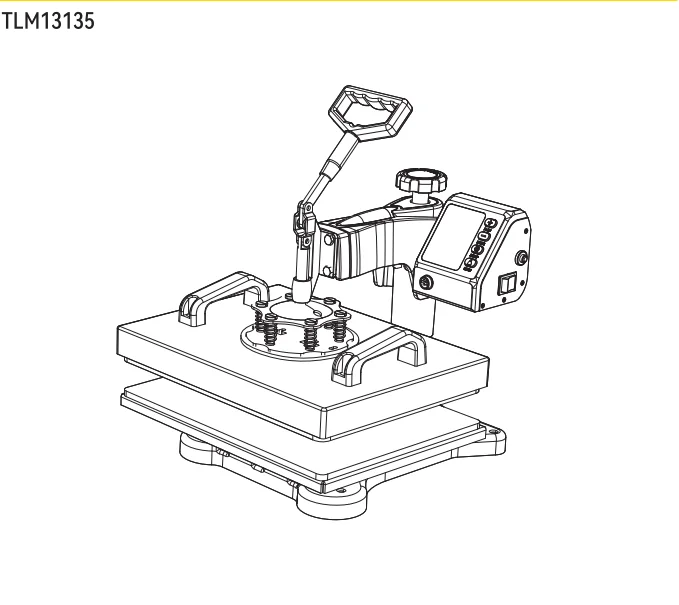
In the realm of crafting and customization, the functionality of transfer machines plays a pivotal role. By mastering the intricate layout and individual elements of these devices, users can enhance their proficiency and achieve remarkable results in their projects.
Each segment of these machines serves a distinct purpose, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the operation. Delving into the specifics of these components reveals the ultimate synergy between design and function, ensuring optimal performance.
Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice enthusiast, comprehending the assembly of these units will empower you to navigate the complexities of customization with confidence. A thorough grasp of these essentials is invaluable for achieving high-quality results in your creative endeavors.
Understanding Heat Press Components
This section aims to explore the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of thermal transfer equipment. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and achieving desired results.
- Heating Element: The core of the machine, responsible for generating the necessary temperature.
- Upper Plate: This surface applies pressure and facilitates contact with the material.
- Lower Plate: Supports the item being worked on, providing stability.
- Control Panel: Allows users to set temperature and timing, ensuring precision.
- Safety Features: Mechanisms that prevent overheating and ensure user protection.
Understanding these components allows users to effectively utilize the equipment and enhance their crafting or production process.
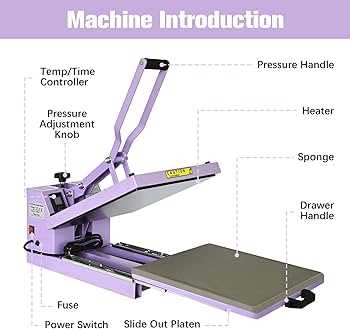
Essential Parts of a Heat Press
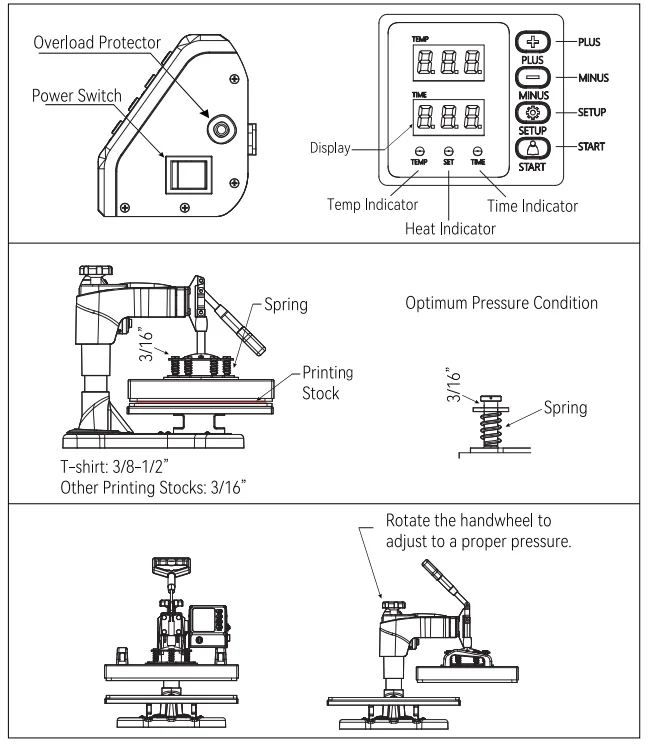
Understanding the core components of a transfer machine is crucial for achieving optimal results in your crafting projects. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring effective application and precision.
Upper Plate: The top surface is designed to apply pressure evenly, ensuring that the material adheres properly to the substrate. It is often heated to facilitate the transfer process.
Lower Plate: This base supports the item being customized and provides stability during the application of heat and pressure.
Temperature Control: A vital feature that allows users to set and maintain the desired heat level, crucial for different types of materials.
Pressure Adjustment: This mechanism enables the operator to modify the amount of pressure applied, which is essential for different projects and substrates.
Timer: A built-in feature that alerts users when the application time is complete, helping to avoid over or under-processing.
Control Panel: The interface where users can adjust settings such as temperature, time, and pressure, ensuring a tailored experience for various applications.
Safety Features: Important components that help prevent accidents, including auto shut-off mechanisms and heat-resistant handles.
By delving into these key components, users can maximize efficiency and achieve the ultimate quality in their creative endeavors.
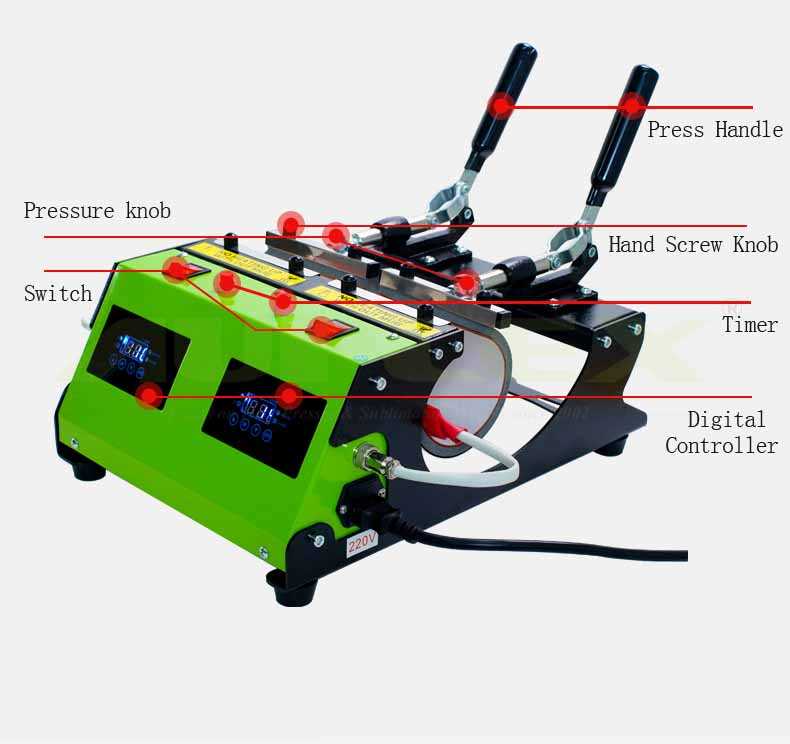
Functionality of Each Component
This section delves into the essential roles played by each element in the machinery used for applying designs onto various surfaces. Understanding these functions is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring effective operation.
Key Elements and Their Roles
- Heating Element: This component is responsible for generating the necessary temperature to activate the adhesive properties of transfer materials.
- Pressure Mechanism: It exerts the force needed to ensure proper contact between the substrate and the transfer, enhancing adhesion.
- Control System: This unit allows the user to set and monitor the temperature and time, ensuring precise application for different materials.
- Base Plate: The sturdy surface where the material rests; it helps maintain stability and supports even distribution of heat and pressure.
- Protective Cover: This feature prevents accidental contact with the heating element, ensuring safety during operation.
Additional Functional Components
- Thermostat: Regulates temperature, maintaining optimal conditions for the transfer process.
- Timer: Automatically counts down the required application time, allowing for consistent results.
- Handle: Facilitates easy operation, enabling users to open and close the unit smoothly.
- Feet or Base Stabilizers: Provide stability and prevent movement during use, ensuring consistent performance.
Each of these components works in concert to achieve the desired outcome, emphasizing the importance of understanding their individual contributions to the overall functionality of the equipment.
Common Heat Press Designs Explained

In the world of thermal transfer, various configurations are employed to achieve optimal results for different materials and applications. Understanding these designs can enhance efficiency and output quality, enabling users to select the most suitable model for their specific needs.
Clamshell Model
This design resembles a clam, opening from the top. It is compact and ideal for smaller workspaces. The straightforward operation allows for quick placement and removal of items, making it a popular choice among beginners.
Swing-Away Model
The swing-away type features a top platen that swings to the side, providing unobstructed access to the lower platen. This design reduces the risk of burning or damaging materials during placement, offering a safer option for intricate projects.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
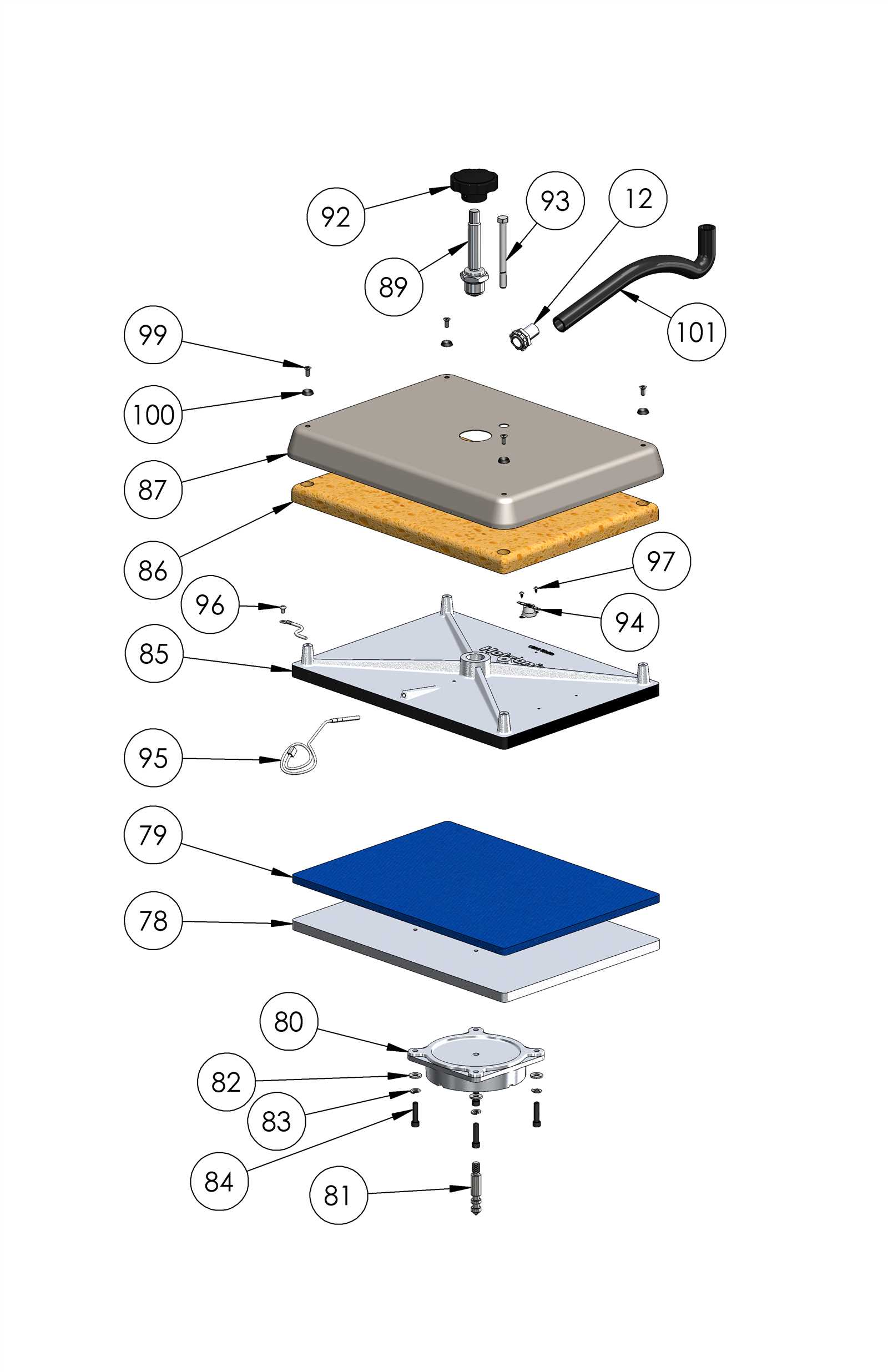
Proper care and regular upkeep are essential for ensuring the extended lifespan of your equipment. By following a few simple practices, you can avoid common issues and enhance performance, ultimately saving time and resources.
Here are some key recommendations to maintain your apparatus effectively:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Cleaning | Remove residue and buildup after each use to prevent interference with operation. |
| Check for Wear | Inspect components regularly for signs of damage or deterioration, replacing as necessary. |
| Calibrate Settings | Ensure that all settings are accurate to maintain optimal function and avoid overheating. |
| Follow Manufacturer Guidelines | Adhere to recommended maintenance schedules and practices provided by the manufacturer. |
| Store Properly | Keep the machine in a dry, cool environment to prevent moisture-related issues. |
Implementing these strategies will help you achieve better results and prolong the life of your equipment, making your investment more worthwhile.
Troubleshooting Heat Press Issues
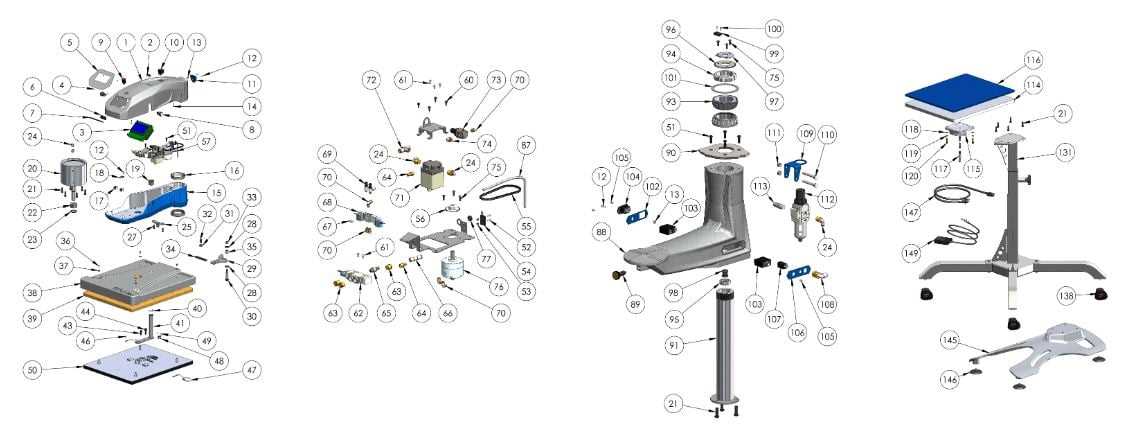
When operating a transfer machine, various challenges may arise that can affect performance and output quality. Understanding common problems and their solutions can help users maintain efficiency and achieve desired results. This section aims to provide guidance on identifying and resolving typical issues encountered during operation.
Common Problems and Solutions
One frequent issue is inconsistent temperature distribution. This can result in uneven transfers, leaving some areas under- or over-applied. To address this, check the calibration of the temperature settings and ensure that the heating element is functioning properly. Regularly inspecting the surface for wear or damage is also essential to maintain even heating.
Pressure and Alignment Concerns
Improper alignment or pressure can lead to subpar results. Users should verify that materials are correctly positioned before operation. Additionally, adjusting the pressure settings according to the thickness of the substrate being used is crucial. If issues persist, examine the machine for any obstructions or misalignments that may hinder effective application.
Choosing the Right Heat Press Model
Selecting the appropriate machinery for your crafting or production needs is crucial for achieving quality results. With a variety of options available, it’s important to understand what features and specifications will best suit your projects.
Consider the following factors when making your choice:
- Size: Determine the dimensions of the items you plan to work with. Larger surfaces allow for bigger designs, while smaller units are more portable.
- Type: Evaluate whether you need a clamshell, swing-away, or multi-function model based on your workspace and usage frequency.
- Temperature Range: Ensure that the machine can reach and maintain the required temperatures for your specific materials.
- Pressure Settings: Adjustable pressure is essential for different substrates. Look for models that allow you to customize this feature.
- Durability: Invest in a reliable option that can withstand frequent use and is built with quality materials.
Additionally, research brands and read reviews to gauge user experiences. A well-chosen model can enhance your efficiency and the quality of your final products.
Safety Precautions While Using Equipment
Ensuring a secure environment during the operation of machinery is crucial for both efficiency and well-being. Adhering to specific guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
General Guidelines
- Always read the user manual before starting any machinery.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Maintain a clean and organized workspace.
- Ensure all safety guards are in place and functional.
Operating Procedures
- Check for any visible damage to the equipment before use.
- Keep hands and loose clothing away from moving parts.
- Never leave the machine unattended while in operation.
- Turn off the equipment and unplug it when not in use.
Innovations in Heat Press Technology
The evolution of thermal transfer machinery has led to remarkable advancements, enhancing both efficiency and user experience. Recent developments focus on precision, speed, and versatility, allowing creators to explore new possibilities in their craft.
Smart Controls have emerged as a significant breakthrough, integrating digital interfaces that enable real-time adjustments. Users can monitor temperature and duration with greater accuracy, ensuring consistent results across various materials.
Additionally, energy-efficient designs are gaining traction. Manufacturers are prioritizing sustainability, creating models that consume less power while maintaining high performance. This not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes environmental impact.
Modular systems are also on the rise, offering customizable components that can be easily replaced or upgraded. This adaptability allows businesses to scale operations without needing to invest in entirely new machinery, making it a cost-effective solution for many.
Furthermore, advanced heating technologies, such as infrared and induction, are being implemented to improve heat distribution. These methods ensure uniform application across surfaces, significantly reducing the likelihood of inconsistencies.
Overall, the integration of these innovations is transforming the landscape of thermal transfer machinery, empowering users to achieve higher standards in their creative endeavors.