When it comes to managing household wastewater, understanding how different elements of the underground setup work together is crucial for effective operation. Each piece plays a specific role in processing and filtering waste, ensuring the system functions efficiently and reduces environmental impact. By recognizing the significance of each component, you can better maintain the entire setup and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Key elements within this structure collaborate to separate solids from liquids, allowing treated water to be safely absorbed into the ground. Regular maintenance and timely repairs of these integral components can significantly extend the life of the installation, making it more sustainable over time. A clear grasp of how these elements interact will not only enhance the system’s efficiency but also help prevent potential issues before they become major problems.
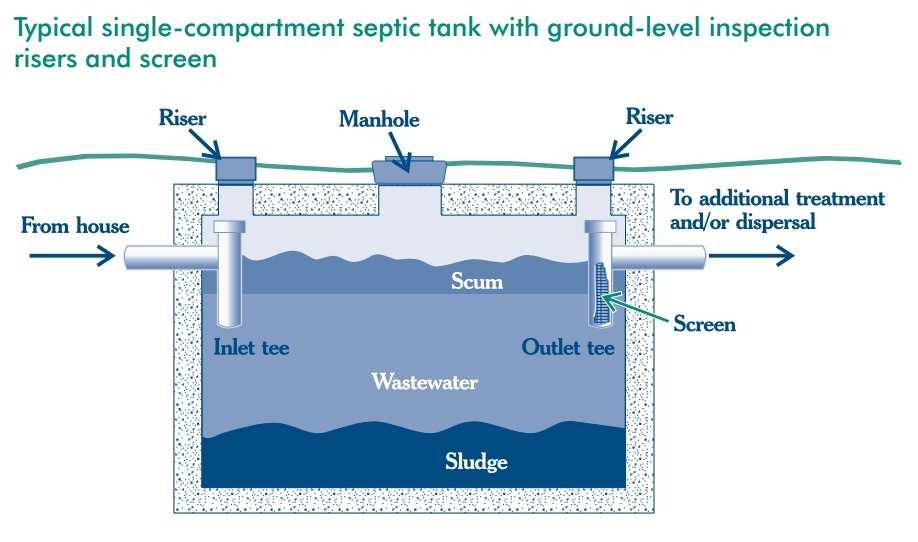
Septic Tank Parts Diagram
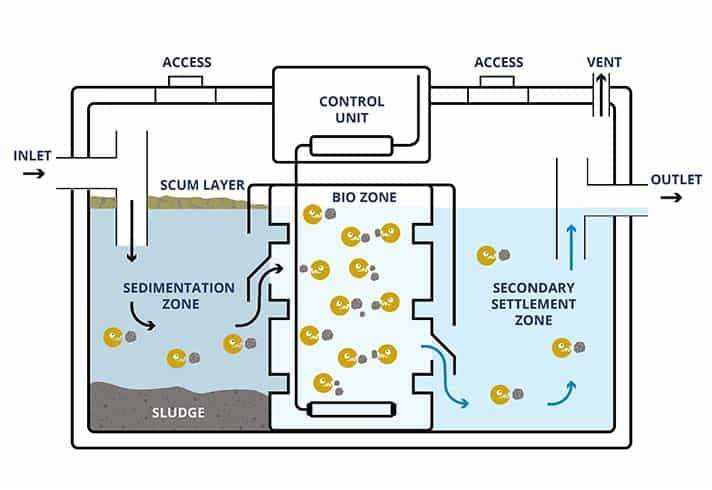
Understanding the components of an underground wastewater treatment system is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. This system features various elements that work together to treat and distribute waste efficiently. Each part plays a unique role in the process, ensuring the effective breakdown of materials and safe disposal of liquids.
Main Elements of the System
- Inlet Pipe: This pipe allows wastewater to enter the main chamber from the household, guiding the flow toward the treatment process.
- Main Chamber: The initial compartment where solids settle and begin breaking down through natural processes.
- Outlet Pipe: Directs treated water from the system into the soil absorption area, allowing for further filtration.
- Distribution Box: Balances the flow of treated liquid to ensure even distribution across the drainage area.
- Drain Field: A series of trenches or beds that allow liquids to seep into the ground, completing the treatment cycle.
Additional Features
- Access Riser: Provides easy access to the system for maintenance and inspections, often covered with a secure lid.
- Baffles or T-shaped Outlets: Prevent solids from exiting the main chamber, ensuring only liquids move to the next stage.
- Pumping Mechanism: Required in some
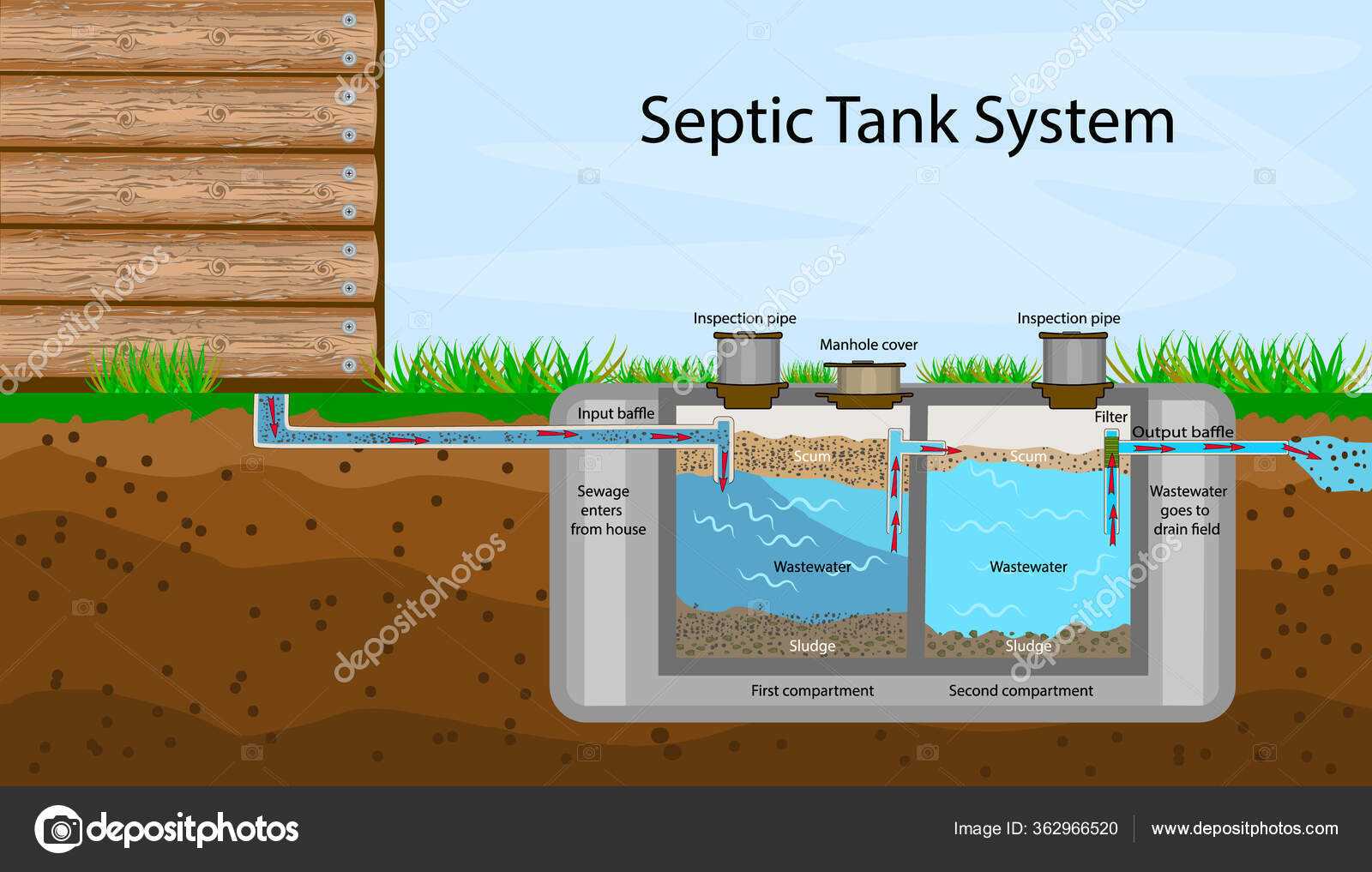
Understanding the Septic System Layout
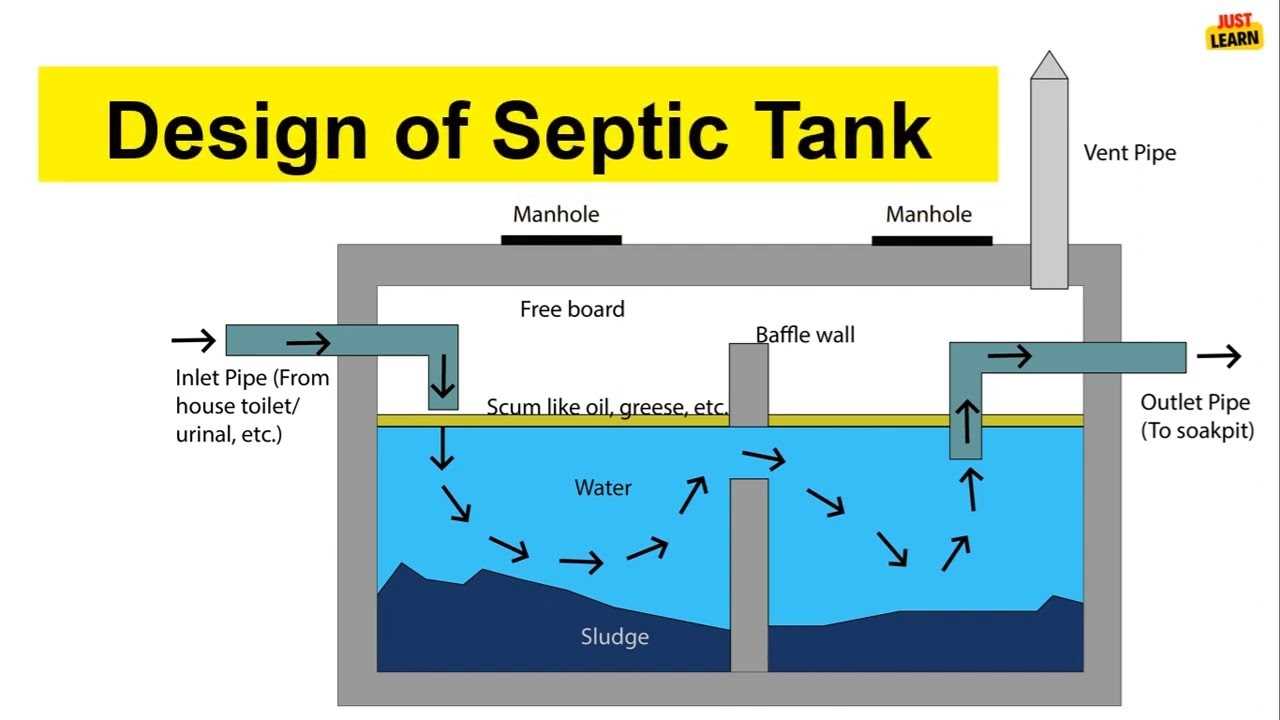
Grasping the overall layout of a wastewater management system is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. The system consists of various components working together to process and treat wastewater efficiently. By comprehending how these elements are interconnected, homeowners can better manage their system’s health and longevity.
The structure typically includes separate areas for waste collection, initial treatment, and further filtration before returning clean water to the environment. Each section plays a distinct role, with specific features that facilitate the movement and treatment of waste. Understanding these features will help in identifying potential problems and ensuring proper function.
Component Function Inlet Pipe Transfers wastewater from the household to the initial collection area. Treatment Chamber Allows solid waste to settle while lighter materials float, aiding in separation. Outlet Pipe Directs treated liquid towards the filtration zone for further processing. Drainage Field Disperses processed liquid into the soil, where natural filtration occurs. Key Components of a Septic Tank

The functioning of an underground wastewater system relies on various elements working together to process and treat the outflow effectively. Understanding these essential components can help ensure proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Main Chamber: The primary area where waste materials settle, allowing for the separation of solids from liquids.
- Inlet Pipe: Directs the incoming flow of wastewater into the system, ensuring an even distribution.
- Outlet Pipe: Responsible for guiding the treated liquid out of the system into the drainage field.
- Access Ports: Openings that provide entry for inspection, pumping, and maintenance activities.
- Distribution Box: Ensures that the liquid waste is evenly distributed across the drain field, promoting efficient absorption.
- Vent Pipe: Allows gases to escape, helping to maintain a balanced internal pressure.
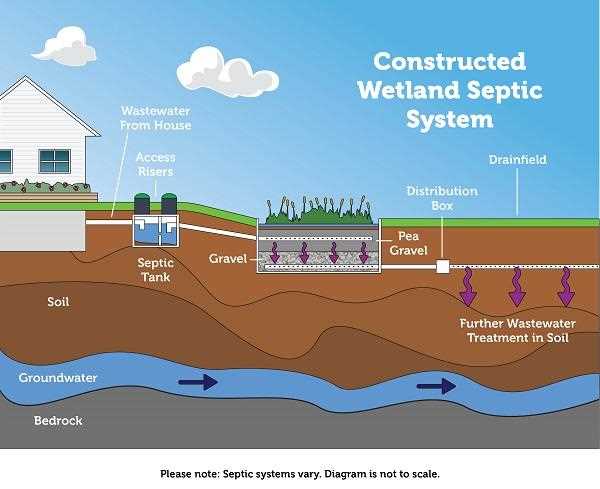
How the Drain Field Works
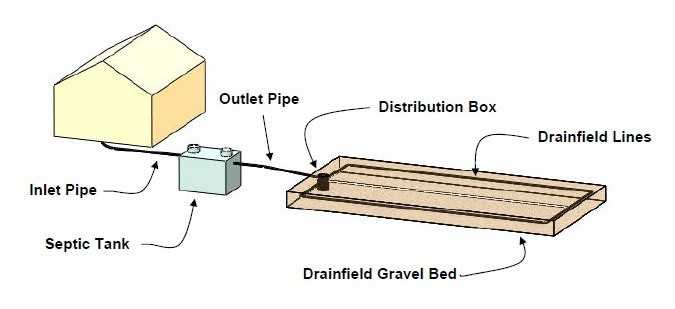
The drain field plays a crucial role in managing wastewater by allowing it to disperse and filter through the soil. This underground system ensures that liquid flows away efficiently, reducing the risk of contamination. It serves as a natural filter, where organic matter and impurities are gradually broken down and absorbed by the surrounding environment.
Water from the system is distributed through a network of pipes, releasing it into the ground at a controlled rate. As it passes through layers of gravel and soil, harmful substances are removed, making the water safe as it continues to travel further into the earth. Proper functioning of this process is essential for maintaining the health of the surrounding area.
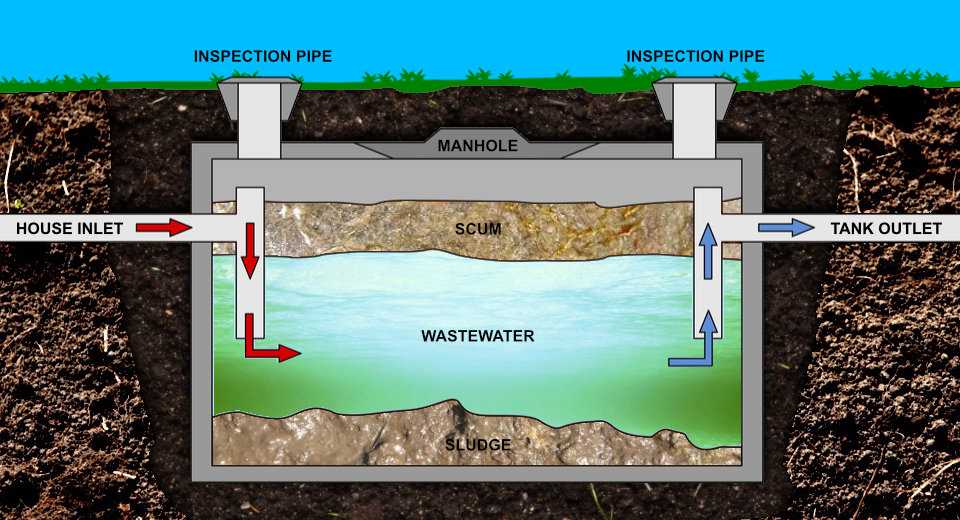
Septic Tank Inlet and Outlet Explained
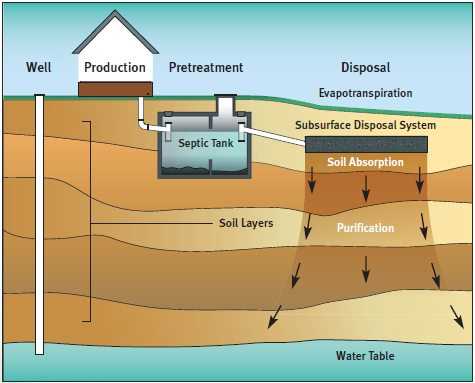
The entry and exit points play a crucial role in managing wastewater flow within the system. These components ensure that waste materials are directed properly, promoting efficient separation of liquids and solids. Understanding how these points function is key to maintaining an effective setup for treating household wastewater.
How the Entry Point Works
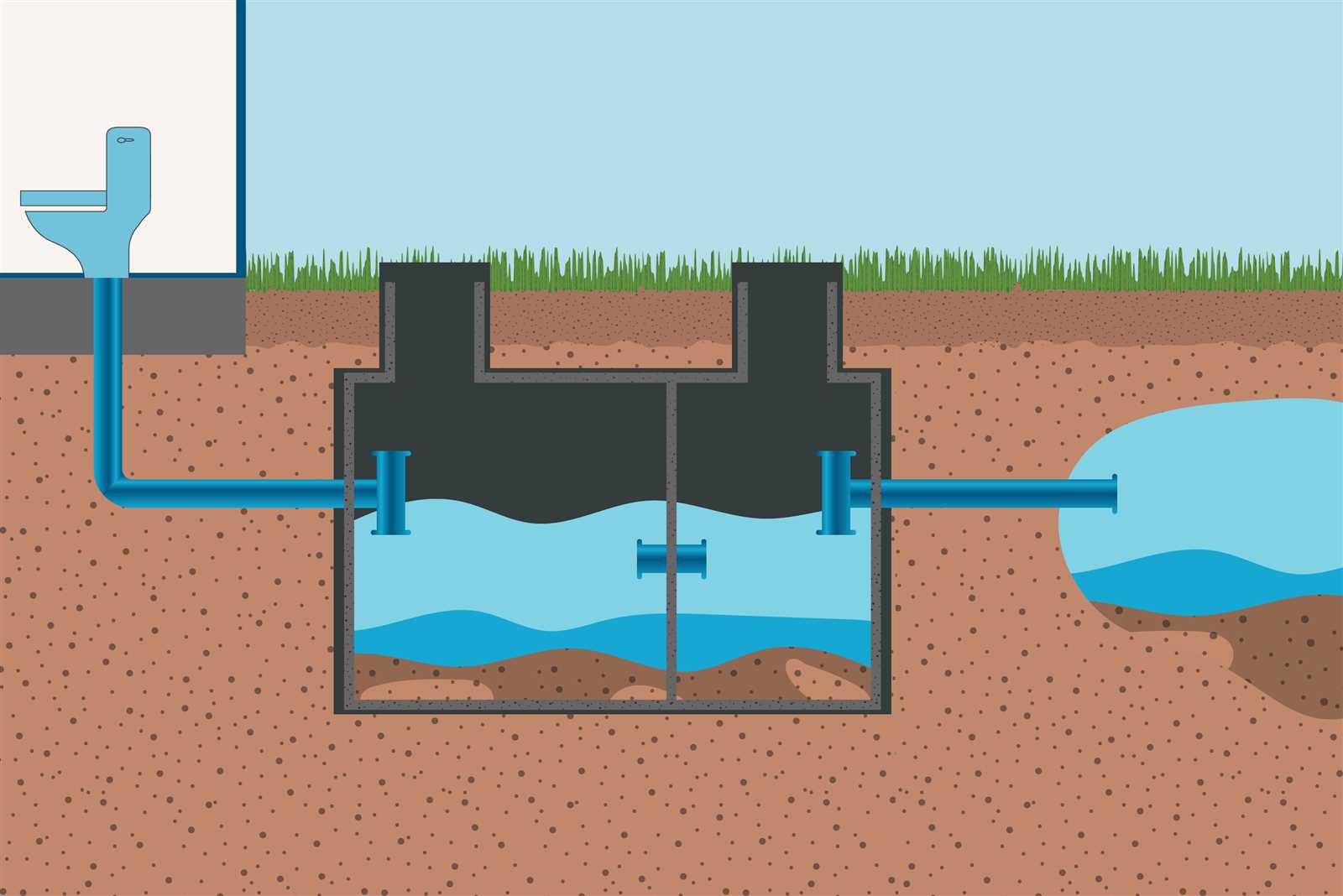
The entry section allows wastewater to flow into the system. It directs incoming liquid to minimize disturbance, helping the system start the natural process of separating solids from liquids. This point is typically designed to reduce turbulence, ensuring a smoother process within the main chamber.
The Role of the Exit Point
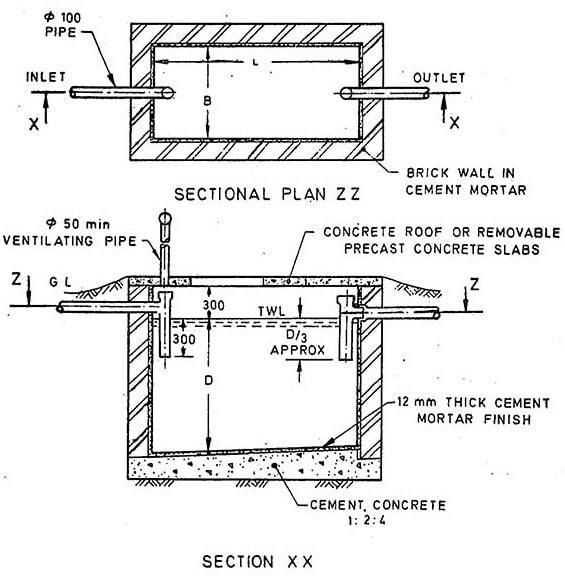
The exit section is essential for allowing treated liquid to leave the system. It ensures that only the clearer liquid, after settling, flows out, while heavier materials remain. This outflow is often connected to a drain field where further natural treatment occurs.
- The entry reduces turbulence to aid separation.
- The exit directs clearer water out for further treatment.
- Both points are crucial for proper flow and efficiency.
Role of Baffles in the System
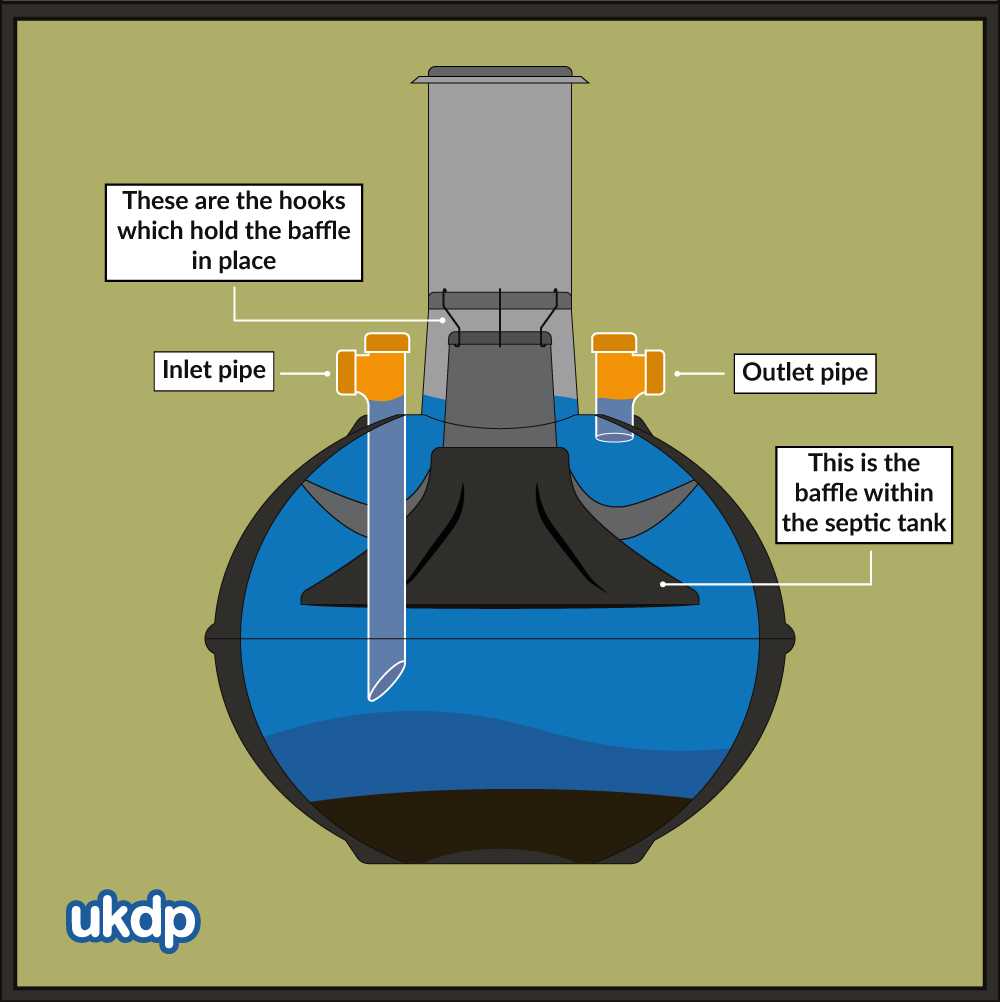
Baffles play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency of wastewater management systems. By directing the flow of water and solids, they help ensure proper separation of materials, which is essential for the overall functioning of the unit. Their placement within the system aids in preventing the rapid movement of solids, allowing for a smoother processing of waste.
How Baffles Improve Flow Control
Installed at strategic points, baffles help to regulate the internal flow dynamics. They slow down incoming wastewater, ensuring that heavier particles settle, while lighter materials are kept from exiting too quickly. This flow control minimizes the risk of blockages and extends the lifespan of the system.
Enhancing System Performance with Proper Baffle Design
The design and positioning of baffles can significantly impact the performance of the wastewater unit. Properly placed baffles create an optimal environment for breaking down waste, enhancing the separation process, and ensuring that the system operates more efficiently. Choosing the right design can lead to reduced
Piping Configuration for Septic Systems
The arrangement of the pipes plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient wastewater management in these installations. A well-designed network allows for the proper flow and distribution of water throughout the system, minimizing blockages and promoting effective treatment. It is important to create a layout that balances accessibility and functionality, while accounting for the landscape and local regulations.
Inlet and Outlet Connections are essential components that guide the water into and out of the treatment area. The connections must be properly aligned to prevent backflow and ensure a steady flow. Typically, inlet lines are positioned at a higher elevation to facilitate gravity-based movement, while outlet pipes guide the treated water towards the drainage area or leach field.
Another critical aspect is the use of baffles or tees within the system to control the flow direction and velocity, which helps in separating solids from liquids more effectively. This setup prevents solid materials from escaping into downstream sections, maintaining the system’s overall efficiency.
Septic Tank Filters and Their Purpose
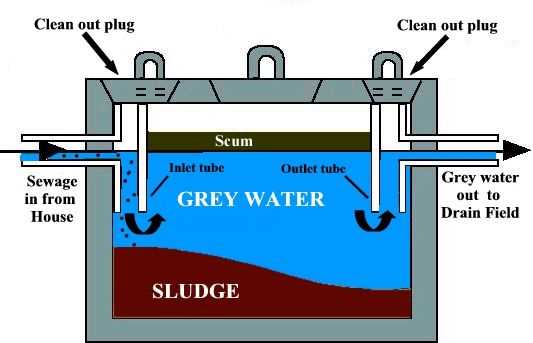
Filters play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of wastewater systems. They are designed to prevent solid waste and debris from entering further stages of the treatment process, ensuring a smoother and more effective operation. By capturing unwanted particles, filters help reduce the risk of blockages and other issues that can arise over time.
How Filters Work
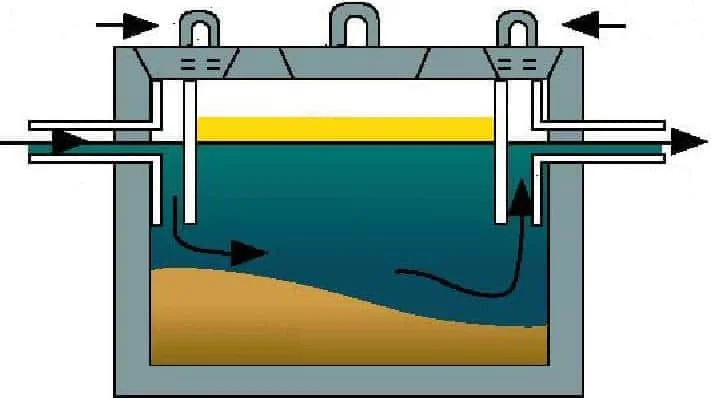
Placed at the outlet, these devices act as a barrier, allowing liquid to pass while retaining larger particles. This separation minimizes the accumulation of sludge in the system, making maintenance less frequent and more manageable. Over time, cleaning or replacing the filter is necessary to maintain optimal flow.
Benefits of Using Filters
- Reduces the frequency of pump-outs by trapping solids.
- Prevents clogging in drain fields or other areas downstream.
- Improves the overall efficiency of the waste management system.
By incorporating filters, homeowners can enhance the system’s reliability and extend its service life.
Understanding the Distribution Box Function
The distribution box plays a crucial role in managing wastewater flow, ensuring that it is evenly directed towards multiple drainage areas. This component serves as a gateway, where incoming liquid is diverted through various outlets, facilitating proper dispersal into the ground. Its efficient operation helps maintain a balanced load across all drainfields, preventing saturation in any one section.
Maintaining even flow is essential to avoid issues such as pooling or uneven distribution. The box’s internal design and positioning allow it to adjust to fluctuating water levels, adapting the flow accordingly. With this mechanism, each drainfield can function effectively, promoting a long-lasting system.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the distribution box ensure optimal performance. Over time, sediments or blockages can accumulate, which may disrupt the balanced flow. Addressing these problems early can help avoid costly repairs and extend the life of the entire drainage system.