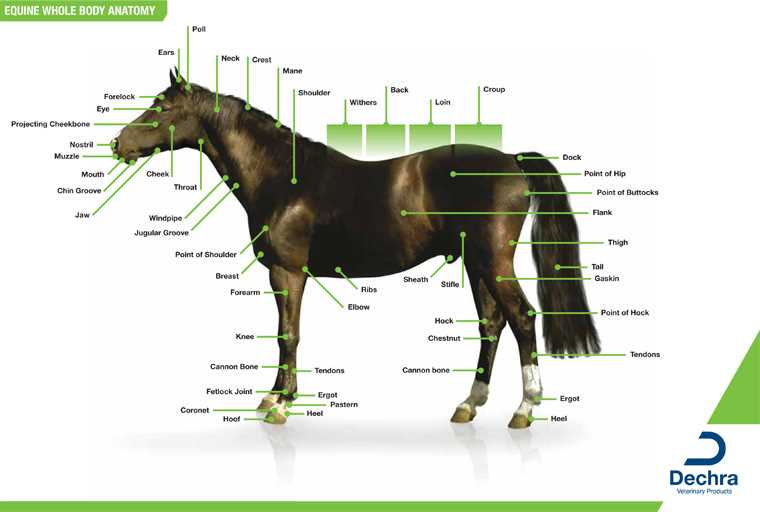
To fully grasp the physical structure of a large four-legged creature, it’s important to explore how each element contributes to its overall functionality. This complex system, made up of various regions and features, serves a wide range of purposes, from movement to strength.
Examining the connections between different segments reveals how this living organism is able to perform a variety of tasks. The interaction of muscular and skeletal components, as well as other vital areas, creates a harmonious system that supports both agility and power.
By identifying and studying these individual sections, one can better appreciate the intricacies involved in the movement and health of this majestic being. This knowledge allows for a deeper understanding of its behavior and overall well-being.
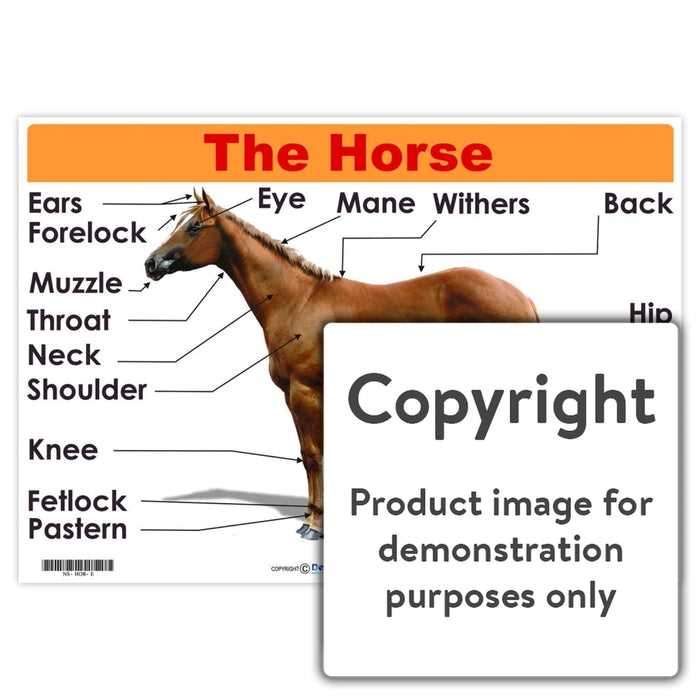
Horse Diagram of Body Parts
Understanding the various components of an equine’s structure is essential for anyone looking to improve their knowledge of these animals. Each element plays a vital role in the creature’s functionality and well-being, and recognizing these elements can greatly enhance one’s ability to care for and work with these animals effectively.
Key Areas of the Exterior

The exterior of these creatures is divided into multiple sections, each with specific functions and characteristics. The upper section includes areas responsible for mobility, strength, and posture, while the lower section features elements that ensure stability and balance. Recognizing the unique features of each section aids in identifying overall health and performance.
Significant Structural Features
In addition to their surface anatomy, these animals possess distinctive characteristics that impact their movement, agility, and endurance. From the frame that supports their large mass to the components that allow for swift and graceful movement, the relationship between various sections creates a well-coordinated system. By studying these connections, one can gain deeper insights into their care and management.
Main Regions of a Horse’s Anatomy
The external structure of this majestic animal can be divided into several key sections, each playing a crucial role in movement, balance, and overall functionality. These areas, though distinct in their functions, work in harmony to allow for graceful motion and strength. Understanding these regions is essential for better care and handling, as well as for those studying the physical attributes of this animal.
Top Section
This region includes the uppermost areas, providing stability and control. These sections are responsible for maintaining balance and enabling various forms of movement, from walking to galloping.
Lower Section
The lower areas consist of powerful muscles and joints that support the animal’s weight and allow for its incredible speed and endurance. Proper maintenance of these sections is critical for the animal’s well-being.
| Region | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top Section | Maintains balance, controls motion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower Section | Supports weight,
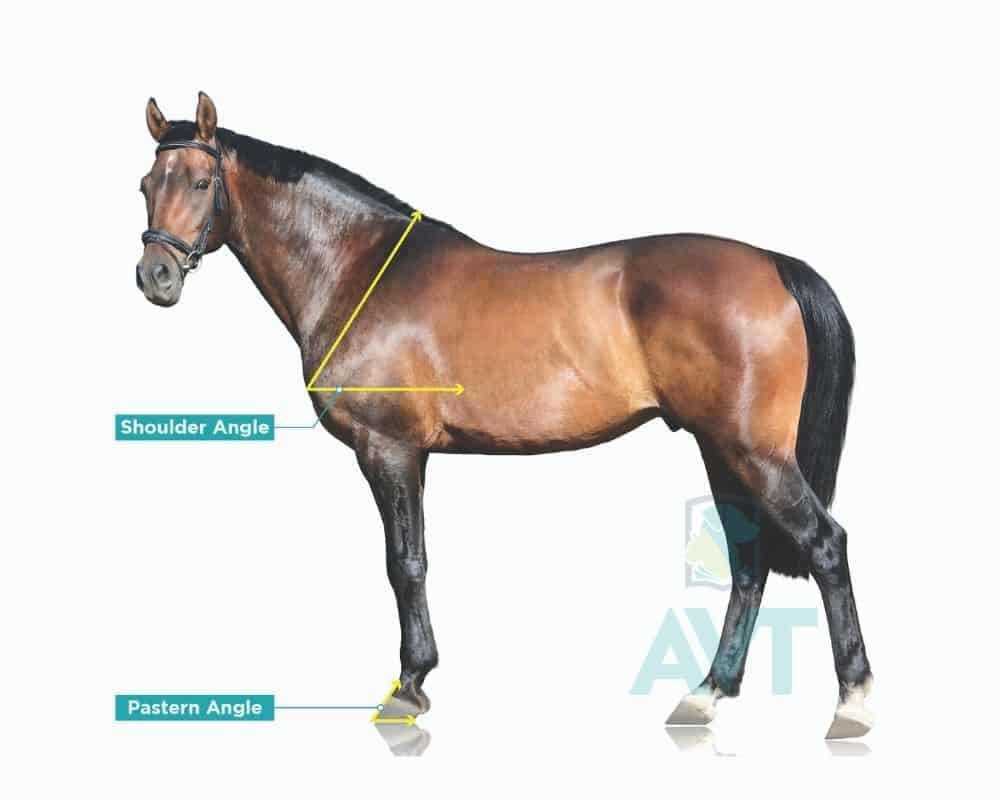
Detailed Structure of the Equine HeadThe front section of this animal’s anatomy plays a crucial role in its daily life, offering essential functions such as sensory perception, feeding, and communication. Its intricate makeup includes numerous interconnected elements that allow for a wide range of movement and capabilities.
Understanding the detailed makeup of this region helps in comprehending how these creatures navigate their environment and interact with it effectively. Overview of Limb Functions in HorsesIn many species, the limbs are essential for movement and stability, playing a crucial role in various physical activities. These appendages support the body’s weight, enabling swift movement, balance, and agility. Each section of the limb contributes to this functionality, ensuring fluid and efficient locomotion. Both the front and rear extremities perform distinct roles. The front limbs, for instance, absorb impact and provide balance during movement, while the rear ones generate power for propulsion. The coordination between these different parts allows for precise control and adjustment during various tasks, from running to standing still. The joints, muscles, and tendons within these extremities contribute to overall flexibility and strength, making them adaptable to diverse physical challenges. Understanding how these structures interact reveals the complexity and efficiency of movement in animals. Identifying the Major Muscles of a Horse
The muscular structure of this magnificent creature is crucial for its strength, speed, and agility. Understanding the key muscle groups helps in enhancing overall performance and maintaining health. These muscle networks play a pivotal role in movement, posture, and endurance, making them essential to study for anyone working with these animals. Key Muscles in the Forelimbs: The front limbs bear much of the weight during motion, relying on strong groups for stability and movement. These regions control the forward propulsion, while also supporting the balance during galloping or turning. Powerful Muscles in the Hindlimbs: The rear sections are the powerhouse of motion, providing thrust and acceleration. These muscles are vital for leaping, sprinting, and maintaining stability, making them central to any analysis of movement capabilities. By recognizing the various muscle groups, handlers and veterinarians can better care for and optimize the physical capabilities of these animals. Skeletal System Breakdown in HorsesThe framework of an equine individual serves as a critical support structure, enabling mobility, strength, and protection for vital organs. Understanding this intricate system is essential for anyone involved in the care and management of these magnificent creatures. This section explores the components of the framework, highlighting their significance and functionality. Key Components of the Framework
The structural system consists of various elements, each playing a specific role. The major components include:
Functionality and ImportanceThe elements of the framework work in unison to facilitate essential movements and behaviors. Some key functions include:
Understanding the intricacies of this supportive structure enhances our appreciation of these remarkable animals and informs better care practices. Understanding Equine Digestive System Layout
The intricate design of a equine’s digestive structure is crucial for effective nutrient absorption and overall health. This complex system consists of various segments, each playing a vital role in processing food. A comprehensive understanding of this configuration can enhance care practices and improve dietary management. The following table illustrates the key components involved in the digestive process:
Common Joint Locations in HorsesUnderstanding the fundamental areas where articulations occur is essential for anyone involved in equine care. These critical sites not only facilitate movement but also play a significant role in the overall well-being of these magnificent creatures. By recognizing where these connections are located, one can better appreciate their function and importance. Key articulation areas include:
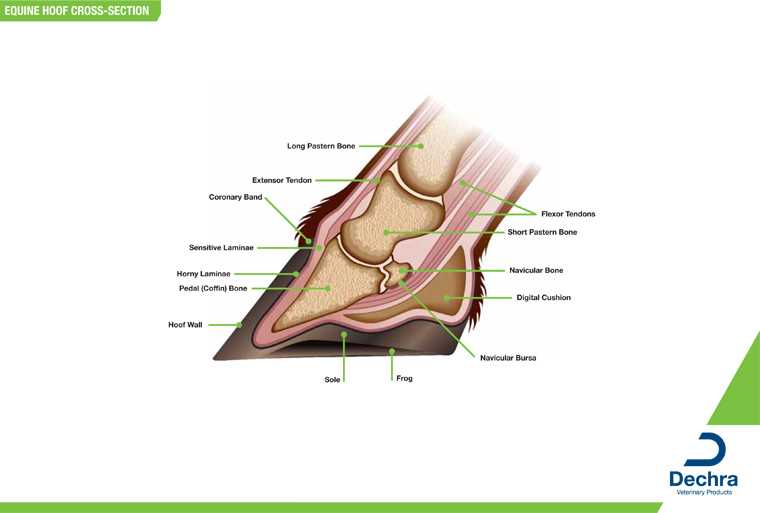
Awareness of these locations can aid in recognizing potential issues, enhancing training practices, and ensuring proper care for the animal. Exploring Hoof Anatomy and Structure
The intricate composition of the hoof plays a vital role in the overall function and health of an animal. Understanding the elements that contribute to its strength and resilience is crucial for ensuring mobility and well-being. The hoof is composed of multiple layers and structural features that work together to support the weight and movement. Key Structural Elements
The hoof can be divided into various sections, each with its own purpose. From the outer protective layer to the inner core, every part contributes to maintaining stability and balance. Below is an overview of these important sections.
|