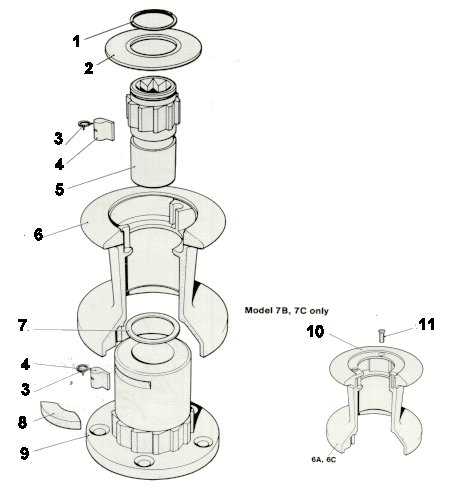
In this section, we delve into the intricate details of the foundational elements depicted in a visual representation. This graphic portrayal unveils the fundamental constituents that collectively contribute to the operational framework of a maritime device used for anchoring and hoisting.
Highlighted Features
Identified through a systematic breakdown, these highlighted attributes serve as pivotal components essential for seamless functionality. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall performance and reliability of the mechanical system designed for nautical applications.
Key Elements and Their Functions
This segment focuses on elucidating the primary attributes and operational functions associated with these critical constituents. Understanding their specific roles aids in comprehending the integrated mechanism that powers the marine apparatus.
Understanding the Components of a Windlass
The mechanism used for raising and lowering anchors is a critical part of maritime operations. This equipment comprises several essential elements that work together to facilitate smooth and efficient functionality. Understanding these components enhances both the operational knowledge and maintenance practices for users.
Motor: At the core of the system is a powerful motor, which drives the entire assembly. This component converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, providing the necessary force to operate the device.
Drum: The cylindrical structure is where the line is wound. It plays a crucial role in managing the length of the rope or chain as it is reeled in or let out, ensuring a secure hold.
Gearbox: This part connects the motor to the drum and allows for the adjustment of speed and torque. It ensures that the movement is efficient and appropriately scaled for the task at hand.
Control System: A user-friendly interface allows operators to engage or disengage the mechanism easily. This system often includes buttons or switches that enable precise control of the lifting process.
Remote Switch: For added convenience, many setups feature a remote switch that enables operation from a distance. This feature enhances safety, allowing users to control the equipment without being directly next to it.
Safety Features: Various built-in safeguards, such as circuit breakers and limit switches, prevent overloading and ensure safe operation. These components are vital for maintaining reliability and reducing the risk of accidents.
Each of these elements plays a significant role in the overall performance of the anchoring mechanism. By familiarizing oneself with their functions, users can ensure optimal operation and maintenance, leading to improved reliability and longevity.
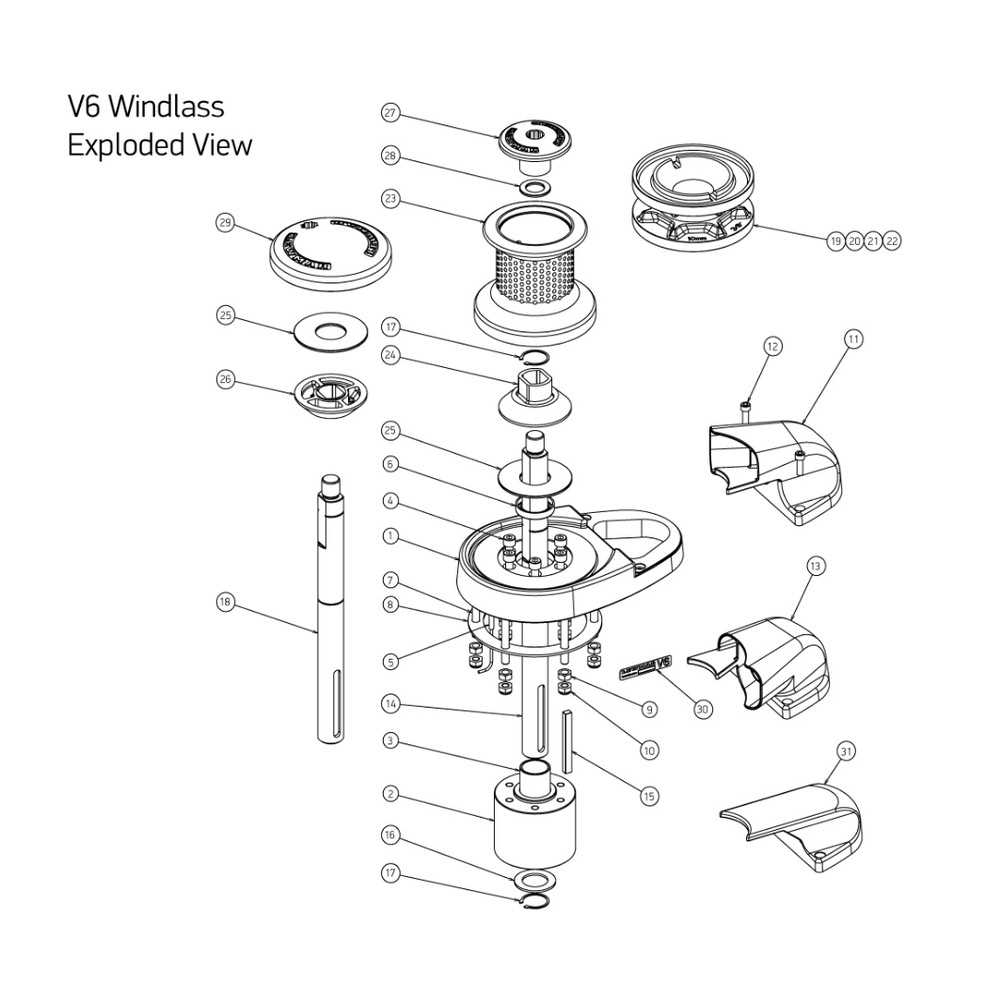
Key Mechanical Elements in Lewmar Systems
Understanding the essential mechanical components in marine systems is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. These systems are designed with precision engineering to handle the demanding conditions of marine environments. By focusing on specific elements, one can gain insights into their functions and how they contribute to the overall efficiency of the system.
The primary components include drive mechanisms, control units, and safety features, each playing a vital role in the operation and management of the equipment. A closer look at these elements reveals the intricate design and functionality that ensure seamless operation, providing peace of mind to users.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Drive Mechanism | The system responsible for translating electrical or hydraulic energy into mechanical motion, enabling movement and operation. |
| Control Unit | A user interface that allows operators to manage and monitor the system’s functions, ensuring precise control over its operations. |
| Safety Features | Components designed to prevent overloads and mechanical failures, enhancing reliability and protecting both the equipment and users. |
Exploring Electrical Connections for Lewmar Windlasses
Understanding the electrical linkages in anchoring systems is crucial for optimal performance and reliability. Proper wiring ensures that all components function smoothly, enhancing safety and efficiency during operation. This section delves into the essential connections, offering insights into best practices for installation and maintenance.
Key Components of the Electrical System
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary energy for operation.
- Control Switch: Regulates the activation of the device.
- Battery Connection: Links the energy source to the system.
- Circuit Breaker: Protects against overloads and faults.
Best Practices for Wiring Installation
- Ensure all connections are clean and secure to prevent short circuits.
- Use marine-grade wiring to withstand harsh conditions.
- Label wires clearly to facilitate troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Regularly inspect connections for corrosion and wear.
By adhering to these guidelines, users can ensure a reliable electrical framework for their anchoring equipment, contributing to a safer and more efficient boating experience.
Common Electrical Issues and Fixes
Electrical systems in marine applications can experience a variety of problems, leading to inefficiencies and potential failures. Understanding these issues is crucial for maintaining reliable operation. Here are some common electrical problems encountered and their respective solutions.
1. Insufficient Power Supply
A frequent issue arises when the power supply does not meet the demands of the equipment. This can result in inconsistent performance or complete shutdowns.
- Check battery connections for corrosion or looseness.
- Ensure batteries are fully charged and in good condition.
- Inspect wiring for any damage or wear that may impede power flow.
2. Faulty Connections
Loose or corroded connections can disrupt electrical flow, leading to intermittent functionality.
- Examine all connectors for signs of rust or corrosion.
- Tighten any loose connections to ensure a secure fit.
- Consider replacing any worn or damaged connectors to restore reliability.
By addressing these common electrical challenges, users can enhance the overall performance and longevity of their marine systems.
Maintenance Tips for Long-lasting Windlass Performance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your anchoring system, regular maintenance is essential. By implementing a few straightforward practices, you can enhance reliability and minimize the risk of failures during critical moments. This section offers valuable insights into maintaining your device effectively.
Begin by regularly inspecting the mechanisms for any signs of wear or damage. Pay attention to components such as gears, chains, and motor elements, ensuring they are functioning smoothly. Cleaning the unit thoroughly is crucial, as debris and salt buildup can lead to corrosion and hinder operation.
Lubrication is another vital aspect of maintenance. Applying the appropriate lubricant to moving parts helps reduce friction and wear, prolonging the lifespan of your equipment. Be mindful to use products specifically designed for marine applications, as they are formulated to withstand harsh environments.
Additionally, check all electrical connections and ensure they are secure. Corrosion can lead to poor performance or complete failure, so cleaning terminals and applying protective coatings can be beneficial. Regularly test the system to ensure it responds promptly and accurately to controls.
Lastly, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance recommendations. Adhering to these suggestions can provide tailored advice to keep your anchoring system in peak condition. Implementing these practices will not only enhance the efficiency of your equipment but also contribute to safer and more enjoyable experiences on the water.
Preventative Care to Reduce Wear
Maintaining the longevity of mechanical equipment is essential for optimal performance and reliability. Implementing regular upkeep practices can significantly minimize wear and tear, extending the lifespan of critical components. By adhering to a systematic maintenance routine, users can ensure that their systems operate smoothly and efficiently.
Key strategies include regular inspections, timely lubrication, and prompt repairs. These practices not only enhance functionality but also help prevent unexpected failures, reducing costly downtime. The following table outlines essential care tips to consider:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Weekly | Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to components. |
| Lubrication | Monthly | Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction. |
| Electrical System Check | Quarterly | Inspect wiring and connections for corrosion or wear to ensure proper functioning. |
| Component Testing | Annually | Conduct functional tests on critical parts to verify operational efficiency. |
| Cleaning | As Needed | Remove debris and contaminants that may interfere with operation. |
By integrating these preventative measures into routine practices, users can effectively reduce the risk of wear and ensure that their equipment remains in excellent working condition.
Choosing the Right Windlass Chain and Rope
When it comes to selecting the appropriate chain and rope for anchoring systems, various factors must be considered to ensure reliability and performance. The right combination of materials and specifications can greatly influence the effectiveness of your anchoring setup, enhancing safety and usability while minimizing wear and tear.
First, it’s essential to understand the specific requirements of your anchoring equipment, including load capacity and environmental conditions. The materials used in both chain and rope can vary significantly, offering different strengths, weights, and resistances to wear and corrosion. Below is a comparison of common options available in the market:
| Type | Material | Breaking Strength (lbs) | Corrosion Resistance | Weight (lbs per ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chain | Galvanized Steel | 2,500 | High | 0.5 |
| Chain | Stainless Steel | 2,800 | Very High | 0.4 |
| Rope | Polyester | 1,200 | Moderate | 0.2 |
| Rope | Dyneema | 3,000 | High | 0.1 |
Ultimately, selecting the right chain and rope involves evaluating your unique anchoring needs and the specific conditions you will encounter. Prioritizing quality and compatibility will lead to a safer and more effective anchoring experience.
Compatibility and Optimal Performance
Ensuring that all components of a marine anchoring system function seamlessly together is crucial for achieving peak efficiency. The harmony between various elements significantly influences the overall effectiveness and longevity of the equipment. Understanding compatibility among different units allows users to make informed decisions, enhancing both safety and performance.
Key Considerations for Compatibility
- Material Quality: Select components made from corrosion-resistant materials to withstand harsh marine environments.
- Load Capacity: Ensure that each part can handle the maximum load expected during operation.
- Power Requirements: Match the voltage and power specifications to guarantee proper function.
- Connection Types: Verify that all connections are compatible in terms of size and design for secure fittings.
Maintaining Optimal Functionality
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine checks to identify wear and tear early, preventing failures.
- Proper Installation: Follow manufacturer guidelines for installation to ensure all components work together effectively.
- Usage Monitoring: Keep an eye on performance metrics to detect any inconsistencies that may indicate compatibility issues.
- Upgrades and Replacements: When replacing parts, consider the latest models that offer improved compatibility and features.
Troubleshooting Windlass Operation Problems
When dealing with issues related to anchoring mechanisms, identifying the root cause of malfunction is essential for effective resolution. Various factors may contribute to operational failures, ranging from electrical malfunctions to mechanical wear. This section provides guidance on diagnosing and rectifying common issues encountered during operation.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Power Supply Problems:
- Check the battery voltage; ensure it is sufficiently charged.
- Inspect wiring connections for corrosion or loose contacts.
- Verify that the control switch is functioning properly.
- Mechanical Failures:
- Examine the gears and motor for signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure that the anchor line is free of tangles and obstructions.
- Lubricate moving parts as recommended to prevent friction issues.
Diagnostic Steps
- Start by testing the power source and electrical connections.
- Run the system to observe any unusual noises or behaviors.
- Document any discrepancies and follow up with targeted repairs.
By systematically addressing these areas, you can enhance the reliability and performance of your anchoring system, ensuring a smoother experience on the water.
Identifying and Resolving Common Failures
Understanding typical issues that can arise with marine anchoring systems is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and safety. Many users encounter malfunctions that can disrupt operations, often stemming from wear and tear, improper maintenance, or environmental factors. Recognizing these problems early can lead to timely interventions, ensuring seamless functionality and preventing further complications.
One common challenge is the inconsistent operation of the system, which may result from electrical faults or poor connections. Inspecting wiring for corrosion and ensuring secure connections can often resolve this issue. Additionally, it’s essential to check the power supply and control mechanisms to guarantee they are functioning correctly.
Another frequent problem is jamming, typically caused by debris or corrosion within the mechanism. Regularly cleaning the components and lubricating moving parts can help maintain smooth operation. If jamming persists, disassembling the unit for a thorough inspection may be necessary to identify blockages or damaged parts.
Overheating can also be a concern, often indicating that the motor is working harder than it should be. This may result from a heavy load or mechanical resistance. Ensuring that the load is appropriate and that all components are free of obstructions can help mitigate this issue.
Lastly, unusual noises during operation can signal potential problems. Grinding or clunking sounds often suggest misalignment or damaged parts. Observing these sounds closely and addressing them promptly can prevent more significant failures down the line.