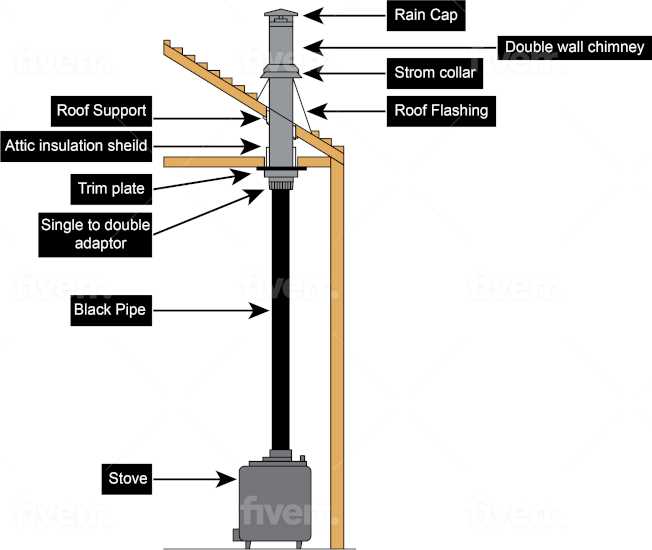
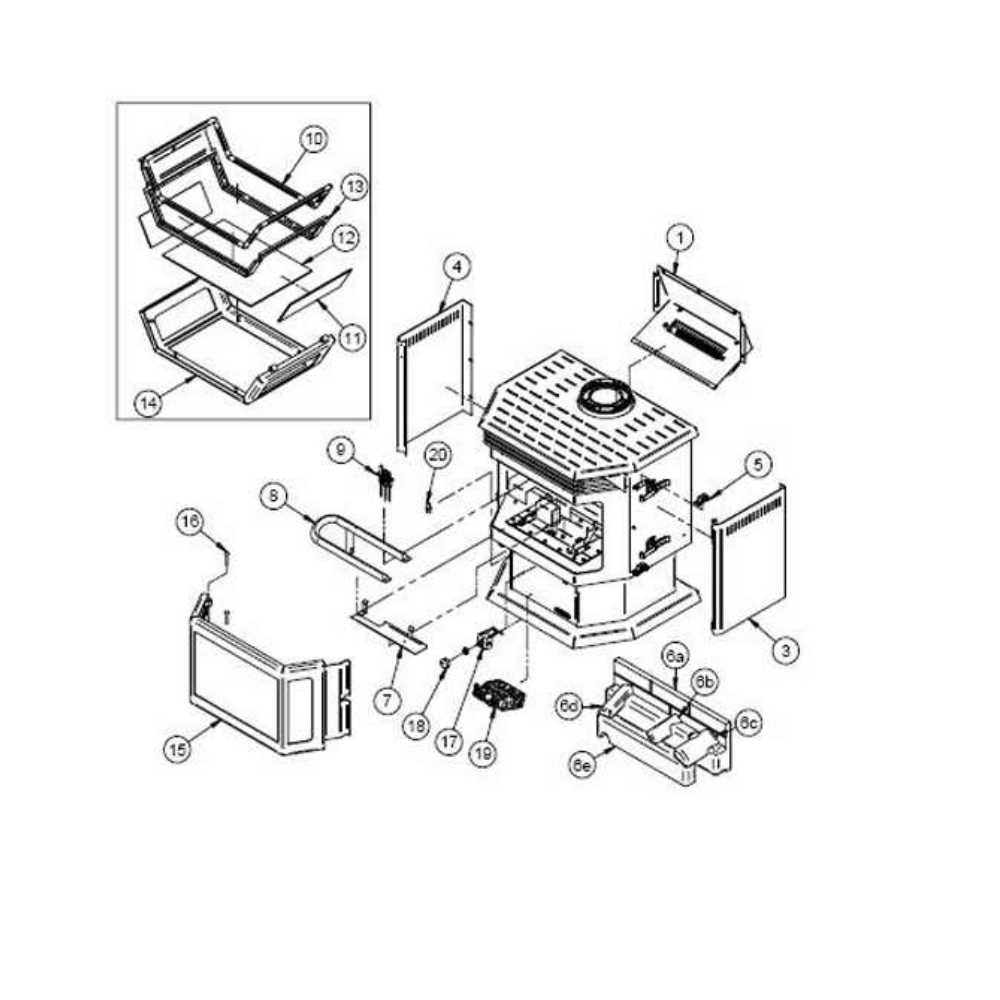
Exploring the intricate elements of heating devices unveils a world of engineering designed to optimize warmth and efficiency. Each segment plays a crucial role, contributing to the overall functionality and reliability of the system. Familiarity with these components enhances both maintenance practices and user experience.
Within this discussion, we will delve into the essential elements that form the backbone of these heating solutions. By examining their configuration and interconnections, we can better appreciate how they work together to generate and distribute heat effectively. This knowledge not only empowers users but also aids in troubleshooting common issues.
Whether you are a homeowner seeking to understand your system better or a professional looking to refine your expertise, grasping the layout and function of each component is indispensable. This insight will pave the way for informed decisions regarding installation, repair, and optimization of heating systems.
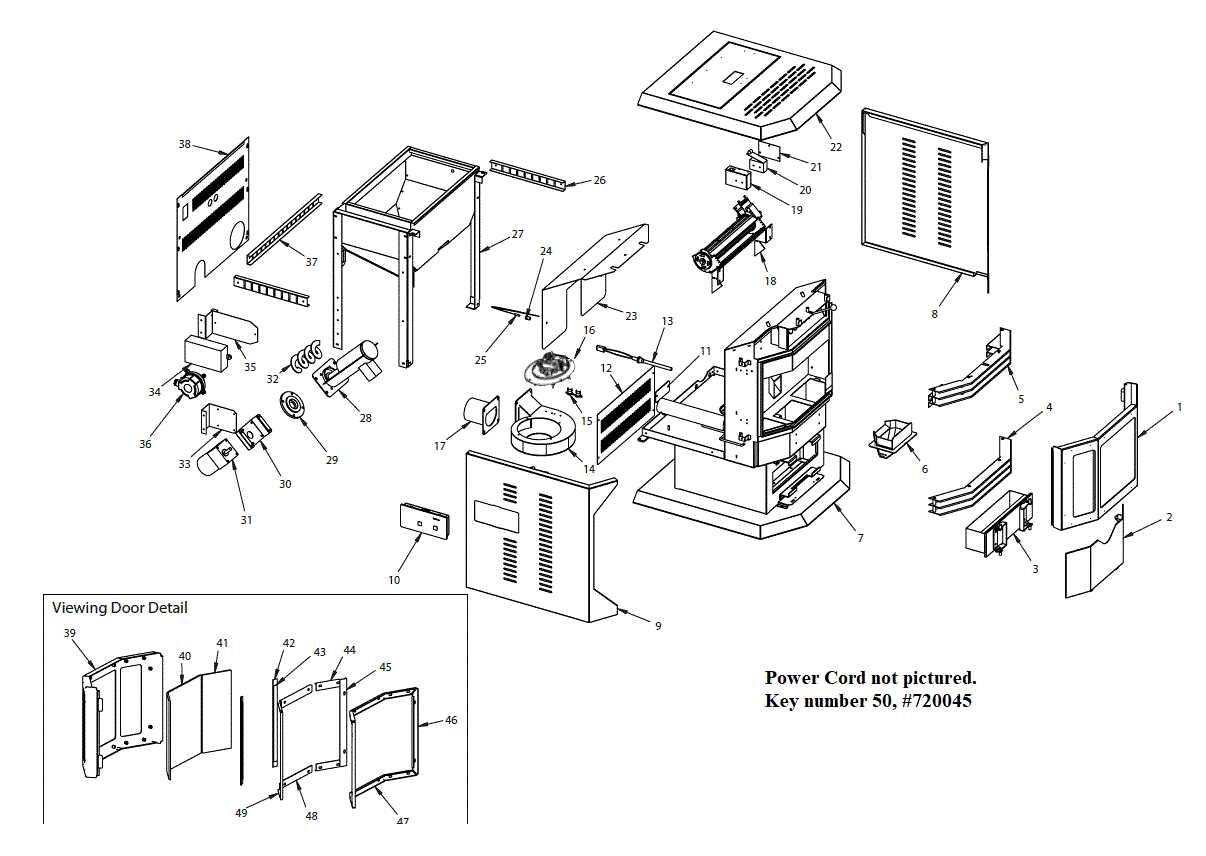
Understanding Wood Stove Components
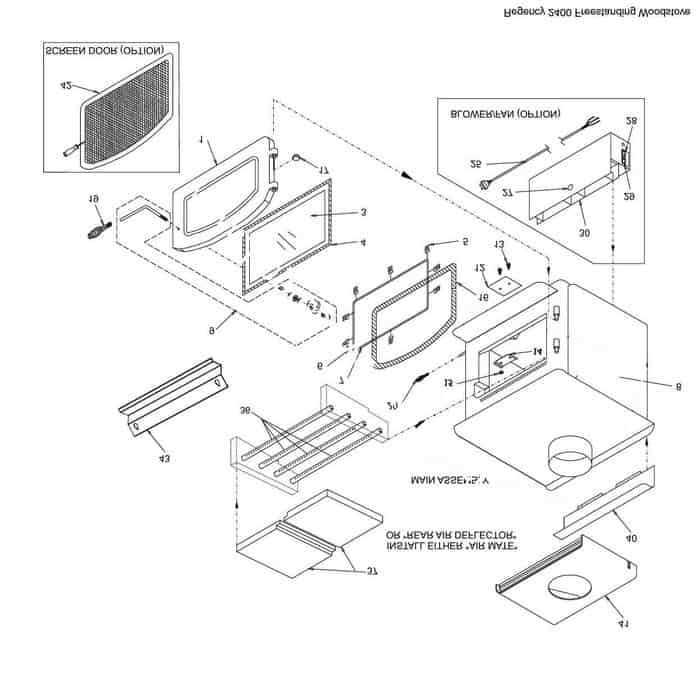
When it comes to efficient heating, understanding the key elements that make up a solid heating unit is essential. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring heat is generated, controlled, and safely distributed within the space. Gaining insight into the structure of these units helps in optimizing performance and prolonging their lifespan.
Core Functional Elements
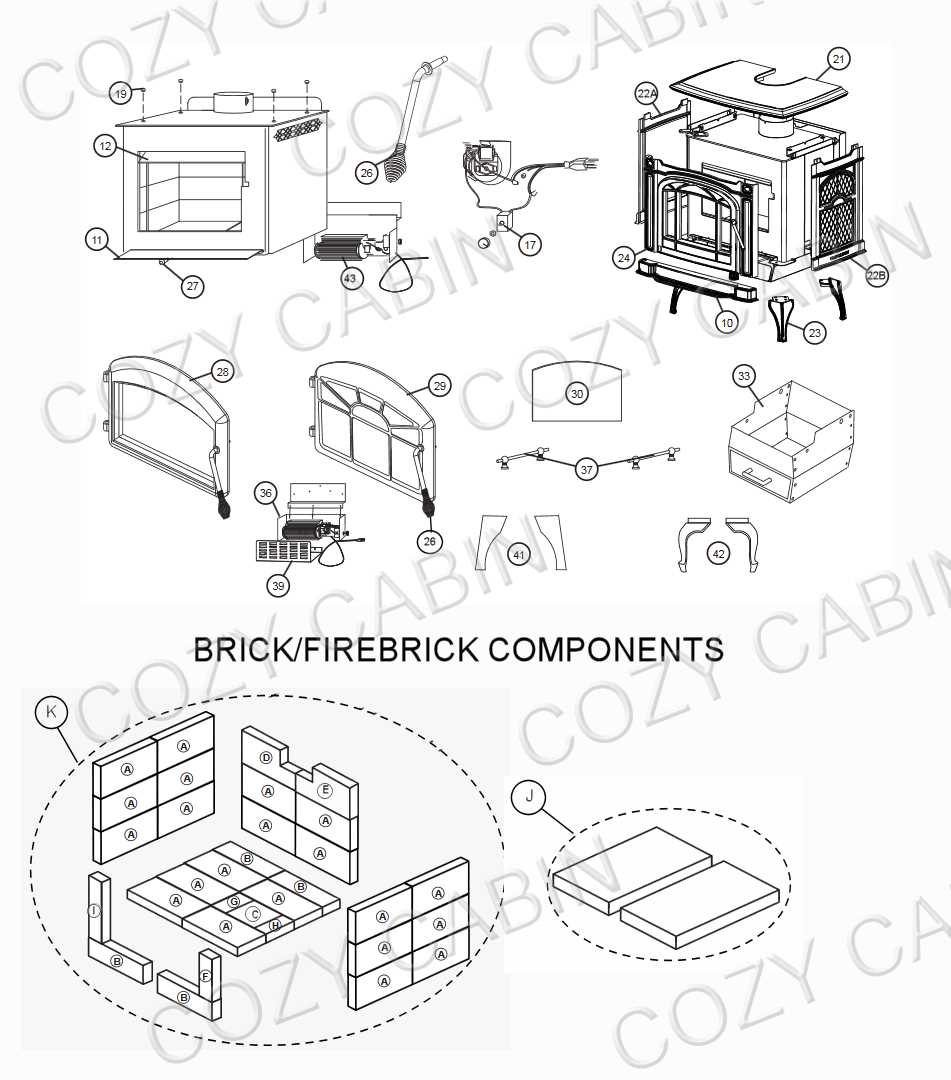
The primary function of such units revolves around managing heat production and airflow. The combustion chamber is where fuel is burned, while an array of vents, air intakes, and exhaust systems regulate oxygen levels and expel harmful gases. A well-maintained combustion area is crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste. The way heat circulates within the chamber also determines how evenly warmth is spread throughout the room.
Essential Supporting Features
Additional features enhance safety, usability, and control over the heating process. These include temperature regulation mechanisms, safety barriers, and viewing windows. The material and design of the structure also contribute to heat retention and durability. A solid frame, paired with effective insulation, ensures that the energy generated is preserved for as long as possible, reducing the need for constant fueling.
Maintenance is key to ensuring all elements function properly. Regular cleaning and checking of all components can prevent inefficiencies and prolong the lifespan of the entire system. Each element, no matter how small, contributes to the overall success of the unit, highlighting the importance of understanding their individual roles.
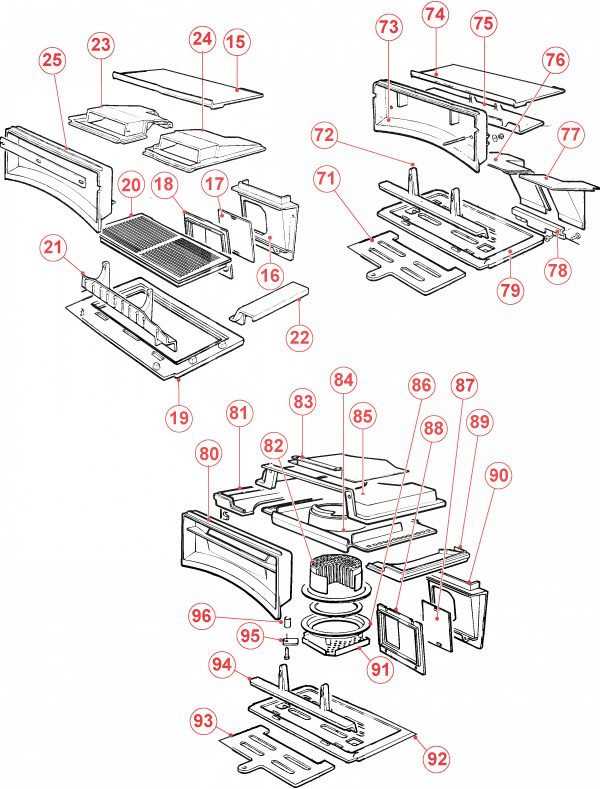
Essential Parts of a Wood Stove
Understanding the core components of a heating appliance is key to its efficient operation and longevity. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring that the system burns fuel safely, produces adequate heat, and operates smoothly. These units are typically composed of several critical sections that work together to create a functional and effective heating solution for homes and spaces.
Key Functional Elements
The main assembly includes structures that control airflow, manage heat output, and contain the combustion process. The system typically features a chamber for fuel, a mechanism for regulating air intake, and components designed to help remove excess gases and smoke. These functions help maintain a steady and controlled burn, ensuring the appliance runs safely and efficiently.
Safety and Maintenance Features
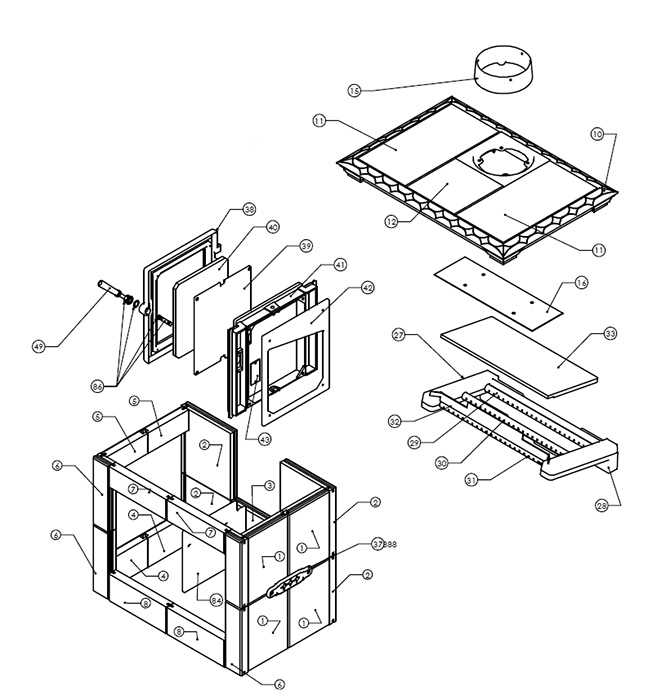
How Wood Stoves Generate Heat
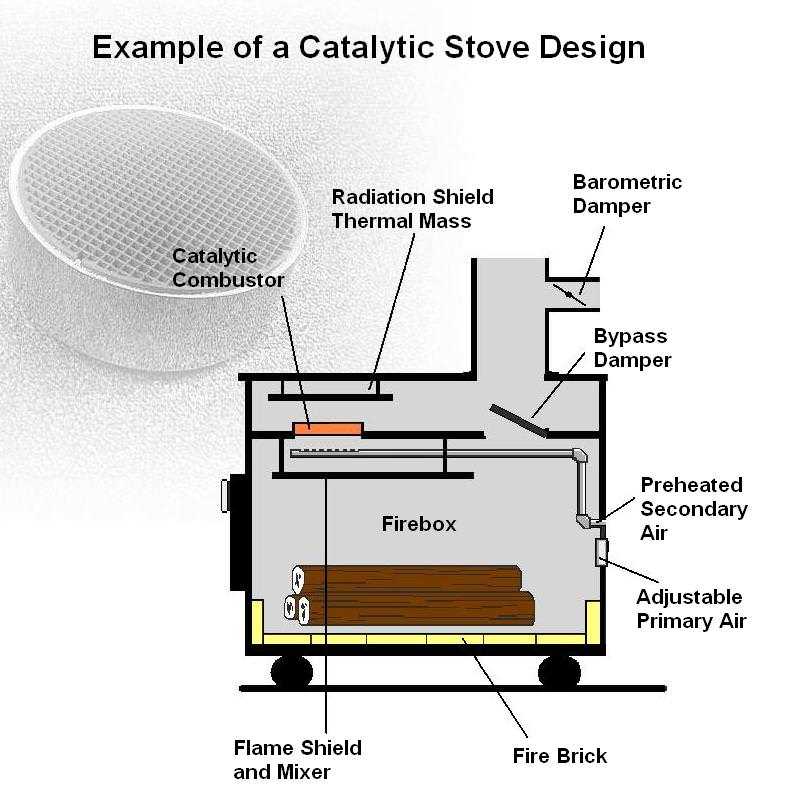
Fires have been used for centuries as a primary source of warmth, and the mechanism behind how they provide heat is both efficient and simple. By igniting natural fuel, a controlled combustion process occurs, producing both heat and light. The generated warmth is then transferred to the surrounding environment, increasing the temperature in the space. Several factors contribute to this process, including the quality of the fuel, the airflow, and the materials that absorb and radiate the heat produced.
Combustion Process
The fire within the combustion chamber ignites when the fuel is introduced to sufficient heat and oxygen. During combustion, the chemical reaction breaks down the fuel, releasing energy in the form of heat. The higher the temperature of the flames, the more efficient the reaction, ensuring that most of the energy is converted into warmth rather than wasted as smoke or unburned gases. The setup of the unit helps regulate this process to optimize energy output.
Heat Distribution
Once heat is generated, it needs to be spread throughout the area. This is done in several ways: through radiation, convection, and conduction. Radiant heat is emitted directly from the hot surfaces, warming nearby objects and people. Convection involves heated air rising and circulating, warming the surrounding space. Conductive surfaces absorb heat and transfer it to the air, ensuring consistent warmth throughout the room.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Radiation | Heat is emitted directly from hot surfaces, warming nearby objects and people. |
| Convection | Heated air rises and circulates, warming the surrounding space. |
| Conduction | Heat is absorbed by surfaces and transferred to the air for even warmth distribution. |
Common Materials Used in Construction
When designing and assembling heating devices, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in ensuring durability, performance, and safety. Various components are constructed from materials that not only meet the functional requirements but also contribute to the aesthetic appeal and heat efficiency of the unit. These materials are chosen based on their ability to withstand high temperatures, resist corrosion, and provide structural integrity over time.
Metal alloys are widely used due to their strength and heat resistance. Materials like cast iron and steel are particularly favored for their ability to endure extreme temperatures without warping or deteriorating. Cast iron, for instance, offers excellent heat retention properties, while steel provides flexibility and durability.
Refractory materials are essential for lining the interior surfaces of heating units. These substances, such as firebrick or ceramic tiles, are designed to resist intense heat and prevent thermal damage to the structural components. Their purpose is to protect sensitive parts from the direct effects of high temperatures and enhance the overall heat efficiency.
Insulation is another key consideration. Materials like mineral wool or ceramic fiber help retain heat within the system, improving energy efficiency while keeping the external surfaces cooler. Proper insulation is essential for reducing energy consumption and ensuring the safety of users by preventing heat-related accidents.
Maintenance Tips for Stove Longevity
Ensuring the long-lasting functionality of your heating appliance requires regular care and attention. Implementing a few straightforward practices can significantly enhance its performance and lifespan. This section outlines essential strategies to keep your unit in optimal condition.
Regular Cleaning
Accumulated debris can hinder efficiency and pose safety risks. Thoroughly clean the interior and exterior surfaces on a regular basis. Remove ash, soot, and any buildup that could obstruct airflow. Utilize appropriate tools and avoid harsh chemicals that may damage the finish.
Inspect and Replace Components
Periodic examination of essential components is crucial. Check gaskets, seals, and any mechanical elements for wear and tear. Replacing worn parts promptly can prevent larger issues and ensure smooth operation. Regular maintenance checks will help you identify potential problems before they escalate.
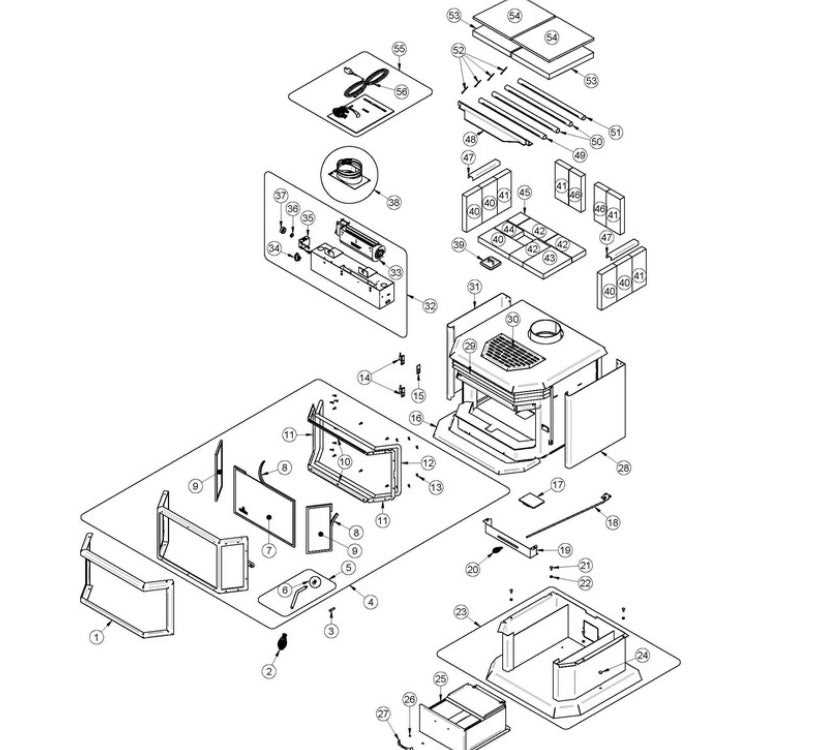
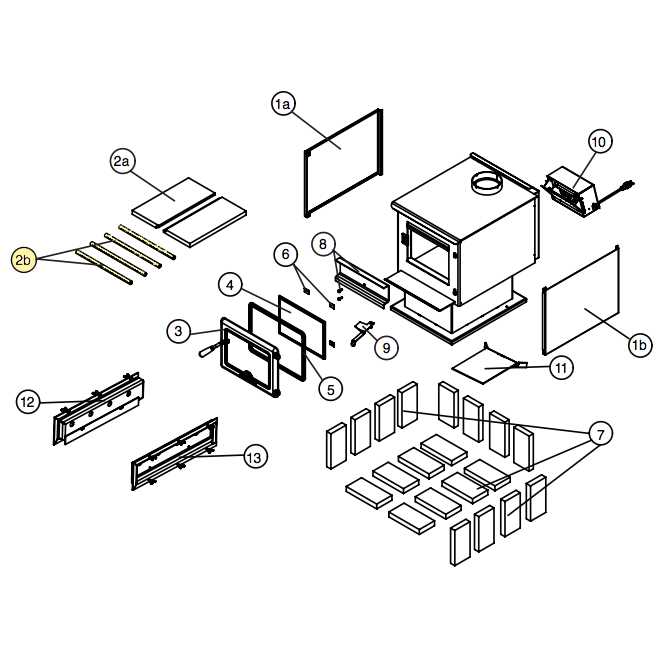
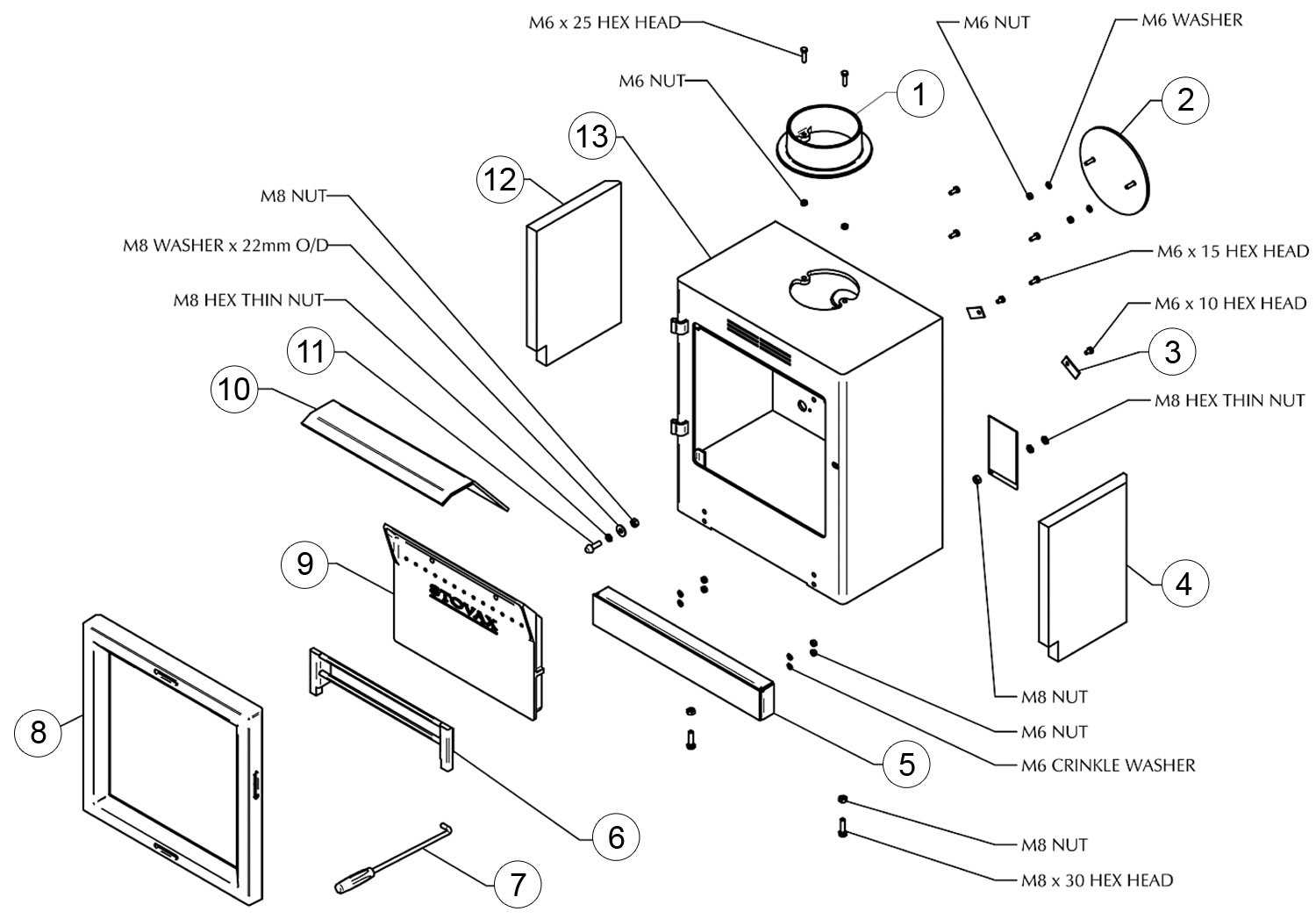
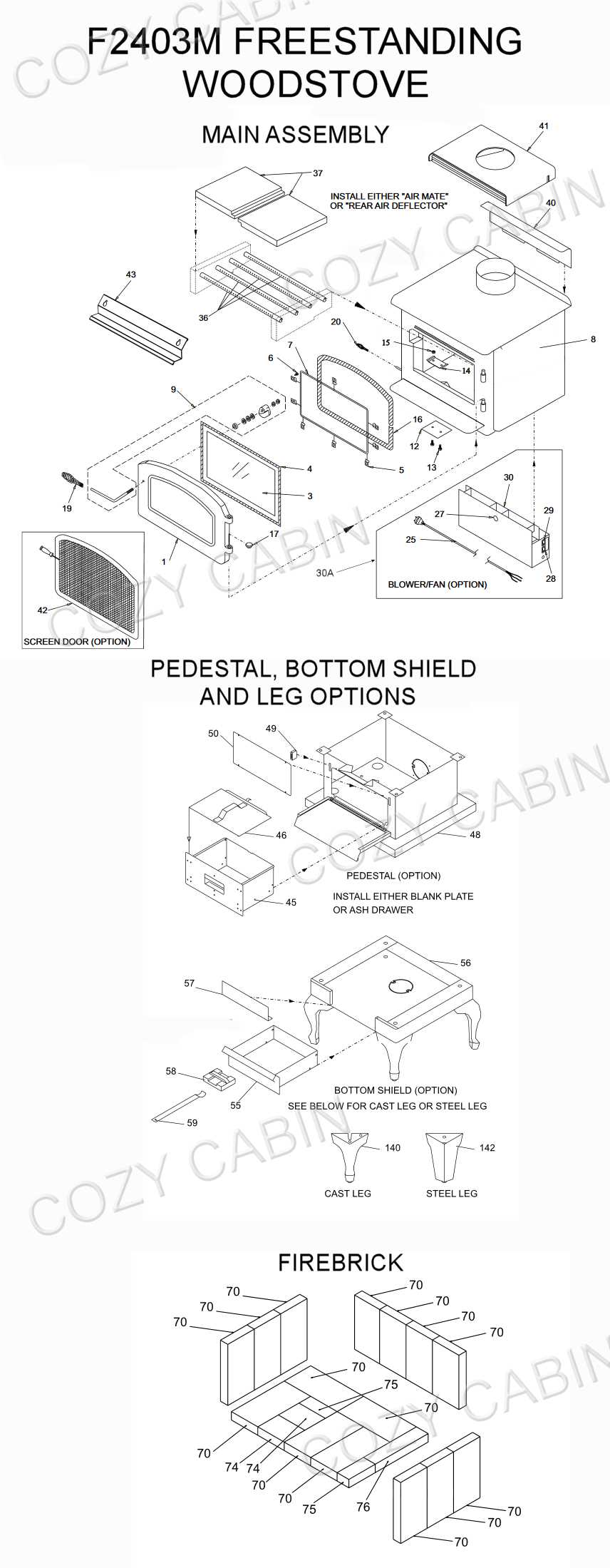
Identifying Parts in a Diagram
Understanding the components of a heating appliance is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. By recognizing each element within a schematic, users can ensure optimal functionality and safety.
- Burner Assembly: The section responsible for combustion.
- Chimney Connector: The conduit for exhaust gases.
- Heat Exchanger: The part that transfers heat to the surrounding area.
- Control Mechanism: The interface for adjusting temperature and airflow.
Familiarity with these components enhances the ability to address issues effectively.
Safety Features of Wood Stoves
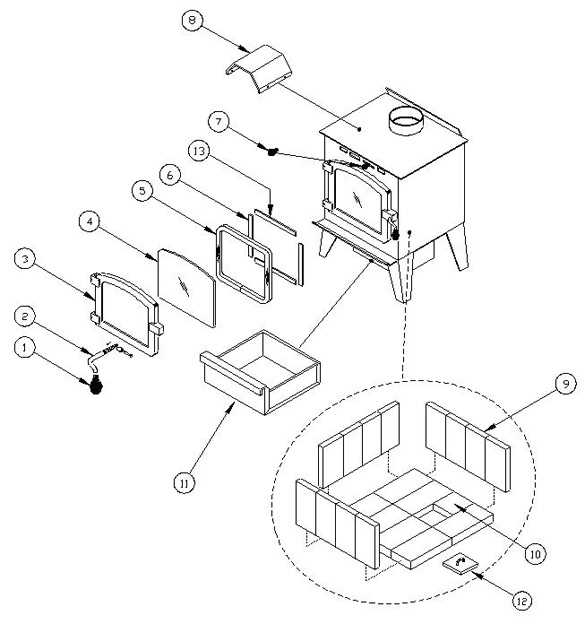
Ensuring the safe operation of heating devices is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring a comfortable and secure environment. Various design elements contribute to minimizing risks associated with fire and heat. Understanding and properly utilizing these features can significantly enhance safety in any space where these appliances are used.
- Heat Shields: Protective barriers placed around the appliance help to reduce the temperature of surrounding surfaces, preventing the risk of fire from nearby combustibles.
- Fireproof Materials: High-quality materials used in construction are resistant to high temperatures, ensuring that the unit can withstand intense heat without deteriorating or catching fire.
- Ventilation Systems: Proper exhaust systems ensure that harmful gases are safely directed out of the home, preventing the buildup of dangerous fumes like carbon monoxide.
- Automatic Shutoff Mechanisms: Some models come equipped with automatic shutoff features that kick in when the internal temperature exceeds a safe limit, reducing the risk of overheating.
- Thermostatic Control: Temperature regulation systems prevent overheating by maintaining the appliance at a consistent, safe level, ensuring efficient and controlled use of heat.
- Safety Doors and Glass: Secure, heat-resistant doors and thick glass panels prevent the accidental escape of sparks or embers, further minimizing the chances of igniting nearby objects.
- Non-slip Feet: Stable feet or bases ensure that the appliance remains securely in place, reducing the likelihood of tipping over and causing damage or injury.
Incorporating these safety features into the design of heating appliances can greatly reduce potential hazards, providing users with peace of mind while enjoying the warmth and comfort they offer.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Maintaining an efficient heating appliance can often present various challenges. Identifying and resolving these problems promptly can ensure optimal performance and safety. Below are some common issues users may encounter along with their respective solutions.
- Poor Heating Efficiency:
If the unit is not producing adequate warmth, check for:
- Blockages in the airflow.
- Insufficient fuel quality.
- Improper assembly or installation.
- Excessive Smoke:
Smoke escaping into the living space can be concerning. Possible causes include:
- Clogged chimney or flue.
- Incorrect fuel usage.
- Temperature imbalances inside the chamber.
- Unusual Noises:
Sounds that deviate from the norm may indicate issues. Consider checking for:
- Loose components.
- Debris interfering with moving parts.
- Wear and tear on mechanical elements.
- Overheating:
If the appliance becomes excessively hot, investigate:
- Malfunctioning thermostats.
- Improper ventilation.
- Fuel supply issues leading to overburning.
lessCopy code
Regular maintenance and timely interventions can greatly extend the lifespan of your appliance while ensuring safety and efficiency. If problems persist, consulting a professional may be necessary.
Upgrading Your Wood Stove System
Enhancing your heating system can significantly improve efficiency and comfort in your living space. By integrating modern technologies and optimizing components, you can create a more effective and sustainable solution for your home. Consider the following aspects when planning your upgrade.
Benefits of Upgrading
- Increased efficiency in heat distribution
- Reduced fuel consumption
- Improved air quality
- Enhanced safety features
Key Areas to Focus On
- Heating Element: Consider high-efficiency options.
- Insulation: Upgrade materials for better thermal retention.
- Ventilation: Implement modern systems to enhance airflow.
- Control Systems: Integrate smart technology for optimal performance.