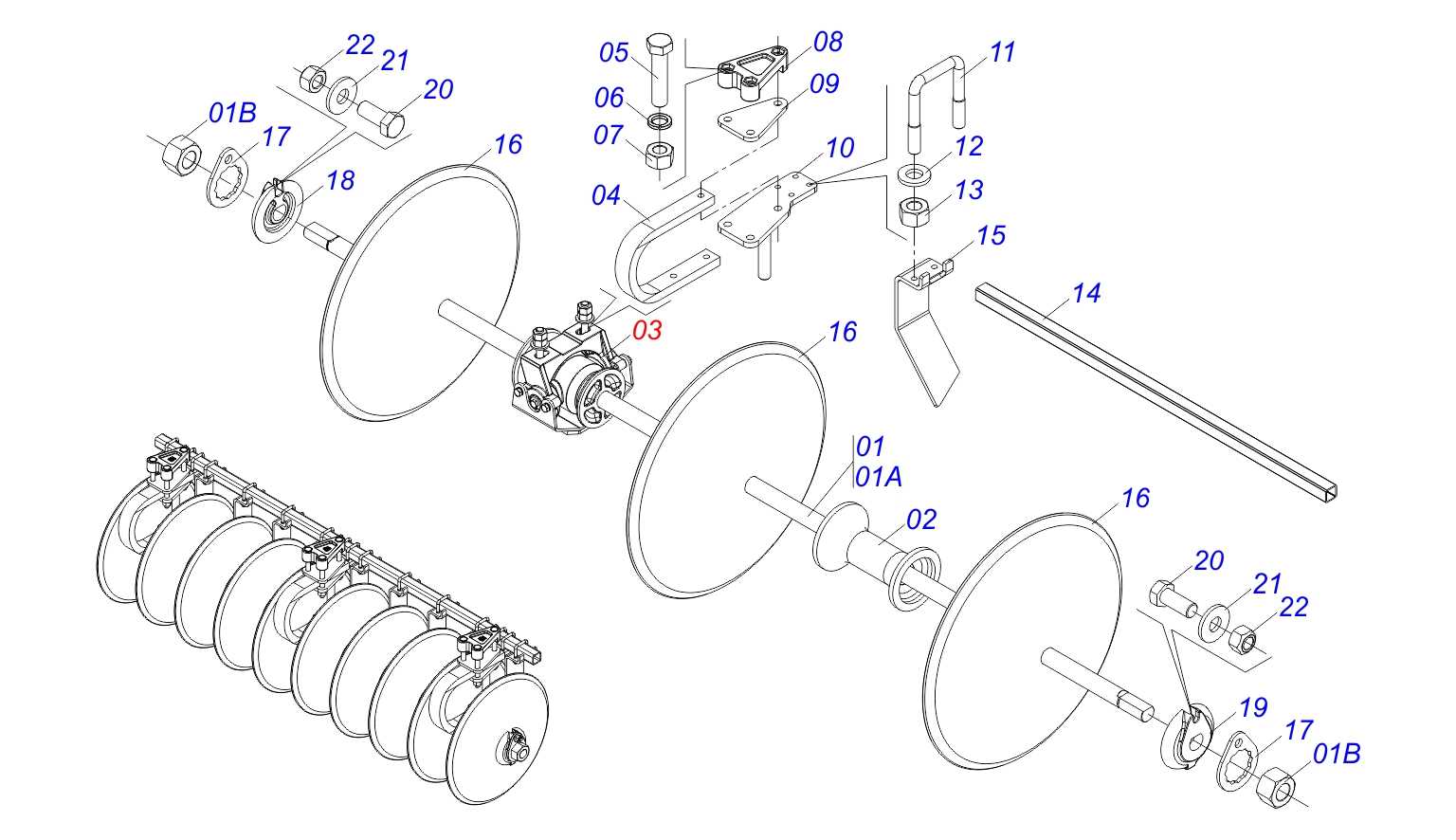
Understanding the critical elements of your off-road machine can make all the difference when it comes to ensuring its smooth performance and longevity. Whether you’re an experienced rider or just starting out, having a clear picture of how each mechanism operates allows you to address issues swiftly and prevent potential breakdowns. Familiarizing yourself with the core components is a crucial step in effective upkeep.
In this section, we’ll delve into the essential mechanical systems that power your rugged vehicle. From engine configurations to the suspension setup, knowing how these systems work together ensures better handling and a safer riding experience. Regular maintenance of these elements will not only extend the life of your machine but also enhance overall performance on challenging terrains.
By exploring the key elements of your vehicle’s structure, you’ll gain insight into how to keep it running smoothly and reliably, no matter the conditions. Paying attention to these critical systems is vital for optimal functionality and long-term durability.
Overview of the Coleman CT200U-EX Parts Diagram

This section provides a comprehensive look at the components and structure of a popular off-road vehicle. Understanding the layout and key elements can help maintain and repair the machine efficiently. Each section is designed to guide enthusiasts through the different systems and their respective functions, ensuring a smoother experience when handling repairs or replacements.
Main Mechanical Elements
The vehicle consists of multiple critical systems that contribute to its overall performance. These are primarily divided into areas responsible for movement, control, and safety. Below, we outline these elements for a clearer understanding.
- Engine assembly: The heart of the machine, driving all major functions.
- Transmission: Essential for managing power distribution and speed control.
- Fuel system: Ensures consistent power through regulated fuel delivery.
- Brake system: Vital for ensuring reliable stopping power.
Frame and Suspension
Understanding the Engine Components
The engine is the core of any mechanical system, driving the motion and power that make vehicles functional. By exploring its individual components, one can gain insight into how each part contributes to the overall performance and efficiency. A deeper understanding of these elements can help in maintaining, troubleshooting, and improving engine functionality.
Below is a breakdown of the essential parts and their roles:
- Cylinder: This is the space where fuel combustion occurs, generating the necessary force to drive the system forward.
- Piston: A crucial element that moves within the cylinder, converting the energy from combustion into mechanical power.
- Crankshaft: The component responsible for translating the piston’s linear motion into rotational energy, which powers the vehicle’s movement.
- Spark Plug: Ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, initiating the combustion process that powers the engine.
- Carburetor: A device that mixes air and fuel in the correct ratio to ensure efficient combustion inside the cylinder.
Understanding the inte
Brake System and Its Key Parts
The brake mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and control of any vehicle. It allows for the gradual or immediate slowing down, as well as complete stopping, providing the rider with confidence during operation. Without a properly functioning braking system, maneuverability and safety are compromised.
One of the central components of this system is the brake lever, which initiates the process. The caliper then engages to apply force to the rotor or drum, depending on the type of system. The brake pads or shoes, in turn, create friction that ultimately decelerates the vehicle. Equally important is the brake cable, which connects the lever to the caliper, ensuring the necessary force is transmitted effectively.
Another vital aspect is the rotor or drum, which receives the pressure applied by the caliper and helps convert k
Suspension and Frame Design Breakdown
The suspension and frame architecture play a crucial role in ensuring stability, comfort, and durability. This section will explore the core principles behind the structure, highlighting how different components work together to provide a smooth and controlled ride across various terrains.
Frame Structure
The frame is the foundation of any vehicle, designed to endure stress while maintaining a lightweight profile. Key aspects include:
- Material selection: Lightweight yet strong materials, such as steel or aluminum, are used to balance durability with agility.
- Reinforcement points: Strategic reinforcement areas enhance structural integrity where high stress is most likely, such as around joints and the suspension mounts.
- Geometry: The frame’s shape directly influences stability and maneuverability, offering a balance between flexibility and strength.
Suspension System
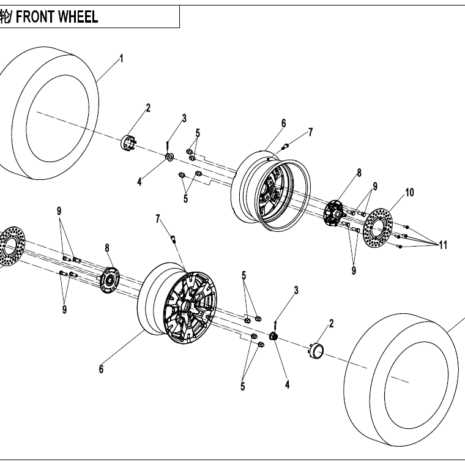
The suspension system works in tandem with the frame, absorbing shocks and ensuring the vehicle maintains traction and comfort. Key features include:
- Shock absorbers: These components dampen the impact from rough surfaces, m
Electrical Wiring and Connections Guide
This section provides essential information on the electrical systems of small vehicles, focusing on the wiring and connections that ensure optimal performance. Understanding how to properly connect and maintain electrical components is crucial for safety and efficiency. A clear grasp of the layout and functionality of these systems can help troubleshoot common issues and enhance the overall reliability of the vehicle.
When working with electrical systems, it’s vital to familiarize yourself with the various components, such as batteries, switches, and wiring harnesses. Each part plays a significant role in the operation of the vehicle, and knowing how they interact can prevent potential malfunctions. Before making any modifications, ensure that you have a complete understanding of the circuit layout, including the power flow and grounding methods.
To begin, carefully inspect all connections for corrosion or damage. Loose or frayed wires can lead to electrical failures or shorts, so it is essential to secure all terminals tightly. Use appropriate connectors and ensure that they are rated for the specific voltage and current levels required. In addition, consider using heat-shrink tubing or electrical tape to protect exposed connections from moisture and debris.
When replacing or upgrading components, always adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications regarding wire gauge and connector types. Properly sized wires can handle the necessary current without overheating, reducing the risk of fire or component damage. If modifications are made, consult wiring schematics to confirm that changes do not interfere with the vehicle’s electrical integrity.
Finally, routine maintenance is key to preserving the longevity of electrical systems. Periodically check connections, clean terminals, and test the functionality of switches and lights. Staying proactive can help identify issues early and prevent more significant problems in the future.
Fuel System Components and Functions
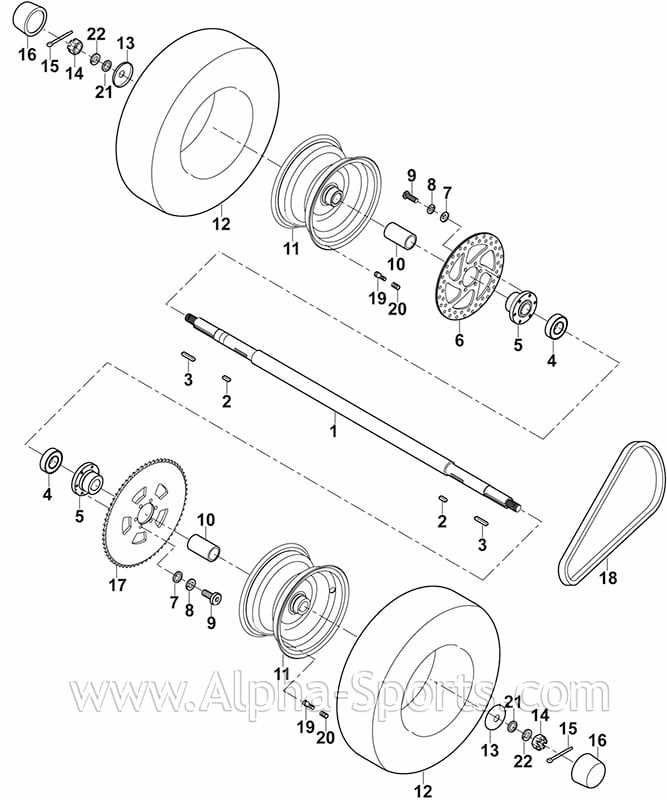
The fuel system plays a critical role in the operation of small engine vehicles, ensuring a steady supply of energy to power the engine. Understanding its components and their functions is essential for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency.
- Fuel Tank: The primary reservoir for storing fuel. It holds the necessary liquid that feeds the engine, designed to minimize evaporation and leakage.
- Fuel Line: A tube that transports fuel from the tank to the engine. It is designed to withstand pressure and prevent leaks, ensuring a smooth flow of fuel.
- Fuel Filter: A crucial component that removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. This helps protect the engine and enhance its longevity.
- Fuel Pump: An essential device that moves fuel from the tank to the engine. It maintains consistent pressure, allowing for efficient combustion.
- Carburetor: A mechanism that mixes air and fuel in the correct proportions for combustion. It plays a vital role in engine performance, affecting acceleration and fuel efficiency.
- Fuel Injector: In systems with fuel injection, this component delivers precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber, optimizing efficiency and reducing emissions.
- Choke: A device that restricts airflow to the engine during startup, enriching the fuel mixture to facilitate easier ignition in cold conditions.
Each of these components works together to create a reliable and efficient fuel system, contributing to the overall performance and functionality of the vehicle.
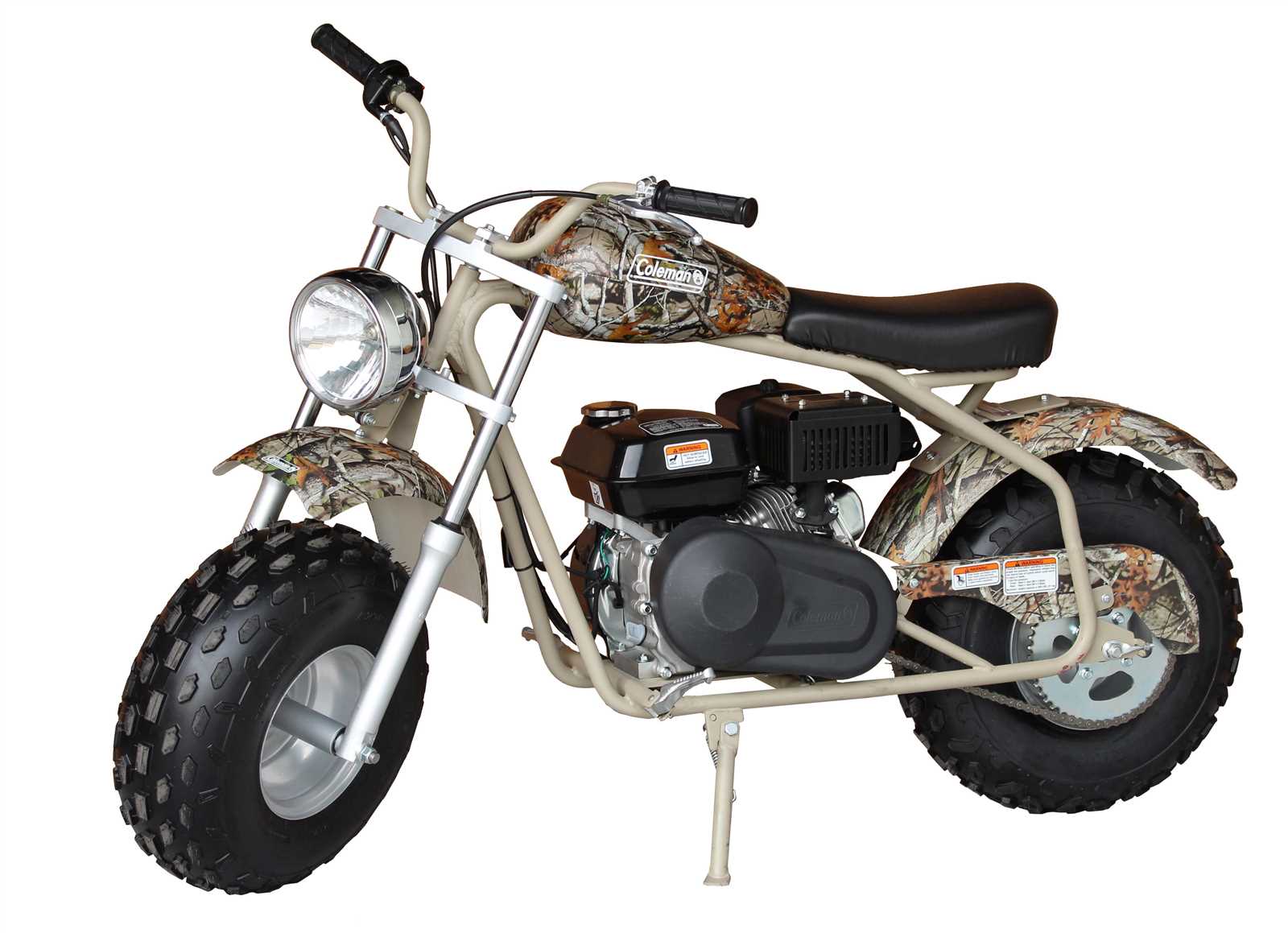
Handlebars, Controls, and Cable Setup

The proper arrangement of handlebars and controls is essential for ensuring a smooth and safe riding experience. A well-designed setup not only enhances comfort but also allows for better maneuverability and control. This section focuses on the critical components involved in the configuration of handlebars, controls, and cables, emphasizing their roles in optimizing performance.
Components of the Handlebar System
The handlebar system consists of several key elements that work together to provide stability and control:
- Handlebars: These are the primary interface between the rider and the vehicle, allowing for steering and balance.
- Grips: Attached to the ends of the handlebars, grips provide comfort and traction for the rider’s hands.
- Controls: Including throttle, brakes, and switches, these elements are crucial for operating the vehicle safely.
- Cables: Essential for transmitting input from the controls to the various mechanical systems, ensuring responsive action.
Setting Up Controls and Cables

To achieve optimal performance, careful attention must be given to the installation and adjustment of controls and cables:
- Adjust Handlebar Height: Ensure that the handlebars are positioned at a comfortable height for the rider, allowing for natural arm positioning.
- Install Grips: Securely attach the grips to the handlebars, ensuring they are free from slippage.
- Position Controls: Arrange the throttle, brake, and other controls within easy reach of the rider’s hands.
- Route Cables: Carefully route cables to avoid sharp bends or kinks, which can impede performance.
- Test Functionality: After installation, test all controls to confirm they operate smoothly and efficiently.
A well-executed handlebar and control setup contributes significantly to the overall riding experience, allowing the operator to navigate with confidence and ease.
Exhaust System: Structure and Maintenance
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of small engines. Its primary function is to direct harmful gases away from the engine and reduce emissions, while also minimizing noise. Understanding the components and maintenance practices of this system is essential for ensuring optimal operation and longevity.
Components of the Exhaust System
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipes.
- Exhaust Pipes: Transport exhaust gases from the manifold to the muffler.
- Muffler: Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases as they exit the system.
- Exhaust Tip: The final part that expels gases into the atmosphere, often designed for aesthetic appeal.
Maintenance Tips
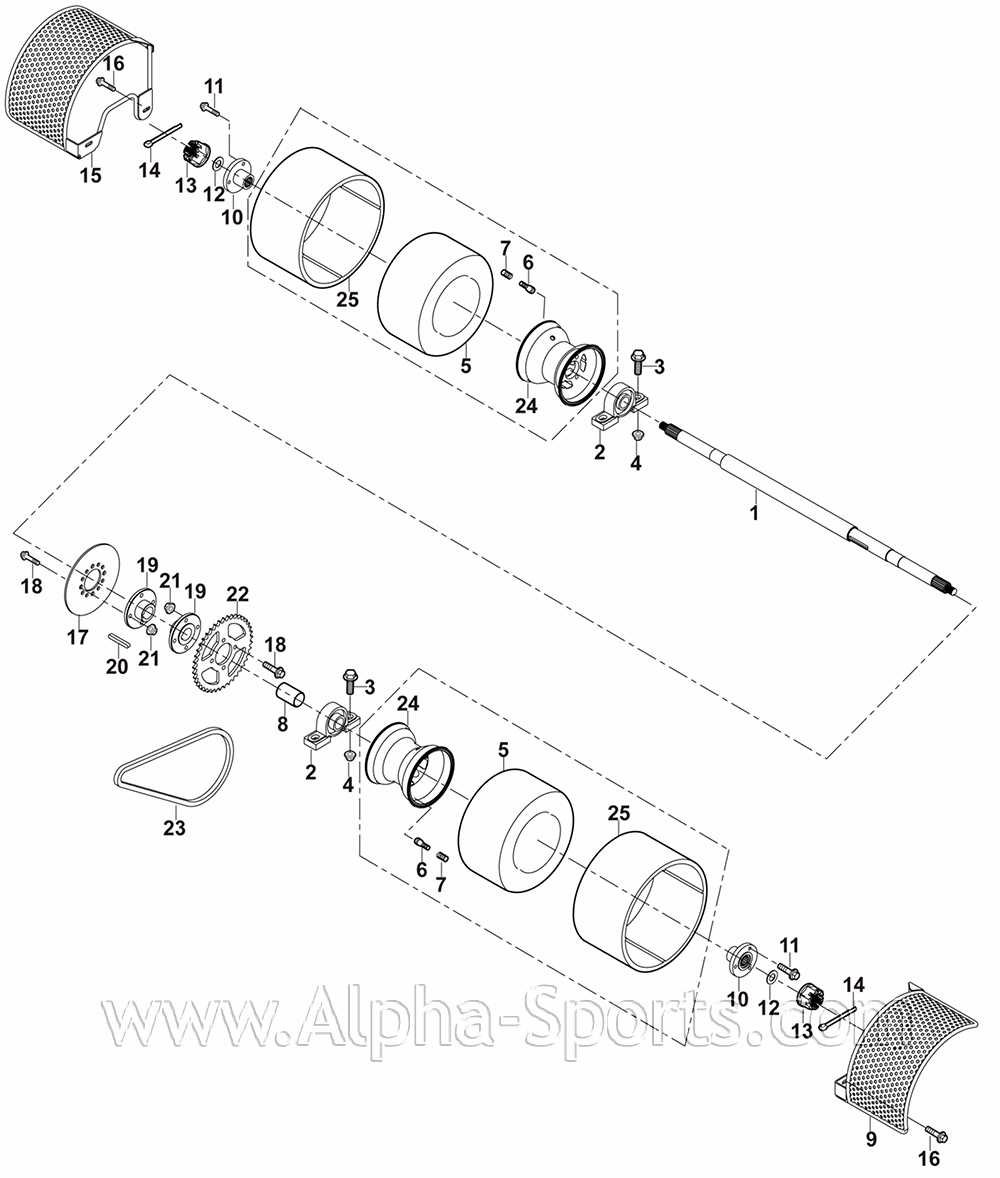
- Regularly inspect the exhaust components for any signs of rust or damage.
- Ensure that all connections are secure to prevent leaks, which can lead to decreased performance.
- Clean the exhaust system periodically to remove carbon build-up and improve efficiency.
- Check for unusual noises that may indicate issues with the muffler or pipes.
Proper upkeep of the exhaust system not only enhances performance but also contributes to a more environmentally friendly operation. By following these guidelines, users can ensure their engines run smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Parts

When dealing with mechanical equipment, it’s essential to understand that various components can lead to performance issues. Identifying these problems early can prevent costly repairs and ensure smooth operation. This section will explore typical challenges associated with these components and provide guidance on resolving them effectively.
Identifying Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of malfunction is the first step in effective troubleshooting. Here are some common indicators to watch for:
- Unusual noises during operation
- Loss of power or acceleration
- Increased vibration
- Fluid leaks
- Inconsistent performance
Common Solutions
Once you’ve identified the symptoms, you can proceed with the following troubleshooting strategies:
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion.
- Inspect for Wear: Look for signs of wear on components that may need replacement.
- Test Electrical Systems: Use a multimeter to check for proper voltage and current flow.
- Consult the Manual: Refer to the equipment’s manual for specific troubleshooting procedures.
- Seek Professional Help: If issues persist, it may be time to consult a professional technician.
By systematically addressing these common issues, you can enhance the reliability and longevity of your equipment.