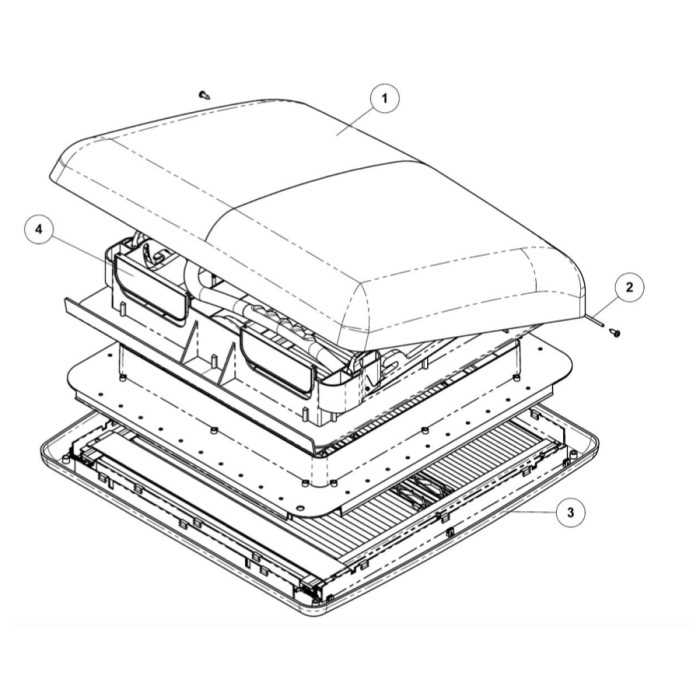
In the world of architectural design, natural light plays a pivotal role in enhancing the ambiance and functionality of indoor spaces. Properly integrating openings in the roof not only improves aesthetic appeal but also boosts energy efficiency. To ensure optimal performance and longevity, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the various elements involved in these installations.
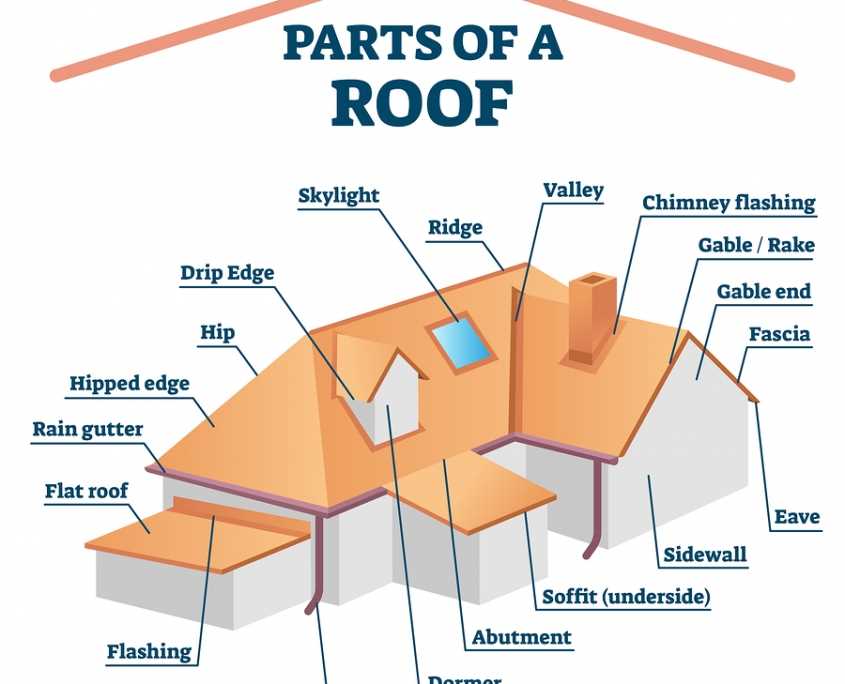
The interplay between different sections of a rooftop installation is crucial for both aesthetic and functional purposes. Each component has a specific role, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the structure. Knowledge of these elements enables homeowners and builders to make informed decisions regarding installation, maintenance, and repair.
By exploring the individual features and their respective functions, one can gain insights into how these installations operate as a cohesive unit. Whether for new construction or retrofitting existing structures, a comprehensive grasp of these components ensures that the desired benefits of natural lighting are fully realized while maintaining structural integrity.
Understanding Skylight Components
When considering the structure of a light-transmitting installation on a roof, it’s essential to grasp the various elements that contribute to its functionality and aesthetic appeal. These components work in harmony to provide illumination, ventilation, and weather protection, enhancing the overall environment of a space.
Main Elements
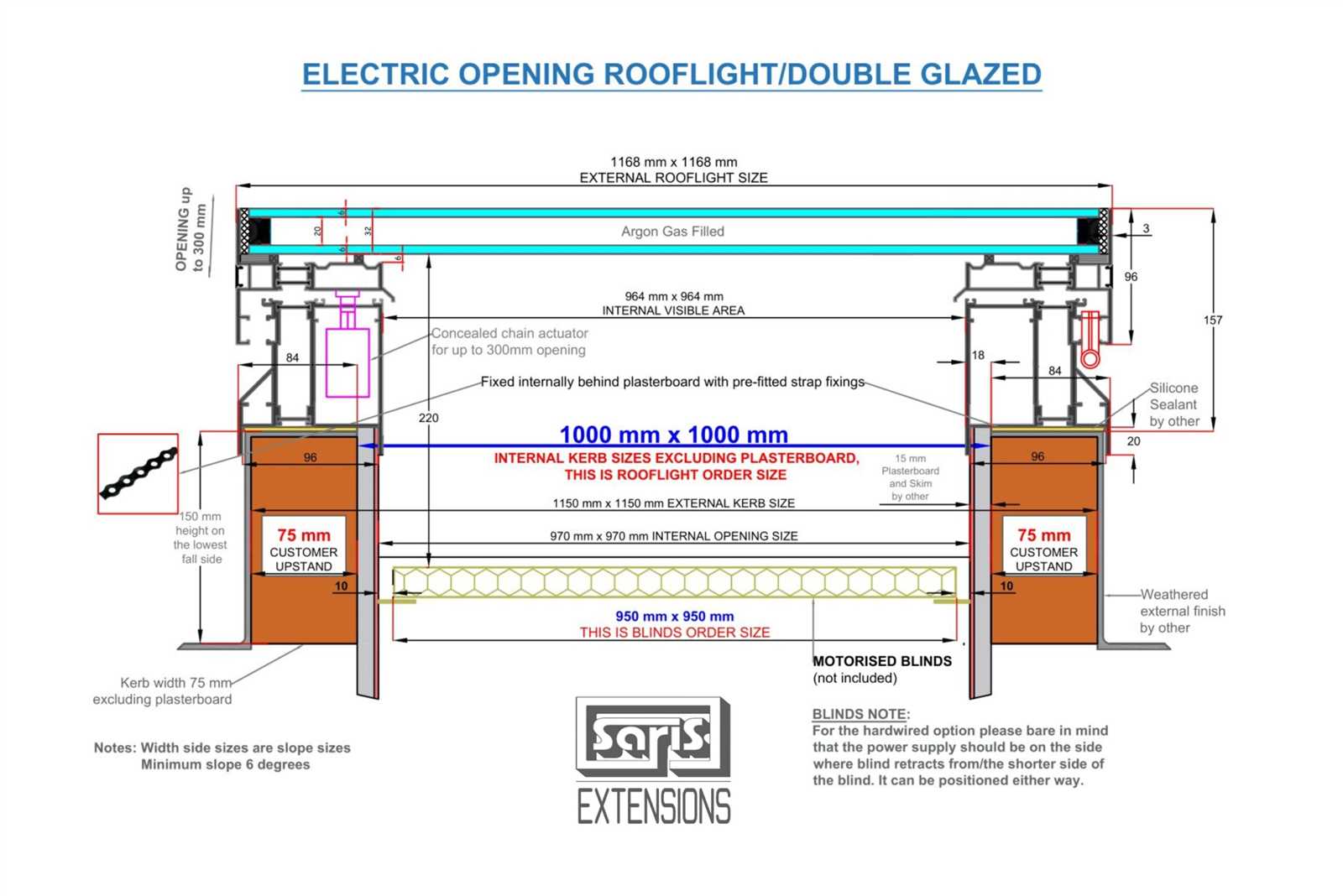
- Frame: The supportive structure that holds everything in place, often made from durable materials to withstand external pressures.
- Glazing: The transparent or translucent material that allows natural light to penetrate while providing insulation and UV protection.
- Flashings: Components that ensure a watertight seal around the installation, preventing leaks and water damage.
- Ventilation Features: Mechanisms that allow for airflow, which helps regulate temperature and humidity inside the building.
Additional Considerations
- Insulation: Materials that reduce heat loss or gain, contributing to energy efficiency.
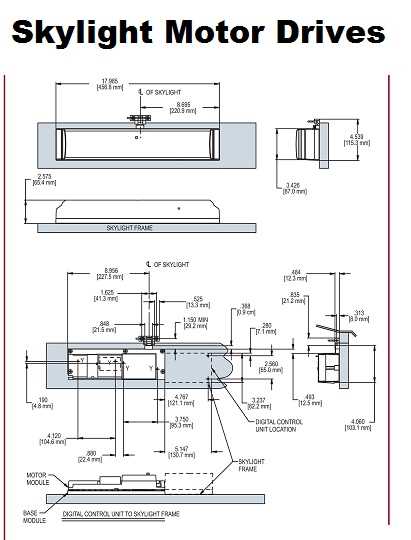
- Control Systems: Automated or manual options that allow users to adjust light levels or ventilation as needed.
- Accessories: Optional additions such as shades, blinds, or decorative elements that enhance functionality and style.
Understanding these elements is crucial for making informed decisions regarding installation, maintenance, and enhancements. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring that the structure performs effectively while providing a welcoming atmosphere.
Types of Skylight Systems Available
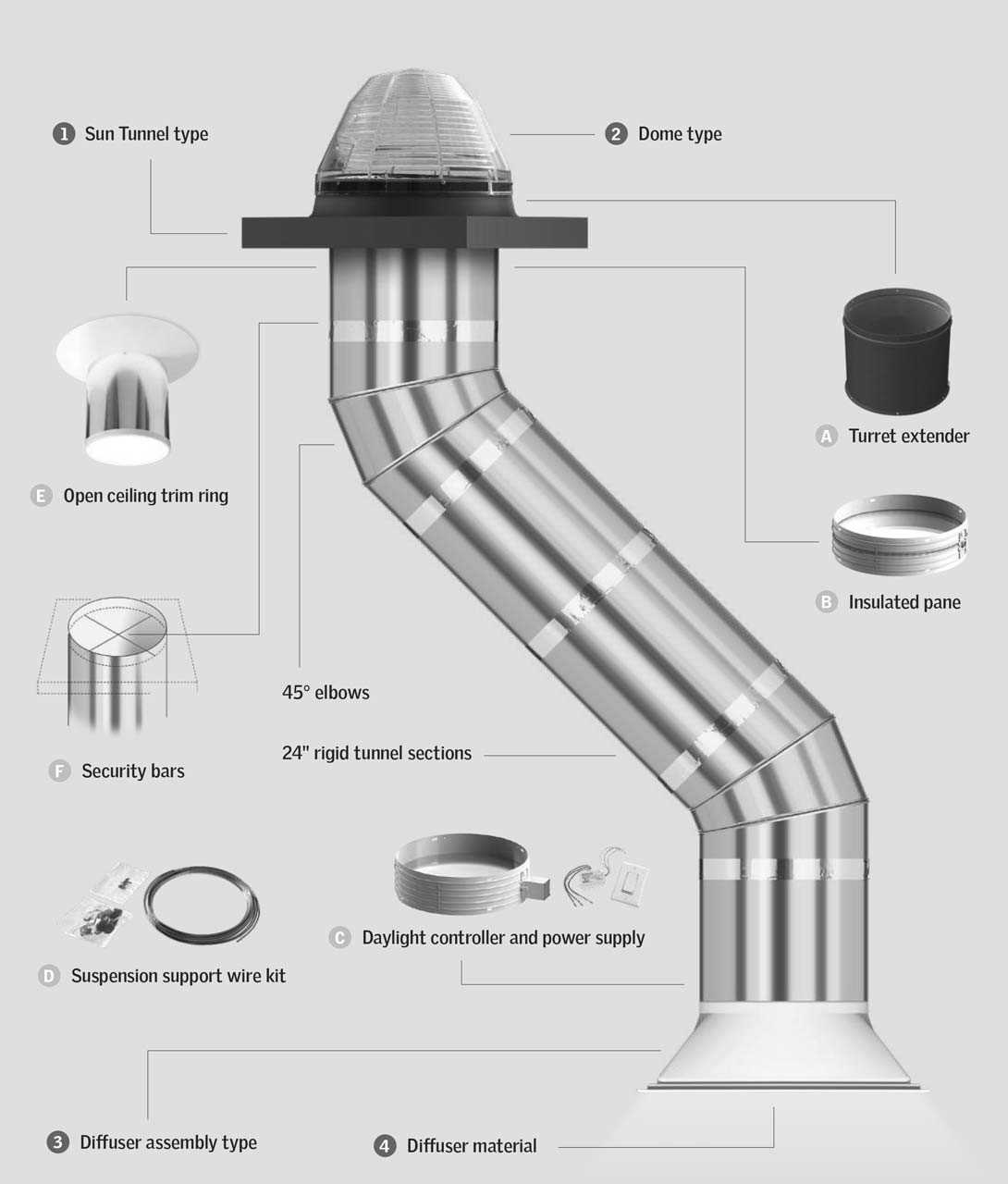
There are various configurations of light-enhancing structures designed to bring natural illumination into indoor spaces. Each design offers unique benefits and aesthetic appeal, catering to different architectural styles and functional needs. Understanding the different options can help homeowners and builders make informed choices based on their specific requirements.
Fixed Structures
Fixed structures are designed to remain stationary, allowing sunlight to filter through without any movable elements. They are ideal for areas where ventilation is not a primary concern. These installations are often crafted from durable materials that provide excellent insulation while maximizing light exposure.
Ventilated Models
Ventilated models incorporate mechanisms that enable opening and closing, facilitating airflow alongside natural lighting. These designs are particularly beneficial in spaces that require fresh air circulation, such as kitchens or bathrooms. By promoting ventilation, they enhance indoor comfort while still allowing ample sunlight to enter.
Key Features of Skylight Design
The incorporation of overhead glazing structures in architectural design serves to enhance natural illumination while contributing to the overall aesthetic appeal of a space. These installations provide numerous benefits, ranging from energy efficiency to improved well-being for occupants.
Natural Light Optimization: One of the primary advantages of these structures is their ability to maximize the entry of sunlight. Strategically placed, they can significantly reduce the need for artificial lighting, leading to lower energy consumption and costs.
Enhanced Aesthetics: The visual impact of these openings cannot be understated. They create a sense of openness and connection to the outdoors, making spaces feel larger and more inviting. The design can be tailored to complement various architectural styles, enhancing the building’s character.
Ventilation Options: Many designs allow for adjustable openings, providing a means of natural ventilation. This feature not only contributes to air quality but also helps regulate indoor temperatures, creating a more comfortable environment.
Energy Efficiency: When designed with proper materials and orientation, these structures can improve a building’s energy performance. Utilizing energy-efficient glazing can minimize heat loss in winter and reduce heat gain in summer, promoting sustainability.
Durability and Weather Resistance: Quality materials ensure that these installations withstand various weather conditions. Proper sealing and structural integrity are essential to prevent leaks and maintain performance over time.
Customization: The flexibility in design allows for customization according to specific needs and preferences. Shapes, sizes, and glazing options can be adapted to fit individual projects, ensuring functionality and aesthetic coherence.
Installation Process Overview
This section outlines the essential steps for successfully integrating a natural light-enhancing feature into a structure. The installation procedure involves careful planning and execution to ensure optimal performance and aesthetic appeal. Understanding each stage is crucial for achieving a seamless integration with the existing architecture.
Preparation and Planning
Before commencing the installation, it is important to assess the area where the feature will be positioned. This includes evaluating the structural integrity, measuring dimensions, and selecting appropriate materials. Proper preparation ensures that the installation proceeds smoothly and adheres to local building codes.
Installation Steps
The following table summarizes the key steps involved in the installation process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gather all necessary tools and materials for the installation. |
| 2 | Mark the installation area and ensure accurate measurements. |
| 3 | Prepare the opening by removing any obstructions and reinforcing the structure as needed. |
| 4 | Install the framing components, ensuring they are level and securely fastened. |
| 5 | Seal the edges to prevent air and water leakage. |
| 6 | Complete any finishing touches to blend the installation with the surrounding area. |
Following these steps will facilitate a successful integration of the natural light-enhancing feature, enhancing the overall ambiance of the space while ensuring durability and functionality.
Maintenance Tips for Skylights
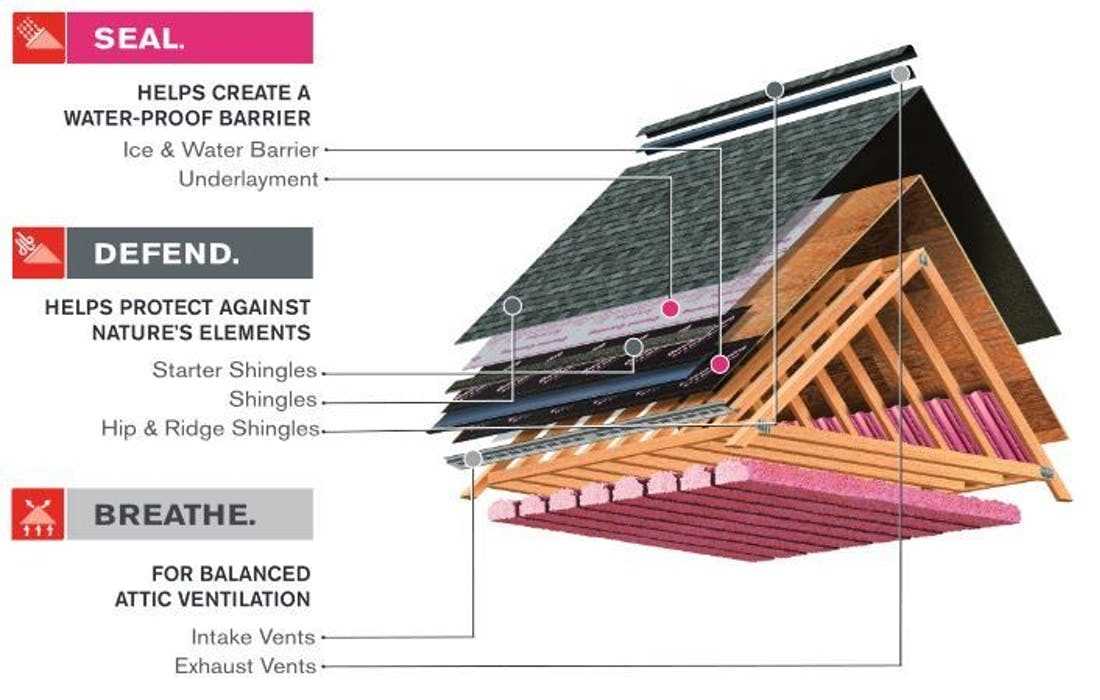
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and functionality of any overhead glass installation in your home. This includes checking for any signs of wear or damage that could lead to leaks or energy inefficiency. Proactive care can help maintain a comfortable indoor environment while preventing costly repairs down the line.
First and foremost, inspect the sealing around the perimeter periodically. Any cracks or gaps should be addressed immediately to prevent moisture from entering. Replacing old or deteriorated weatherstripping can greatly enhance insulation and energy efficiency.
Additionally, keep the surface clear of debris, such as leaves or dirt, which can obstruct drainage systems and lead to water buildup. Cleaning the glass regularly will not only improve visibility but also maximize natural light entering the space.
Lastly, consider having a professional evaluation at least once a year. They can identify potential issues that may not be immediately visible and offer solutions tailored to your specific installation. By taking these steps, you can enjoy the benefits of your overhead installation for years to come.
Common Issues with Skylight Parts
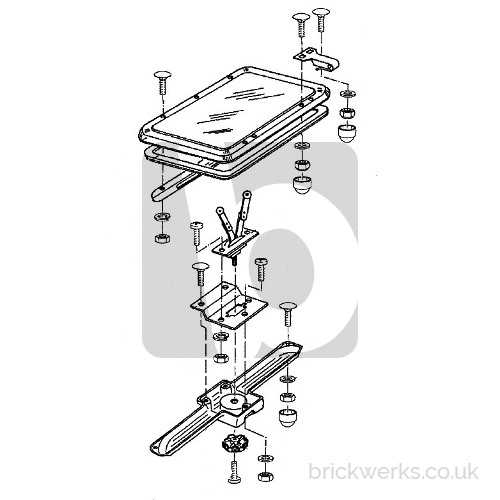
In the realm of overhead lighting solutions, various components can encounter challenges that may affect their functionality and durability. Understanding these issues can help users effectively address and prevent problems, ensuring a longer lifespan for these fixtures. Below are some common concerns and their potential solutions.
Frequent Problems
- Leakage: Water intrusion is a prevalent issue, often resulting from poor installation, damaged seals, or deteriorating materials.
- Condensation: Excessive moisture can lead to fogging or water droplets forming on the surface, indicating insufficient ventilation.
- Cracks and Breaks: Extreme temperatures or impact can cause fractures, compromising both aesthetics and integrity.
- UV Damage: Prolonged exposure to sunlight may cause fading or degradation of the frame and surrounding materials.
Prevention and Maintenance
- Regularly inspect seals and gaskets for wear and replace them as necessary.
- Ensure adequate ventilation to minimize humidity buildup.
- Use protective coatings to shield surfaces from harmful UV rays.
- Promptly repair any visible cracks or damages to prevent further issues.
Materials Used in Skylight Manufacturing
The creation of structures designed to allow natural light into interiors relies on a variety of materials, each selected for its specific properties and performance characteristics. The choice of components significantly impacts durability, insulation, and aesthetic appeal, making material selection a crucial aspect of design and functionality.
Common Materials
- Glass: A prevalent option, offering clarity and excellent light transmission. Variants include tempered, laminated, and low-emissivity glass, each providing different benefits in terms of safety, insulation, and energy efficiency.
- Plastic: Often utilized for its lightweight and shatter-resistant qualities. Polycarbonate and acrylic are popular choices, known for their impact resistance and UV protection.
- Metal: Commonly used in frames and structural supports, materials such as aluminum and steel provide strength and stability. They are also favored for their corrosion resistance when properly coated.
- Wood: Used primarily in traditional designs, it adds aesthetic warmth and can be treated for improved durability against weather conditions.
Innovative Options
- Composite materials: Combining different elements, these materials can enhance performance while reducing weight.
- Eco-friendly alternatives: Sustainable options, such as recycled materials or those with a low environmental impact, are becoming increasingly popular among environmentally conscious consumers.
Benefits of Natural Light from Skylights
Harnessing sunlight through openings in the roof brings numerous advantages to both residential and commercial spaces. This method of illumination enhances the overall environment, promoting well-being and efficiency. By incorporating natural light, interiors can feel more expansive and inviting, contributing to a healthier living or working atmosphere.
One of the primary benefits is the reduction in energy costs. By maximizing daylight, reliance on artificial lighting diminishes, leading to significant savings on electricity bills. Furthermore, the presence of sunlight can improve mood and productivity, making spaces feel more uplifting and energizing.
Additionally, the influx of natural light can positively impact the aesthetics of a room, enhancing colors and textures. This organic lighting can also help maintain a comfortable temperature, reducing the need for artificial heating or cooling.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces reliance on artificial lighting, leading to lower electricity costs. |
| Mood Enhancement | Improves psychological well-being and increases productivity. |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Enhances the appearance of interiors, highlighting colors and textures. |
| Temperature Regulation | Helps maintain a comfortable indoor climate, reducing heating and cooling needs. |