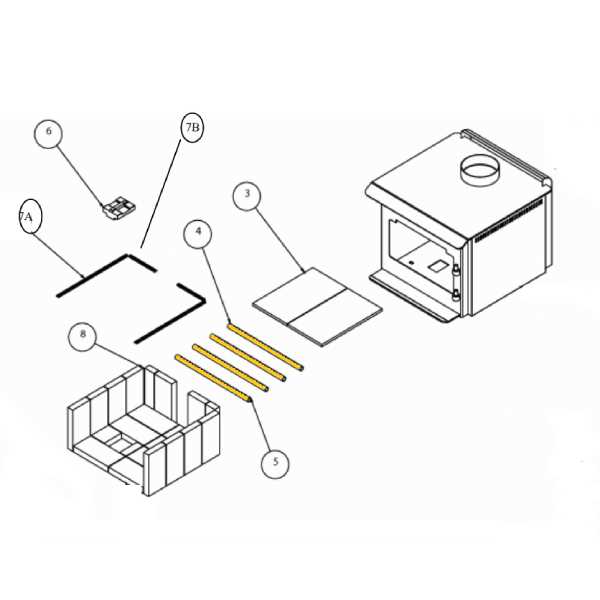
The efficiency and functionality of a heating device greatly depend on its individual elements and how they interact. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance, safety, and comfort. Familiarizing oneself with these elements can enhance user experience and promote better maintenance practices.
In exploring the intricate assembly of these heating solutions, one can appreciate the thoughtful design behind each section. From the outer casing to the internal mechanisms, understanding the layout and purpose of these units helps in troubleshooting and improving overall efficiency.
Knowledge of these essential features not only empowers users but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship involved in creating effective heating solutions. By recognizing how each component contributes to the device’s operation, one can make informed decisions regarding usage and care.
Understanding Wood Burning Stove Components
Exploring the essential elements of a heating appliance reveals the intricate relationships between its various components. Each part plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency, creating a harmonious system that converts fuel into warmth.
Key Elements and Their Functions
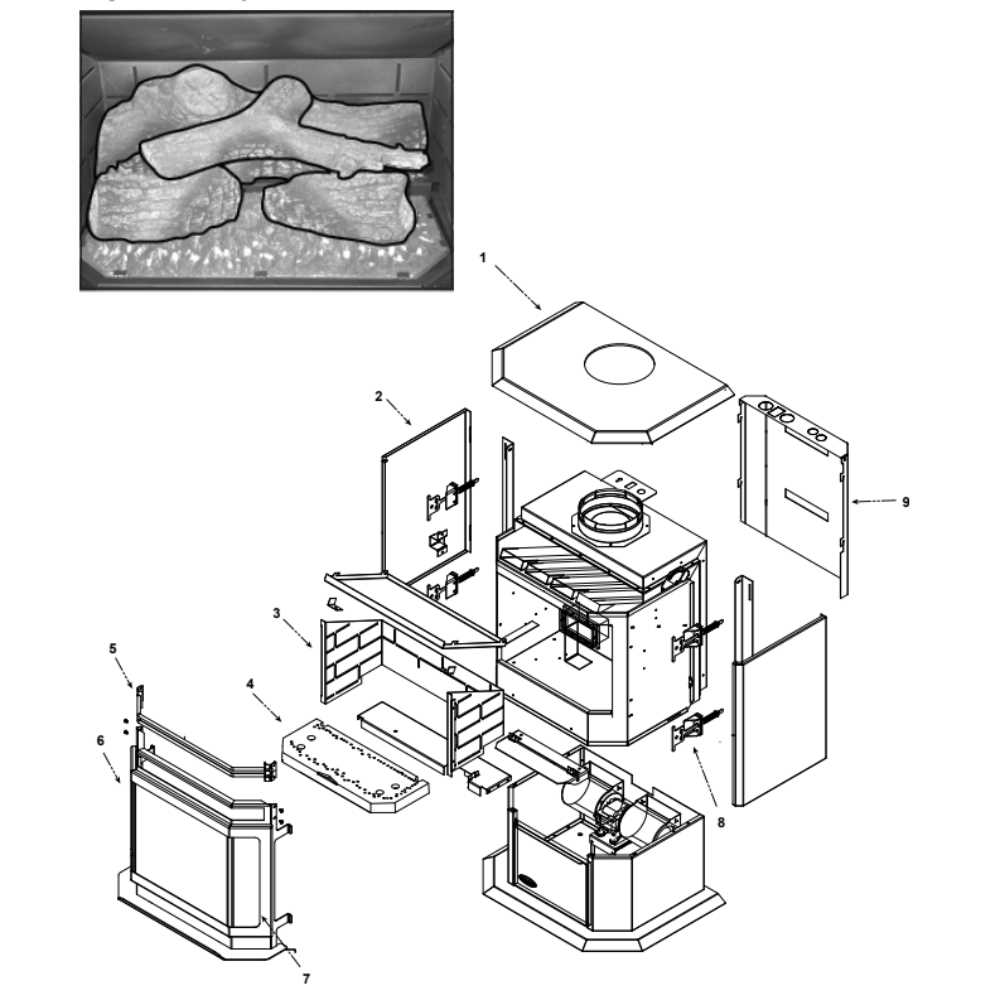
To truly grasp how this apparatus operates, it’s important to identify its major components. Each section serves a distinct purpose, contributing to the overall functionality and safety of the device.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Firebox | Where fuel is ignited and combustion occurs. |
| Flue | Allows smoke and gases to exit the unit safely. |
| Grate | Supports the fuel and allows airflow for combustion. |
| Ash Pan | Collects ash for easy disposal after use. |
Importance of Understanding Each Component
Comprehending these individual elements is vital for effective operation and maintenance. This knowledge empowers users to make informed decisions, ensuring their heating system remains efficient and safe over time.
Key Parts of a Wood Stove
Understanding the essential components of a heating appliance is crucial for both effective operation and maintenance. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring efficiency and safety, contributing to the overall performance of the unit. Familiarity with these features enhances the user experience and can lead to more informed choices when selecting or servicing the equipment.
- Firebox: This is where the fuel is ignited and burned. It is designed to withstand high temperatures while providing an efficient combustion process.
- Flue System: A vital component for ventilation, the flue allows smoke and gases to exit the unit safely. It helps maintain proper airflow for combustion.
- Grate: Positioned at the bottom of the combustion chamber, this feature holds the fuel and allows ash to fall through, promoting better airflow and efficiency.
- Door: This element provides access to the combustion chamber for loading fuel and cleaning. It is typically equipped with a sealing mechanism to prevent smoke leakage.
- Ash Pan: Located beneath the grate, this receptacle collects ash and residue, making it easier to clean and maintain the heating appliance.
- Heat Exchanger: Designed to maximize heat transfer, this component helps circulate warmth throughout the space by drawing cool air in and distributing heated air out.
- Control Mechanism: This allows users to adjust the air supply, controlling the burn rate and temperature within the chamber for optimal performance.
Each of these components works in harmony to create an efficient and effective heating solution. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements are essential for optimal functionality and longevity of the appliance.
How a Wood Stove Works
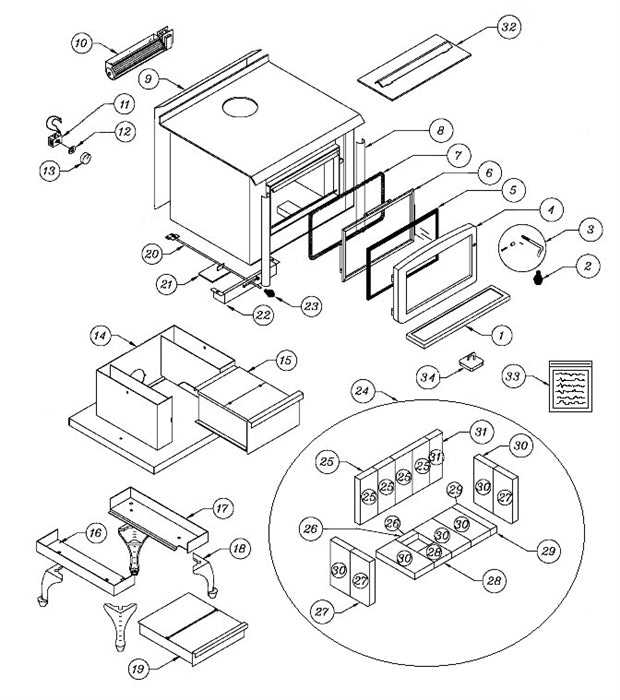
The process of generating heat through the combustion of organic materials is both efficient and intriguing. At the core of this mechanism lies a well-designed system that optimizes airflow and fuel consumption, resulting in a reliable source of warmth for various spaces.
Combustion Process
The initial step involves introducing fuel into the combustion chamber. As the material ignites, a chemical reaction occurs, releasing energy in the form of heat. This reaction not only raises the temperature within the enclosure but also generates gases that are essential for sustaining the fire. Effective management of these gases is crucial for maintaining optimal efficiency.
Heat Distribution
The generated warmth radiates outward, providing comfort and coziness to the surrounding area. Many systems incorporate fans or natural convection to enhance the circulation of heated air, ensuring that warmth reaches every corner. Additionally, insulated designs help retain heat for extended periods, allowing for continuous comfort even after the initial fuel source has been consumed.
Common Materials Used in Stoves
When it comes to heating appliances, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in their efficiency, durability, and overall performance. Different elements contribute to the structure, heat retention, and safety of these devices, making material selection an essential consideration for manufacturers and users alike.
Cast Iron is a popular choice due to its excellent heat retention and even distribution. This material can withstand high temperatures and is known for its longevity, making it a reliable option for those seeking a long-lasting solution.
Steel, particularly when used in its thicker forms, offers a lightweight yet robust alternative. It heats up quickly and provides good responsiveness, allowing for efficient temperature control during operation.
Firebrick is often utilized for its insulating properties, protecting the outer surfaces from excessive heat. This material can endure high temperatures and is designed to withstand the rigors of prolonged use, ensuring safety and performance.
Glass is increasingly used for doors and viewing panels, offering a modern aesthetic while allowing users to enjoy the visual aspect of the flame. Special tempered varieties are employed to withstand high temperatures without compromising safety.
Gaskets and Seals made from durable materials are essential for maintaining efficiency by preventing air leaks. Proper sealing ensures optimal combustion and enhances overall performance.
In conclusion, the combination of these materials not only affects the functionality of heating appliances but also influences their design and user experience. Understanding the properties of each element can aid in selecting the right device for specific needs.
Importance of Proper Ventilation
Effective airflow is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient environment in any space that involves heat generation. Adequate circulation of fresh air not only enhances the overall performance of heating appliances but also significantly reduces the risk of hazardous situations arising from poor air quality.
Without sufficient ventilation, harmful gases can accumulate, leading to potential health risks for occupants. This is particularly important in enclosed areas where combustion occurs. Proper airflow helps to:
- Ensure the complete combustion of fuels, reducing the emission of harmful byproducts.
- Prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas that can be deadly in high concentrations.
- Regulate humidity levels, preventing excess moisture that can lead to mold growth and structural damage.
- Improve comfort by maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the space.
Moreover, following local regulations and standards regarding ventilation can help avoid legal issues and enhance safety. It is advisable to regularly check and maintain ventilation systems to ensure they are functioning properly.
In summary, ensuring proper airflow is not just a technical requirement; it is essential for health, safety, and comfort in any environment utilizing heat sources.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular care is essential for ensuring the durability and efficient performance of your heating appliance. By following a few key practices, you can maximize its lifespan and maintain optimal functionality.
Routine Cleaning
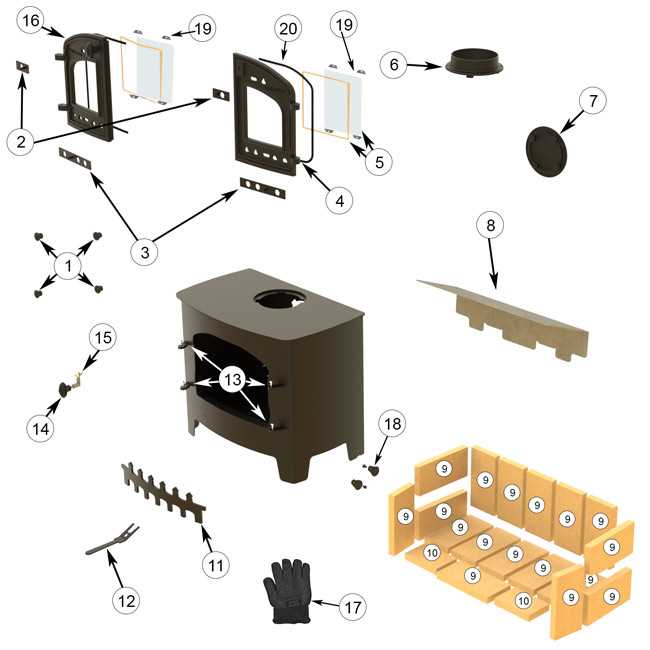
Consistent cleaning prevents the buildup of debris and enhances efficiency. Focus on removing ash and soot from internal surfaces and ensure proper airflow.
Inspections and Repairs
Conduct periodic assessments to identify wear and tear. Address any issues promptly to avoid more significant problems down the line.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean the interior | Weekly |
| Check seals and gaskets | Monthly |
| Inspect for cracks | Seasonally |
| Professional servicing | Annually |
Safety Features to Consider
When utilizing a heating appliance, ensuring optimal safety is paramount. It’s essential to be aware of the various protective mechanisms that enhance user security and mitigate risks associated with heat generation. A comprehensive understanding of these features can provide peace of mind while enjoying warmth during colder months.
First and foremost, a well-designed ventilation system is critical. Proper airflow prevents the accumulation of harmful gases, ensuring that the environment remains safe and breathable. Additionally, having an effective air intake and exhaust system significantly reduces the chances of overheating.
Another important feature is the presence of thermal insulation materials. These materials help in maintaining the appliance’s exterior temperature, minimizing the risk of accidental burns. Furthermore, look for models equipped with automatic shut-off mechanisms that activate in case of malfunction, providing an additional layer of protection.
Finally, consider safety barriers or screens that can prevent accidental contact with hot surfaces. Ultimately, choosing an appliance with robust safety features is vital for a secure and enjoyable experience.
Choosing the Right Stove Size
Selecting the appropriate size for your heating appliance is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency. A well-sized unit ensures effective warmth distribution, comfort, and energy conservation, while preventing issues such as overheating or inadequate heating.
When determining the ideal dimensions, consider the space you intend to heat. Assess the square footage of the area and account for factors like insulation, ceiling height, and the presence of large windows. A larger room may require a more substantial unit, whereas a smaller area can benefit from a compact design.
Heat output is another vital aspect to evaluate. Different models have varying heating capacities, typically measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units). Knowing the required BTUs for your specific space will help you select a model that meets your heating needs without wasting energy.
Furthermore, consider the layout of your space. An open floor plan may allow for a smaller unit, while closed-off areas might necessitate a larger appliance to ensure even heat distribution. Additionally, think about the placement of the appliance; positioning it in a central location can enhance its effectiveness.
Ultimately, the goal is to strike a balance between size and efficiency. Consult with experts or refer to manufacturer guidelines to find a suitable option tailored to your home’s requirements. Making the right choice will lead to a more comfortable and sustainable living environment.
Fuel Types for Wood Burning
Choosing the right sources of energy is essential for efficient operation and optimal heat output. Various materials can serve as effective fuel, each offering distinct characteristics and benefits.
- Hardwood: Known for its high density, hardwoods like oak and maple provide long-lasting heat and minimal smoke.
- Softwood: Species such as pine and fir ignite quickly and produce a lively flame, ideal for quick warmth.
- Pellets: Compressed biomass products deliver consistent energy with lower emissions and are often easier to handle.
- Logs: Traditional fuel source; selecting well-seasoned logs enhances efficiency and reduces creosote buildup.
Understanding the characteristics of these fuel types can ultimately enhance your heating experience and ensure a more sustainable approach.