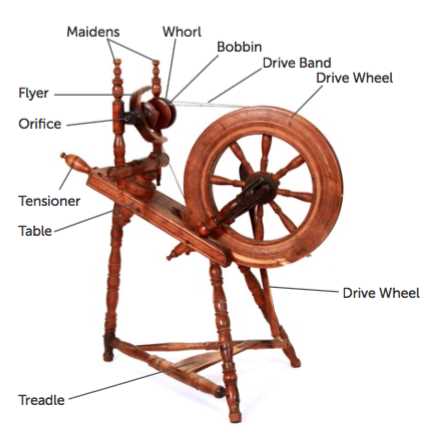

When delving into the mechanics of ancient tools used in fiber processing, it’s essential to understand how each element contributes to the overall function. These devices, integral to textile creation, involve a combination of moving and stationary elements, each designed to perform specific tasks that support the efficient transformation of raw materials into threads. A clear understanding of how these components interact can enhance both appreciation and expertise in their operation.
To fully grasp the design of these mechanisms, one must consider the relationship between various elements, such as the main rotating mechanism, the guiding structure, and the motion-transfer system. Each plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth and continuous operation of the tool. This complexity in design reflects the ingenuity behind such devices, which have stood the test of time and evolved through centuries.
Breaking down the structure and function of each segment offers insight into their contribution to the overall system. Whether you’re working with a modern version or a historical reproduction, this understanding will improve both the practical and theoretical aspects of using these tools efficiently and with precision.
Understanding Spinning Wheel Mechanics
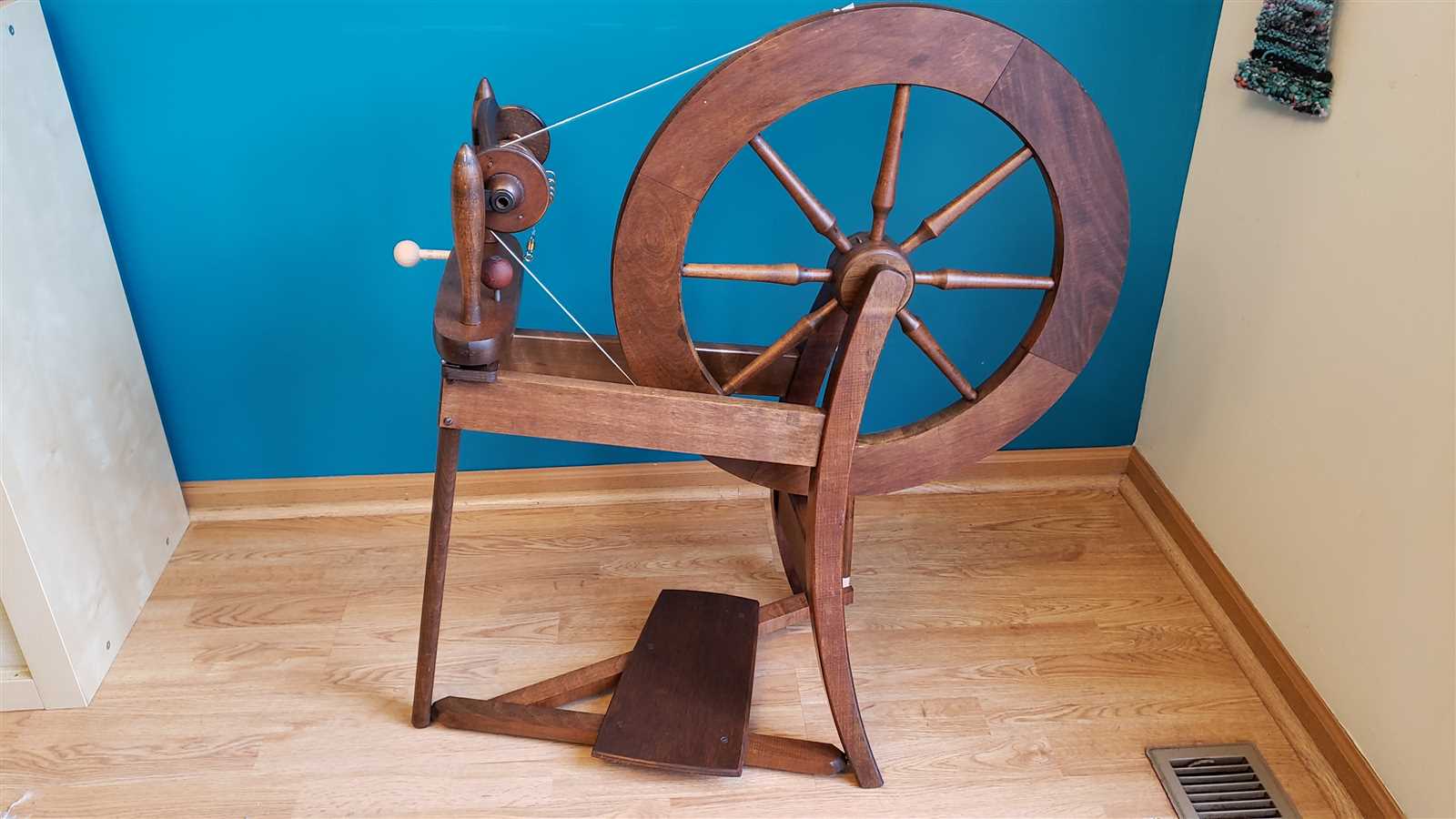

The mechanics of traditional textile tools involve a series of interconnected components working together to transform raw fibers into thread or yarn. Each element plays a crucial role in the process, ensuring that the fibers are twisted, stretched, and wound onto a spindle in a continuous manner. The efficiency and smooth operation of these devices rely heavily on the precise coordination of motion and tension across the various sections.
The main functions of these tools include the ability to draft fibers, apply twist, and control the tension, all of which are essential for creating strong and even yarn. The drive mechanism, often powered by a foot pedal or hand-operated crank, provides the necessary force to set the components into motion. Meanwhile, the spindle collects the finished thread as it’s drawn from the fiber mass, while the tensioning system ensures that the yarn is neither too loose nor too tight.
By understanding how these elements interact, one can appreciate the fine balance required to produce high-quality thread. Even small adjustments to one component can significantly affect the outcome, highlighting the importance of a well-tuned device for optimal performance.
Key Components of a Spinning Wheel
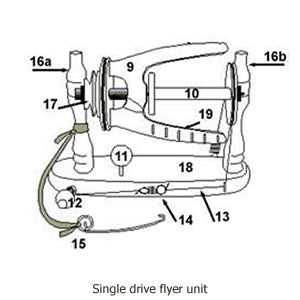
When crafting yarn, several essential elements come together to facilitate the process. Each component plays a crucial role in transforming raw fibers into finished thread. Understanding the functionality of these individual components is fundamental for both novice and experienced artisans. The structure allows for smooth operation, efficient fiber handling, and consistent output, ensuring quality results in the final product.
Main Elements for Fiber Manipulation

At the core of this setup are the pieces that directly interact with the fibers. These elements are responsible for drawing, twisting, and winding the fiber into thread. Their careful alignment and interaction contribute to the quality and consistency of the final material. A well-calibrated assembly allows the artisan to control tension, twist, and speed for optimal results.
Auxiliary Components for Support
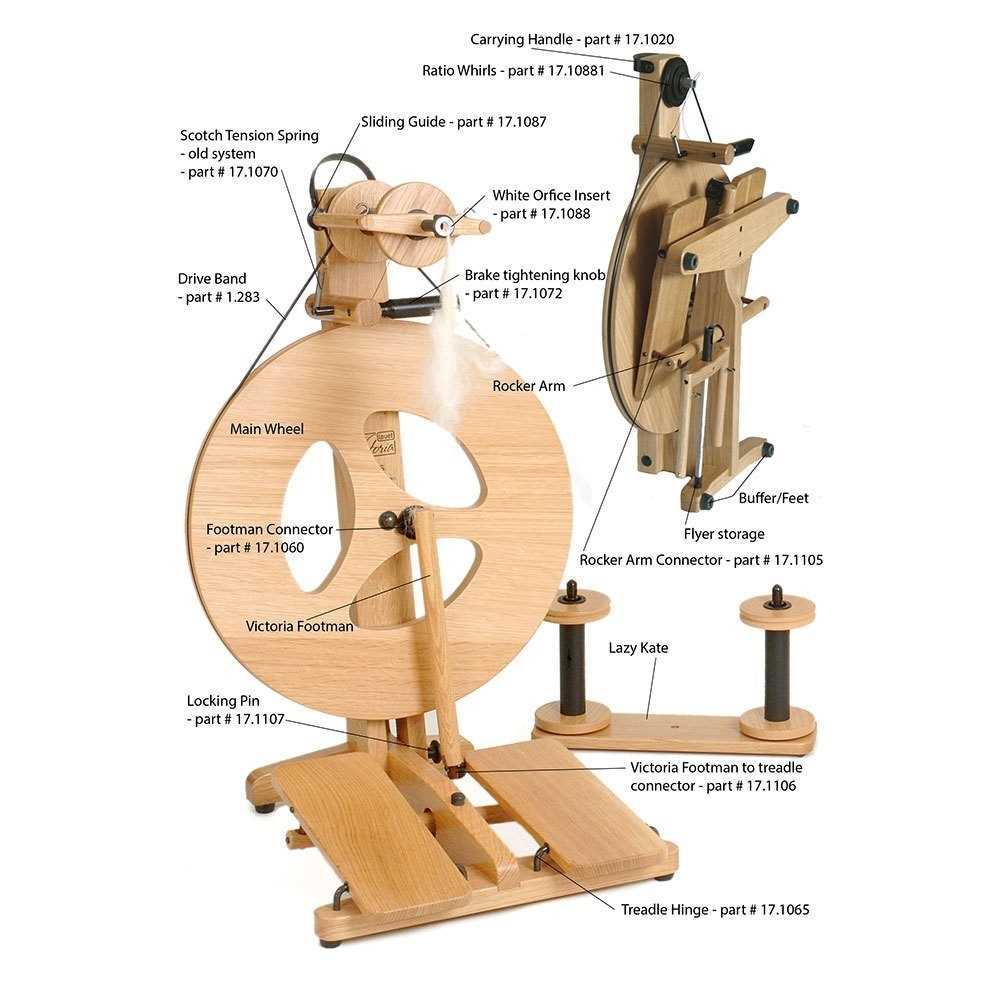
While the primary elements manage the fiber, other supporting components provide stability and ease of use. These are often designed to help manage the flow, keep everything in balance, and reduce friction during operation. A thoughtful design of these additional elements can enhance the overall user experience by making the process smoother and more intuitive.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Drive Mechanism | Generates movement and controls the speed of rotation. |
| Bobbin | Collects the spun fiber, allowing it to be stored and wound into skeins. |
| Flyer | Guides the fiber onto the bobbin, maintaining even distribution and tension. |
| Treadle | Allows the operator to control the rotation through foot pedals, enabling hands-free operation. |
| Orifice | Serves as the entry point for the fiber, guiding it to the spinning area. |
How the Spinning Wheel Functions
This section explores the intricate mechanism behind the traditional textile tool, focusing on how it transforms fibers into thread. By examining its components and their interactions, we can gain a deeper understanding of its operational principles.
Basic Mechanism
- The primary function involves the continuous rotation of a spindle.
- As fibers are drawn out, they are twisted together to form yarn.
- This twisting action is facilitated by a foot pedal that controls the motion.
Key Components
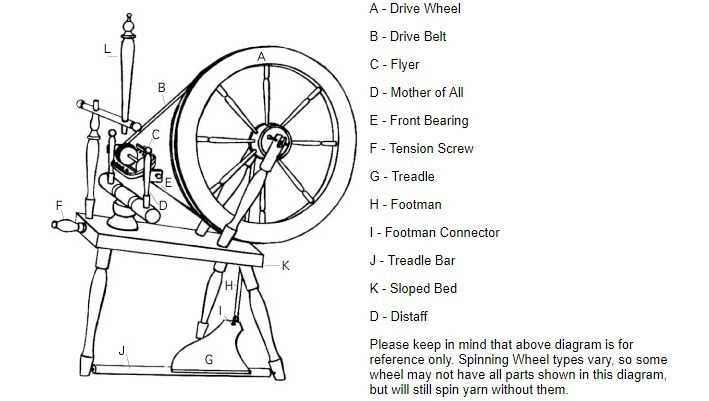
- Drive Band: Transfers motion from the pedal to the spindle.
- Orifice: The entry point for fibers, guiding them into the twisting area.
- Bobbin: Collects the finished yarn, allowing for easy removal.
Essential Parts for Yarn Creation
Creating yarn from fibers involves a series of crucial components that work together to transform raw materials into finished threads. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring the smooth and efficient production of high-quality strands.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Drive Wheel | Generates motion to twist fibers together. |
| Bobbin | Holds the spun thread securely during the process. |
| Distaff | Supports and feeds fibers into the spinning mechanism. |
| Tensioning Device | Regulates the tightness of the yarn as it’s created. |
| Flyer | Twists fibers while guiding them onto the bobbin. |
Spinning Wheel Maintenance Tips
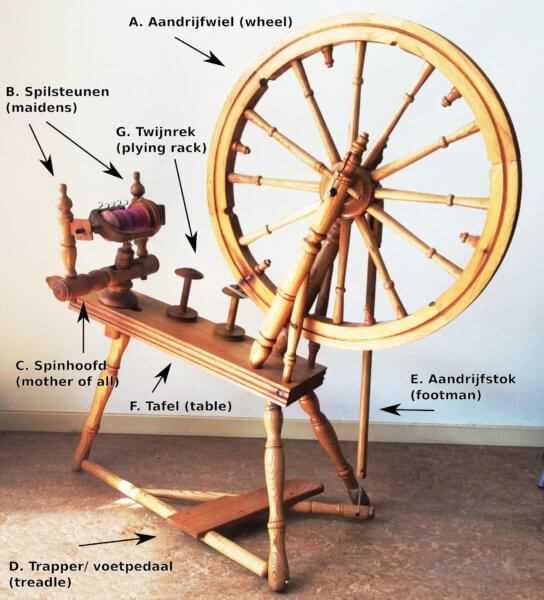
Proper care is essential for the longevity and performance of your crafting equipment. Regular attention to its components can prevent wear and enhance your overall experience. Here are some essential practices to keep in mind.
Regular Cleaning

Ensure that you keep your apparatus clean from dust and fibers. Use a soft cloth to gently wipe down surfaces, and consider using a brush for hard-to-reach areas. Neglecting cleanliness can lead to buildup that may affect functionality.
Lubrication and Adjustment
Applying appropriate lubricant to moving elements is crucial for smooth operation. Check for any loose connections or misalignments regularly. Timely adjustments can prevent larger issues and enhance performance significantly.
Choosing the Right Wheel for You
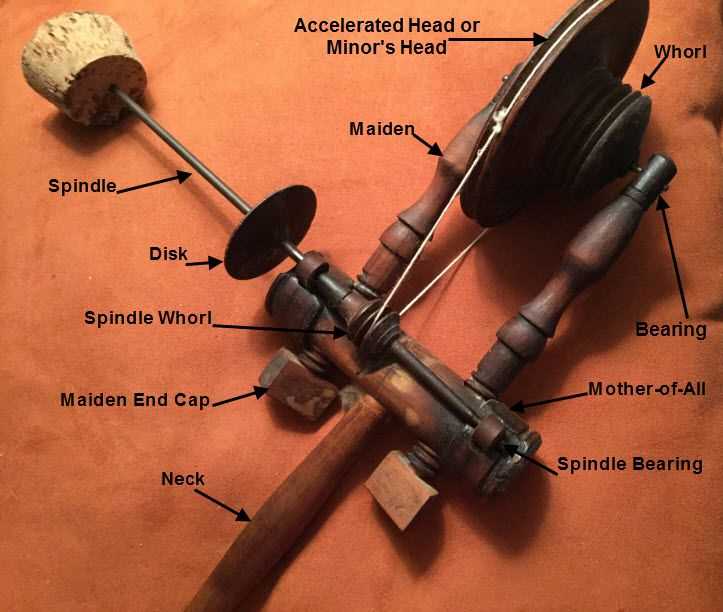

Finding the perfect instrument for your fiber arts journey can be a transformative experience. Understanding your unique needs and preferences is essential to making an informed choice that enhances your crafting process. This section aims to guide you through key considerations, ensuring you select a model that resonates with your style and aspirations.
Consider Your Crafting Style
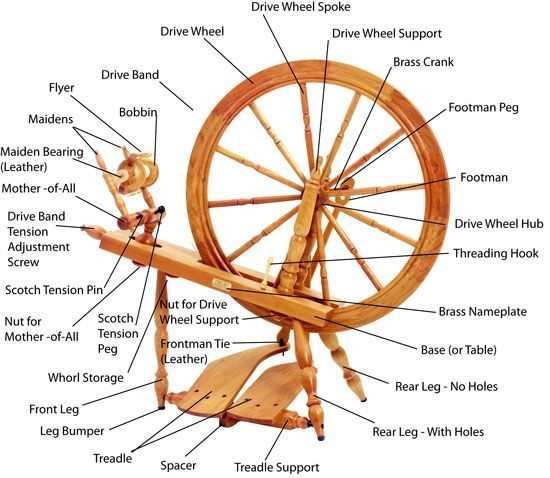
Different approaches to fiber manipulation require various functionalities. Are you drawn to intricate patterns or simpler designs? Assessing your artistic goals will help narrow down the options that align with your vision.
Assess the Features
Every model offers distinct features that can significantly impact your experience. Pay attention to aspects like ease of use, portability, and adjustability. Evaluating these factors will lead you to the ultimate choice that complements your creative journey.
Troubleshooting Spinning Wheel Issues

Addressing challenges that arise during the use of a fiber processing device can significantly enhance your crafting experience. Understanding common problems and their solutions allows for smoother operation and improved results.
| Issue | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Difficulty in achieving consistent tension | Improper setup, worn components | Adjust the tension mechanism, replace worn parts |
| Unusual noise during operation | Lack of lubrication, misalignment | Lubricate moving parts, check alignment |
| Fiber not feeding smoothly | Clogged feed area, incorrect drafting | Clear any blockages, adjust drafting technique |
| Difficulty in starting | Power source issues, worn drive components | Check power connections, replace drive parts |
Spinning Wheel Parts and Their Purpose
Understanding the components of a textile crafting tool is essential for anyone looking to create yarn efficiently. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, ensuring smooth operation and high-quality results. Familiarity with these elements can enhance both the crafting experience and the final product.
Main Components
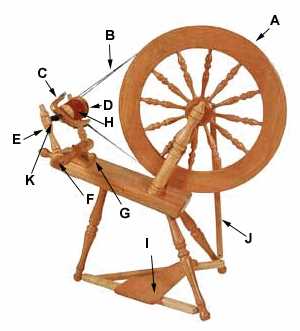
Different segments work in harmony to transform fiber into yarn. Below is a table that outlines these essential components along with their specific functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Drive Wheel | Provides motion to the system, allowing for the twisting of fibers. |
| Flyer | Guides the fiber and helps in forming the twist into yarn. |
| Tension Knob | Adjusts the tension on the fiber to control the thickness of the yarn. |
| Orifice | Allows the fiber to pass through while maintaining the structure of the spun material. |
Additonal Elements

In addition to the primary components, several auxiliary elements contribute to the crafting process. Understanding these can further improve your technique:
| Auxiliary Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Bobbin | Holds the finished yarn, allowing for easy handling and storage. |
| Footman | Connects the drive mechanism, allowing the user to pedal and generate movement. |
| Distaff | Supports the fiber supply, keeping it organized and accessible. |