When it comes to maintaining older agricultural equipment, understanding how the various mechanical elements fit together is crucial. This guide offers a detailed look into the essential systems that keep such machines operational. By exploring these systems, you can better grasp how each element plays its role in ensuring smooth functionality.
Each section of this article provides insights into individual mechanical assemblies, breaking down their function and layout. This structure allows for a clear understanding of how different mechanisms interconnect, facilitating both repairs and upgrades.
Through this comprehensive breakdown, users can identify specific mechanical areas of interest, making it easier to address any maintenance needs or technical improvements.
Understanding Key Components of Ford 3000 Tractor

In this section, we will explore the most important mechanical elements that contribute to the efficient operation of agricultural machinery. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring smooth performance, and understanding these can help improve maintenance and repair tasks.
The power unit is at the heart of the machine, converting energy into mechanical motion. The transmission system, consisting of gears and linkages, is responsible for transferring that power to the wheels, enabling motion and control. The hydraulic system ensures the lifting and positioning of heavy equipment, playing a crucial role in versatility.
Equally essential is the braking system, which guarantees safe operation in diverse terrains. Steering mechanisms allow for precise control and maneuverability, especially in tight spaces. Lastly, the electrical components manage various auxiliary functions, ensuring everything from ignition to lighting works as expected.
Exploring the Engine System Layout
The internal system powering agricultural machines is a complex arrangement of components designed to work together seamlessly. Understanding the organization of these components helps in maintaining optimal performance and efficiency. This section provides a detailed look at the various segments within the power unit’s structure and their interconnected roles.
Core Components of the Engine
- Cylinder Block: The central housing that forms the foundation for the internal processes, ensuring the combustion chambers are enclosed safely.
- Pistons and Crankshaft: These elements work together to convert the energy from combustion into mechanical motion, driving the machine forward.
- Fuel Injection System: Precisely controls the fuel supply to each cylinder, crucial for efficient combustion and energy release.
- Cooling Mechanism: This part keeps the system from overheating, maintaining temperature balance to avoid engine damage.
Auxiliary Systems Supporting Engine Functionality

- Lubrication System: Reduces friction between moving parts, prolonging the lifespan of vital components and ensuring smooth operation.
- Air Intake and Exhaust: Regulates the flow of air necessary for combustion and safely removes exhaust gases after energy has been extracted.
- Electrical Circuit: Powers essential systems like the starter motor and sensors, ensuring reliable performance under varying conditions.
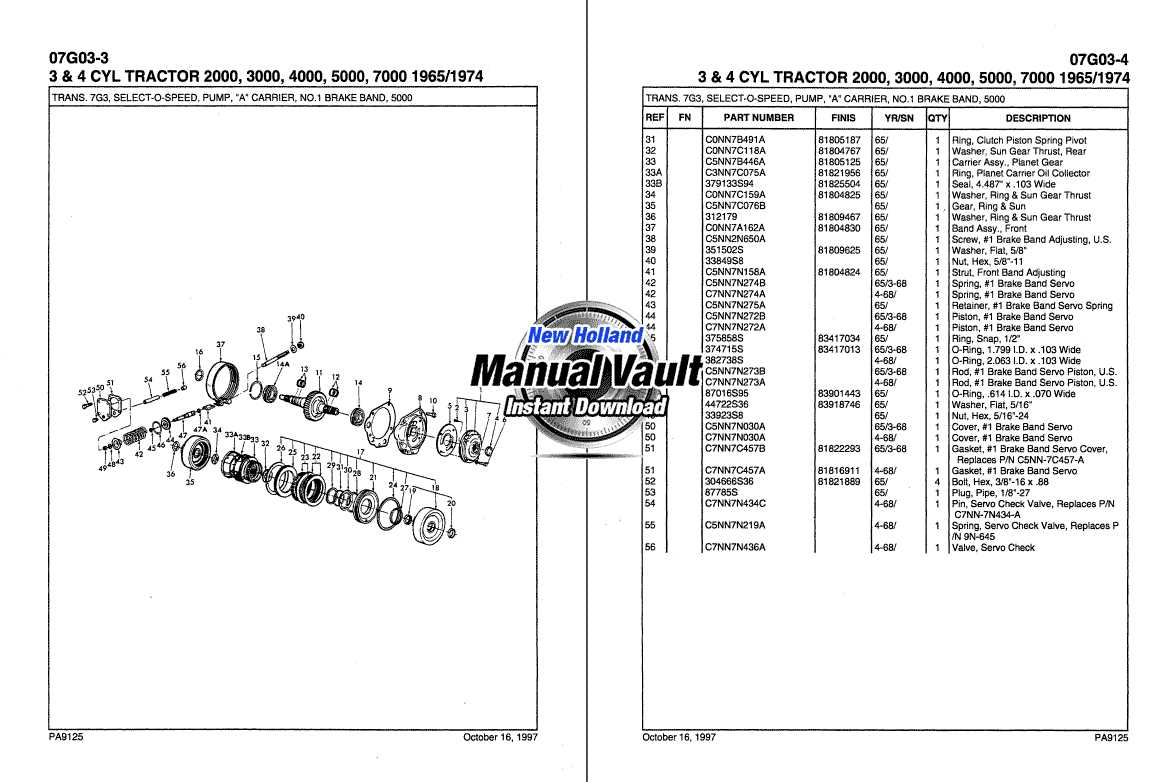
Transmission Assembly and Functions Overview
The transmission system plays a vital role in the operation of any machinery, acting as the intermediary between the power source and the wheels. Its main responsibility is to control the application of power, ensuring that it is delivered efficiently to the ground. This system is composed of various interconnected components, each serving a unique purpose in managing speed, torque, and direction of movement.
Main Components of the Transmission System
The assembly consists of several key elements that work together to transmit power. These include gears, shafts, and linkages that ensure seamless operation across different speeds and loads. Understanding the interaction between these components helps in maintaining optimal functionality and prolonging the system’s life span.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Input Shaft | Receives power from the engine and transmits it to the gears. |
| Gear Set | Allows adjustment of speed and torque by engaging different gear ratios. |
| Clutch Assembly | Enables smooth engagement and disengagement of power to the drivetrain. |
| Output Shaft | Transfers the modified power to the final drive system. |
Functional Benefits of a Well-Maintained Transmission
Proper maintenance of
Fuel System Configuration and Diagram

The fuel delivery setup is essential for ensuring efficient combustion and optimal performance. This section outlines the components and layout involved in channeling fuel from the storage unit to the combustion chamber, highlighting the key elements that contribute to a reliable and consistent fuel supply.
- Fuel Tank: Acts as the reservoir, where fuel is stored before entering the system. Its capacity and positioning are crucial for steady fuel flow.
- Fuel Pump: This component is responsible for drawing fuel from the reservoir and supplying it under pressure to the engine’s injection system.
- Fuel Lines: A series of conduits that transport fuel between components, ensuring a smooth flow from the storage unit to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Positioned between the pump and injection system, it removes impurities from the fuel, preventing contamination of the engine.
- Injectors: These precision devices spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold, ensuring optimal atomization for combustion.
The overall structure of this system is designed to optimize fuel delivery, reduce wastage, and ensure that the engine receives a clean, uninterrupted supply. Proper maintenance of each element in this network is essential for long-term efficiency and performance.
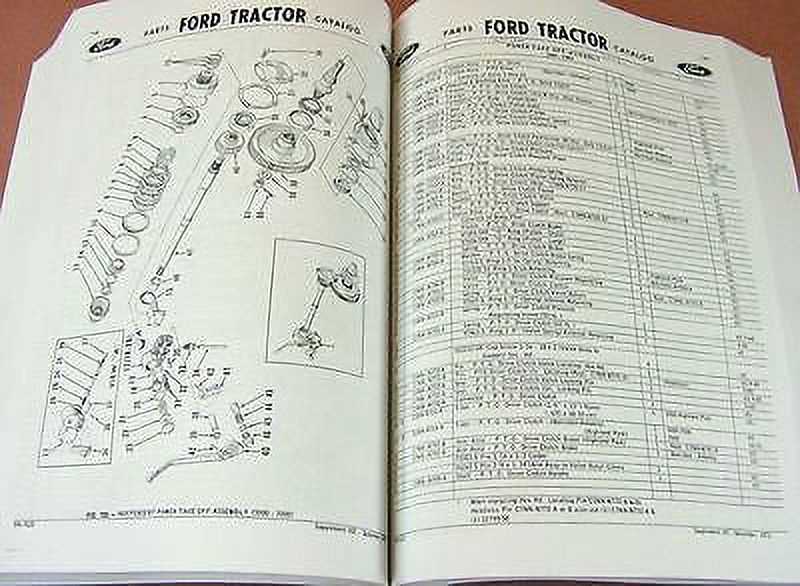
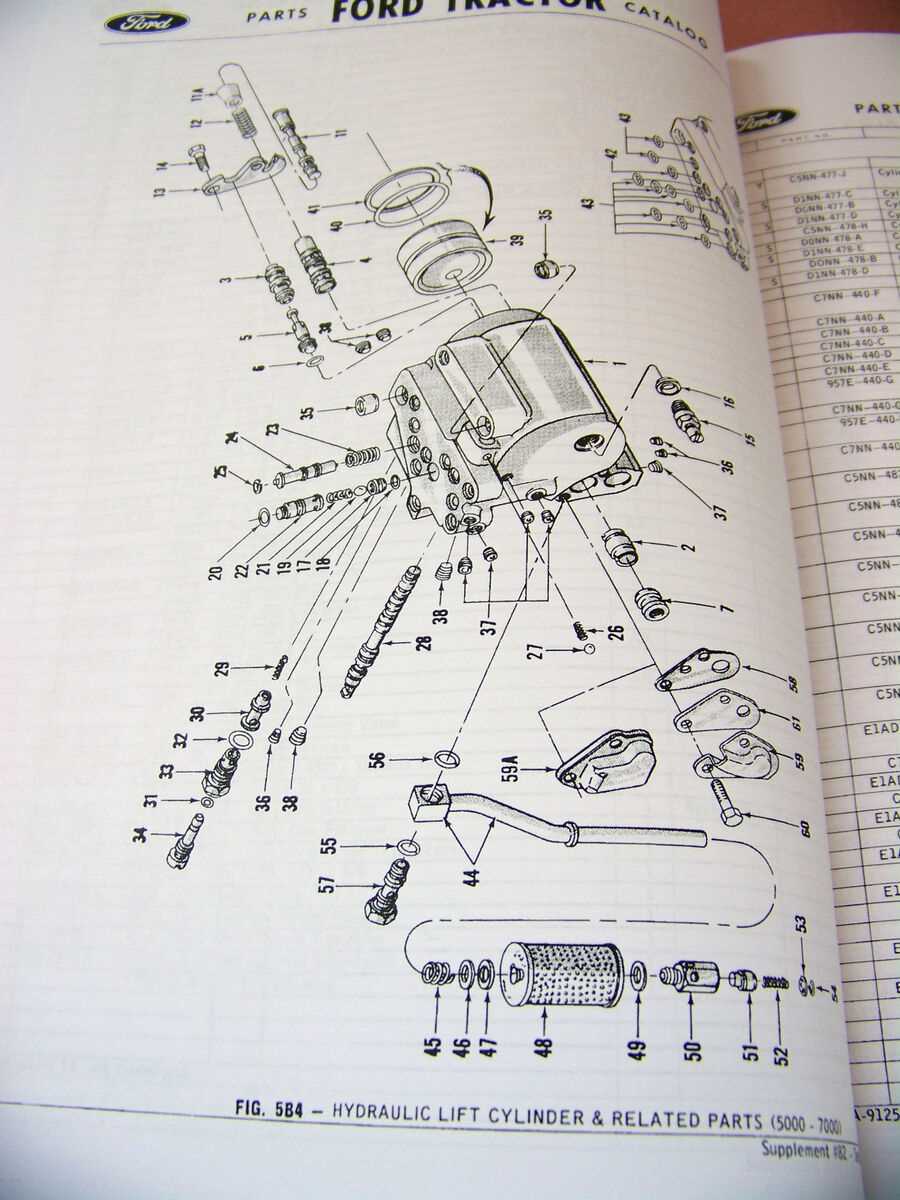
Hydraulic System Breakdown for Ford 3000
The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in powering various functions of the equipment, ensuring smooth operation of lifting, lowering, and positioning mechanisms. Understanding the layout and functioning of this system is essential for maintaining efficiency and addressing potential issues that may arise over time.
Main Components of the Hydraulic Circuit
The system consists of several key elements, including a pump, fluid reservoir, control valves, and cylinders. The pump generates pressure, moving fluid through the lines to actuate the working parts. Control valves regulate the flow and direction of this pressurized fluid, while the cylinders convert the hydraulic energy into mechanical motion, allowing precise control of attachments and other functions.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Common problems within the system may include leaks, pressure drops, or malfunctioning valves. Regular inspection and maintenance of hoses, seals, and the fluid levels can prevent these issues. When troubleshooting, it’s essential to check for proper fluid circulation and monitor any unusual noises or delayed responses in the hydraulic functions.
Electrical Wiring and Key Parts Identification
Understanding the electrical system and its components is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in heavy machinery. Proper identification of key elements ensures that all connections are correct and that the system operates efficiently. This section provides an overview of how to identify important components within the electrical setup and how to manage wiring for long-lasting functionality.
Essential Electrical Components
- Battery: Acts as the primary source of power for starting the engine and powering electrical systems when the engine is off.
- Alternator: Responsible for generating electrical power while the engine is running, ensuring the battery remains charged.
- Starter Motor: A key component for igniting the engine by providing the necessary torque to start the combustion process.
- Wiring Harness: A system of wires that connects various electrical components, enabling communication and power distribution.
- Fuses and Relays: Protects the electrical system from overloads and ensures circuits operate safely.
Identifying Key Parts and Connections
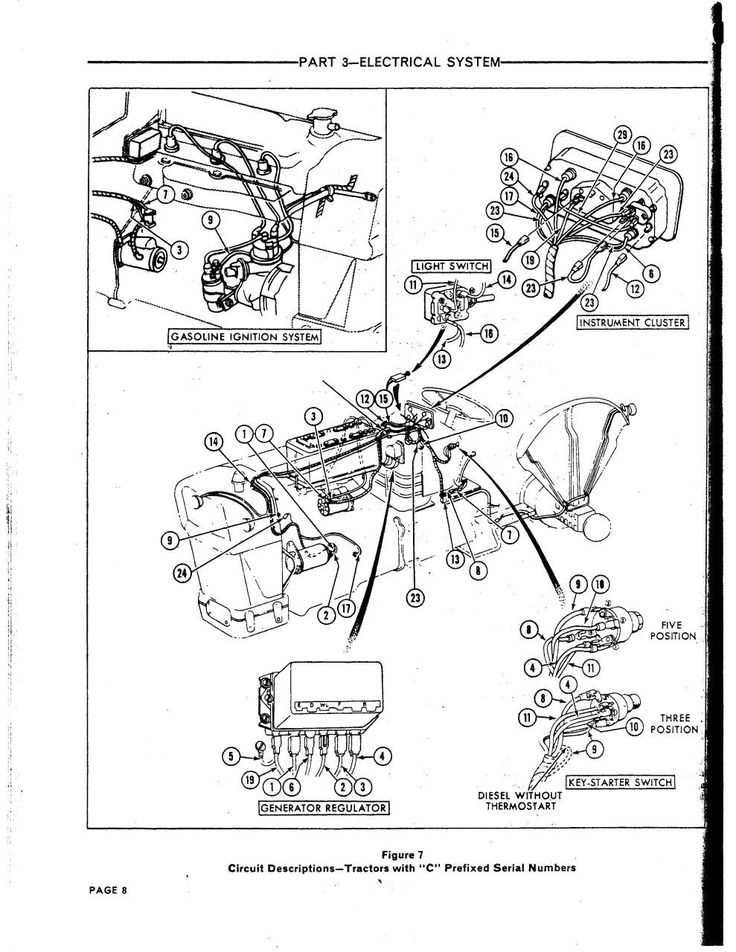
Recognizing the placement and function of each component is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues. Proper wiring connections ensure the correct flow of current and prevent damage to sensitive components. Regular inspections and familiarity with the system layout help in maintaining performance.
- Ensure all wires are securely connected to prevent short circuits.
- Identify color-coded wires for correct reassembly after repairs.
- Examine connections for signs of wear or corrosion, which can hinder performance.
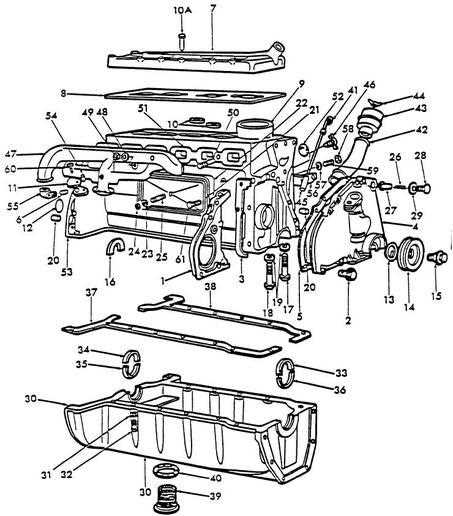
Cooling System Components Explained

The cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining the optimal temperature of an engine, ensuring that it operates efficiently and does not overheat. A properly functioning cooling mechanism prevents engine components from being damaged by excessive heat, which can lead to performance issues or costly repairs.
Radiator: The radiator is the primary component responsible for dissipating the heat from the engine. It circulates coolant through the engine and expels the excess heat into the atmosphere, ensuring that the engine remains within a safe operating temperature range.
Water Pump: This pump is essential for circulating coolant throughout the engine and the radiator. It ensures that the coolant flows effectively, allowing the heat to be absorbed and transported to the radiator for cooling.
Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the temperature by controlling the flow of coolant. It remains closed when the engine is cold, allowing it to heat up quickly, and opens once the desired temperature is reached, ensuring a steady flow of coolant to maintain the proper operating temperature.
Coolant Reservoir: The coolant reservoir stores extra coolant, which is used to maintain the system’s pressure and provide additional liquid when needed. It also helps in preventing air from entering the system, which could lead to overheating.
Cooling Hoses: These flexible tubes carry coolant between the various components of the system, ensuring that the liquid flows smoothly and efficiently between the radiator, water pump, and engine.
Each of these components works in unison to create an efficient and reliable cooling system, which is vital for the longevity and performance of the engine. Without a properly maintained cooling system, an engine is at risk of overheating, which can cause significant damage over time.
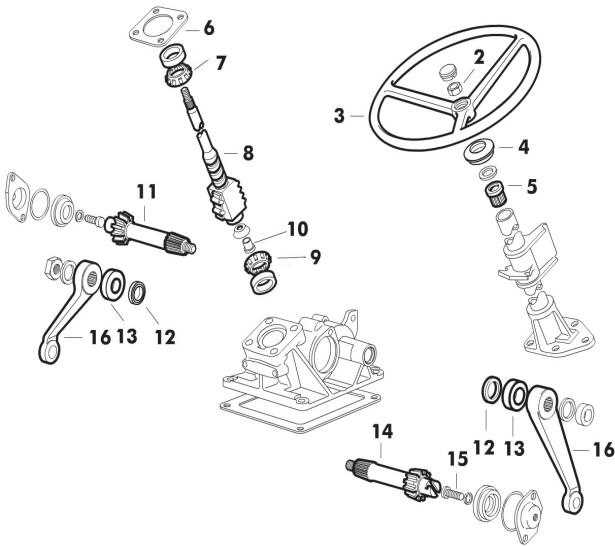
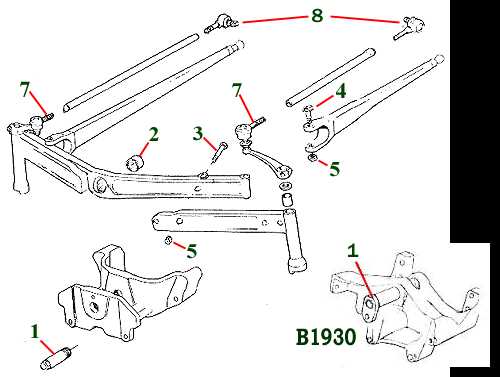
Steering Mechanism and Related Parts
The steering system plays a critical role in ensuring smooth and precise movement of the vehicle, allowing it to change direction efficiently. This mechanism is composed of several interconnected components that work together to translate the driver’s input into movement of the front wheels. A properly functioning steering assembly is essential for maintaining control and stability, especially during heavy-duty operations.
The key elements that make up the steering assembly include the steering wheel, steering column, steering arms, and linkage. Each of these elements serves a specific function in the transmission of movement from the driver to the wheels. The steering wheel initiates the turning motion, while the column transmits that motion to the connecting parts. The linkage system ensures that the movement is transferred effectively to the wheels, allowing them to pivot accurately.
Additional components such as tie rods and ball joints are crucial for maintaining the alignment and flexibility of the system. Over time, these parts can wear down, leading to reduced steering precision. Regular maintenance and replacement of these components help ensure the vehicle operates safely and efficiently, even under challenging conditions.
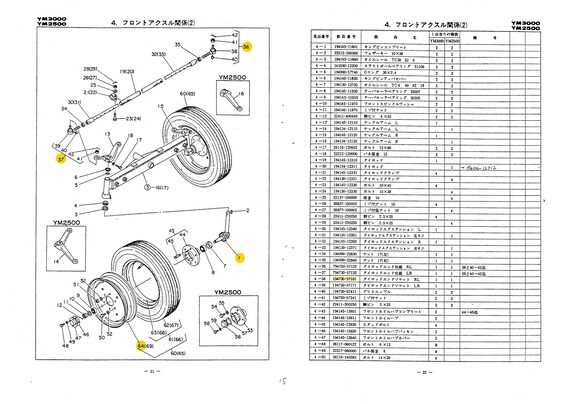
Axle and Suspension Systems Overview
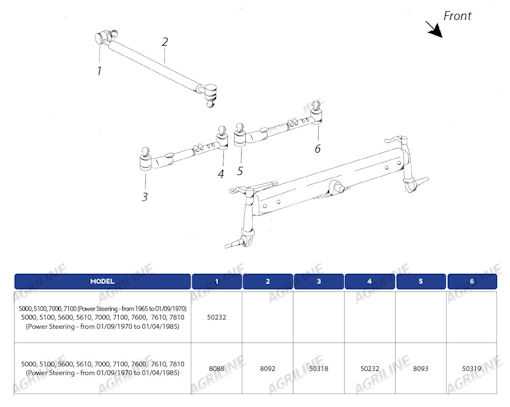
The axle and suspension systems play a crucial role in ensuring stability and smooth operation of heavy machinery. These components are designed to bear the weight of the vehicle and facilitate its movement across different terrains. The axle system provides the connection between the wheels and the main body, while the suspension system absorbs shocks and vibrations, contributing to overall performance and comfort during operation.
In essence, these systems work together to ensure the equipment can function optimally in varying conditions, whether on rough, uneven surfaces or flat, hard ground. Proper maintenance and understanding of these systems are vital for maximizing the longevity and efficiency of the equipment.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Front Axle | Supports the front wheels and allows for steering control. |
| Rear Axle | Transmits power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling movement. |
| Suspension Springs | Absorbs shocks and vibrations to ensure smooth operation. |
| Shock Absorbers | Helps in reducing the impact of uneven surfaces on the vehicle’s ride quality. |
| Leaf Springs | Provide additional support to the rear axle and enhance load-bearing capacity. |