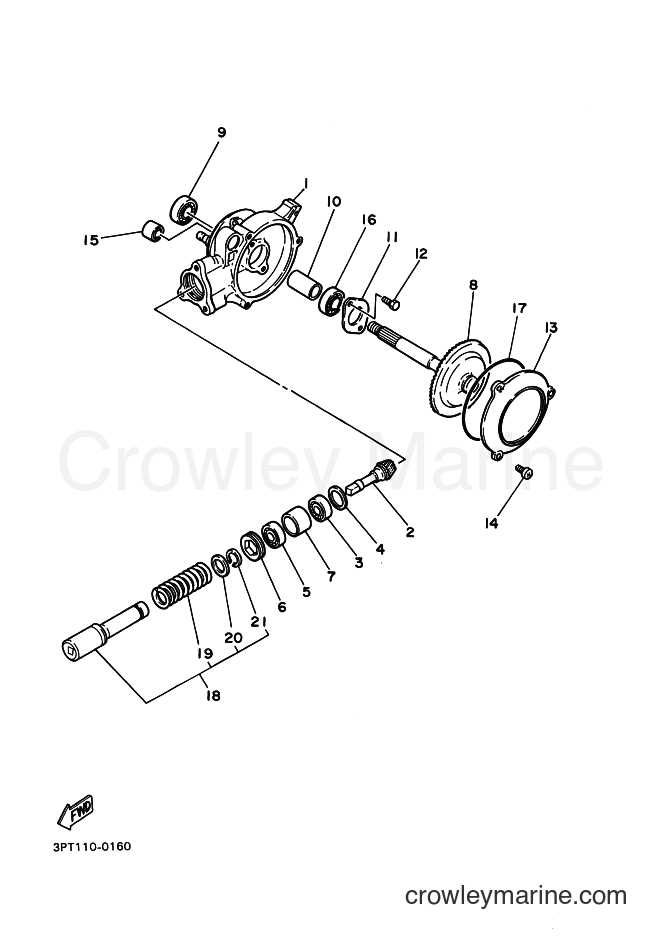
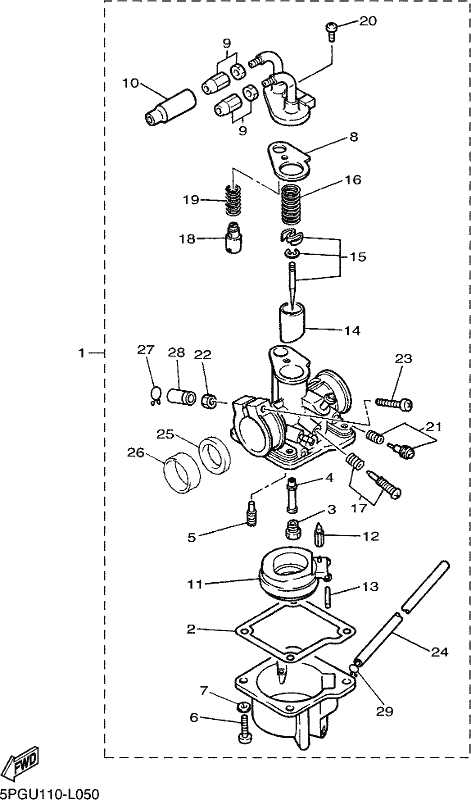
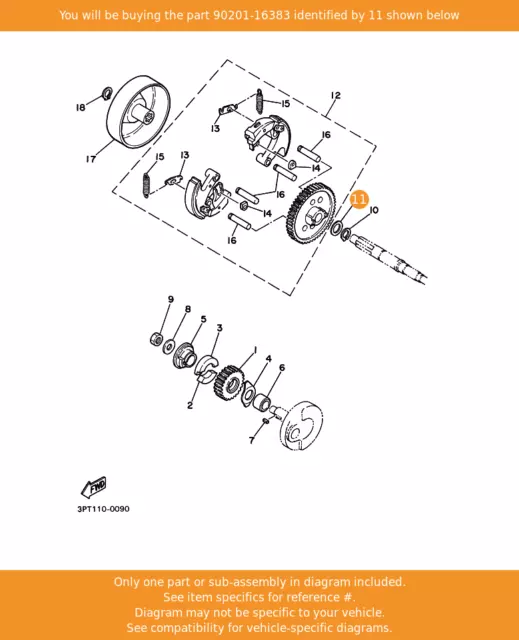
When it comes to maintaining a small two-wheeler, knowing how each element functions is essential for both performance and safety. Every piece plays a role in ensuring that the vehicle runs smoothly, from its engine to its smallest structural element. Whether you are tuning the mechanics or replacing broken items, having a clear overview of the structure helps significantly.
For enthusiasts and riders alike, recognizing the interplay of each element within the system can be a game-changer. It not only provides insights into proper upkeep but also aids in troubleshooting issues efficiently. Having detailed knowledge about how everything fits together allows for quicker adjustments and upgrades when necessary.
In this section, we will explore the fundamental components, offering a closer look at their arrangement and function, ensuring that both beginners and seasoned mechanics can benefit from the insights provided.
Essential Components of a PW50
Understanding the Frame Structure
The framework of a small motorcycle serves as the backbone, providing essential support and stability. Its design influences the vehicle’s balance, durability, and overall performance. The composition and assembly of this key component ensure that all other elements, from the engine to the handlebars, are securely positioned.
Core Components of the Framework
The framework consists of several interconnected sections, each playing a distinct role. These parts work together to create a strong foundation, supporting both the rider and the mechanical components. Below is a breakdown of some of the primary structural elements:
| Component | Function | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Frame | Holds the engine and other crucial elements, ensuring overall stability. | ||||||||||
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy to power the system and start the engine. |
| Ignition Coil | Transforms low voltage from the battery into high voltage to ignite the fuel-air mixture. |
| Regulator | Maintains consistent voltage levels in the electrical system to prevent damage to components. |
| Wiring Harness | Facilitates connections between various electrical components, ensuring proper communication. |
| Fuse Box | Protects the electrical system by preventing overloads and short circuits through fuses. |
Wiring Configuration
The configuration of wires is vital for ensuring that the electrical flow is both safe and efficient. Proper insulation and routing of wires help prevent short circuits and damage to the components. Awareness of the wiring layout aids in troubleshooting, allowing technicians to quickly identify and resolve issues that may arise during operation.
The Role of Suspension in Performance

The suspension system of a vehicle significantly influences its overall functionality and handling. By managing how the wheels interact with the terrain, it ensures a smooth ride while providing stability during various maneuvers. An effective suspension setup can enhance control, allowing the rider to navigate challenging conditions with confidence.
Key aspects of suspension that contribute to performance include:
- Shock Absorption: Reduces the impact from bumps and uneven surfaces, maintaining comfort and control.
- Stability: Keeps the vehicle balanced, especially during turns or rapid acceleration.
- Traction: Maximizes grip on the ground, ensuring efficient power transfer from the engine to the wheels.
- Adjustability: Allows fine-tuning of the system to match different riding conditions and personal preferences.
Overall, a well-engineered suspension not only enhances comfort but also optimizes performance, making it a critical element in vehicle design.
Air Filter and Intake Design
The design of the air filtration and intake system plays a crucial role in optimizing engine performance. An efficient setup ensures that the engine receives a steady supply of clean air, which is vital for combustion efficiency and overall functionality.
In this context, the air filter serves as a protective barrier, preventing contaminants such as dust and debris from entering the engine. The design should facilitate easy airflow while effectively trapping harmful particles. Choosing the right material for the filter can enhance its efficiency, contributing to better engine health.
The intake system’s configuration significantly impacts air velocity and volume. An ergonomic design allows for smoother airflow, reducing turbulence and enhancing the engine’s responsiveness. Employing curved paths can further optimize airflow dynamics, promoting a more efficient combustion process.
Ultimately, a well-thought-out air filtration and intake design can lead to improved power output and fuel efficiency, underscoring the importance of this component in the overall performance of the engine.