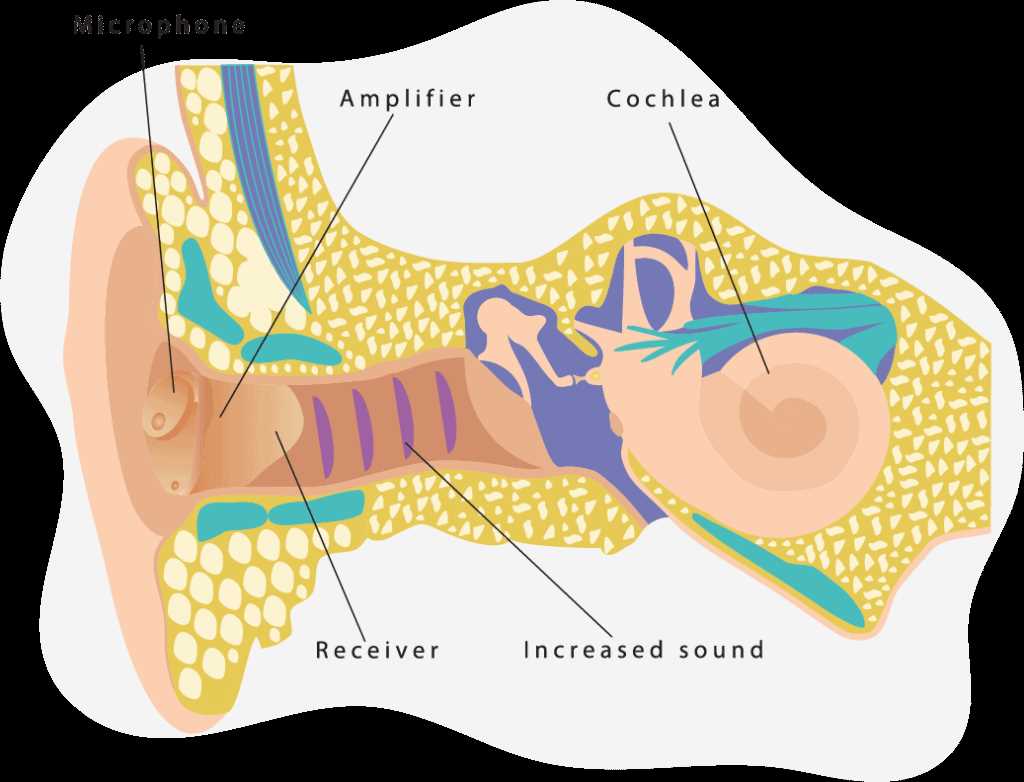
Devices designed to enhance auditory perception are complex instruments composed of various elements that work in unison to improve sound quality. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that users receive the best possible auditory experience, tailoring the device to individual needs and preferences.
Exploring these components reveals the intricate design and technology that contribute to effective sound processing. From sensors that capture sound waves to amplifiers that increase volume, understanding how these elements interact can demystify the technology behind modern auditory enhancement.
Additionally, recognizing the significance of each component allows users to make informed choices when selecting devices tailored to their lifestyle. By familiarizing oneself with the functionalities of these elements, individuals can better appreciate the advancements in auditory technology and how they contribute to improved communication and quality of life.
Understanding Hearing Aid Components
To grasp the intricacies of auditory enhancement devices, it is essential to explore the various elements that contribute to their functionality. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance, transforming sound waves into clear auditory signals. This understanding enables users to appreciate the technology behind these devices and enhances their experience.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Microphone | Catches sound from the environment and converts it into electrical signals. |
| Amplifier | Boosts the electrical signals to enhance sound intensity. |
| Receiver | Transforms amplified signals back into sound waves for the user to hear. |
| Battery | Provides the necessary power for the device to operate. |
| Control Circuit | Manages the device’s settings and processes incoming sounds for clarity. |
Types of Hearing Aids Explained
Understanding the various forms of auditory assistance devices can significantly enhance the experience for individuals with hearing challenges. Each type is designed with unique features and functionalities, catering to different needs and preferences. This section will explore the distinct categories available in the market today.
Behind-the-Ear Devices
These instruments sit comfortably behind the outer ear, connecting to a custom earpiece that fits snugly in the ear canal. Durability and ease of handling make them a popular choice, especially for those requiring higher amplification. They often come with advanced features, including wireless connectivity and customizable settings.
In-the-Ear Devices
Designed to fit directly in the ear, these models offer a discreet solution while providing excellent sound quality. Their compact design is particularly appealing for those who prefer a less visible option. Despite their size, they often include innovative technology that enhances user experience, such as background noise reduction and directional microphones.
Key Functions of Hearing Aid Parts
Understanding the essential components of auditory devices reveals their crucial roles in enhancing sound perception. Each element plays a significant part in transforming environmental noises into clearer signals tailored to the user’s needs.
The microphone captures external sounds, converting them into electrical signals. These signals are then processed by the amplifier, which boosts their strength for clearer transmission. The receiver takes these enhanced signals and transforms them back into audible sound, ensuring a seamless listening experience.
Additionally, the battery provides necessary power to sustain the device’s operation, while the controls allow users to adjust settings according to their preferences. Overall, each component is integral to ensuring optimal functionality and user satisfaction.
How to Read a Hearing Aid Diagram
Understanding a schematic representation of assistive devices is essential for users and professionals alike. These illustrations provide valuable insights into the structure and functionality of the devices, allowing for better maintenance and customization.
Here are some key elements to consider when examining such a representation:
- Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the common symbols used. Each symbol often corresponds to a specific component, such as microphones, amplifiers, and batteries.
- Labels: Pay attention to labels, which usually indicate the function of each part. They often include numerical values or letters that represent different features.
- Connections: Look for lines or arrows that depict how components are interconnected. Understanding these links is crucial for grasping how the device operates as a whole.
- Color Coding: Some illustrations use colors to differentiate between various functions or types of components. Recognizing these color cues can enhance your understanding.
By focusing on these elements, users can effectively interpret the schematic, leading to improved knowledge and troubleshooting capabilities.
Common Issues with Hearing Aid Parts
Understanding the challenges that can arise with assistive listening devices is essential for maintaining their functionality. Various components can experience problems that may affect overall performance. Identifying these issues early can lead to effective solutions and improved user experience.
Here are some typical challenges associated with these devices:
- Battery Problems:
- Short battery life
- Corrosion at the contacts
- Improper insertion of batteries
- Sound Quality Issues:
- Distorted audio
- Feedback noise
- Inconsistent volume levels
- Physical Damage:
- Cracks or breaks in the casing
- Worn-out or damaged tubing
- Loose or missing components
- Moisture Exposure:
- Accumulation of moisture in the device
- Corrosion of internal elements
- Malfunctioning due to dampness
- Software Glitches:
- Incompatibility with mobile devices
- Outdated firmware
- Issues with connectivity
Being aware of these common issues can help users take proactive measures to ensure their devices operate smoothly. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any concerns can significantly enhance the overall experience.
Maintenance Tips for Hearing Aids
Proper upkeep of these essential devices is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention can prevent common issues and enhance the user experience. Here are some effective strategies to maintain them in excellent condition.
1. Daily Cleaning: Regularly clean the external surfaces using a soft, dry cloth to remove dirt and moisture. This simple step helps prevent buildup that could impair functionality.
2. Moisture Management: Protect your devices from excessive humidity. Consider using a drying container or desiccant when not in use to keep them moisture-free.
3. Battery Care: Always replace batteries as recommended by the manufacturer. Store spare batteries in a cool, dry place to extend their lifespan.
4. Regular Checks: Frequently inspect the components for any signs of wear or damage. Addressing minor issues early can prevent more significant problems later.
5. Professional Servicing: Schedule periodic visits with an audiologist for a thorough checkup. Professional maintenance can help ensure everything is functioning as intended.
6. Avoid Exposure: Keep devices away from extreme temperatures and environments, such as saunas or swimming pools, which could cause damage.
Implementing these tips can significantly enhance the performance and durability of your devices, ensuring a better auditory experience.
Innovations in Hearing Aid Technology
Recent advancements in auditory devices have significantly transformed the way individuals experience sound. These innovations focus on enhancing clarity, connectivity, and user comfort, enabling a more personalized auditory experience. The integration of modern technology allows for improved functionality and user interaction, making these devices more effective and user-friendly.
Key Features of Modern Devices
Today’s auditory devices incorporate various features that address diverse needs and preferences. Some of the notable advancements include:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Connectivity | Integration with smartphones and other devices for seamless streaming and control. |
| Noise Reduction | Advanced algorithms that filter background noise for clearer sound in challenging environments. |
| Rechargeable Batteries | Elimination of disposable batteries, offering convenience and sustainability. |
| Customizable Settings | User-friendly apps that allow for personalized sound adjustments and environment settings. |
The Future of Auditory Devices
The future holds promising developments with the potential for even more sophisticated solutions. Research in artificial intelligence and machine learning may lead to devices that adapt automatically to various environments, providing users with a truly intuitive experience. Additionally, ongoing efforts in miniaturization and design will likely yield devices that are not only more powerful but also discreet and aesthetically pleasing.
Choosing the Right Hearing Aid Model
Selecting an appropriate device is crucial for ensuring optimal auditory experiences. With numerous options available, understanding individual needs and preferences is the first step toward making an informed decision.
Consider factors such as lifestyle, degree of hearing loss, and comfort. Some models are designed for active individuals, while others cater to quieter environments. Evaluating these aspects will help narrow down choices.
Next, explore various styles and technologies. From behind-the-ear to completely-in-canal designs, each type offers unique benefits. Additionally, advancements in digital sound processing can greatly enhance clarity and reduce background noise.
Finally, consult with a professional to receive personalized recommendations. A specialist can provide insights based on comprehensive assessments, ensuring the selected device meets your specific requirements effectively.