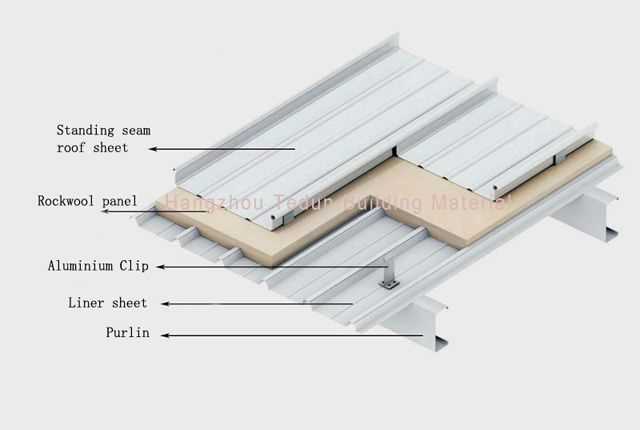
The structure of a building’s upper layer plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and durability. Understanding the various elements that constitute this layer can significantly enhance one’s appreciation of its functionality and design. Each element serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall performance and aesthetic of the construction.
In this section, we will explore the essential components that make up this protective covering. From the foundational elements to the finishing touches, every aspect is designed to work harmoniously, providing insulation, weather resistance, and visual appeal. By examining these components, one can gain insight into the intricate engineering that supports modern constructions.
Whether you are planning a new project or renovating an existing structure, recognizing these key elements is vital. It not only aids in selecting the right materials but also ensures that the installation process adheres to best practices. Understanding how each component interacts will ultimately lead to a more resilient and efficient structure.
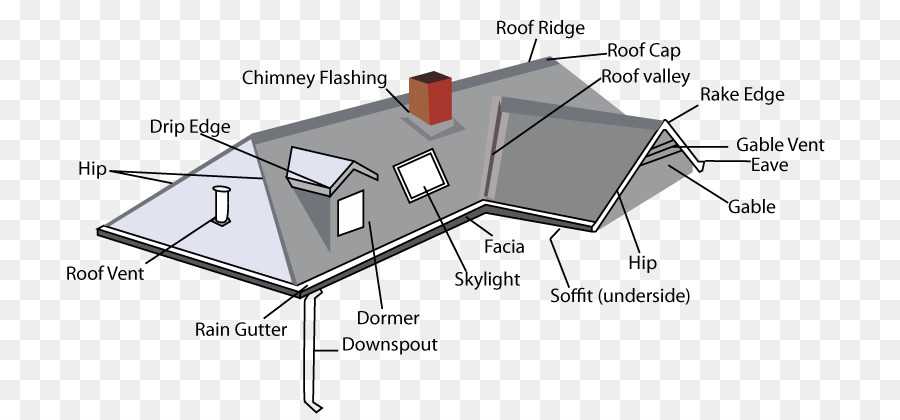
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the various elements that constitute a durable top covering system. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring longevity and performance, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the structure.
Key Components Overview
The following list outlines the essential components typically found in such systems:
- Panels: The primary material that forms the exterior layer, available in various shapes and sizes.
- Flashings: Essential elements that provide waterproofing at critical junctions, preventing leaks.
- Underlayment: A protective layer installed beneath the outer material for added insulation and moisture resistance.
- Gutters: Systems designed to channel rainwater away, protecting the foundation and reducing erosion.
- Fascia: A horizontal board located at the roof’s edge, offering structural support and aesthetic appeal.
Functions and Importance
Understanding the role of each component enhances the knowledge of how these systems work together:
- Weather Protection: Each element contributes to safeguarding against environmental factors.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper insulation and materials can significantly affect energy consumption.
- Structural Integrity: The components must work in harmony to maintain the overall strength and durability.
Installation Considerations
When planning for installation, it is vital to consider the following:
- Ensure proper alignment and fitting of all elements.
- Utilize high-quality materials for enhanced durability.
- Adhere to local building codes and standards to ensure compliance.
Main Elements of Metal Roofing
The structural components of a durable overhead system play a crucial role in its overall performance and longevity. Understanding these key elements is essential for anyone looking to install or maintain a high-quality covering that withstands various weather conditions. Each part contributes to the efficiency, safety, and aesthetics of the construction, ensuring that it serves its purpose effectively over time.
Key Components Overview
Several fundamental components work together to create a reliable overhead shield. From the protective surface to the support structure, each piece must be carefully selected and installed to provide optimal functionality. Below is a table summarizing these essential elements:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Panel | The main covering element that provides protection against the elements. |
| Flashing | Sealing strips that prevent water from entering vulnerable areas. |
| Underlayment | A moisture barrier that adds an extra layer of defense. |
| Support Structure | The framework that provides stability and supports the covering. |
Importance of Quality Materials
Choosing high-quality materials for each component is vital for the durability and efficiency of the entire structure. Using robust materials can significantly enhance resistance to weather impacts and reduce maintenance costs over time. Proper installation techniques further ensure that each element functions harmoniously within the system.
Common Materials Used in Metal Roofs
Various substances are utilized in the construction of overhead coverings, each offering distinct advantages and characteristics. The choice of material significantly impacts durability, aesthetics, and performance, making it essential to consider options carefully.
| Material | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and easy to work with. | Can be more expensive than other options. |
| Steel | Strong, durable, and available in various finishes. | Susceptible to rust without proper coating. |
| Copper | Long-lasting and visually appealing; develops a patina over time. | High initial cost and requires skilled installation. |
| Zinc | Excellent corrosion resistance and self-healing properties. | Can be prone to scratches and dents. |
| Galvanized Steel | Affordable and offers decent rust protection. | Less durable than aluminum and copper. |
Benefits of Metal Roof Systems
Utilizing durable coverings for buildings has gained significant popularity due to their remarkable advantages. These structures offer an array of features that enhance their functionality, longevity, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these benefits can aid homeowners and builders in making informed decisions when selecting the appropriate materials for their projects.
Longevity and Durability
One of the primary advantages of these coverings is their extended lifespan. Unlike traditional materials, they resist various environmental factors, ensuring they maintain their integrity over time. This durability translates to less frequent replacements and repairs, resulting in long-term cost savings.
Energy Efficiency
Another significant benefit lies in their ability to improve energy efficiency. Many options are designed with reflective properties, helping to reduce heat absorption. This feature can lead to decreased energy consumption for cooling systems, making buildings more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
| Feature | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Longevity | Lasts longer than traditional materials |
| Durability | Resists weather-related damage |
| Energy Efficiency | Lowers energy costs |
| Low Maintenance | Requires minimal upkeep |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable materials |
Installation Process for Metal Roofs
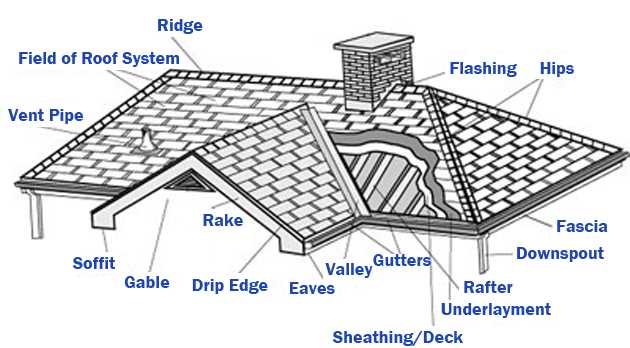
Successfully placing a protective covering on a structure involves several critical steps. This phase not only ensures durability and resilience but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of the building. Proper preparation and execution are essential for achieving optimal results.
Here is a general overview of the steps involved in the installation:
- Preparation of the Area:
- Remove any existing coverings or debris.
- Inspect the underlying structure for damage and make necessary repairs.
- Ensure the surface is clean and dry.
- Measurement and Layout:
- Accurately measure the dimensions of the surface.
- Mark guidelines for placing the new covering.
- Installation of Underlayment:
- Lay down a protective layer to guard against moisture.
- Secure the underlayment with appropriate fasteners.
- Placement of Panels:
- Begin at one end and work your way across the surface.
- Ensure panels overlap as specified by manufacturer instructions.
- Fasten each panel securely to the underlying structure.
- Installation of Flashing and Accessories:
- Apply flashing around chimneys, vents, and other protrusions.
- Install any additional accessories, such as ridge caps or closures.
- Final Inspection:
- Check for secure fastening and proper alignment.
- Look for any potential leaks or issues.
- Make necessary adjustments to ensure a tight seal.
Following these steps carefully will contribute to a successful installation process, ensuring longevity and protection for the structure.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
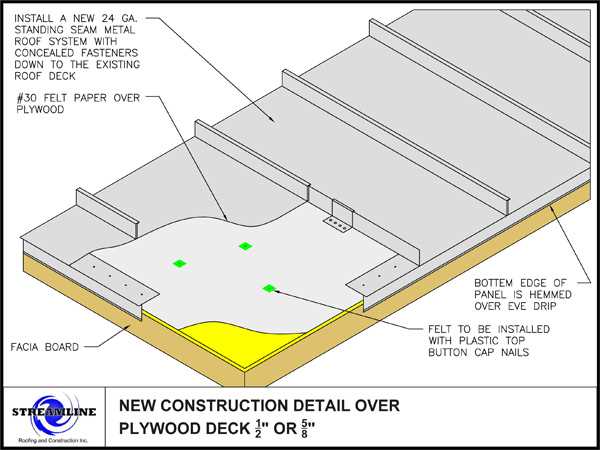
Ensuring the durability of your installation requires consistent care and attention. Regular upkeep can prevent deterioration and enhance the lifespan of your structure. Here are some essential practices to maintain its integrity over time.
Regular Inspections
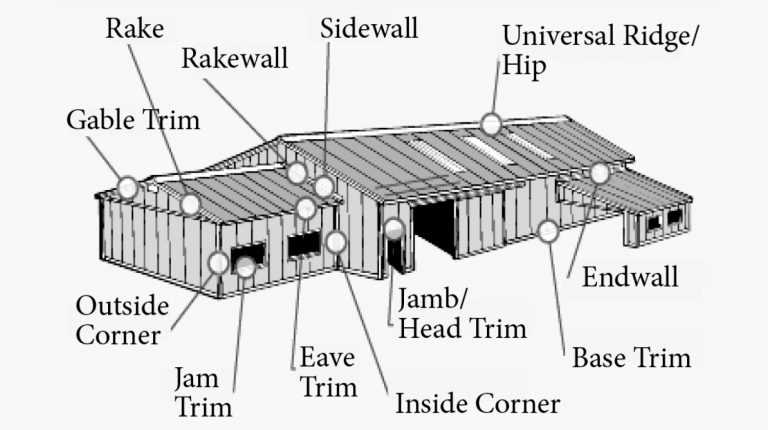
Frequent evaluations are crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Consider the following:
- Inspect for rust or corrosion at least twice a year.
- Check for loose fasteners or connections.
- Look for any signs of wear or damage from extreme weather conditions.
Cleaning and Debris Removal
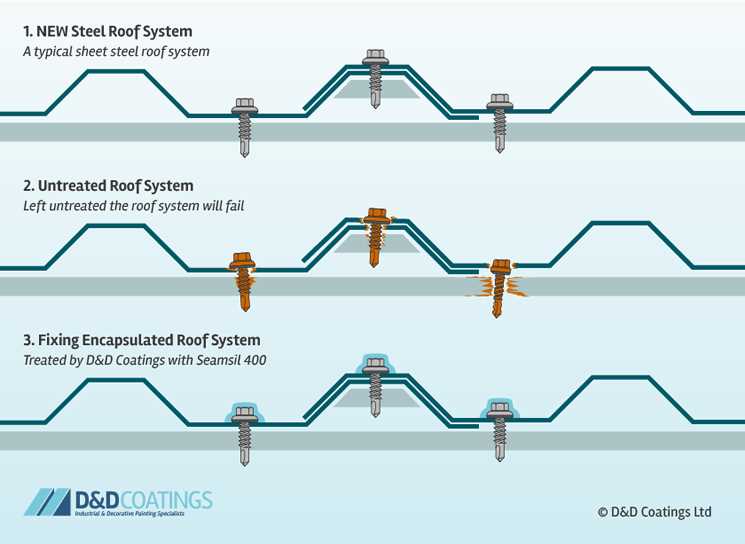
Keeping the surface clear of debris is vital for optimal performance. Regular cleaning helps in preventing clogging and buildup:
- Clear leaves and branches after storms or seasonal changes.
- Use a soft-bristle brush or blower to remove dirt and dust.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals that may cause harm to the surface.
Common Issues and Solutions
When it comes to various types of protective coverings, several challenges may arise that can affect their performance and longevity. Understanding these typical problems and their corresponding remedies is crucial for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of these structures.
Frequent Problems Encountered
Several issues can compromise the durability of protective coverings. These include leaks, rust formation, and improper installation. Identifying these challenges early can prevent further damage and costly repairs.
Effective Remedies
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Leaks | Inspect seams and joints for damage; apply appropriate sealant to prevent water ingress. |
| Rust | Regularly check for corrosion; treat affected areas with rust inhibitor and repaint as necessary. |
| Poor Installation | Consult a professional for proper installation techniques and re-evaluate the current setup if needed. |
Innovations in Metal Roofing Technology
The landscape of construction materials has evolved significantly, leading to enhanced durability, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal. Recent advancements have introduced innovative solutions that not only improve functionality but also contribute to energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. These developments reflect a growing trend towards more efficient and resilient structures.
| Innovation | Description |
|---|---|
| Coatings | Advanced coatings enhance resistance to corrosion and UV damage, extending lifespan. |
| Energy Efficiency | Reflective surfaces reduce heat absorption, promoting energy savings in cooling. |
| Recyclability | Modern materials are designed for easy recycling, reducing environmental impact. |
| Lightweight Materials | Innovative alloys and composites decrease weight, simplifying installation and reducing structural demands. |
| Modular Systems | Pre-fabricated components allow for quicker assembly and customizable designs. |
Choosing the Right Metal Roof Design
When it comes to selecting a suitable covering for your structure, various styles and configurations are available to consider. The choice not only impacts the overall aesthetic but also the functionality and durability of the installation. Understanding the options can help ensure a decision that aligns with both personal preferences and practical requirements.
Factors to Consider
Several key elements should guide your selection process. First, assess the climate of your area, as this influences the durability and insulation properties required. Additionally, consider the architectural style of your building; different styles may complement certain designs better than others. Lastly, think about maintenance needs, as some configurations require more upkeep than others.
Popular Designs
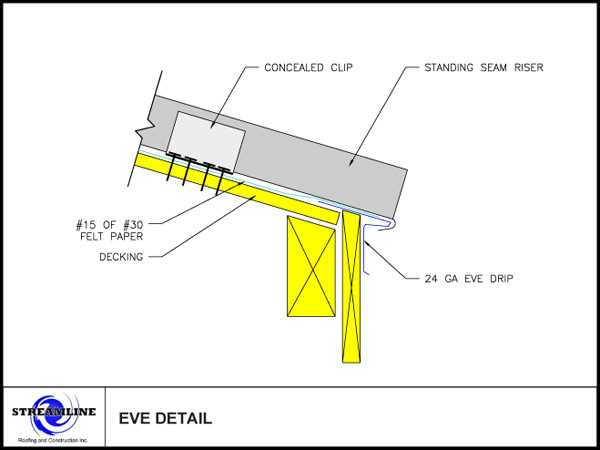
Among the various configurations, standing seam and corrugated profiles stand out for their unique advantages. Standing seam offers a sleek, modern appearance with excellent water drainage capabilities, making it a popular choice for contemporary structures. On the other hand, corrugated styles provide a classic look and are often more budget-friendly, making them ideal for agricultural or industrial applications.