Language is a complex system that allows us to communicate thoughts, emotions, and ideas effectively. Within this intricate web of expression, various elements work in harmony to create meaning and clarity. Each component plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall structure and function of our communication.
By examining the fundamental categories that form the foundation of language, we can gain insight into how we construct sentences and convey our messages. Recognizing these categories not only enhances our understanding but also improves our ability to articulate thoughts clearly and coherently.
This exploration invites us to delve into the essential classifications that define how words interact and function within sentences. Grasping these classifications is the ultimate key to mastering effective communication, enriching both our writing and speaking skills.
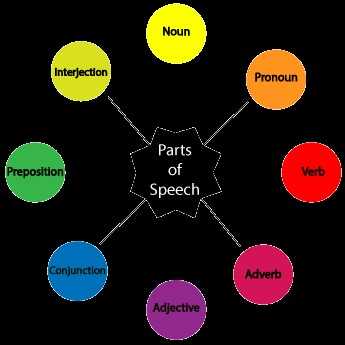
Diagram of Parts of Speech
Understanding the various components that form the backbone of language is essential for effective communication. Each element plays a distinct role, contributing to the richness and clarity of expression. This section explores the different classifications that make up the structure of language.
Categories of Language Components
Each classification serves a unique function, influencing how we convey thoughts and ideas. Below is a brief overview of these categories:
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
| Nouns | Represent people, places, things, or ideas. |
| Verbs | Express actions or states of being. |
| Adjectives | Modify nouns, providing additional detail. |
| Adverbs | Alter verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, often indicating manner or degree. |
| Pronouns | Substitute for nouns to avoid repetition. |
| Prepositions | Show relationships between different elements in a sentence. |
| Conjunctions | Connect words, phrases, or clauses. |
| Interjections | Express emotions or reactions, often standing alone. |
Significance of Understanding Components
Recognizing these classifications not only aids in grammar and composition but also enhances the ability to analyze and construct sentences effectively. A firm grasp of these elements is vital for anyone looking to improve their linguistic skills.
Understanding Parts of Speech

Grasping the fundamental elements that construct sentences is essential for effective communication. Each component plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall meaning and structure of language. Recognizing these elements enhances both writing and comprehension skills, allowing for clearer expression of thoughts and ideas.
Categories of Language Elements
These essential building blocks can be categorized into various types, each serving a specific function. Here are the main classifications:
- Nouns: Represent people, places, things, or ideas.
- Verbs: Indicate actions, occurrences, or states of being.
- Adjectives: Describe or modify nouns, providing additional detail.
- Adverbs: Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, often indicating manner, place, or time.
- Pronouns: Substitute for nouns to avoid repetition.
- Prepositions: Show relationships between nouns or pronouns and other words in a sentence.
- Conjunctions: Connect words, phrases, or clauses.
- Interjections: Express strong emotions or sudden bursts of feeling.
The Importance of Each Component
Understanding how these classifications interact is crucial for crafting coherent sentences. Here’s why each element is vital:
- Nouns: Serve as the foundation, representing the subjects or objects of sentences.
- Verbs: Bring action or existence to the subjects, forming the core of statements.
- Adjectives: Enrich descriptions, allowing for more vivid imagery.
- Adverbs: Provide nuance, helping clarify how actions are performed.
- Pronouns: Enhance fluency by preventing redundancy.
- Prepositions: Create connections, providing context and clarity.
- Conjunctions: Ensure coherence, linking ideas and clauses seamlessly.
- Interjections: Convey emotion succinctly, adding personality to language.
Nouns: Foundations of Language
Nouns serve as the cornerstone of communication, providing a means to identify and categorize the world around us. They embody the essence of objects, concepts, and beings, forming the bedrock upon which sentences are constructed.
Types of Nouns
- Common Nouns: General terms for a class of objects or entities.
- Proper Nouns: Specific names that distinguish individual items.
- Collective Nouns: Words that represent groups of individuals or things.
- Abstract Nouns: Concepts that cannot be physically touched, like ideas or feelings.
Importance of Nouns
- Provide clarity and specificity in communication.
- Facilitate the expression of thoughts and ideas.
- Serve as subjects or objects in sentences, essential for structure.
Verbs: The Action Words
In the realm of language, there exists a category that encapsulates movement, existence, and change. These dynamic elements play a pivotal role in conveying what characters do or what states they experience. Their presence in sentences brings vigor and clarity, allowing for the expression of ideas and emotions in an engaging manner.
Types of Verbs

Verbs can be classified into various types based on their functions and characteristics. Understanding these distinctions enhances comprehension and usage.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Action Verbs | Words that describe physical or mental actions. |
| Linking Verbs | Words that connect the subject to additional information about the subject. |
| Helping Verbs | Auxiliary words that assist the main verb in expressing tense, mood, or voice. |
Importance of Verbs
Verbs serve as the foundation of sentences, allowing for the construction of meaningful statements. They facilitate the expression of thoughts and actions, making communication both effective and lively. Mastering the use of these essential words is crucial for fluency and eloquence in any language.
Adjectives and Adverbs: Describing and Modifying
In the realm of language, certain words play a crucial role in adding depth and clarity to our expressions. These terms enrich our sentences by providing more information about nouns and verbs, allowing for a vivid portrayal of actions, qualities, and states. Understanding their function enhances communication and comprehension.
Understanding the Roles
Descriptive words, such as adjectives, give attributes to nouns, while modifying words, like adverbs, adjust verbs or even other modifiers. This duality enables speakers and writers to convey precise meanings and nuances in their messages.
Examples of Usage
| Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Adjective | The quick fox | Describes the noun “fox” with speed. |
| Adverb | Runs swiftly | Modifies the verb “runs” to indicate manner. |
Pronouns: Substituting for Nouns
Pronouns serve a crucial function in language by taking the place of nouns, thus streamlining communication. This substitution allows speakers and writers to avoid repetition and maintain clarity in their expressions. By using these versatile words, we can convey ideas more fluidly while focusing on the action or context rather than the entities involved.
Types of Pronouns
There are several categories of pronouns, each serving a distinct purpose:
- Personal Pronouns: These refer to specific people or things, such as “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” “we,” and “they.”
- Possessive Pronouns: These indicate ownership, including “mine,” “yours,” “his,” “hers,” “its,” “ours,” and “theirs.”
- Demonstrative Pronouns: These point to specific items, like “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those.”
- Interrogative Pronouns: Used to ask questions, such as “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “what,” and “which.”
- Relative Pronouns: These connect clauses or phrases, including “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “which,” and “that.”
- Indefinite Pronouns: These refer to nonspecific items or people, such as “someone,” “anyone,” “everyone,” “nobody,” “everything,” and “many.”
The Role of Pronouns in Communication
Using pronouns enhances the fluidity of language and aids in clarity. Here are a few advantages:
- Reduction of Redundancy: Pronouns help avoid the awkward repetition of nouns, making sentences smoother.
- Contextual Clarity: They allow for easy reference to previously mentioned subjects, thus maintaining coherence.
- Emphasis on Action: By replacing nouns, the focus can shift to the actions or descriptions rather than the entities.
In conclusion, pronouns are indispensable tools in our linguistic toolkit, enabling us to communicate more effectively and efficiently.
Prepositions: Linking Ideas
Prepositions serve as crucial connectors in our language, enabling us to convey relationships between different elements in a sentence. They guide readers through thoughts and enhance clarity, making the flow of ideas more cohesive.
These linking words can indicate various relationships, such as:
- Location: showing where something is situated
- Time: indicating when an action occurs
- Manner: explaining how something is done
- Reason: providing justification or purpose
Understanding how to use these connectors effectively can elevate writing and improve communication. Here are some common prepositions:
- in
- on
- at
- between
- for
By mastering these words, one can create a more engaging and articulate narrative, ultimately enhancing the overall impact of the message.
Conjunctions: Connecting Thoughts

In the realm of language, certain words serve a pivotal role in linking ideas and creating a cohesive flow in communication. These connecting terms not only join individual elements but also enhance clarity and comprehension in both written and spoken forms. Understanding their function can significantly improve one’s ability to express complex thoughts succinctly.
The Role of Conjunctions
Connecting words can be categorized based on their specific functions. They play a crucial role in establishing relationships between various components within sentences. Here are the primary categories:
- Coordinating Conjunctions: These unite elements of equal importance.
- Subordinating Conjunctions: These introduce dependent clauses, providing additional context.
- Correlative Conjunctions: These work in pairs to link balanced phrases.
Examples in Action

To illustrate their usage, consider the following examples:
- Coordinating: “I wanted to go for a walk, but it started to rain.”
- Subordinating: “Although it was late, she decided to continue studying.”
- Correlative: “Either you join us for dinner, or we will eat without you.”
By mastering these connecting words, one can craft sentences that are not only more engaging but also easier to understand. This enhances the overall effectiveness of communication, whether in writing or conversation.
Interjections: Expressing Emotion
Interjections serve as vibrant bursts of feeling within language, allowing speakers to convey their emotional states succinctly. These expressions capture a wide range of sentiments, from joy and surprise to frustration and sorrow, enriching communication with their immediacy.
Understanding the Role
Functioning independently, interjections often stand alone, providing a powerful means to express reactions. Words like Wow!, Ouch!, and Hooray! resonate with listeners, invoking shared feelings and enhancing engagement.
Examples in Context
Consider how an interjection can transform a simple sentence: “I won!” can become “Yay! I won!” This shift amplifies the emotional impact, making it more relatable and exciting.
The Ultimate Impact
Ultimately, these expressions serve as an essential tool in human interaction, providing clarity and depth. They bridge the gap between thought and feeling, allowing for richer conversations and stronger connections.