In the intricate web of life, various elements intertwine in unexpected ways, revealing fascinating relationships. This section delves into the unique overlaps between the organic world of vegetation and the complex structure of living organisms. By examining these associations, we can uncover profound insights about both realms.
Through a thoughtful analysis, it becomes apparent that certain characteristics create intriguing parallels. The comparison draws attention to how various features resonate across different domains, fostering a deeper understanding of their significance. By embracing this interconnectedness, we not only broaden our perspectives but also enhance our appreciation for the intricacies of life.
As we navigate this exploration, the focus will be on identifying shared attributes and recognizing how these similarities contribute to the greater picture. This journey promises to illuminate the remarkable unity underlying diverse forms, showcasing the beauty of their coexistence.
Venn Diagram Basics Explained
This section delves into fundamental concepts surrounding a popular method for illustrating relationships between different sets. By utilizing overlapping circles, one can visualize how various categories intersect and share common characteristics, enabling a clearer understanding of their connections.
Typically, this technique serves as a tool for educators and researchers, allowing them to present complex information in a simplified manner. The overlap of circles represents shared traits, while the distinct areas highlight unique attributes of each set. This visual aid is invaluable in numerous fields, from mathematics to social sciences, fostering better comprehension of intricate relationships.
| Set A | Set B | Intersection |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristic 1 | Characteristic 3 | Common Trait |
| Characteristic 2 | Characteristic 4 | Common Trait |
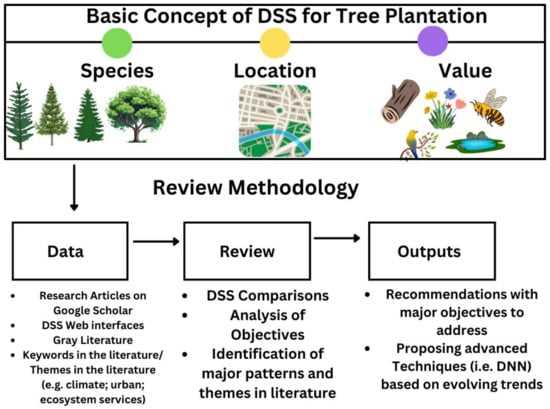
Understanding Trees and Their Anatomy
This section delves into the fascinating world of botanical structures, exploring the various components that contribute to the vitality and functionality of these magnificent organisms. Each element plays a vital role in the overall health and growth of the plant, serving specific purposes that ensure survival and reproduction in diverse environments.
Key Components of Botanical Structures
- Roots: These underground structures anchor the plant in place while absorbing essential nutrients and moisture from the soil.
- Trunk: The central stem provides support, enabling the organism to reach upward for sunlight while also facilitating the transport of water and nutrients.
- Branches: Extending from the trunk, these appendages support leaves and flowers, maximizing exposure to sunlight.
- Leaves: The primary site for photosynthesis, these flat structures capture sunlight and convert it into energy.
- Flowers: Reproductive structures that attract pollinators, facilitating the process of fertilization and the production of seeds.
- Fruits: Matured ovaries that protect seeds, aiding in their dispersal to new locations.
Functional Aspects of Botanical Structures
Understanding the roles of these components enhances our appreciation of how organisms interact with their surroundings. Each part is designed to perform distinct functions that contribute to the organism’s growth, reproduction, and overall adaptability. For instance, the extensive root systems are crucial for stabilizing the plant while enabling access to vital resources, whereas leaves play a significant role in energy production.
This interconnectedness illustrates the complexity of these living entities and their ability to thrive in varied ecosystems, highlighting the remarkable adaptations that have evolved over time.
Human Body Structure Overview
The complex organization of the human form consists of various interconnected systems that work in harmony. Each system plays a vital role in maintaining overall functionality, contributing to the organism’s health and well-being. Understanding this intricate architecture provides insight into how each element collaborates to support life.
At the core, the skeletal framework provides stability and protection, serving as a scaffold for muscles and organs. Muscles facilitate movement, while the circulatory network ensures nutrient delivery and waste removal. The nervous system coordinates actions, responding to internal and external stimuli.
In addition, the respiratory and digestive systems play crucial roles in sustaining energy levels and overall vitality. The interplay between these components illustrates the remarkable efficiency of the human structure, highlighting the importance of each system in promoting health and resilience.
Shared Characteristics of Trees and Bodies
Both flora and living organisms exhibit remarkable similarities that highlight their interconnectedness within the natural world. These parallels can be observed in their structural components, functions, and responses to environmental stimuli. Understanding these shared traits can enhance our appreciation for the complexity and beauty of life forms around us.
Structural Similarities
Stems in vegetation and bones in organisms serve as critical support systems, maintaining overall structure and stability. While stems transport essential nutrients and water, bones provide a framework that safeguards vital organs. Both systems are designed to adapt to external pressures, ensuring resilience and functionality.
Growth and Development
The processes of growth in plants and development in living beings showcase similarities in response to their environments. Both entities undergo phases that enable them to thrive, adjusting to factors such as light, nutrients, and moisture. This adaptability is crucial for survival, illustrating the dynamic nature of life.
Branches: Trees vs. Body Limbs
This section explores the similarities and differences between the extensions of vegetation and human appendages. Both structures serve vital functions in their respective systems, playing crucial roles in support, mobility, and overall health. A closer examination reveals intriguing parallels in their design and function, providing insight into the interconnectedness of nature and anatomy.
Structural Comparison
The extensions of flora are typically characterized by their branching patterns, which maximize sunlight exposure and nutrient absorption. Similarly, human limbs exhibit a complex structure that enables movement and dexterity. Both types of extensions are essential for survival, whether it’s capturing light for growth or navigating the environment.
Functional Significance
The functionality of these extensions is paramount. In vegetation, branches facilitate the transport of resources throughout the organism, while in humans, limbs are vital for interaction with the world. Understanding the roles played by these structures highlights the efficiency and adaptability inherent in both biological systems.
Roots and Their Biological Functions
These subterranean structures play a crucial role in the life of various organisms, serving multiple essential purposes that contribute to overall vitality and stability. Their primary responsibilities extend beyond mere anchoring; they are intricately involved in the processes that sustain growth and development.
Nutrient Absorption

One of the fundamental functions of these structures is to absorb vital nutrients and minerals from the soil. This process ensures that organisms receive the necessary elements for various physiological activities.
Water Regulation
In addition to nutrient uptake, these entities play a significant role in regulating water within organisms. Through a complex system of uptake and distribution, they help maintain hydration levels essential for survival.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Uptake | Extraction of essential minerals and nutrients from the soil for growth. |
| Water Absorption | Facilitates the intake of water to support metabolic processes. |
| Stabilization | Anchors organisms to the ground, providing structural integrity. |
| Storage | Stores carbohydrates and other nutrients for future use. |
Tree Rings and Growth Patterns
The study of annual growth increments provides valuable insights into the life history of plants. Each ring serves as a record of the environmental conditions experienced throughout the years, reflecting the resilience and adaptability of these organisms.
These growth layers can reveal a wealth of information about various factors, including:
- Seasonal climate variations
- Soil nutrients
- Water availability
- Insect infestations
By analyzing these increments, researchers can uncover patterns that indicate:
- Periods of drought or excessive rainfall
- Growth spurts due to favorable conditions
- Stress responses from harsh environments
Furthermore, these rings can aid in dating historical events, providing a timeline that chronicles the changes in the ecosystem over time. This information is crucial for understanding ecological dynamics and guiding conservation efforts.
Leaves and Skin: Functional Comparisons
Both foliage and dermal layers serve essential roles in the vitality and protection of organisms. While they originate from distinct biological systems, their functions exhibit intriguing parallels that underscore their importance in maintaining homeostasis and responding to environmental challenges.
Protection Against External Factors
Foliage acts as a shield, defending the plant from various threats such as pests and extreme weather. Similarly, the skin provides a barrier for living beings, safeguarding against harmful microorganisms, physical injuries, and dehydration. Both structures are vital in minimizing damage and maintaining overall health.
Regulatory Functions
Another notable similarity lies in their regulatory capabilities. Leaves play a crucial role in photosynthesis, controlling gas exchange and transpiration to optimize energy production. In parallel, the epidermis manages temperature and moisture levels in the body, assisting in thermoregulation and fluid balance. This regulatory function highlights their significance in the survival of both plants and animals.
Environmental Impact on Both Systems
The interaction between natural ecosystems and biological entities reveals profound connections that influence their respective health and sustainability. Each system not only adapts to its surroundings but also plays a crucial role in shaping environmental conditions. Understanding these interdependencies is essential for promoting balance and resilience within both realms.
Natural elements contribute significantly to the overall well-being of living organisms, providing essential resources for growth and development. Conversely, the existence and functionality of living beings often affect the ecological landscape, driving evolutionary changes and influencing habitat quality. This reciprocal relationship underscores the necessity of preserving ecological integrity to support the vitality of biological systems.
Moreover, anthropogenic activities exert substantial pressure on both domains. Deforestation, pollution, and climate change threaten the stability of ecosystems, while also impacting the physiological and psychological aspects of living organisms. Mitigating these adverse effects requires a concerted effort to foster sustainable practices that enhance the resilience of both environments and life forms.
Ultimately, recognizing the shared vulnerabilities and strengths of these systems encourages a holistic approach to environmental stewardship. By prioritizing sustainability, societies can ensure the longevity and health of both natural ecosystems and living entities, creating a harmonious future.