
Understanding the structure of a wind instrument is essential for both beginners and seasoned musicians. Each component plays a unique role in producing the harmonious sounds that define its voice. Knowing the names and functions of these elements can greatly enhance the learning process, allowing players to develop a deeper connection with their instrument.
The instrument is composed of several distinct sections, each contributing to the overall performance. From the mouthpiece to the body and beyond, every section is designed with precision. Mastery of these elements is crucial for achieving optimal sound quality and control during play.
By examining the different components closely, musicians can gain valuable insights into how they work together to create beautiful music. This knowledge is not only important for playing but also for proper maintenance, ensuring the longevity and performance of the instrument over time.
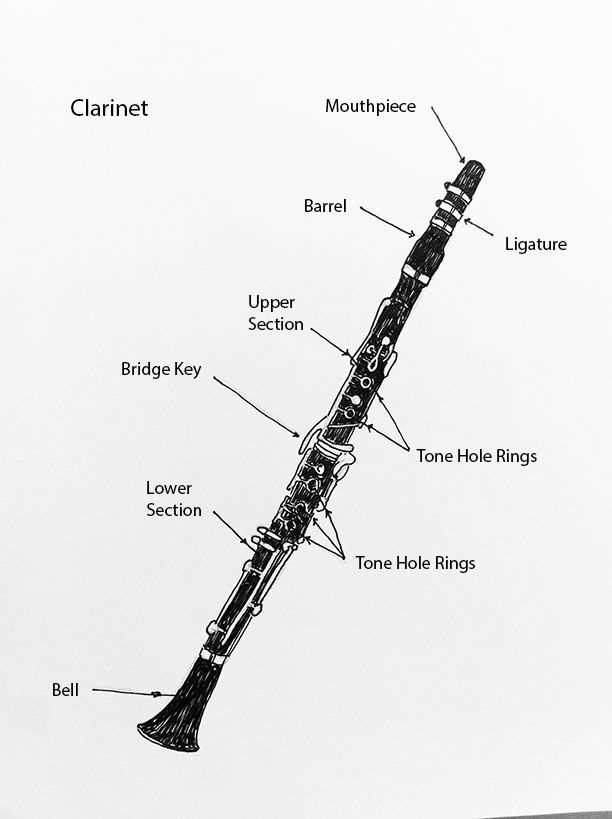
Overview of the Clarinet Structure
The instrument is composed of several key sections, each playing a vital role in its overall function. These elements are designed to work in harmony, allowing for a wide range of sound production. The arrangement of these components ensures precision and fluidity in performance.
Main Body Components
The central portion of the instrument consists of interconnected pieces that form the core. Each section has been meticulously crafted to control airflow and tone. The design of these components directly affects the resonance and quality of the sound produced.
Supporting Elements
Additional features are integrated into the instrument to enhance its usability and playability. These features, while not responsible for sound production, contribute significantly to the player’s comfort and the overall ease of handling. Their placement ensures that the instrument remains balanced and responsive during use.
Main Body Components of the Clarinet
The instrument’s structure consists of several essential sections that work together to produce sound. Each section has a specific role, contributing to both the tone and playability of the instrument. Understanding these components is key to mastering its use and ensuring its proper maintenance.
One of the central sections is the upper portion, where most of the finger holes are located. This part is responsible for producing the higher notes and requires precision in fingering technique. Below it lies the middle section, which connects the upper and lower sections, ensuring smooth transitions between different ranges of sound.
The lower portion includes additional tone holes and is essential for generating the deeper sounds. Together with the upper sections, it balances the overall sound. These parts are interconnected and designed to allow ease of play and efficient sound projection.
Clarinet Mouthpiece and Its Function
The mouthpiece plays a crucial role in producing sound, as it is where the musician creates the vibration needed for the instrument to resonate. Its design and material significantly impact the tone and overall sound quality. Understanding how this component works allows performers to control various aspects of their performance, from intonation to dynamics.
Structure and Material: The construction of the mouthpiece affects how air flows through the instrument, influencing the ease of playing and tonal characteristics. The internal dimensions, such as the facing curve and the chamber, are vital in determining sound projection and clarity.
Sound Production: When air passes through the mouthpiece, it vibrates the reed, which in turn generates sound waves. The musician’s embouchure, or the way they position their lips and control airflow, directly interacts with the mouthpiece, shaping the pitch and timbre of the sound produced.
Barrel: Purpose and Design
The barrel is a crucial element in shaping the instrument’s sound and overall performance. It plays a key role in controlling airflow, which directly affects the tonal quality and resonance. Its structure and dimensions are specifically designed to balance acoustic properties, ensuring a smooth connection between other sections and enhancing the player’s experience.
Functionality
The primary function of the barrel is to fine-tune the pitch and sound projection. By adjusting its length or design, subtle changes can be made to the overall tuning, allowing the musician to achieve greater precision in performance. This component also helps to create a more focused and centered sound.
Design Variations
Barrels come in different shapes and sizes to accommodate various playing styles. Some may feature a tapered design, which narrows towards one end, while others maintain a more cylindrical form. Materials can range from wood to synthetic options, each influencing the instrument’s tonal characteristics in unique ways.
- Cylindrical designs offer more consistent tuning across the range.
- Tapered versions may provide enhanced tonal flexibility.
- Material choices affect warmth, brightness, and overall timbre.
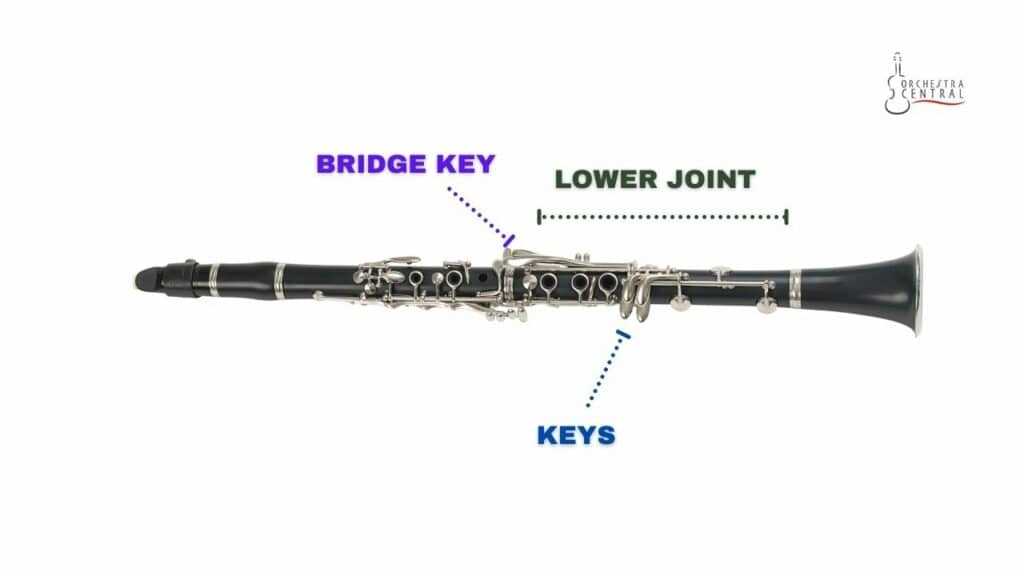
Clarinet Upper Joint: Key Features

The central section of this woodwind instrument is vital for producing rich and resonant tones. This middle portion houses essential mechanisms that allow for smooth transitions between different registers and notes. By interacting with these mechanisms, the musician can precisely control the pitch and sound quality. Let’s explore the distinctive features of this component that contribute to the instrument’s performance.
| Feature | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keys | These metal levers cover tone holes and help control the pitch by opening and closing various sections. | ||||||||||||
| Tone Holes | Openings that influence sound production when covered or uncovered by the musician’s fingers or the keys. | ||||||||||||
| Bridge Mechanism | A crucial linkage that connects with the lower section, ensuring coordinated movement of keys for seamless play. | ||||||||||||
| Tenon | This joint connects with the lower part, secured with a cork, ensuring stability and airtightness. |
| Placement Position | Sound Quality | Dynamic Range |
|---|---|---|
| Center Position | Balanced tone with clarity | Wide range, good control |
| Forward Position | Bright and piercing sound | Increased projection, slight instability |
| Backward Position | Warm and mellow tone | Reduced projection, smoother dynamics |
In summary, mastering the nuances of placement can profoundly affect the player’s expression and the instrument’s versatility, allowing for a richer musical experience.


