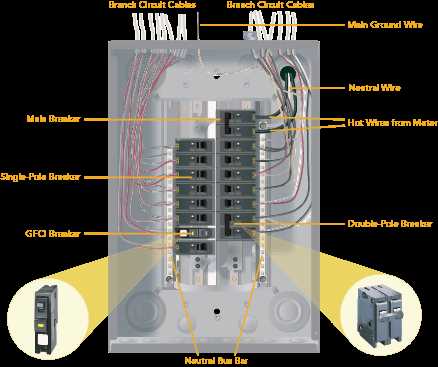
In modern infrastructure, the efficient management of electrical flow is crucial for safety and functionality. Each system comprises various essential elements, each serving a unique role in the overall operation.
Grasping the layout of these components is vital for both professionals and enthusiasts. By exploring how each segment interacts, one can appreciate the intricate design that ensures reliable energy distribution.
Furthermore, having a clear visualization of these structures allows individuals to identify potential issues and streamline maintenance processes. A well-organized approach ultimately leads to enhanced performance and safety.
Understanding Electrical Panel Basics
This section aims to provide a foundational understanding of the essential components involved in managing and distributing electrical power within a structure. By grasping these fundamentals, one can appreciate the role each element plays in ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Main Switch | Controls the entire power supply. |
| Circuit Breakers | Protect against overloads and short circuits. |
| Bus Bars | Distribute current to various circuits. |
| Grounding System | Enhances safety by preventing electrical shock. |
| Enclosure | Protects internal components from damage. |
Key Components of Electrical Panels
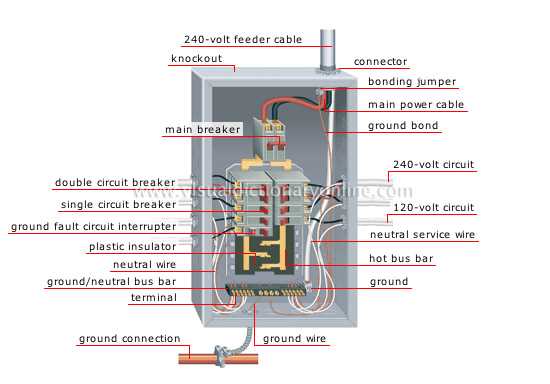
The essential elements within a distribution system play a crucial role in ensuring safety and functionality. Understanding these vital components can help in maintaining and troubleshooting these systems effectively.
Power Supply Units
At the heart of the system, power supply units convert incoming voltage to usable levels. Their reliability directly impacts the overall performance, making regular inspection and maintenance essential.
Protection Devices
Protection devices, such as circuit breakers and fuses, serve as the first line of defense against overloads and short circuits. These components prevent potential damage and ensure the safety of the entire system.
Functionality of Circuit Breakers Explained
In any system where power distribution occurs, it is crucial to have mechanisms that ensure safety and reliability. One of the key components that fulfill this role is a device designed to automatically interrupt the flow of current in case of anomalies. Understanding how this device operates is essential for maintaining the integrity of the overall system.
Protection Against Overcurrent
This device serves as a safeguard against excessive current, which can lead to overheating and potential hazards. When the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, the device trips, effectively halting the flow of electricity. This action prevents damage to wiring and connected appliances, ensuring a safe environment.
Resettable Functionality
Another significant feature of this component is its ability to be reset after a trip occurs. Unlike fuses that require replacement, this device can be restored to its operational state simply by flipping a switch. This convenience not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes downtime, making it a vital element in modern systems.
Importance of Bus Bars in Systems
Bus bars play a crucial role in the effective distribution of power within various systems. These conductive elements facilitate the efficient transfer of electricity, ensuring that energy reaches its intended destinations with minimal loss. Their significance cannot be overstated, as they contribute to both the reliability and safety of electrical operations.
Here are some key reasons why bus bars are vital:
- Efficient Energy Distribution: They allow for the seamless flow of current, reducing resistance and energy waste.
- Space Optimization: Their compact design helps in saving space within installations, making systems more organized.
- Enhanced Safety: By centralizing connections, they minimize the risk of short circuits and electrical failures.
- Ease of Maintenance: Their design simplifies inspection and maintenance, allowing for quicker troubleshooting and repairs.
- Scalability: Bus bars can be easily expanded or modified to accommodate future upgrades and changes in demand.
In summary, the integration of bus bars in various configurations leads to more efficient, safe, and manageable power distribution systems, highlighting their indispensable role in modern setups.
Role of Main Disconnect Switch
The main disconnect switch serves a critical function in controlling the flow of power within a system. It acts as a safety mechanism, allowing users to quickly isolate the supply during maintenance or emergencies. This essential component ensures that equipment can be safely accessed without the risk of electrical shock or damage.
Primarily, this switch provides a reliable means to cut off energy, enhancing both safety and operational efficiency. By enabling a clear disconnect point, it simplifies the process of troubleshooting and repairs.
Furthermore, its placement within the system design is vital, as it must be easily accessible yet strategically located to prevent accidental engagement. Understanding its role is crucial for anyone involved in the management and upkeep of electrical systems.
Identifying Wiring Terminal Connections
Understanding the various connection points within a system is crucial for safe and effective operation. Recognizing the different terminals allows for proper installation and troubleshooting, ensuring that all components function harmoniously together. Familiarity with these connections can significantly reduce the risk of errors during setup and maintenance.
Terminals are typically designed to accommodate specific wire types and sizes, making it essential to match them correctly. Below is a table highlighting common terminal types and their characteristics.
| Terminal Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Ring Terminal | Features a circular hole for secure fastening with a screw. | Battery connections, grounding. |
| Spade Terminal | Flat end that allows for easy attachment and removal. | Signal connections, component interfaces. |
| Butt Connector | Cylindrical shape used to join two wires together. | Wire splicing. |
| Push-On Terminal | Designed for quick and easy installation, no tools required. | Low-voltage applications. |
| Block Terminal | Multiple connection points within a single unit for organized wiring. | Distribution systems, modular setups. |
By recognizing these terminal types and their applications, users can ensure proper connectivity and enhance the overall reliability of their systems. Proper identification of these connections is fundamental for both new installations and ongoing maintenance tasks.
How to Read Electrical Diagrams
Understanding visual representations of circuitry is essential for anyone working with power systems. These illustrations convey complex information in a simplified manner, allowing individuals to interpret how components interact within a system. Familiarity with these representations can enhance troubleshooting and installation processes.
Start with Symbols: Every illustration includes a set of standardized symbols that represent various components. Familiarizing yourself with these symbols is crucial, as they form the foundation of interpretation. For instance, a circle might represent a light source, while a square could indicate a switch.
Follow the Flow: Pay attention to the direction of current flow. Lines connecting symbols often indicate paths through which energy travels. Understanding this flow can help identify potential issues or areas for modification within the system.
Read the Labels: Annotations and labels provide important context. They often include specifications such as voltage ratings, amperage, and other critical details. Make it a habit to review these annotations to gain a comprehensive understanding of the system’s capabilities.
Break it Down: If a representation seems overwhelming, break it into smaller sections. Analyze each component individually before connecting them back to the larger system. This methodical approach can make it easier to grasp complex configurations.
Practice Regularly: Like any skill, reading these representations improves with practice. Regular exposure to various configurations will enhance your ability to quickly understand and navigate these essential tools in the field.
Safety Features in Electrical Panels
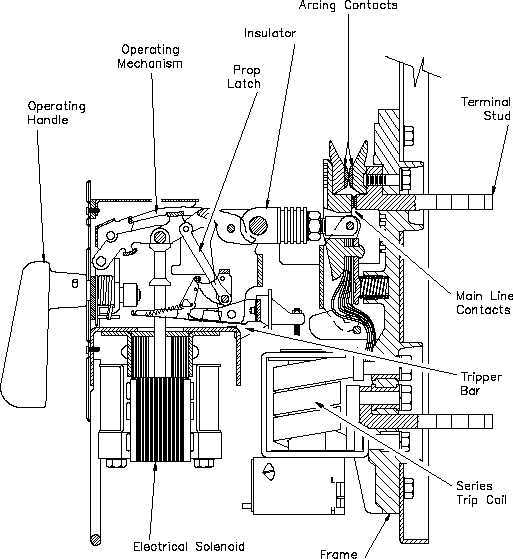
Ensuring the protection and reliability of any power distribution system is paramount. Various safety elements play a crucial role in preventing hazards and maintaining functionality in residential and commercial environments. These features not only safeguard users but also enhance the longevity of the entire system.
- Circuit Breakers: Automatically interrupt the flow of electricity during overloads or short circuits, minimizing the risk of fires.
- Fuses: Serve as sacrificial devices that melt under excessive current, cutting off the electrical supply and protecting the circuitry.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): Detect imbalances in electrical flow and shut off power to prevent shock hazards.
- Surge Protectors: Shield equipment from voltage spikes, ensuring operational safety and protecting valuable appliances.
- Lockable Disconnect Switches: Allow safe disconnection from the power source during maintenance, preventing accidental energization.
- Proper Enclosures: Keep internal components protected from dust, moisture, and unauthorized access, which could lead to dangerous situations.
Implementing these features not only enhances safety but also promotes a secure environment for all users, emphasizing the importance of regular maintenance and inspections to ensure optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips for Electrical Panels
Proper upkeep of your system components is essential for ensuring safety and functionality. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of these devices but also helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate into serious problems.
Here are some key maintenance suggestions to follow:
- Regular Inspection: Schedule routine checks to assess the condition of all components. Look for signs of wear, rust, or any unusual odors.
- Keep it Clean: Dust and debris can accumulate over time. Use a soft brush or a vacuum to remove dirt from surfaces without causing damage.
- Tighten Connections: Ensure all connections are secure. Loose connections can lead to overheating and pose safety risks.
- Check for Moisture: Humidity can lead to corrosion and short circuits. Inspect for leaks or dampness and address any issues promptly.
- Test Safety Features: Regularly test breakers and fuses to confirm they are functioning correctly. Replace any that show signs of failure.
Implementing these practices will help maintain the efficiency and safety of your system, providing peace of mind for users.