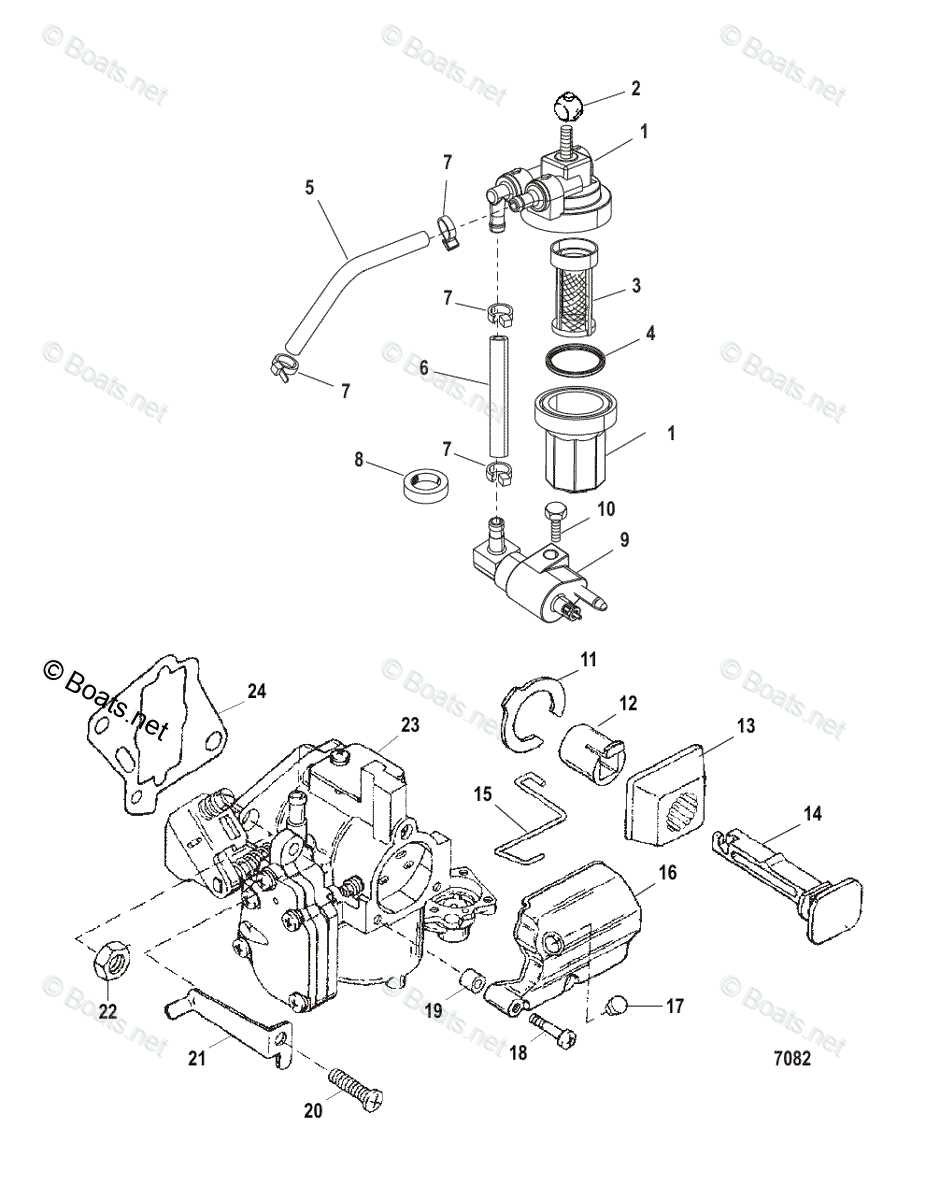
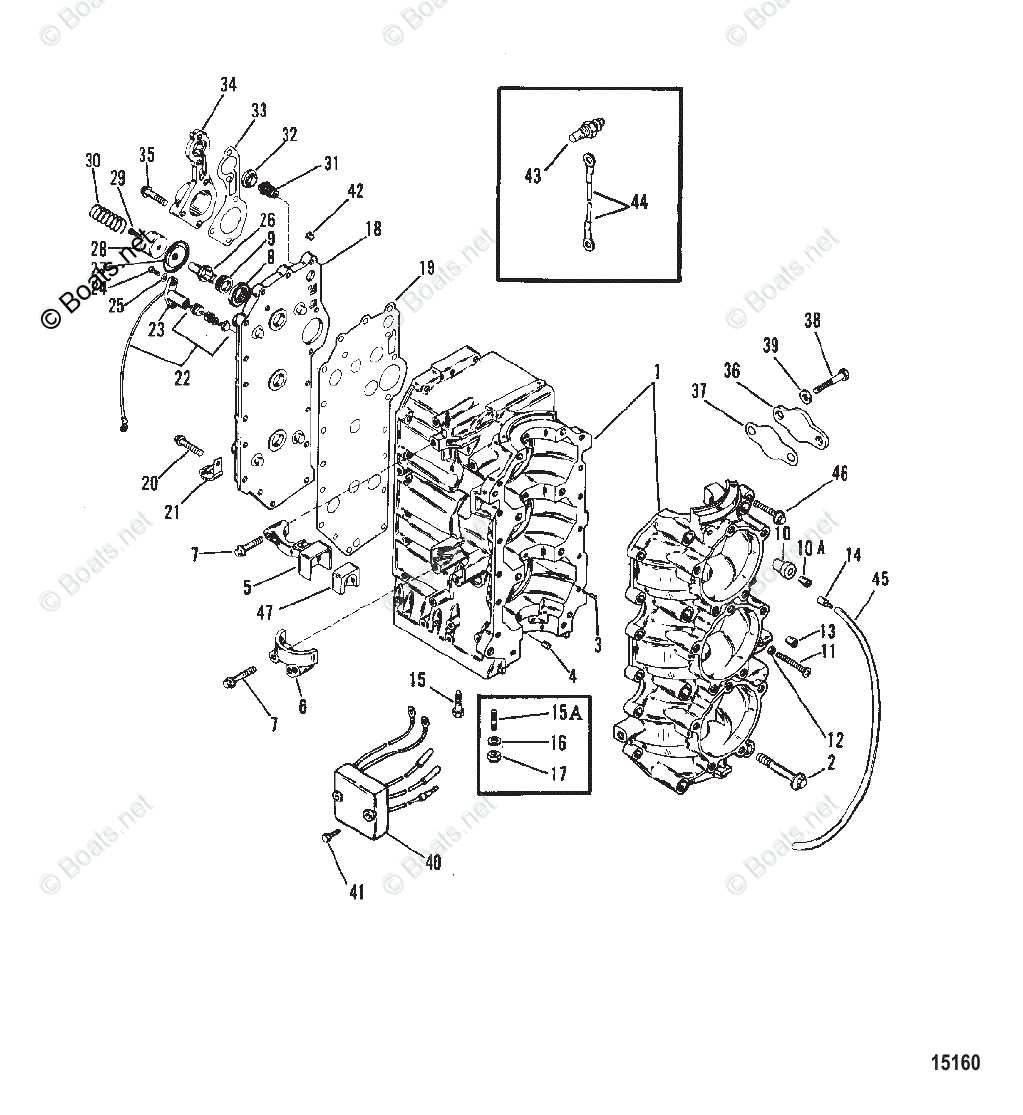
Detailed Fuel System Diagram
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. By understanding the flow of fuel from the tank to the engine, it becomes easier to diagnose issues and maintain efficiency. The components involved in this process work together to deliver fuel accurately and effectively.
At the core of the system, a pump draws fuel from the storage container, guiding it through filters to remove impurities. This prevents blockages and ensures clean fuel reaches the engine. Hoses and connections help in directing the fuel to the carburetor, where it is mixed with air for combustion.
In addition, sensors and valves are responsible for regulating pressure and maintaining the right amount of fuel flow, adapting to different operating conditions. Understanding the arrangement of these components helps in ensuring proper maintenance and resolving common issues like leaks or blockages.
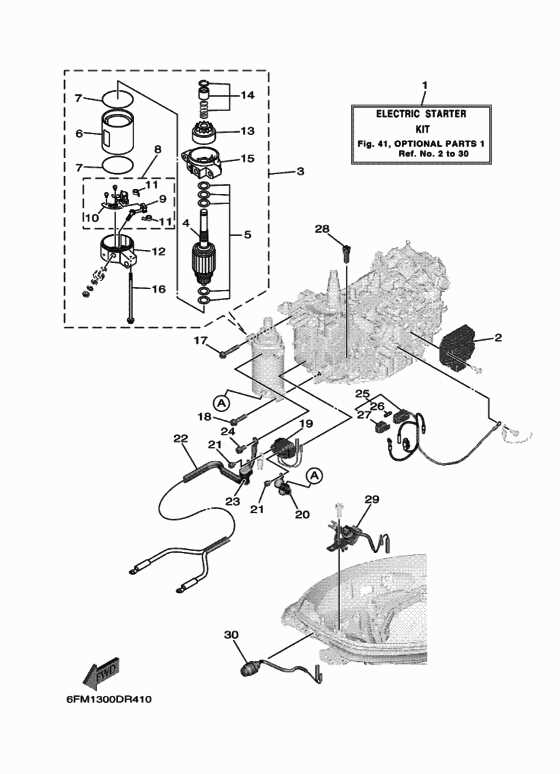
Ignition and Electrical Parts Layout
The ignition system and electrical components play a critical role in ensuring the engine operates efficiently and reliably. This section provides an overview of how these elements are positioned and interconnected, highlighting their key functions in maintaining smooth engine performance.
Ignition System Overview
The ignition setup is responsible for producing the necessary spark to ignite the fuel mixture within the engine. Key components include the ignition coil, spark plug, and related wiring. Each of these elements is strategically placed to ensure optimal functionality, ensuring the engine starts and runs smoothly. The coil delivers high voltage to the spark plug, which then ignites the fuel at precise timing intervals.
Electrical System Components
The electrical system provides the necessary power to various elements, including the starter, lights, and any auxiliary systems. Key elements, such as the battery, alternator, and voltage regulator
Cooling System Components and Functions
The cooling system in a marine engine is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperature, ensuring efficiency and preventing overheating. By circulating coolant through various channels, the system dissipates excess heat, allowing the engine to perform reliably even under challenging conditions.
Main Cooling Channels
At the heart of the system are the coolant passages, which transport the cooling liquid throughout the engine. These channels ensure that heat is absorbed and transferred away from critical components. The circulation process keeps the engine from reaching dangerous temperatures that could lead to damage.
Pumps and Thermostats
A pump drives the cooling fluid through the system, while a thermostat regulates its flow based on temperature. This mechanism ensures that coolant is circulated only when needed, optimizing the engine’s overall performance. In extreme conditions, the system adap
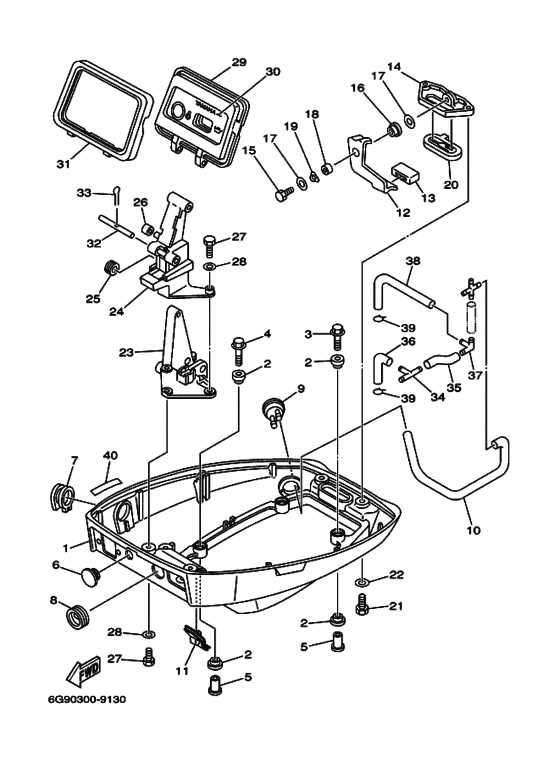
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and performance of a marine engine. It is responsible for directing exhaust gases away from the engine while minimizing backpressure and maintaining optimal airflow. Understanding the arrangement and components of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Typically, the configuration includes elements such as exhaust manifolds, pipes, and outlets. These components work together to facilitate the safe expulsion of gases generated during combustion. Proper alignment and sealing of these parts are vital to prevent leaks, which can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage to the engine.
Moreover, the system must be designed to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, ensuring durability and longevity. Regular inspections and maintenance of the exhaust configuration help to identify any wear or deterioration, allowing for timely repairs and replacements to maintain peak engine performance.
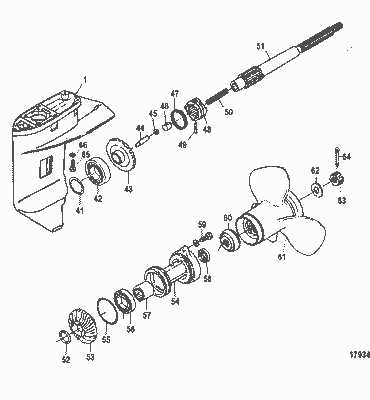
Gearcase and Propeller Assembly
The gearcase and propeller assembly is a crucial component of marine propulsion systems. This assembly ensures efficient power transmission from the engine to the propeller, allowing for optimal performance on the water. Understanding its structure and function is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components Overview
This assembly typically consists of various parts, including the gearset, housing, and propeller. Each element plays a significant role in facilitating smooth operation and maximizing thrust. Proper alignment and condition of these components are vital for the overall efficiency of the propulsion system.
Maintenance Tips
Maintenance Parts and Replacement Guide
This section provides essential information on components necessary for the upkeep and repair of a specific outboard motor. Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity, ensuring that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
Essential Components for Maintenance
- Fuel Filter
- Oil Filter
- Spark Plugs
- Impeller
- Water Pump Kit
- Carburetor Kit
Replacement Recommendations
When replacing any component, consider the following guidelines:
- Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility.
- Use high-quality components to ensure reliability and performance.
- Replace worn or damaged parts promptly to avoid further issues.
- Keep a maintenance log to track replacements and services performed.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
When operating a small outboard motor, several typical challenges may arise. Understanding these common problems can assist users in diagnosing and resolving issues efficiently, ensuring optimal performance during use.
Engine Starting Difficulties
One of the frequent issues is the difficulty in starting the engine. This can stem from various factors, such as fuel delivery problems, ignition system failures, or clogged filters. Regular maintenance and timely inspections can prevent such situations.
Overheating Concerns
Another prevalent problem is overheating, which can lead to significant damage if not addressed promptly. Causes may include insufficient cooling water flow, blocked passages, or malfunctioning thermostats. Identifying these factors early can prolong the motor’s lifespan.
| Issue |
Possible Cause |
Solution |
| Difficulty Starting |
Fuel blockage or ignition failure |
Check fuel lines and spark plugs |
| Overheating |
Clogged cooling passages |
Inspect and clean cooling system |
| Unusual Noises |
Worn components or debris |
Examine parts and clear obstructions |
| Stalling |
Fuel supply issues |
Check fuel filter and pump functionality |