| Piston |
A moving component that transfers the force from combustion to the crankshaft, converting thermal energy into mechanical motion. |
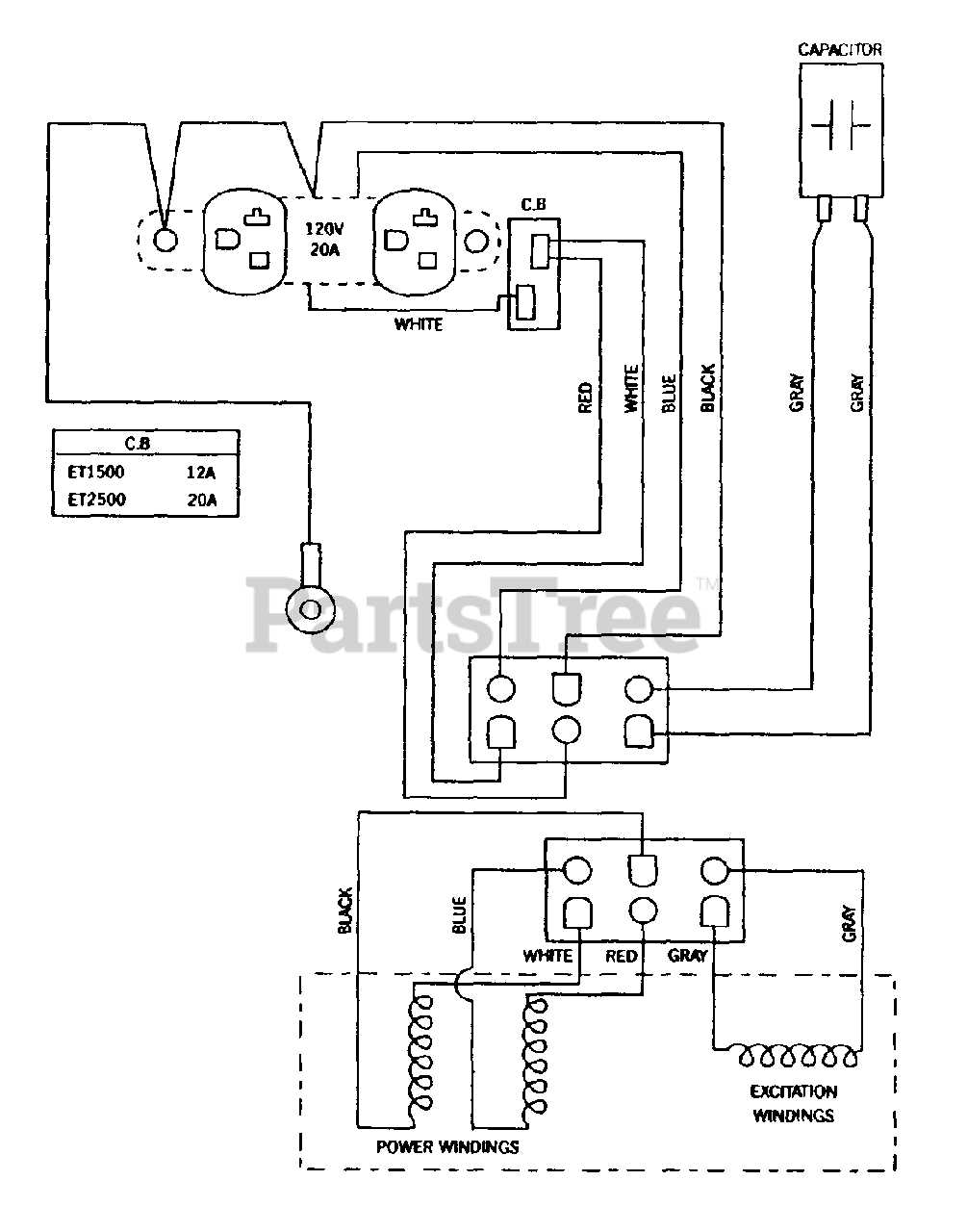
Electrical System Layout and Functionality

The electrical system is a crucial component in any power-producing equipment, ensuring seamless operation and energy distribution. Understanding its structure and how various elements work together is essential for efficient performance. The layout of this system includes several interconnected modules that regulate and control the flow of electricity, ensuring stable and reliable output.
Each element in the system plays a specific role, from the initial conversion of energy to the final delivery of power. These components work in harmony, preventing overloads and optimizing the efficiency of the machine. By maintaining proper functionality, the system ensures consistent operation even in demanding conditions, contributing to overall reliability and safety.
Fuel System Diagram and Operation
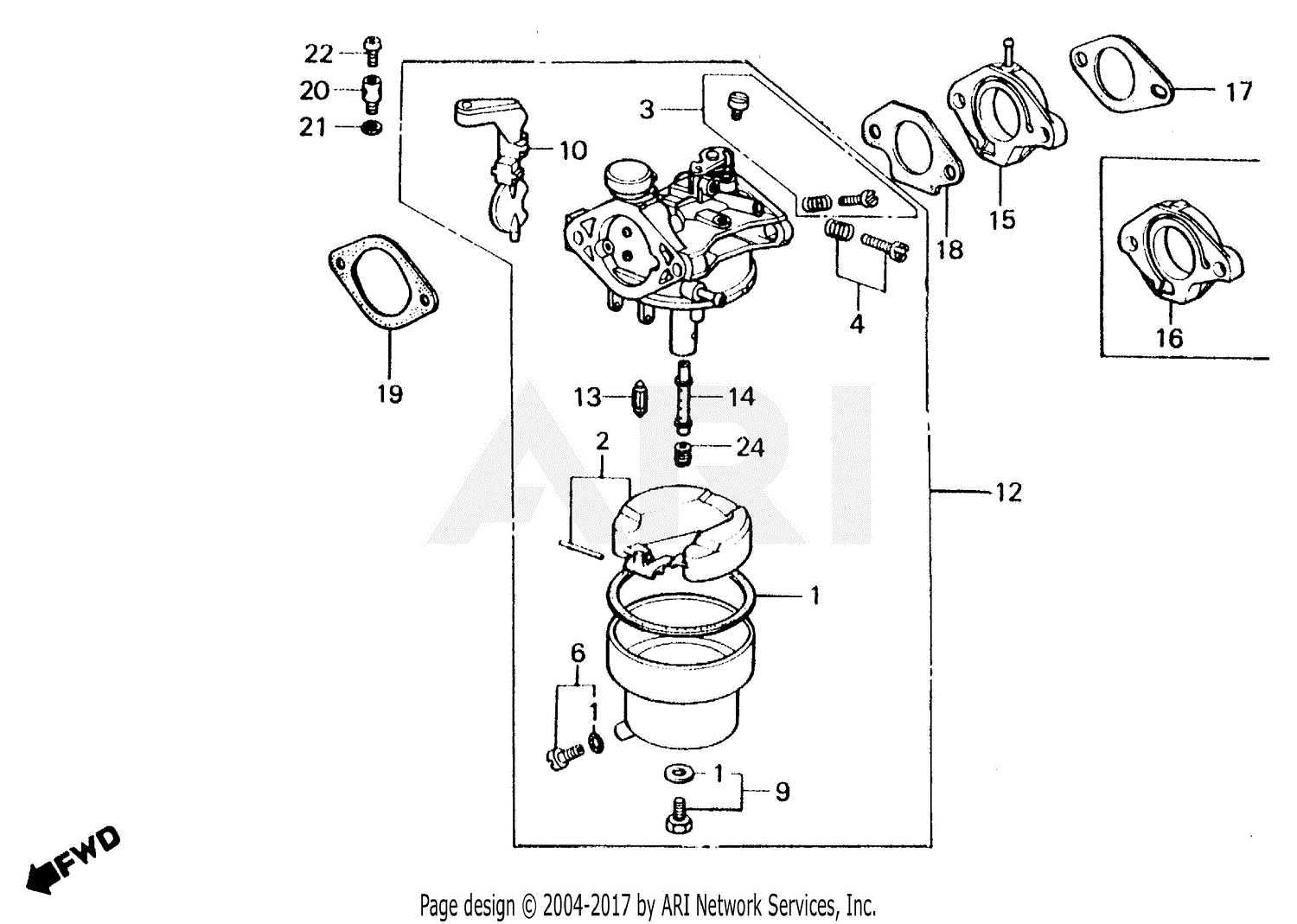
The fuel system is a critical component responsible for managing the flow and supply of fuel to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Understanding how this system works can help in identifying potential issues and ensuring proper maintenance.
Key Components of the Fuel System
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel and supplies it to other parts of the system.
- Fuel Pump: Transfers fuel from the tank to the system under the required pressure.
- Fuel Lines: Channels through which fuel flows from one component to another.
- Fuel Filter: Cleans impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Sprays fuel into the combustion chamber in a fine mist for efficient burning.
Operation of the Fuel System
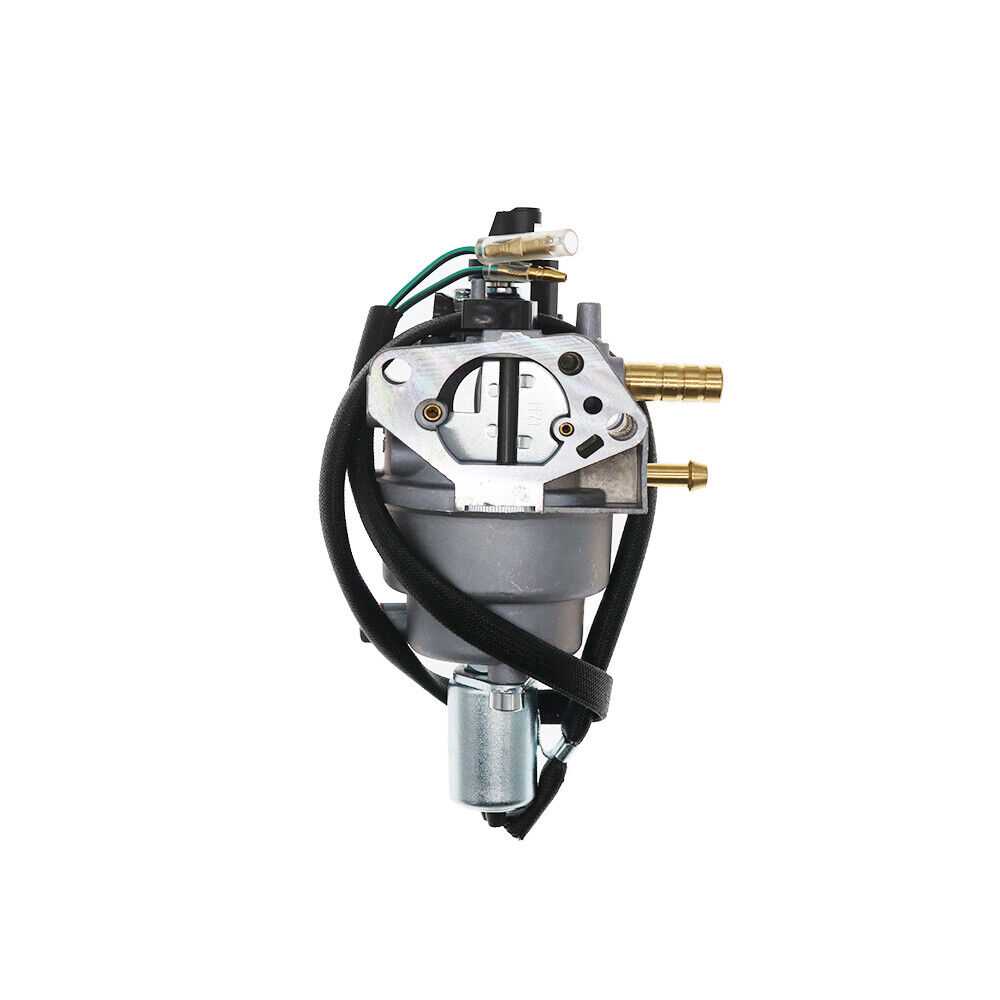

The operation begins with fuel being drawn from the tank through the pump and delivered via the lines. The filter ensures that only clean fuel reaches the injectors, where it is atomized for efficient combustion. This process ensures the
Cooling Mechanism in Firman Generators
Efficient cooling is essential for ensuring smooth operation and longevity of power-producing machines. Overheating can cause significant wear and damage, making it critical to maintain proper temperature control during use.
There are various methods employed to keep the internal components from excessive heat. The design includes several systems working together to dissipate warmth and maintain stability during continuous operation.
- Air-based systems: Many units rely on fans to circulate air over the critical components, helping to disperse heat efficiently.
- Liquid cooling: In some cases, a liquid-based system is utilized to absorb heat, providing more effective cooling in high-performance models.
- Heat sinks: Certain parts are equipped with metal surfaces that conduct and radiate heat away from sensitive areas, preventing damage.
These techniques work in harmony to keep temperatures in check, ensuring durability and optimal functionality.
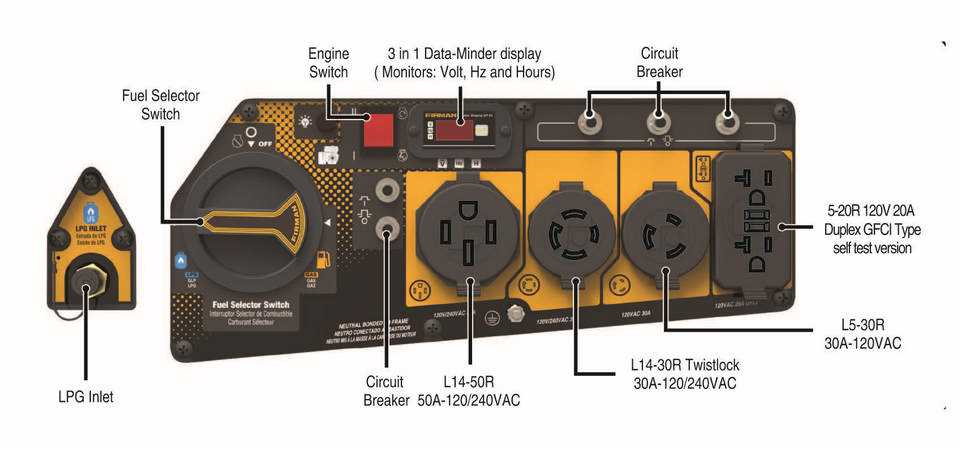
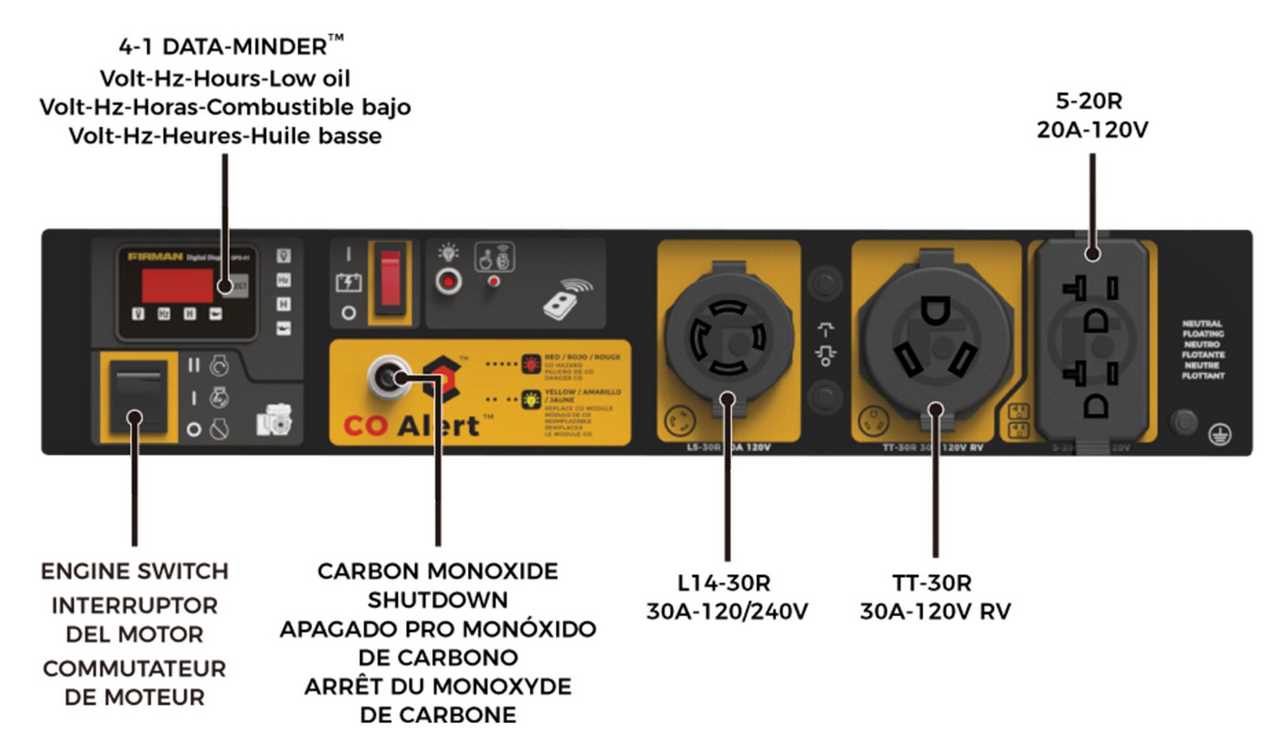
Control Panel and User Interface Features

The control panel serves as the central hub for user interaction, providing essential tools and indicators for efficient operation. Understanding its components enhances usability and ensures optimal performance during various tasks.
- Intuitive Layout: A well-organized interface allows for quick navigation, enabling users to access necessary functions without confusion.
- Power Indicators: Visual signals, such as LED lights, display the operational status, helping users monitor performance easily.
- Control Switches: Easy-to-reach buttons or switches facilitate quick adjustments to power output and settings.
- Digital Displays: Real-time data regarding output, fuel levels, and maintenance reminders provide critical information for effective management.
Familiarity with these features not only enhances user experience but also promotes safety and efficiency during operation.
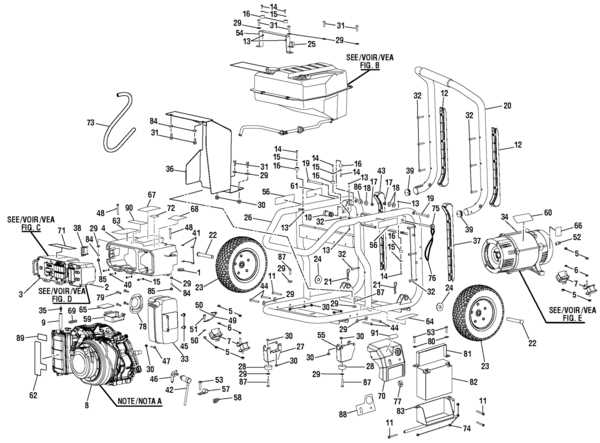
Exhaust System Parts and Their Role

The exhaust mechanism plays a crucial role in the functionality of any engine-driven machine. Its primary purpose is to manage the byproducts of combustion, ensuring that harmful gases are effectively expelled while maintaining optimal performance. Understanding the components of this system is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Main Components of the Exhaust System
- Muffler: This component reduces noise produced during the exhaust process. It uses a series of chambers and baffles to dampen sound waves, providing a quieter operation.
- Exhaust Pipe: This pipe channels exhaust gases away from the engine. It is typically made from durable materials to withstand high temperatures and corrosion.
- Catalytic Converter: This vital part converts harmful emissions into less toxic substances before they exit the system. It helps in reducing pollutants and meets environmental regulations.
- Exhaust Manifold: This piece connects the engine to the exhaust system, collecting exhaust gases from multiple cylinders and directing them into the exhaust pipe.
Functions of Each Component
- The muffler minimizes noise pollution, making the operation more pleasant for users and surrounding environments.
- The exhaust pipe ensures the safe exit of gases, preventing any back pressure that could affect engine performance.
- The catalytic converter plays a significant role in protecting the environment by transforming harmful emissions into safer compounds.
- The exhaust manifold efficiently gathers exhaust gases, optimizing the flow and enhancing overall engine efficiency.
Understanding the roles of these elements is vital for effective maintenance and ensuring optimal performance of the machinery. Regular checks and timely replacements can lead to better efficiency and longer service life.
Maintenance and Replacement of Key Components
Proper upkeep and timely substitution of essential elements are critical to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent unexpected failures and enhance efficiency, reducing downtime and repair costs. Understanding the components that require routine attention is fundamental for effective management.
Regular Inspection Procedures

Implementing a systematic approach to examining the equipment is essential. Key components should be checked for wear, corrosion, and other signs of deterioration. Monitoring fluid levels and ensuring connections are secure contributes to the overall reliability of the system. Creating a schedule for these inspections will help maintain operational standards and identify potential issues before they escalate.
Timely Replacement Strategies

When components show signs of fatigue or malfunction, prompt replacement is vital. Utilizing high-quality substitutes can significantly improve performance and extend the lifespan of the system. It is important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications when selecting new elements to ensure compatibility and efficiency. Keeping a stock of critical components can minimize downtime and facilitate swift repairs when needed.
Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
When operating machinery that provides backup power, it’s essential to recognize and resolve typical challenges that may arise. Many users encounter performance discrepancies, which can stem from various underlying causes. Understanding these issues helps ensure reliable operation and longevity.
First, if the unit fails to start, check the fuel levels and ensure that the ignition system is functioning correctly. Low fuel or a faulty ignition system can prevent the engine from engaging. Additionally, inspecting the battery for charge can resolve many starting issues.
Secondly, unusual noises during operation often signal potential problems. Rattling or grinding sounds may indicate loose components or worn bearings. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to these noises can prevent further damage.
Finally, fluctuations in output voltage can affect the performance of connected devices. This issue may arise from an overloaded unit or issues within the voltage regulator. Monitoring load levels and ensuring proper connections can mitigate these fluctuations.