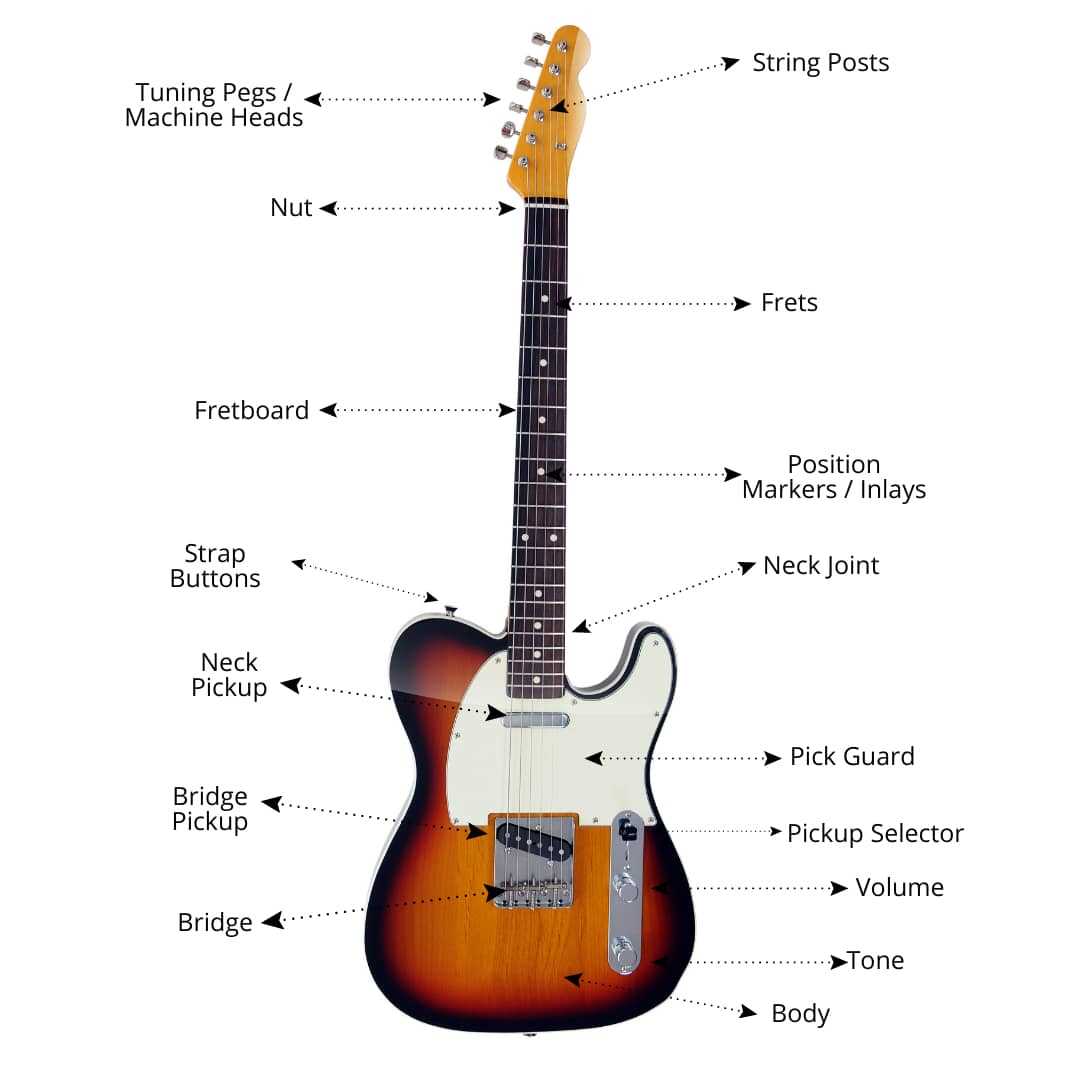
In the realm of stringed musical creations, each component plays a vital role in shaping sound and performance. From the resonance of the body to the tension of the strings, every element contributes to the overall experience of the player and listener alike. Exploring these features reveals the intricate craftsmanship involved in producing melodious tones.
Identifying the various sections of these instruments is essential for both aspiring musicians and enthusiasts. Each section serves a unique purpose, influencing not only the aesthetics but also the acoustics of the instrument. Delving into the specifics allows one to appreciate the artistry behind their construction.
Ultimately, understanding these components enriches one’s connection to the music, fostering a deeper appreciation for the artistry involved. Whether one is a novice or a seasoned player, recognizing how each part interacts enhances the overall musical journey.
Understanding the Acoustic Guitar Anatomy
Exploring the structure of a stringed instrument reveals a fascinating interplay of components that contribute to its unique sound and playability. Each element serves a specific purpose, working together to create the instrument’s character and functionality. Understanding this framework enhances both performance and appreciation of the music produced.
The body acts as a resonating chamber, amplifying the vibrations from the strings. Its shape and materials significantly influence tonal quality. Meanwhile, the neck provides a long, slender platform where finger placement occurs, allowing for a variety of pitches and chords. The fingerboard, positioned on the neck, features frets that facilitate precise note production.
The headstock houses the tuning mechanisms, essential for maintaining pitch accuracy. Tuners allow for adjustments, ensuring the instrument remains in tune with other instruments or vocals. Strings, varying in thickness and material, play a vital role in the instrument’s voice, affecting timbre and sustain.
The bridge anchors the strings to the body, transmitting vibrations effectively. In addition, the soundhole allows sound waves to escape, enhancing projection and resonance. Understanding these components and their functions creates a deeper connection to the music and the craftsmanship behind the instrument.
Essential Components of Acoustic Guitars
The craftsmanship of stringed instruments involves a variety of fundamental elements that contribute to their unique sound and playability. Each component plays a vital role, influencing tone, resonance, and the overall experience of the musician.
Main Features
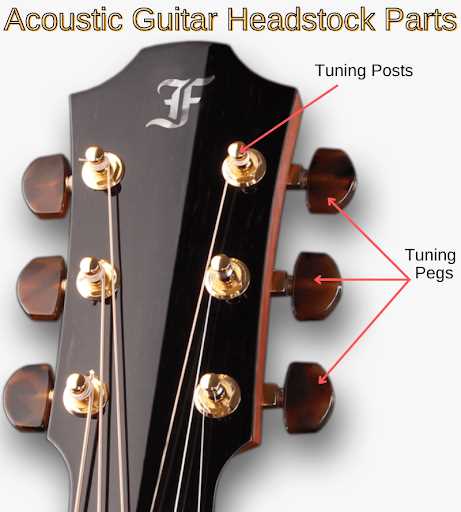

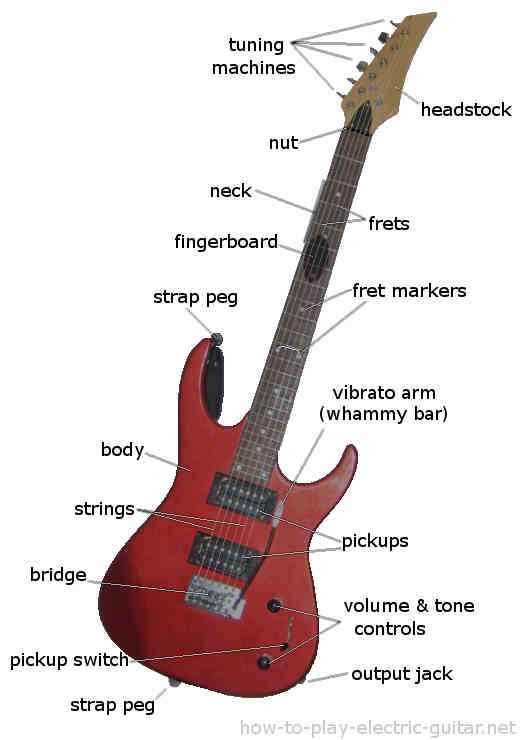
- Body: The large hollow structure that amplifies sound and affects tonal quality.
- Neck: The elongated part allowing the player to press strings and create different notes.
- Headstock: The upper section housing tuning mechanisms, crucial for pitch adjustment.
- Bridge: The component where strings are anchored, impacting intonation and sustain.
Additional Elements
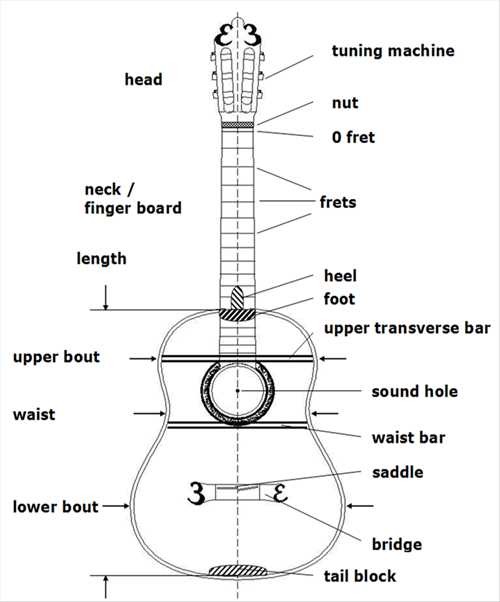
- Fretboard: The surface along the neck with marked positions for finger placement.
- Soundhole: The opening in the body that enhances sound projection.
- Strings: The core feature producing sound when plucked or strummed.
- Pickguard: A protective layer preventing scratches on the body from strumming.
Understanding these crucial elements provides insight into the intricate design and functionality that make stringed instruments a beloved choice for musicians worldwide.
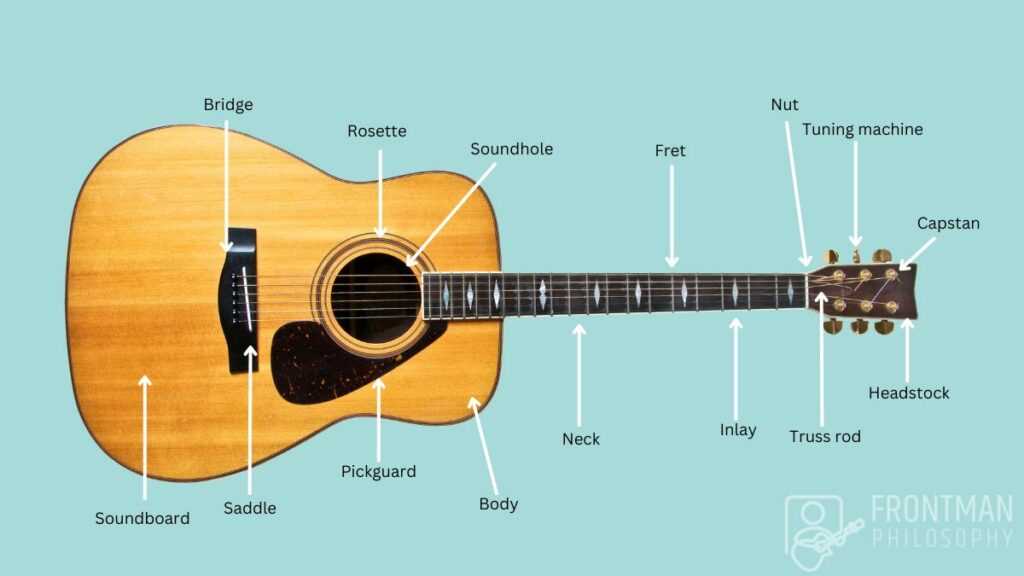
The Role of the Soundboard

The soundboard serves as a vital component in the overall design and functionality of stringed instruments. It plays a crucial role in sound production, influencing the tonal quality and volume. This flat surface interacts with the vibrations generated by the strings, converting them into audible sound waves.
Key Functions
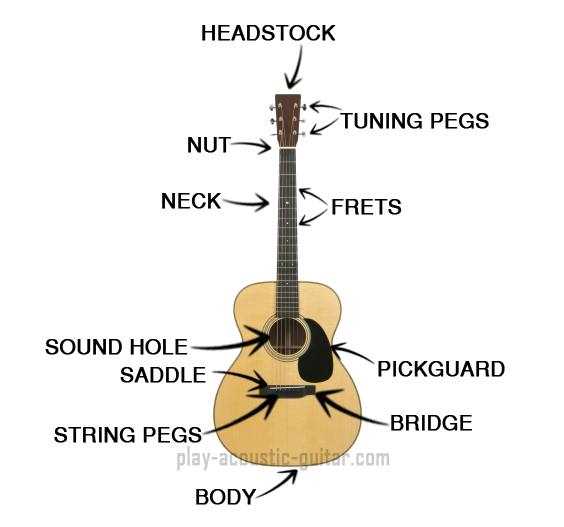
- Vibration Transmission: The soundboard effectively transmits the vibrations from the strings, amplifying the sound.
- Tonal Quality: The material and thickness of the board significantly impact the richness and clarity of the sound produced.
- Resonance: It enhances the resonance of the instrument, allowing for a fuller and more dynamic audio experience.
Materials Used
- Spruce: Known for its excellent tonal properties and responsiveness.
- Cedar: Offers a warmer sound with a more pronounced low-end response.
- Mahogany: Provides a balanced tone with a strong mid-range presence.
In summary, the soundboard is integral to the performance of stringed instruments, shaping their character and enhancing the musician’s experience.
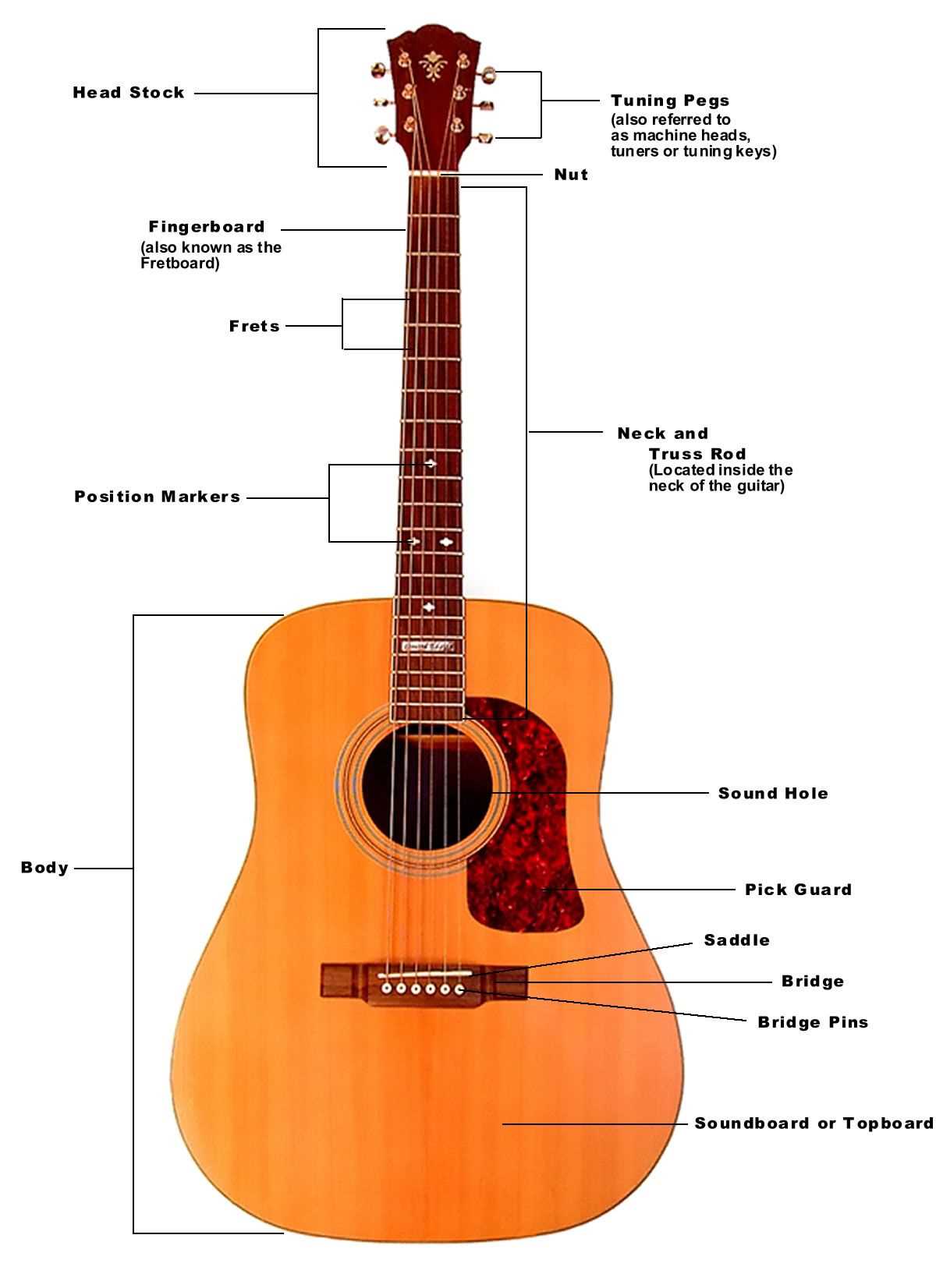
Exploring the Neck and Fretboard
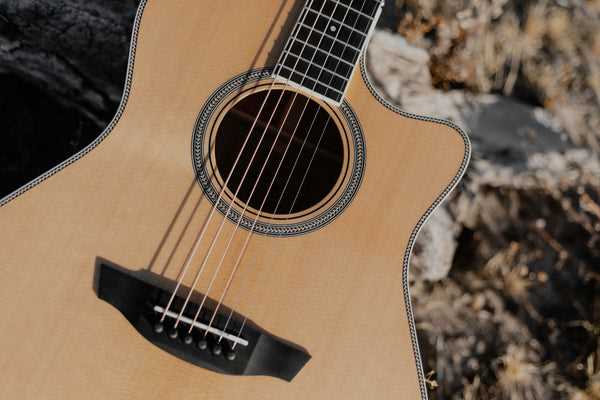

The neck and fretboard serve as vital components for any stringed instrument, enabling musicians to produce a wide range of notes and tones. Understanding the structure and functionality of these elements enhances playing technique and fosters a deeper connection with the instrument. This section delves into the nuances of this crucial area, highlighting its significance in performance and practice.
Construction and Material
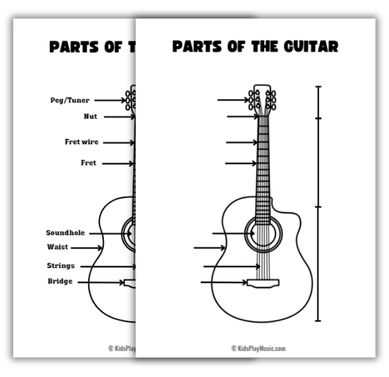
The neck is typically crafted from hardwoods, providing durability and stability. The choice of materials can significantly affect the overall sound quality. The fretboard, usually made from rosewood or ebony, features metal frets that delineate different pitches. The combination of these materials contributes to the instrument’s resonance and playability.
Techniques and Playability

Mastering the neck and fretboard opens up a world of techniques for players. From basic chords to intricate solos, familiarity with finger positioning and movement along these surfaces is essential. Various scales and patterns can be practiced to enhance dexterity and fluidity, allowing for greater musical expression.
Function of the Bridge and Saddle
The bridge and saddle play a crucial role in the overall sound and functionality of stringed instruments. These components serve as the interface where strings connect to the body, influencing both tone and playability.
The bridge acts as a stabilizing element, transferring vibrations from the strings to the instrument’s body. This connection is essential for producing rich, resonant sounds. In addition, it provides a secure anchoring point for the strings, maintaining proper tension.
The saddle, positioned atop the bridge, further refines sound transmission. It helps in height adjustment of the strings, allowing for optimal action and comfort for the player. Together, these elements ensure the instrument produces its ultimate tonal quality.
The Importance of the Sound Hole
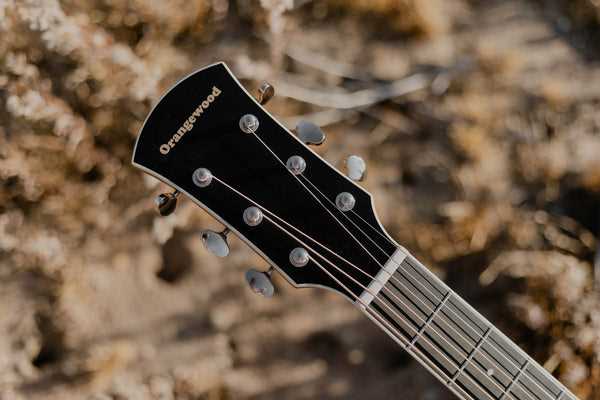

The sound hole plays a crucial role in the overall function and performance of stringed instruments. Its design and placement significantly influence the quality and richness of the sound produced.
Key reasons for its importance include:
- Sound Projection: The opening allows sound waves to escape, enhancing volume and resonance.
- Tone Quality: The size and shape affect tonal characteristics, contributing to warmth and depth.
- Vibration Dynamics: It facilitates the interaction between strings and the body, promoting a fuller sound.
- Feedback Control: Properly designed openings can help manage feedback, especially in amplified settings.
Understanding these aspects allows musicians to appreciate how integral this feature is to their instrument’s performance.
Materials Used in Guitar Construction
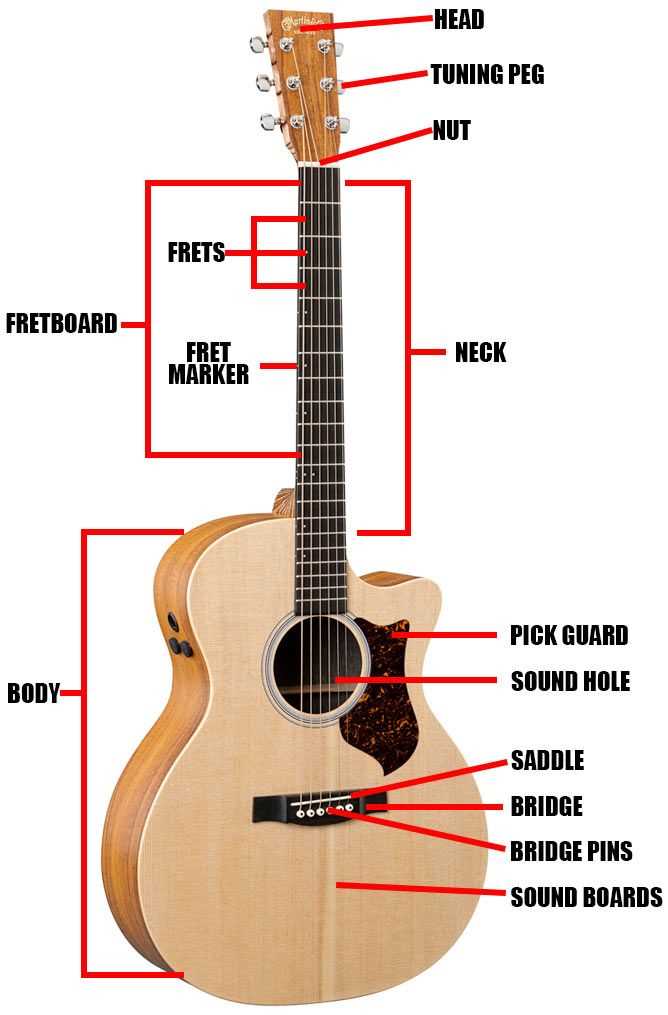
In the world of stringed instruments, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in defining their sound and character. Various elements come together to create a harmonious blend that affects tone, resonance, and durability. Understanding these components allows for a deeper appreciation of craftsmanship and artistry involved.
Wood is often the primary choice, with different species offering unique tonal qualities. Spruce, for instance, is renowned for its bright sound, while mahogany provides a warmer, richer tone. Other woods, such as rosewood and maple, are frequently used for fingerboards and backs, enhancing both aesthetics and acoustics.
Additionally, the use of synthetic materials has gained popularity, particularly in areas requiring enhanced durability or specific sound properties. These innovations can provide consistency and resistance to environmental changes, making them suitable for various playing conditions.
Finally, the choice of hardware, including tuning pegs and bridges, often utilizes metals like brass or steel, contributing to stability and precision in performance. Each material, whether traditional or modern, ultimately shapes the instrument’s voice and longevity.
How Each Part Affects Sound
The various components of a stringed instrument play a crucial role in shaping its tonal quality and resonance. Each element contributes uniquely to the overall acoustic experience, influencing everything from volume to timbre. Understanding these contributions can enhance both the playing and listening experience.
| Component | Influence on Sound |
|---|---|
| Body | Determines projection and tonal richness; larger bodies typically produce a fuller sound. |
| Neck | Affects playability and sustain; the length and material can change the resonance. |
| Strings | Varies in thickness and material, directly impacting brightness and warmth of sound. |
| Bridge | Transfers vibrations from strings to the body; its material influences sustain and clarity. |
| Soundhole | Enhances projection and balance; size and placement can modify tonal characteristics. |
By recognizing how these various elements interact, musicians can make more informed choices when selecting or customizing their instruments to achieve the desired sound.
Maintenance Tips for Guitar Parts
Proper upkeep of your instrument is essential for its longevity and performance. Regular care can prevent wear and tear, ensuring a richer sound and more enjoyable playing experience. Here are some key strategies to keep in mind.
Cleaning and Polishing
To maintain the appearance and functionality of your instrument, regular cleaning is crucial. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to wipe down the surface after each session. For deeper cleaning, consider products specifically designed for wood finishes. Avoid using household cleaners, as they can damage the finish. Regular polishing not only enhances the aesthetic but also protects the wood from moisture and dirt.
String Care and Replacement

Strings play a vital role in sound quality. Regularly inspect them for wear and replace them as needed. Clean your strings after each play using a dedicated string cleaner or a soft cloth to remove sweat and oils. This practice not only prolongs the life of the strings but also improves sound clarity. Consider experimenting with different materials and gauges to find the perfect match for your playing style.