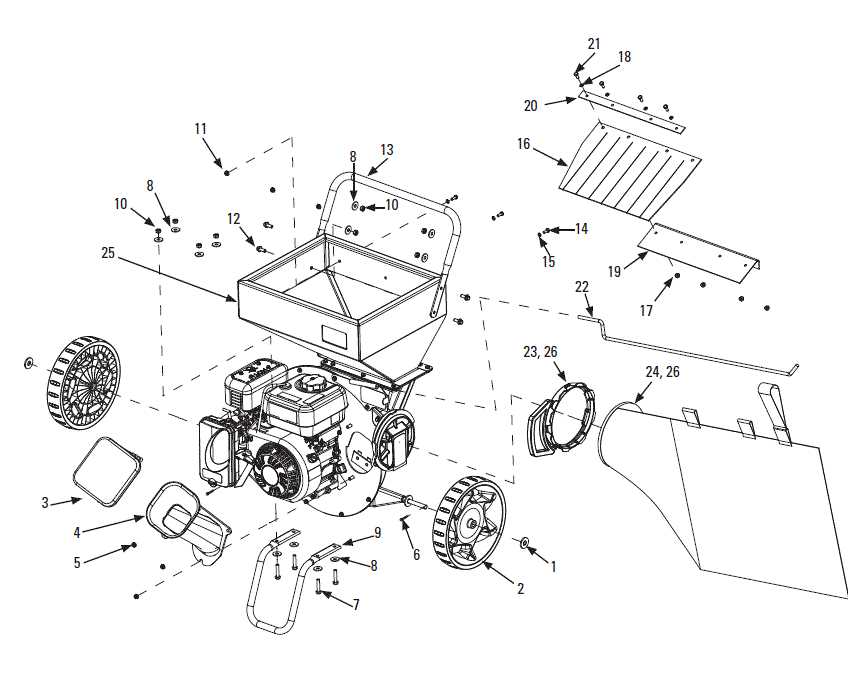
Understanding the arrangement and interaction of various mechanical components is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance of any machine. Whether you’re involved in maintenance or looking to enhance operational efficiency, a detailed view of how individual elements come together can be invaluable. Each piece plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall functionality of the equipment.
By exploring the structure and positioning of these elements, you gain insight into their importance in the overall operation. This can help identify potential wear points, streamline repairs, and improve troubleshooting. Having a clear visualization of how everything is connected aids in keeping the system running smoothly and efficiently.
With this guide, you’ll be able to navigate through the different sections and components, deepening your understanding of their functions. From primary mechanisms to smaller, interconnected parts, every detail is presented to help you maintain and optimize the machine’s performance.
Understanding the Components of a Bandit Chipper
Efficient wood processing equipment relies on various interconnected elements that work together to ensure optimal performance. These elements play crucial roles in handling materials, cutting, and ejecting processed debris, contributing to overall efficiency and safety during use. Knowing the structure and function of these key elements can help maintain the machine’s productivity and extend its lifespan.
Main Structural Elements
- Feed Mechanism: The device pulls raw materials toward the cutting area using a rotating system. This ensures a steady and controlled flow of material.
- Cutting Unit: A vital section that slices or chops the incoming material into smaller pieces, making it ready for disposal or further processing.
- Discharge System: After processing, this component ejects the chopped material through an exit chute or similar pathway.
Additional Features

- Control Panel: A user-friendly interface allows the operator to manage speed, material flow, and safety features.
- Safety Shields: Protective barriers designed to prevent accidents during operation by limiting direct access to moving parts.
- Hydraulic System: Powers various movements within the device, such as feeding and cutting, to ensure smooth operation.
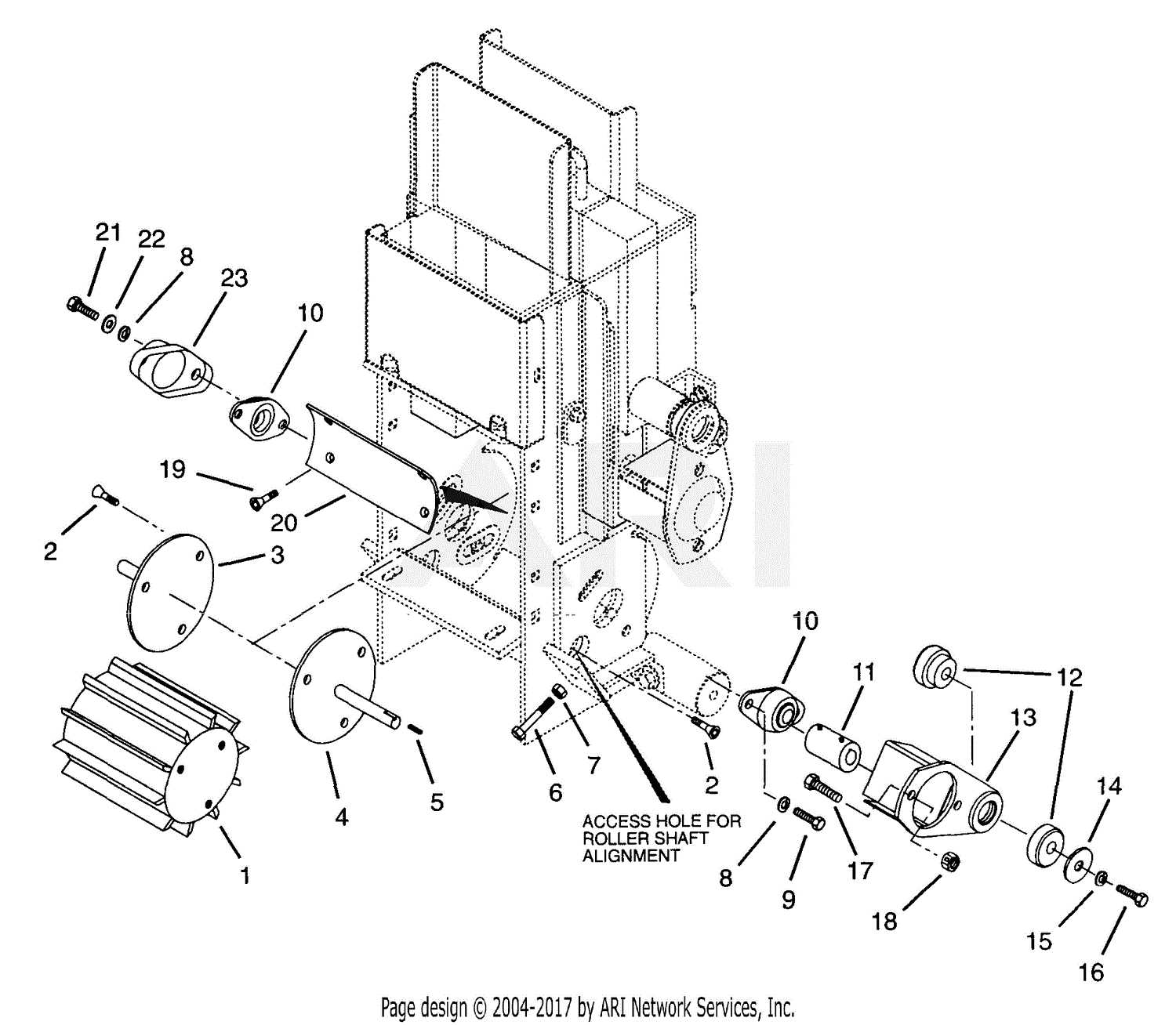
Key Mechanical Parts Overview
In this section, we will explore the main components responsible for the efficient operation of the equipment. These crucial elements ensure proper function and long-term reliability, playing an essential role in the overall system’s performance.
- Engine System: The power source that drives the entire mechanism. It converts fuel into mechanical energy, ensuring continuous operation.
- Transmission Assembly: This unit transfers the energy from the motor to the working elements, facilitating the required movement and control.
- Cutter Mechanism: The primary element responsible for breaking down materials. It features rotating or stationary elements that process materials efficiently.
- Hydraulic System: A network of pumps and valves that controls various moving parts, providing smooth and powerful actuation.
- Feed System: A combination of rollers and guides that ensures materials are directed smoothly into the machine for processing.
- Frame and Support Structures: The sturdy foundation that holds all components together, designed to endure constant pressure and wear.
- Safety Mechanisms: These include sensors, brakes, and other devices that protect both the operator and the machine during operation.
Understanding the role and functionality of these essential components helps in maintaining and optimizing the performance of the entire system.
Hydraulic System Elements in Wood Processing Machines
The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in the functionality of wood processing equipment, providing the power needed for various mechanical movements. This section delves into the core components that make up this essential system, highlighting their roles and interaction within the machinery. Understanding these elements is key to maintaining smooth operations and ensuring efficient processing.
Key Components of the Hydraulic System
- Pumps: These are responsible for generating the hydraulic pressure that drives the fluid through the system, enabling the machine’s various functions.
- Valves: Control the flow and direction of the hydraulic fluid, ensuring that the necessary power is delivered to the right parts of the machine.
- Hoses and Fittings: Serve as conduits for the hydraulic fluid, transporting it between the various components, while ensuring minimal leakage or loss of pressure.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting

- Fluid Levels: Regularly check and maintain proper fluid levels to ensure consistent performance. Low levels can lead to system inefficiencies or damage.
- Leak Inspection: Monitor hoses and fittings for any signs of leakage, as this can significantly affect system pressure and efficiency.
- Valve Operation: Ensure that valves are functioning correctly to prevent disruptions in fluid flow, which can impair machine performance.
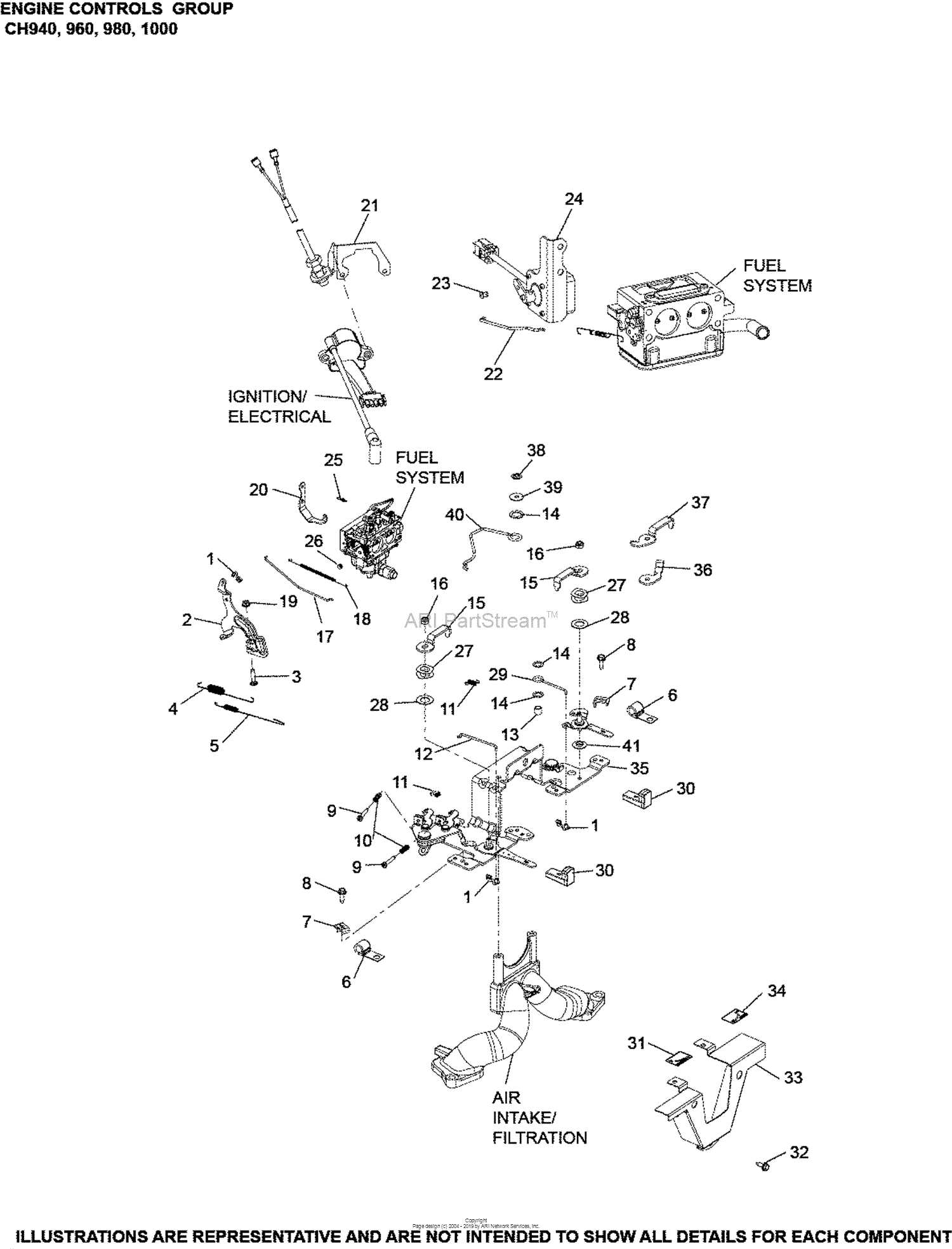
Electrical Components and Wiring Diagram

Understanding the electrical components and their configuration is essential for ensuring the proper functioning of any machinery. This section focuses on the layout and connectivity of the key electrical elements, offering a clear view of how power is distributed and controlled throughout the system.
Electrical systems often include a variety of components, each playing a vital role in managing the overall functionality. Knowing how these elements are interconnected helps in both troubleshooting and maintenance tasks.
- Wiring: Cables and wires serve as the lifelines of the system, carrying electrical signals and power between various modules. Proper arrangement and labeling are critical for safety and ease of repair.
- Switches: These components control the flow of electricity, enabling or disabling certain operations. Their placement and type depend on the specific functionality they manage.
- Relays: Acting as intermediaries, relays switch electrical circuits on and off based on signals from other components, providing an essential layer of control.
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Safety mechanisms designed to prevent overload and protect the system from damage by cutting off the current in the event of a fault.
- Blades: The blades are strategically mounted to rotate at high speed, cutting material into smaller pieces. These sharp, durable components need to be regularly maintained to ensure their effectiveness and longevity.
- Flywheel: The flywheel is a heavy rotating disk that stores kinetic energy. Its role is to maintain momentum, reducing the strain on the engine while ensuring consistent performance. The mass of the flywheel helps to stabilize the cutting process, providing smoother operation even with tough materials.
- Engine Components: Upgrading the motor or its related components can lead to increased power output and efficiency.
- Blades and Cutting Elements: High-quality, sharp cutting tools are essential for optimal performance. Regularly replacing worn blades will maintain cutting precision.
- Hydraulic Systems: Improving hydraulic components can enhance operational speed and overall power, resulting in more effective material processing.
- Belts and Drive Systems: Inspect and replace any worn or damaged belts to prevent operational failures and ensure smooth movement.
Cutting Mechanism: Blades and Flywheel

The cutting system relies on a precisely engineered combination of rotating components, designed to efficiently slice through various materials. This mechanism plays a critical role in the overall performance, ensuring smooth and effective operation during use.
By combining the energy from the flywheel and the sharpness of the blades, this system maximizes efficiency, minimizing energy loss and ensuring clean cuts through tough or fibrous materials.
Maintenance Points for Optimal Performance
Ensuring that your equipment runs smoothly requires regular attention to various key areas. Consistent upkeep not only extends the longevity of your machine but also enhances its overall efficiency. Focusing on critical maintenance points can prevent potential issues and ensure reliable operation over time.
Lubrication and Cleaning

One of the fundamental aspects of maintaining peak performance is keeping all moving components properly lubricated. Regular cleaning helps to remove debris that can lead to blockages or reduced efficiency. Establishing a routine for these tasks will minimize wear and tear on vital parts, promoting smoother operation.
Inspection of Wear Components

Periodic checks for signs of wear or damage are crucial for identifying any elements that may need replacement. Paying attention to areas that experience the most stress will allow you to address problems early, before they escalate into larger mechanical failures. This proactive approach helps to maintain optimal functionality.
Troubleshooting Common Component Failures
Addressing issues with machinery often requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve typical failures in various components. Understanding the signs of malfunction can lead to quicker diagnostics and less downtime. This section outlines common challenges that may arise and provides guidance on how to effectively troubleshoot these problems.
One frequent issue involves abnormal noises during operation, which may indicate wear or damage in moving parts. To diagnose this, listen carefully for any irregular sounds and inspect components for signs of excessive friction or misalignment. Lubrication may be necessary, or parts might need adjustment or replacement.
Another common concern is a decrease in efficiency, which can stem from various factors, including clogged pathways or degraded components. Regularly check for blockages and clean out any debris that may hinder performance. Additionally, verify that all parts are functioning properly and replace any that show signs of wear.
Finally, unexpected shutdowns can be a significant inconvenience. If this occurs, examine the power supply and ensure that all electrical connections are secure. Testing fuses and circuit breakers can also help pinpoint electrical issues that might be causing the machinery to stop unexpectedly.
Upgrading and Replacing Key Parts
Enhancing the performance and longevity of your equipment often involves updating or swapping out essential components. This process not only improves efficiency but also ensures that the machinery operates smoothly and safely. Regular maintenance and timely replacements can lead to significant improvements in functionality.
When considering enhancements, focus on the following critical areas:
Follow these steps to successfully upgrade or replace critical components:
- Identify the components that require attention based on performance analysis.
- Source high-quality replacements that are compatible with your machinery.
- Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper installation procedures.
- Conduct regular inspections to monitor the condition of the new components.
By focusing on these areas and following best practices for replacements, you can significantly enhance the overall performance and reliability of your equipment.
Safety Features and Their Locations
Ensuring the safety of operators and bystanders is paramount in the operation of heavy machinery. This section outlines various protective mechanisms integrated into the equipment, highlighting their significance and specific placements to maximize user security during operation. Familiarizing oneself with these features can greatly reduce the risk of accidents and enhance overall safety standards.
Emergency Stop Mechanism

The emergency stop button is a critical feature designed for immediate deactivation of the machinery in case of an unforeseen situation. Typically located within easy reach of the operator, it is often found on the control panel or on the side of the equipment, ensuring quick access when needed.
Protective Shields and Guards
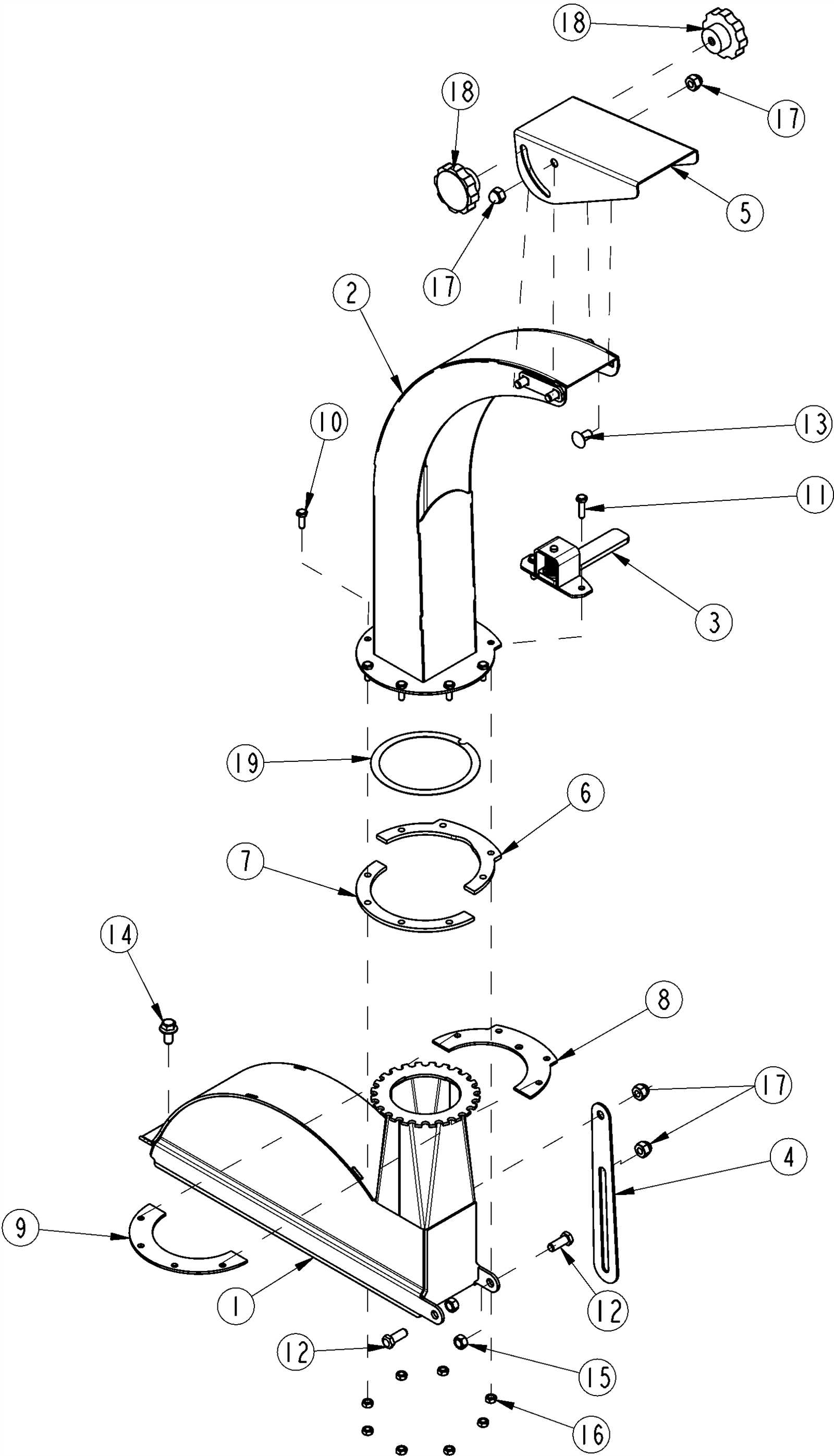
Shields and guards serve to prevent accidental contact with moving parts. These protective barriers are strategically positioned around critical components, often near the feed opening and other high-risk areas. Regular inspection and maintenance of these features are essential to ensure their integrity and effectiveness in safeguarding users.