Understanding the inner workings of agricultural equipment is essential for ensuring smooth and efficient operation. For those maintaining or restoring older machinery, having a clear view of its mechanical layout can simplify the process of identifying and replacing necessary elements. This guide provides a thorough overview of the key components, helping operators navigate complex systems with ease.
With a strong focus on essential elements, this resource is designed to offer clarity and precision. Each section highlights critical areas of the machine, making it easier for users to maintain optimal performance. Whether for repairs or general upkeep, this reference is a valuable tool for keeping machinery in prime condition.
Exploring the main systems and their interactions, the guide ensures that users have a clear understanding of how each part plays a role in the overall functionality. By offering a detailed breakdown, it aims to support both seasoned professionals and those newer to working with these machines.
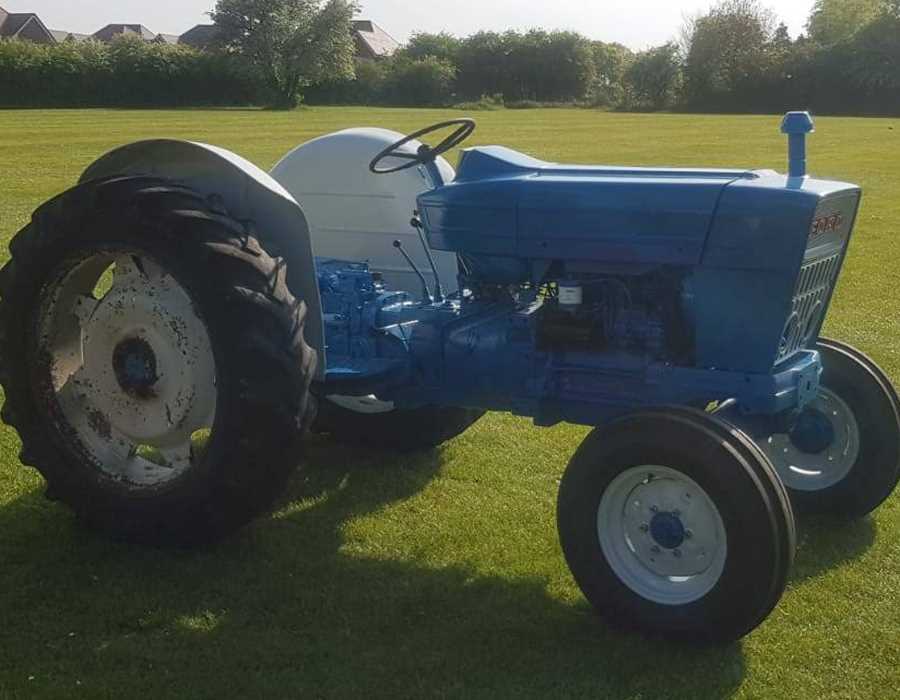
Understanding Key Components of the Ford 4000
The vehicle in question is equipped with a range of essential mechanisms that ensure its functionality and performance. Familiarity with the individual sections and systems can aid in troubleshooting, maintenance, and overall operational efficiency.
- Engine System: The central power source that drives the machine, including key elements such as the fuel pump, cooling system, and air intake mechanisms.
- Transmission: Responsible for controlling the power output and speed adjustments, allowing smooth transitions during various operations.
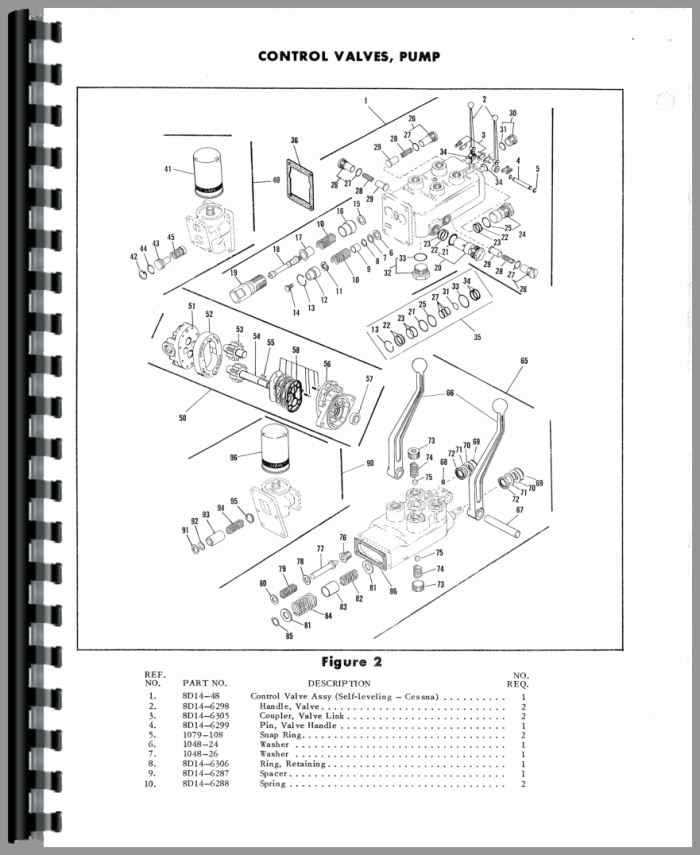
- Hydraulic System: Provides the necessary lifting power, ensuring the machine can handle attachments and implements with ease.
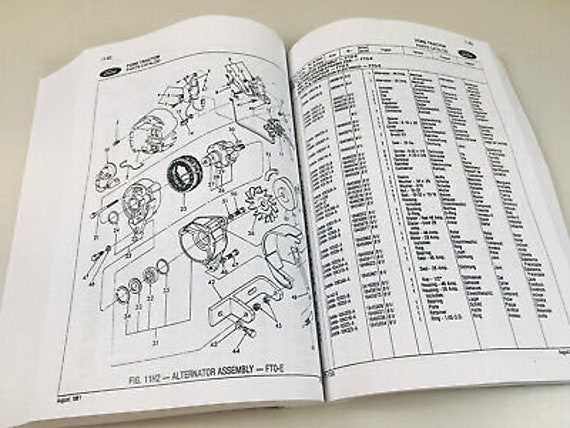
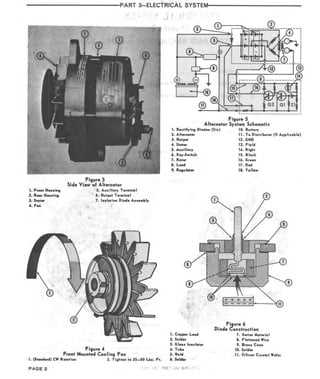
- Electrical Components: Encompasses the battery, alternator, and wiring, vital for ignition, lighting, and other electronic features.
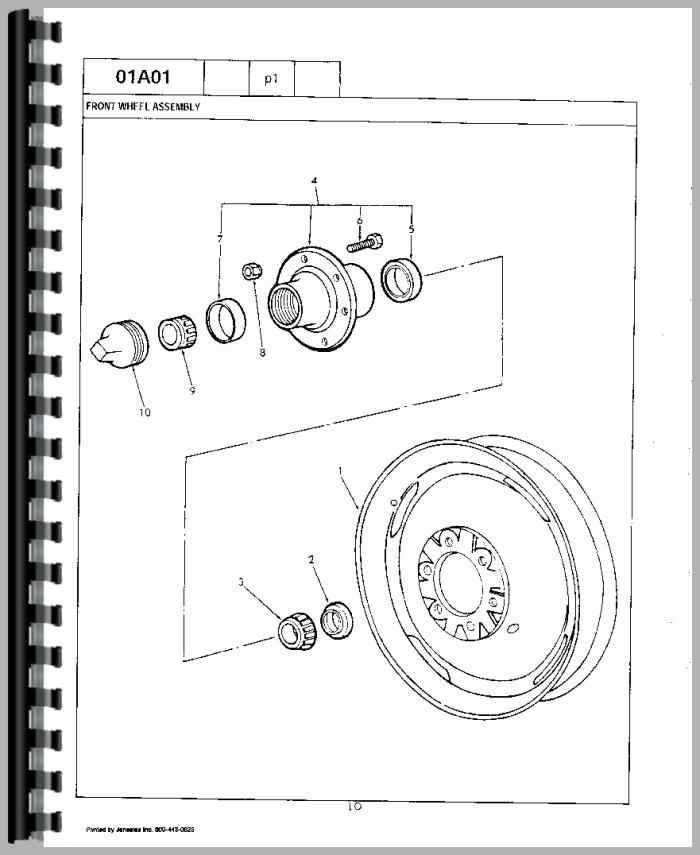
- Steering and Braking: Essential for maneuverability and safety, these systems ensure precise control and stopping power when needed.
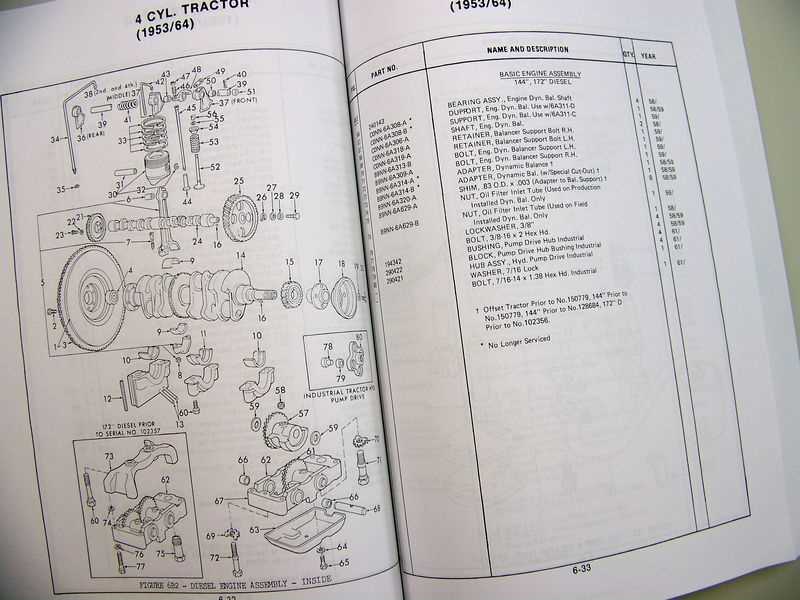
Exploring the Engine Assembly Layout

The structure of the motor’s assembly is crucial for the overall performance and longevity of the machine. Understanding the arrangement of the key components allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting. This section offers a detailed overview of the essential elements that comprise the engine block, focusing on their positioning and interaction within the system.
- Cylinder Block: The foundation that houses the cylinders, acting as the primary structural component. It supports other critical parts and ensures efficient heat dissipation.
- Pistons and Crankshaft: These components work in tandem to convert the energy from combustion into mechanical motion. Proper alignment and synchronization are vital for smooth operation.
- Valves and Camshaft: Regulate the intake and exhaust processes, ensuring the timely movement of gases in and out of the combustion chambers.
- Cooling System: A network of passages and pumps responsible for managing the engine’s temperature, preventing overheating during extended operation.
- Fuel and Air Intake: A set of channels and filters designed to deliver the right mixture of air and fuel to the engine, optimizing combustion efficiency.
Each
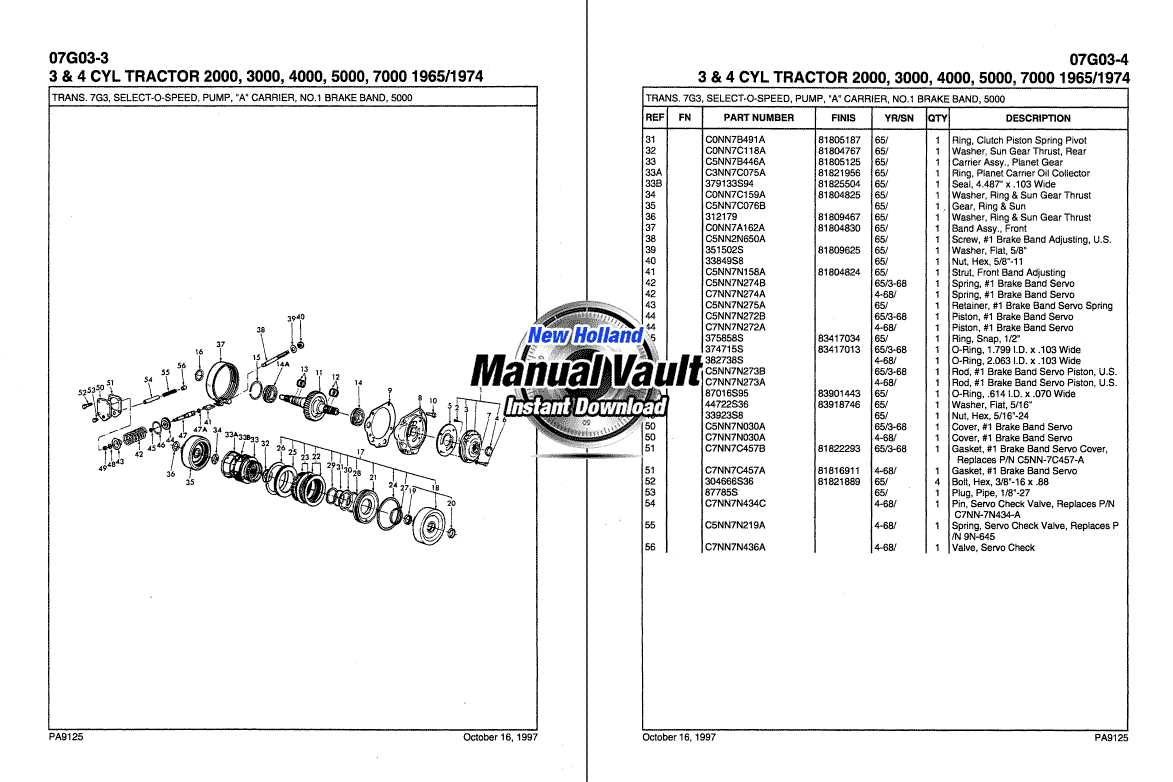
Transmission Parts and Their Functions
The transmission system plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth movement and power distribution within machinery. It consists of various elements that work together to transfer energy from the engine to the wheels. Understanding these components helps in identifying issues and maintaining efficient operation.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Clutch | Engages and disengages power between the engine and transmission system, allowing smooth gear changes. |
| Gears | Control the speed and torque by altering the ratio between input and output forces. |
| Shift Lever | Used to manually select different gears, adapting the machinery’s performance to varying workloads. |
| Synchronizer | Ensures the engagement of gears without grinding by matching their speeds before they lock together. |
| Transmission Housing | Encloses and protects the internal components, providing stability and reducing wear and tear. |