In the world of classical music, the elegance of a certain stringed instrument captivates both players and listeners alike. Its unique structure contributes to its melodious sound, making it a staple in orchestras and solo performances. To fully appreciate its beauty, one must delve into the intricate elements that comprise this beloved instrument.
Each element serves a distinct purpose, influencing not only the instrument’s aesthetic appeal but also its acoustic properties. From the resonant body that amplifies sound to the finely crafted neck that supports precise finger placements, understanding these individual components enhances the overall appreciation of the craftsmanship involved.
Moreover, the interplay between these elements affects how the instrument responds to various techniques, allowing musicians to express a wide range of emotions through their playing. By exploring the fundamental features that make up this stringed marvel, enthusiasts can gain deeper insights into its functionality and artistry.
Understanding the Violin Diagram
This section explores a visual representation that combines data distribution and density. It offers insights into how information can be depicted in a way that highlights variations across multiple categories.
Key elements include:
- Distribution of data points
- Density estimation
- Comparison between groups
To fully grasp its utility, consider the following:
- Identify the central tendency and spread of the data.
- Observe the shape of the representation to infer patterns.
- Utilize it for effective comparisons across different datasets.
This method not only enhances data visualization but also aids in revealing underlying trends that might not be immediately apparent in traditional charts.
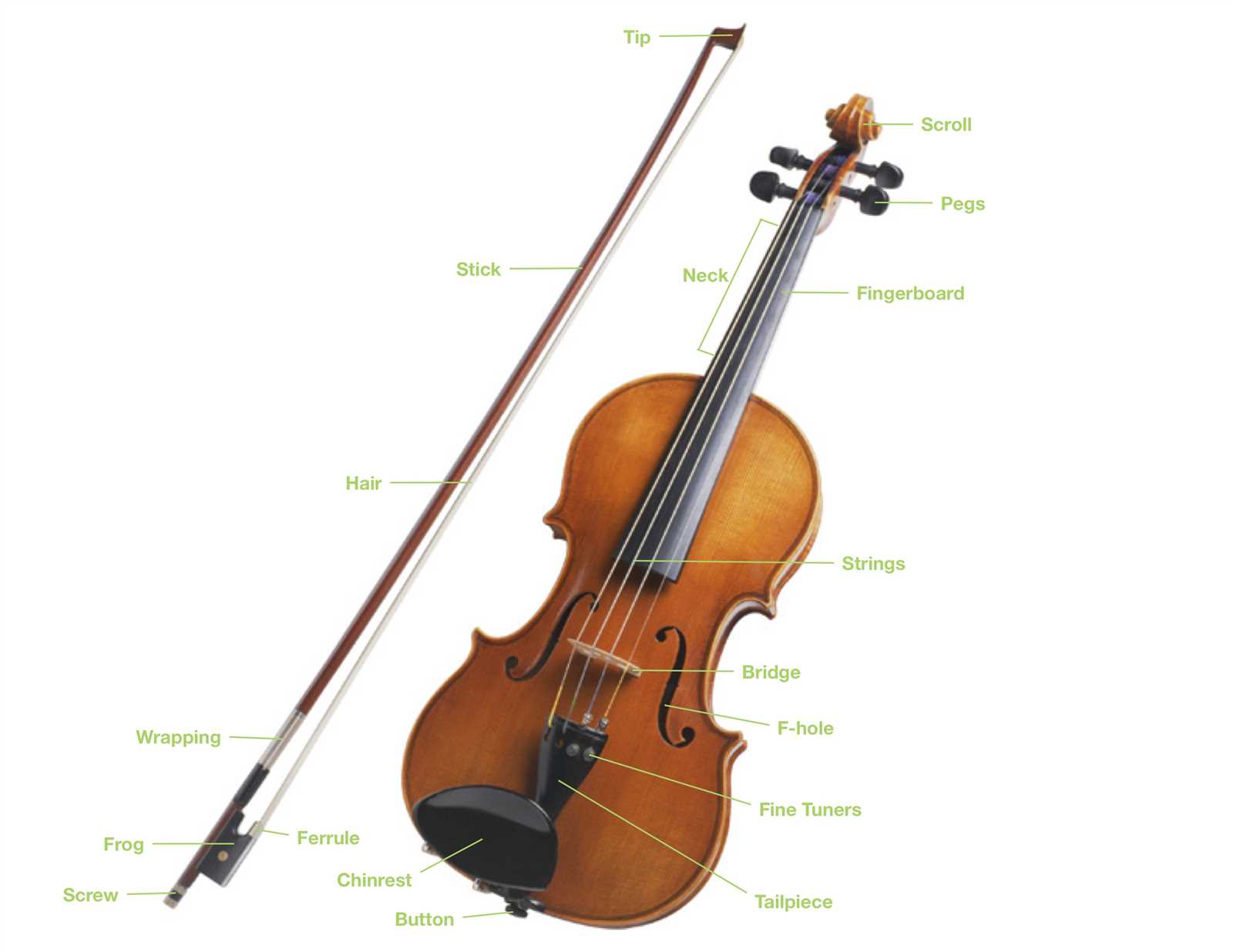
Core Components of Violin Diagram
The intricate design of this statistical representation serves to convey the distribution of data across various categories. Its multifaceted structure allows for a nuanced understanding of the underlying trends, showcasing essential features that highlight the shape and spread of the dataset. Each element plays a crucial role in delivering a comprehensive view of the information presented.
Key Elements
Understanding the fundamental elements is vital for interpreting this graphical form effectively. The components work together to illustrate the density and distribution of values, providing insights that might be overlooked in simpler plots.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Kernel Density Estimation | Offers a smoothed curve representing the distribution of data points. |
| Central Tendency Markers | Indicates measures like the mean or median to show typical values. |
| Interquartile Range | Highlights the spread of the central 50% of the data, indicating variability. |
| Outliers | Displays data points that fall outside the expected range, emphasizing anomalies. |
Visual Impact
The overall visual appeal of this representation enhances its interpretability. The blend of color and form not only attracts attention but also facilitates a deeper understanding of data distributions, allowing analysts to draw meaningful conclusions from the visualized information.
How to Interpret Data Visualizations
Understanding graphical representations of data is crucial for extracting meaningful insights. These visual tools can convey complex information in an accessible format, allowing viewers to grasp trends, relationships, and distributions quickly. To effectively interpret these visuals, one must engage with them critically and contextually.
Key Elements to Consider

- Axes and Scales: Always examine the axes and scales used. They provide context for the data points and help you assess the range and magnitude of the values represented.
- Data Points: Analyze the distribution of data points. Look for clusters, outliers, and gaps that may indicate significant patterns or anomalies.
- Color and Symbols: Colors and symbols can enhance understanding by categorizing data. Pay attention to legends and annotations that explain their meaning.
- Trends and Patterns: Look for visual cues that highlight trends over time or relationships between variables. These can often guide your interpretation of the underlying data.
Questions to Ask
- What story does the visualization tell?
- What are the key takeaways from the displayed information?
- Are there any biases or limitations in how the data is presented?
- How does this visual compare to other representations of the same data?
By considering these elements and questions, you can enhance your ability to interpret and draw conclusions from various data visuals, leading to more informed decisions and deeper understanding.
Applications of Violin Diagrams in Research
Visual representations of data distribution have become essential tools in various fields of research. They provide a comprehensive view of datasets, allowing researchers to analyze patterns, trends, and variations effectively. By illustrating the density of values at different ranges, these graphical tools facilitate deeper insights into the underlying data structures, making them invaluable in both exploratory and confirmatory analyses.
Benefits in Data Analysis
The utilization of these visual tools enhances the interpretability of complex datasets. Researchers can quickly identify key features such as central tendencies, variability, and outliers. This clarity supports better decision-making and hypothesis generation in fields ranging from medicine to social sciences.
Comparative Studies
Another significant application lies in comparative analysis. By overlaying multiple distributions, researchers can visually assess differences and similarities across groups. This capability is particularly useful in experimental research, where the impact of various treatments or conditions needs to be evaluated.
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Medicine | Assessing treatment efficacy across patient groups |
| Social Sciences | Understanding demographic variations in survey responses |
| Environmental Studies | Evaluating ecological data distributions |
| Finance | Analyzing stock return distributions |
Comparing Violin and Box Plots

When visualizing data distributions, two popular graphical representations often come into play: one emphasizes the overall shape and density of the data, while the other provides a clear summary of central tendency and variability. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each can help in selecting the right tool for effective data communication.
Structure and Information Conveyed
The first representation showcases not only the median and quartiles but also the underlying distribution’s density, providing a comprehensive view of how data points are spread across different values. In contrast, the second form focuses on key summary statistics, allowing for quick comparisons between groups without delving into the finer details of the distribution’s shape.
Applications and Use Cases
Choosing between these two methods often depends on the context. For instance, when the goal is to highlight nuances in data distribution, the former serves better by illustrating variations and trends. On the other hand, the latter is preferable for straightforward comparisons, especially when dealing with multiple datasets where clarity and simplicity are paramount.
In summary, both graphical forms have their unique advantages and can be employed effectively based on the specific requirements of the analysis.
Tips for Creating Effective Violin Diagrams

When it comes to visualizing data distributions, clarity and precision are paramount. Crafting an impactful representation requires attention to detail and an understanding of your audience’s needs. Here are some essential strategies to enhance the effectiveness of your visuals.
Choose the Right Data
Before creating your visual representation, ensure that you select the most relevant dataset. This lays the foundation for clear communication.
- Identify key variables that illustrate your main points.
- Consider the context and purpose of your visualization.
- Eliminate unnecessary data that could clutter your representation.
Design for Clarity
A well-structured layout can significantly improve comprehension. Focus on the following design principles:
- Use appropriate scales: Ensure that the axes are scaled properly for accurate interpretation.
- Incorporate color wisely: Use color to differentiate categories, but avoid overwhelming the viewer.
- Add labels and legends: Clearly label each component to facilitate understanding.
Common Mistakes in Data Representation
Data visualization plays a crucial role in communicating information effectively. However, several pitfalls can undermine its clarity and impact, leading to misinterpretations.
- Overcomplicating Visuals: Adding too many elements can confuse the viewer.
- Poor Labeling: Inadequate or unclear labels can obscure the intended message.
- Inconsistent Scales: Using different scales can distort comparisons and lead to inaccurate conclusions.
- Neglecting Color Choices: Inappropriate color schemes can hinder readability and accessibility.
By being aware of these common errors, one can enhance the effectiveness of visual representations and convey data more accurately.
Enhancing Your Presentation with Violin Diagrams
Visual representations are powerful tools for conveying complex data and insights effectively. By incorporating a specific type of graphic display into your presentations, you can highlight distributions and variations within your datasets. This approach not only simplifies information but also engages your audience, making the message more memorable.
Benefits of Using This Graphic Representation
One of the primary advantages of using such visual formats is their ability to show the spread and density of data points simultaneously. Unlike traditional bar charts, these visuals allow for a more nuanced understanding of the underlying patterns, revealing subtleties that might otherwise be overlooked. Utilizing this method can enhance clarity and improve the audience’s grasp of your findings.
Best Practices for Integration
To maximize the impact of these visual tools, consider your audience’s familiarity with the data being presented. Ensure that the graphics are accompanied by clear explanations and contextual information. Color choice and design simplicity are also critical; a well-structured display can guide viewers’ attention to the most significant aspects of the data. By thoughtfully integrating these visuals, you can create compelling presentations that resonate with your audience.
Future Trends in Data Visualization
As the landscape of information continues to evolve, so too does the art of presenting data. Emerging trends suggest a shift towards more interactive and immersive experiences, allowing users to engage with data in innovative ways. This transformation is driven by advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on storytelling through visual means.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality: These technologies are enabling data to be represented in three-dimensional spaces, offering a more intuitive understanding of complex datasets.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is enhancing the ability to analyze and visualize large volumes of data, providing insights and recommendations in real-time.
- Personalization: Tailored visualizations that adapt to individual preferences and contexts are becoming more common, improving user engagement and comprehension.
- Real-time Data Visualization: The demand for up-to-date information is leading to the development of dynamic visual tools that reflect changes instantly, fostering timely decision-making.
- Data Storytelling: Combining narrative techniques with data presentation helps convey messages more effectively, making complex information more relatable.
As these trends gain traction, the future of visualizing information will likely prioritize user experience, accessibility, and the ability to uncover deeper insights from data. Continuous innovation in this field will shape how we interpret and interact with the world around us.