In the realm of architecture and design, the functionality and aesthetic appeal of transparent barriers play a crucial role. These structures not only enhance visibility but also serve practical purposes in various environments, from residential spaces to commercial buildings. A comprehensive analysis of their mechanisms reveals the intricate interplay of elements that contribute to their operation.
The exploration of these components sheds light on how they work in harmony to achieve seamless movement and efficiency. By breaking down the individual segments, we can appreciate the engineering and design principles that underpin their effectiveness. This knowledge is essential for professionals in the field, enabling them to innovate and improve upon existing designs.
Additionally, understanding the layout and relationships between these elements can guide maintenance and repair processes. With a clearer perspective on their configuration, stakeholders can ensure longevity and reliability, thus optimizing the user experience. This discussion aims to provide a detailed overview of the essential characteristics and functions that define this mechanism.
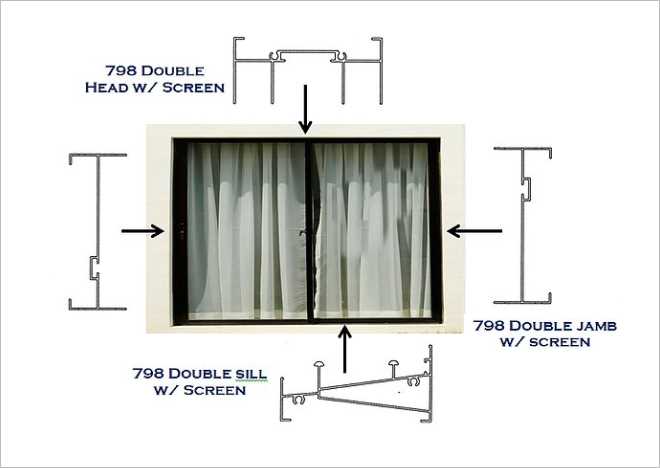
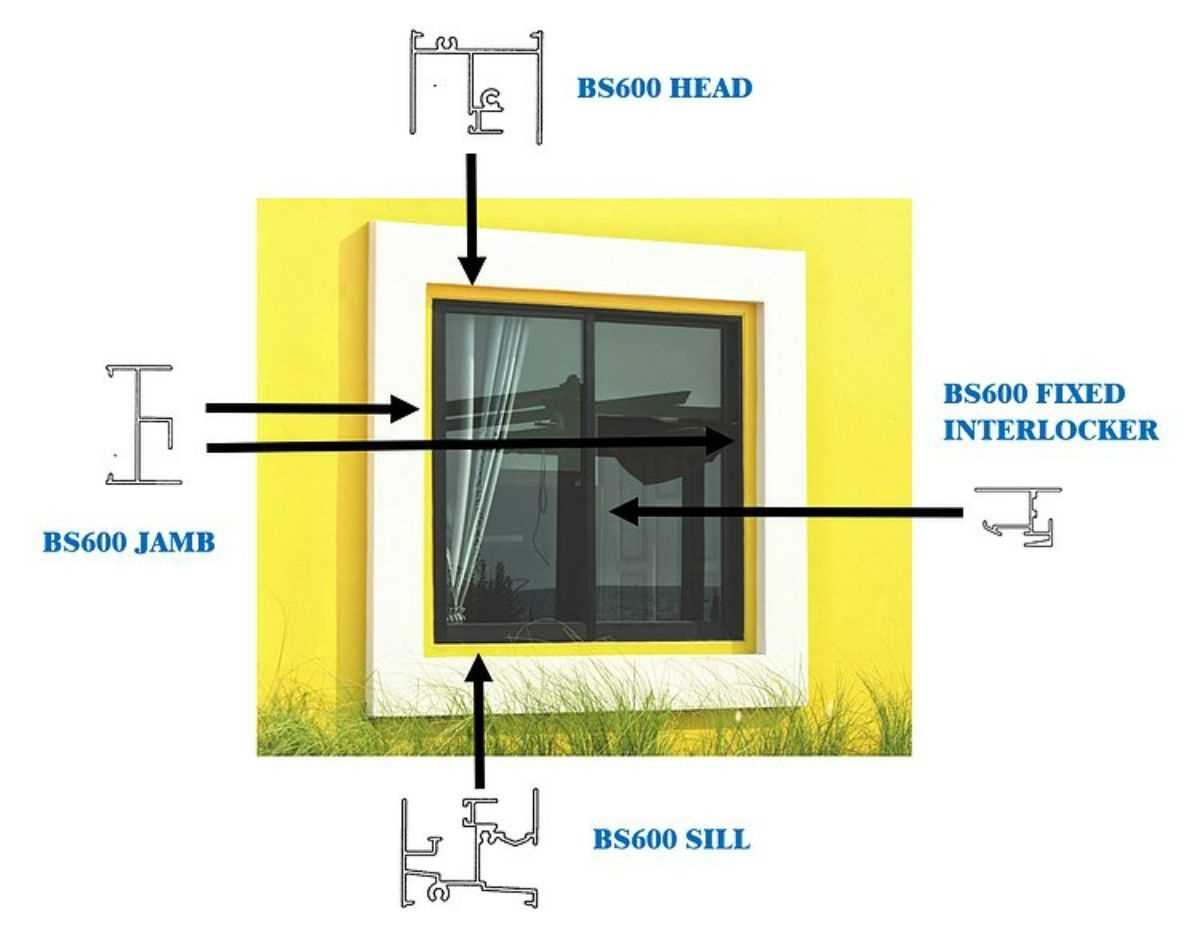
Understanding Sliding Window Mechanism
This section delves into a technique widely employed in data transmission and network communication, facilitating efficient management of data packets. By optimizing the flow of information, this method enhances performance and minimizes delays, ensuring a smooth exchange between systems. It allows for multiple segments of data to be sent simultaneously while maintaining control over the amount of information in transit.
At its core, this approach balances the needs of sender and receiver, preventing congestion and ensuring that the transmission is seamless. By establishing limits on the quantity of data that can be processed at any given time, it enables adaptive adjustments based on the current network conditions.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Optimizes data flow, reducing waiting times. |
| Control | Regulates the volume of data exchanged at once. |
| Congestion Avoidance | Minimizes the risk of overload in network traffic. |
| Adaptability | Adjusts transmission rates based on feedback. |
In summary, this methodology is essential for modern communication systems, enhancing reliability and speed in data exchange. Understanding its principles is crucial for anyone involved in networking and data management.
Key Components of Sliding Windows
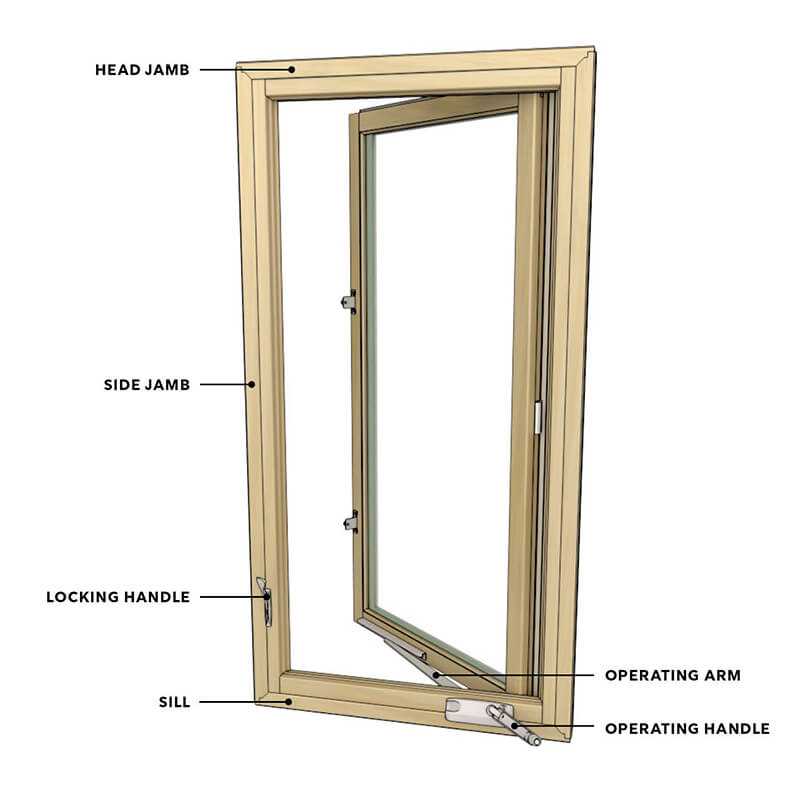
The functionality and efficiency of modern openings rely on several crucial elements that work together harmoniously. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these elements is essential for anyone interested in enhancing their living spaces.
Framework and Track System
The framework serves as the structural backbone, providing stability and support. A well-engineered track system is integral to the seamless movement of the panels. It allows for easy operation while minimizing wear over time. Materials used in these systems often influence both durability and maintenance requirements, making thoughtful selection important.
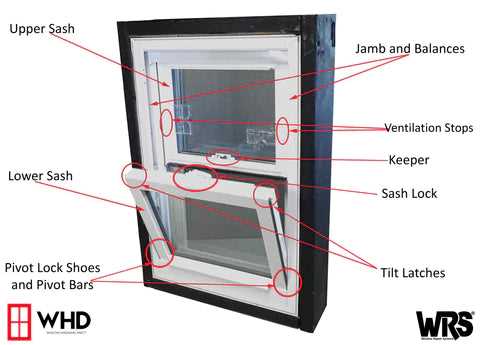
Glazing and Sealing
Glazing significantly impacts insulation and light transmission. Quality glass enhances energy efficiency while offering clarity and aesthetic value. Equally important are the sealing mechanisms that prevent drafts and moisture ingress, ensuring a comfortable interior environment. Proper sealing not only contributes to energy savings but also prolongs the lifespan of the entire installation.
Benefits of Sliding Windows in Design
Incorporating versatile openings into architectural designs offers numerous advantages that enhance both functionality and aesthetics. These elements allow for seamless transitions between indoor and outdoor spaces while optimizing light and ventilation. Their efficient use of space contributes to a more open and airy environment.
- Space Efficiency: These structures occupy minimal floor space, making them ideal for smaller areas.
- Enhanced Natural Light: The expansive glass surface allows ample sunlight, creating brighter interiors.
- Improved Airflow: Their design facilitates better cross-ventilation, promoting a healthier atmosphere.
- Accessibility: The ease of operation enables effortless access to outdoor areas.
- Modern Aesthetic: Their sleek and contemporary look adds a stylish touch to any setting.
Choosing these features can significantly elevate the overall design, providing both practical benefits and visual appeal.
Common Materials Used for Windows
When considering the construction and design of openings in structures, various substances are utilized to enhance durability, aesthetic appeal, and energy efficiency. Understanding the characteristics of these materials is crucial for making informed choices that cater to both functionality and style.
Popular Material Choices
Among the frequently employed substances, each offers unique benefits and limitations that influence overall performance and maintenance requirements.
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | Natural insulation, aesthetic appeal | Requires maintenance, susceptible to rot |
| Vinyl | Low maintenance, energy-efficient | Limited color options, can fade |
| Aluminum | Durable, lightweight | Poor insulation, can corrode |
| Fiberglass | Strong, excellent insulation | Higher cost, limited design options |
Conclusion
Selecting the right material for openings is essential for enhancing both the aesthetic and functional qualities of a space. Each option presents distinct advantages that cater to different needs and preferences, ultimately impacting the overall experience of the environment.
Installation Process for Sliding Windows
The installation of a particular type of opening involves several crucial steps to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This process is essential for creating a seamless interface between the interior and exterior environments, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality.
Begin by preparing the opening, ensuring it is clean, level, and free from any debris. Accurate measurements are vital to guarantee a snug fit for the new structure. Once the area is ready, the next phase involves positioning the frame securely within the designated space, verifying that it is aligned properly to facilitate smooth operation.
After securing the frame, it’s important to insulate and seal around the edges. This step prevents drafts and moisture from entering the living space, contributing to energy efficiency. Carefully applying weather stripping can further enhance the seal, providing additional protection against the elements.
Finally, install the moving components, ensuring they glide effortlessly along their tracks. Test the functionality to confirm that everything operates smoothly. With these steps completed, the installation is successful, allowing for an inviting flow of light and air into the area.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the extended lifespan of mechanical systems requires consistent care and attention. By implementing effective maintenance practices, you can significantly reduce wear and tear, enhance performance, and avoid costly repairs. Below are some essential tips to keep your equipment functioning optimally for years to come.
Regular Inspection
- Conduct frequent visual checks for any signs of wear or damage.
- Listen for unusual noises that may indicate underlying issues.
- Ensure that all components are securely fastened and properly aligned.
Lubrication and Cleaning
- Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to minimize friction.
- Remove dust and debris to prevent buildup that can affect performance.
- Utilize recommended cleaning agents to maintain surface integrity.
By following these practices, you can significantly enhance the reliability and durability of your systems, ensuring they remain effective for a long time.
Energy Efficiency in Sliding Windows
Improving thermal performance in modern architectural designs is essential for reducing energy consumption and enhancing comfort. By focusing on effective sealing and insulation techniques, structures can minimize heat loss in colder months and limit heat gain during warmer seasons. This approach not only benefits the environment but also leads to significant cost savings on energy bills.
The integration of advanced materials and technologies plays a crucial role in achieving optimal energy efficiency. Double or triple glazing, combined with low-emissivity coatings, can drastically improve thermal resistance. Additionally, utilizing frames made from materials with high insulating properties ensures that energy transfer is minimized, creating a more stable internal climate.
Moreover, the design of these features can also contribute to overall energy savings. Strategic placement and orientation can maximize natural light while reducing reliance on artificial lighting. Implementing operable elements allows for better airflow, enhancing ventilation without the need for energy-intensive systems.
Investing in high-performance solutions not only elevates the aesthetic appeal of a structure but also significantly enhances its functionality. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, prioritizing energy-efficient elements in construction and renovation projects is a step towards a greener future.
Popular Styles and Variations Available
In the realm of modern architectural design, a multitude of styles and configurations cater to diverse aesthetic preferences and functional requirements. Each variation offers unique advantages, making it essential for homeowners and designers to explore the options available to find the perfect match for their needs.
| Style | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Casement | Characterized by its hinged design, allowing for outward opening. | Excellent ventilation, unobstructed views, easy cleaning. |
| Sash | A traditional style featuring sliding panels that move vertically. | Classic appeal, easy operation, space-saving. |
| Bay | Projects outward from the main structure, creating a cozy nook. | Enhanced natural light, panoramic views, additional seating area. |
| Picture | Fixed design providing a clear, unobstructed view of the outside. | Maximizes light entry, ideal for framing scenic views. |
| Awning | Opens outward from the top, ideal for rain protection. | Good ventilation, keeps rain out, privacy enhancement. |