
Understanding the inner workings of small machinery engines is essential for anyone involved in maintenance or repair tasks. When it comes to restoring or replacing individual elements, having a structured reference becomes crucial. This guide offers insights into the configuration and connectivity of key components, helping users navigate complex assemblies with ease.
A well-organized schematic simplifies troubleshooting and assists in selecting compatible replacements. This resource serves as a reliable companion for enthusiasts and professionals alike, ensuring smooth restoration or tuning processes. Every element within the layout plays a specific role in overall functionality, and
Overview of 31c707 Engine Assembly
This section provides a comprehensive look at the structure and key elements of a widely used four-cycle power unit. It breaks down the functional arrangement, explaining how various interconnected modules contribute to efficient performance and durability. Designed for smooth operation, this engine offers an optimal balance between fuel consumption and output, making it suitable for multiple applications.
Core Components: The heart of the assembly features a single-cylinder block, enhanced with a precision crankshaft to manage rotational
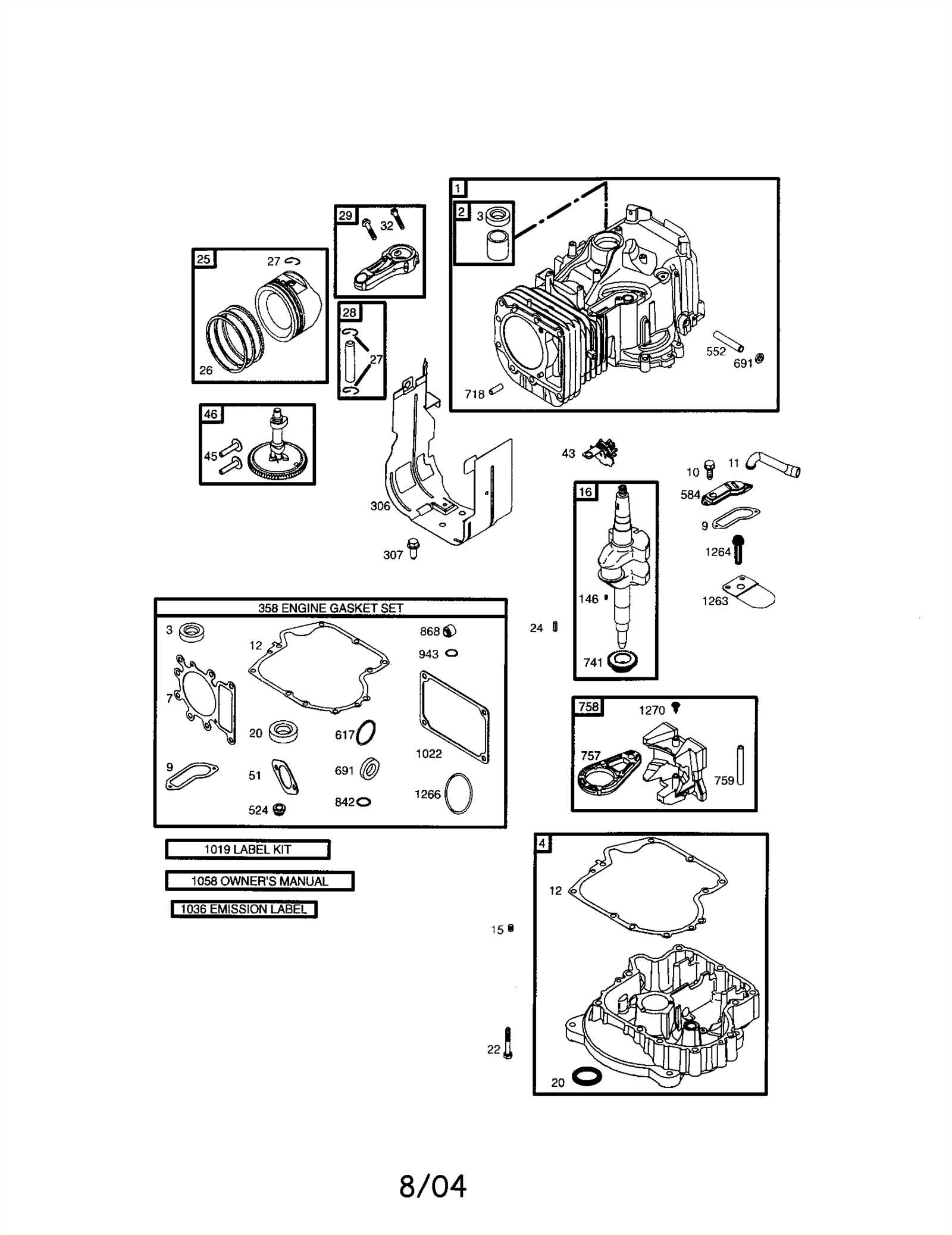
Main Components of the 31c707 Model
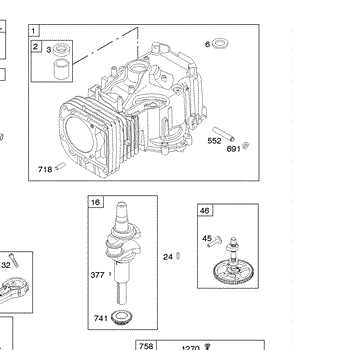
The discussed engine type integrates several critical systems designed to ensure reliable performance across a wide range of conditions. Each element works in harmony to deliver smooth operation, efficient fuel consumption, and extended durability, making it a popular choice in various equipment applications.
The core structure includes a cylinder block and head, which house the combustion process and manage heat distribution. Essential rotating mechanisms, such as the crankshaft and connecting rods, convert
Fuel System Layout and Connections
The section explores the flow and organization of essential components responsible for transporting fuel within the machine. It emphasizes how each element interacts to ensure a smooth supply and proper combustion, contributing to the overall functionality of the engine.
Main Components Overview
The core of the fuel network consists of several key units designed to store, transfer, and regulate the liquid energy source. These elements work in unison, inc
Air Filtration and Carburetor Details
The performance of an internal combustion engine relies heavily on the efficient management of airflow and fuel delivery. An optimal air filtration system ensures clean air intake, preventing contaminants from damaging internal components. Meanwhile, the precise regulation of fuel through the carburetor plays a key role in maintaining smooth engine operation and fuel efficiency.
- Air Filter Types: Filtration systems vary, with foam and pleated paper being the most common. Foam filters are washable and reusable, while paper models offer finer filtration but require replacement over time.
- Filter Maintenance: Regular cleaning or rep
Ignition System Structure and Wiring
The ignition mechanism ensures smooth engine performance by delivering timely electrical impulses for combustion. This section delves into the core components responsible for initiating the spark and explores the wiring connections that maintain proper functionality. Understanding how these elements interact is essential for efficient maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components Overview
The ignition system comprises several interconnected elements, including a coil, spark plug, and control module. The coil amplifies voltage, while the plug ignites the air-fuel mixture inside the cylinder. The control unit regulates the timing to ensure accurate spark delivery, enabling consistent power output.
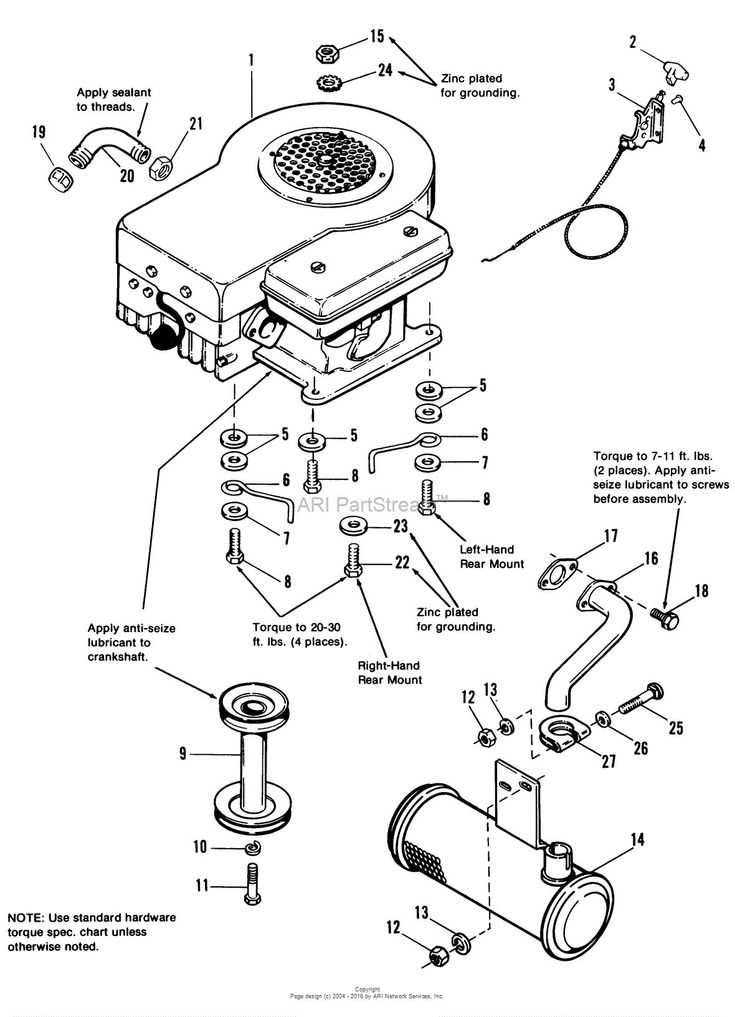
Oil Pump and Lubrication Path 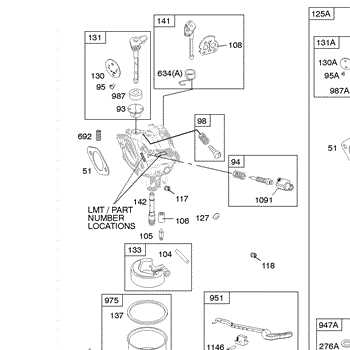
The efficiency of any engine relies heavily on its ability to maintain proper lubrication. A well-designed system ensures that all moving components receive adequate oil flow, reducing friction and wear. This section delves into the mechanisms that facilitate oil circulation and the essential role they play in overall engine performance.
The oil pump serves as the heart of the lubrication system, drawing oil from the sump and distributing it throughout the engine. It operates by creating a pressure differential, which allows oil to flow through various passages and reach critical areas, including bearings, gears, and valve assemblies. Understanding the construction and function of this component is vital for diagnosing potential issues and ensuring optimal operation.
Moreover, the lubrication path is a carefully engineered route that guides oil through different sections of the engine. This path typically includes a series of channels and galleries designed to minimize resistance while maximizing coverage. Regular maintenance, including oil changes and filter replacements, is crucial to keep this system functioning effectively and to prolong the lifespan of the engine.
In summary, the oil pump and its associated lubrication path are integral to maintaining an engine’s health. By ensuring proper oil flow and distribution, these components help to prevent overheating and wear, ultimately contributing to the longevity and reliability of the machine.
Exploded View of the Valve Train
The valve train is a crucial assembly that plays a significant role in the overall performance of an engine. This intricate system ensures the precise timing and operation of the intake and exhaust valves, allowing for optimal airflow and engine efficiency. Understanding its components and their arrangement can provide valuable insights into the mechanics involved in engine operation.
In an exploded view, each part of the valve train is displayed separately, showcasing its relationship with adjacent components. This representation helps to illustrate the function of critical elements such as the camshaft, lifters, pushrods, rocker arms, and valves. By examining these elements closely, one can appreciate how they work together to facilitate smooth operation and responsiveness in an engine.
Camshaft: This component is essential for controlling valve timing and is directly responsible for opening and closing the valves at the correct intervals.
Lifters: These parts connect the camshaft to the pushrods, converting the rotational motion of the cam into vertical movement.
Pushrods: Acting as intermediaries, these rods transmit the motion from the lifters to the rocker arms, ensuring that the valves are activated appropriately.
Rocker Arms: These components pivot to push the valves open and allow them to close, playing a vital role in regulating airflow into and out of the combustion chamber.
Valves: The final components in the valve train, these parts control the intake of air and fuel and the expulsion of exhaust gases, critical for maintaining engine efficiency.
By analyzing the exploded view of the valve train, one can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanical interactions within the engine. This knowledge is invaluable for anyone involved in maintenance, repair, or performance enhancement of internal combustion engines.