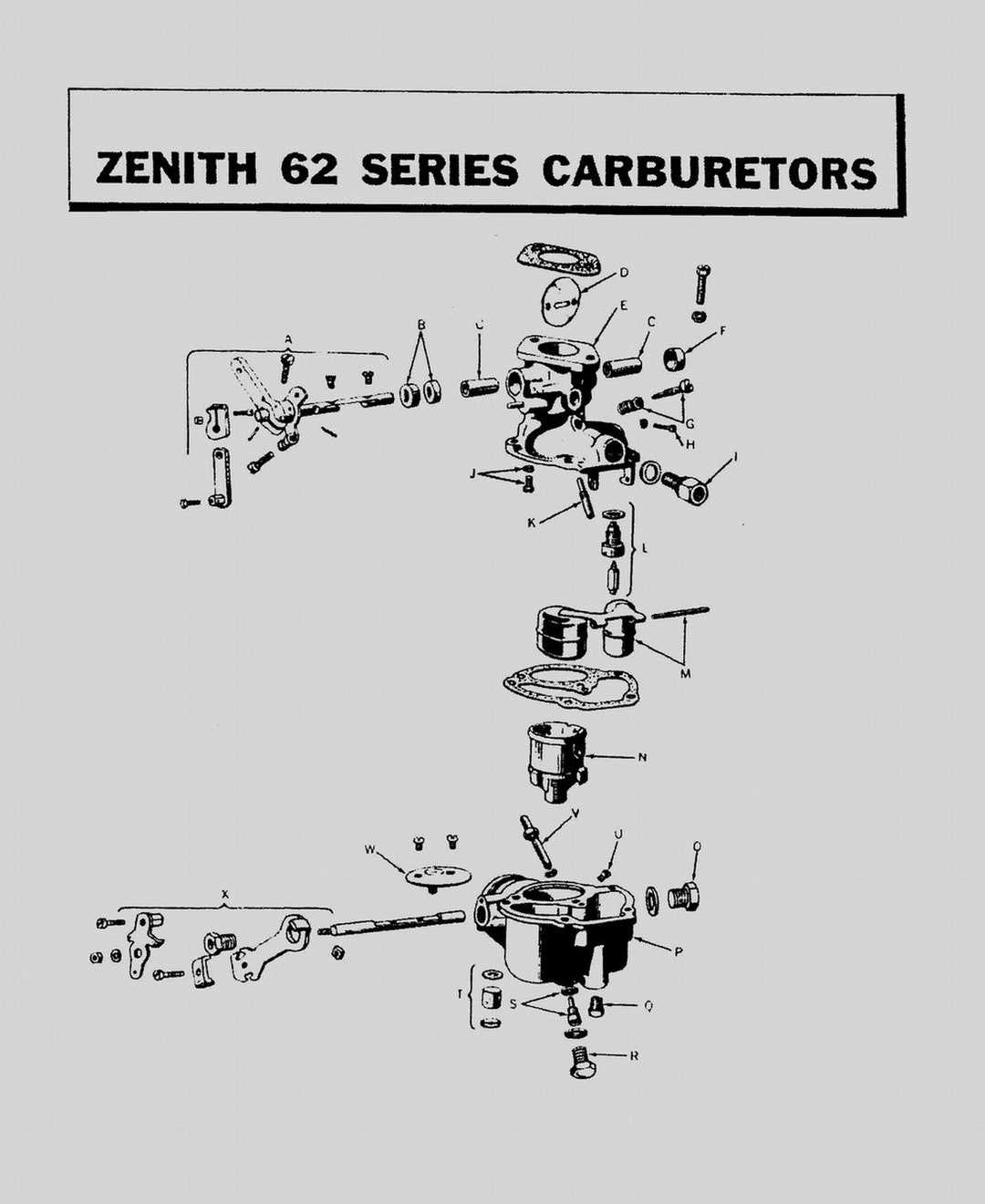
When replacing any worn components, it is vital to choose high-quality substitutes that match the specifications of the original design. Using premium materials not only ensures compatibility but also enhances the durability of the replacements. Furthermore, maintaining a routine inspection schedule can help detect wear patterns and facilitate proactive replacements, ultimately leading to improved engine reliability and efficiency.



