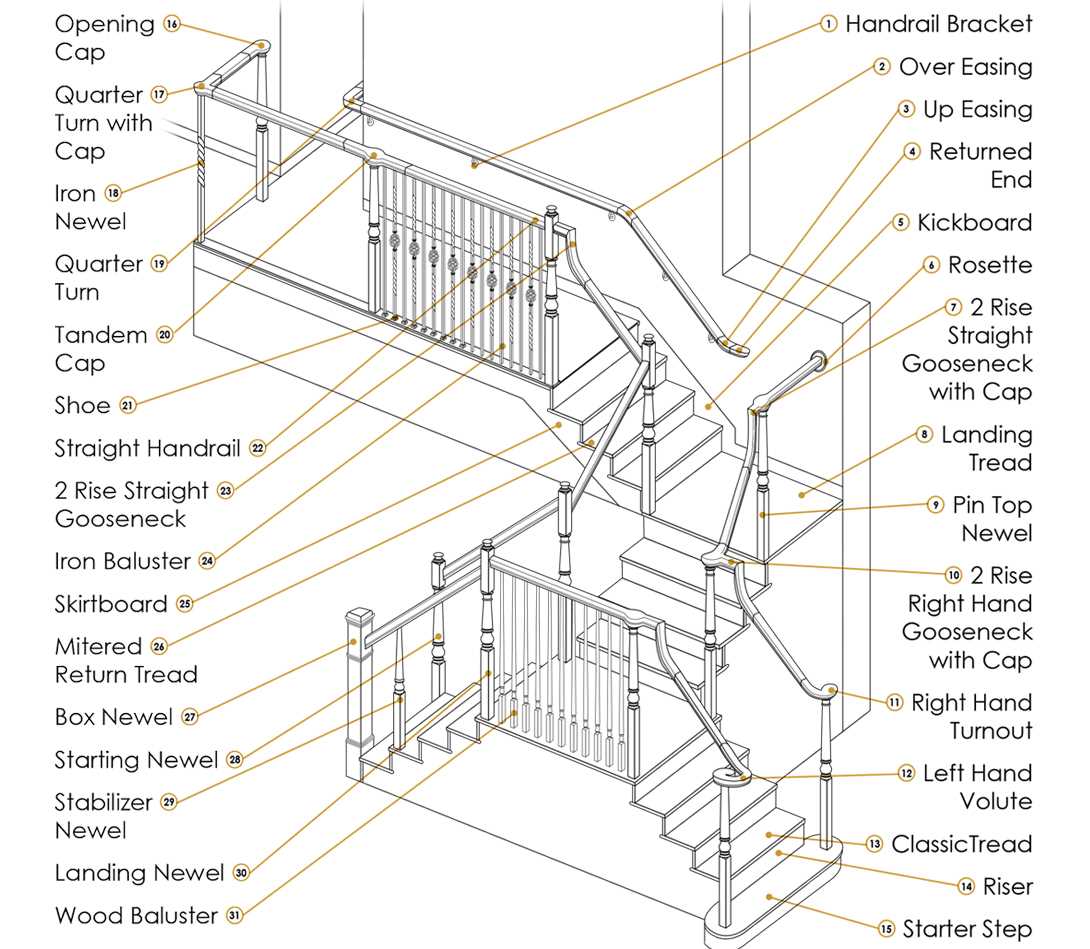
When designing or renovating a multi-level structure, comprehending the various elements that comprise the ascent is essential. Each section plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and aesthetic appeal, influencing both safety and style. By grasping the intricacies of these components, one can make informed decisions that enhance both form and function.
From the supporting structures that provide stability to the surfaces that facilitate movement, every aspect has its significance. Whether considering the materials used or the arrangement of each segment, attention to detail ensures a seamless integration within the larger design. Such awareness not only contributes to the visual charm but also upholds structural integrity, providing confidence for those who utilize the space.
Exploring the variety of elements involved reveals an array of options that can cater to individual preferences and requirements. Understanding how these components interact with one another can lead to innovative design solutions, elevating the overall experience within the environment. Knowledge of this intricate assembly fosters creativity and promotes a well-rounded approach to any building project.
Various designs of upward structures are integral to both functionality and aesthetics in architecture. Each configuration serves distinct purposes, and understanding the elements that constitute these formations is essential for effective planning and construction.
Here are some common configurations along with their components:
-
Straight:
- Run: The horizontal distance between two landings.
- Rise: The vertical height between two steps.
- Tread: The part where one steps, providing the walking surface.
-
Spiral:
- Newel Post: The central support that anchors the structure.
- Winders: Triangular steps that facilitate the curvature.
- Balusters: Vertical posts that support the handrail.
-
Curved:
- Radius: The distance from the center to the edge of the curve.
- Landing: A flat area at the top or bottom of the curve.
- Handrail: The support along the edge, ensuring safety and comfort.
-
L-Shaped:
- Quarter Landing: The flat area where the turn occurs.
- Stringer: The structural support that runs along the sides.
- Carpet or Runner: Material that covers the treads for safety and aesthetics.
Understanding these various configurations and their components can greatly enhance both safety and design in residential and commercial settings.
Understanding Treads and Risers
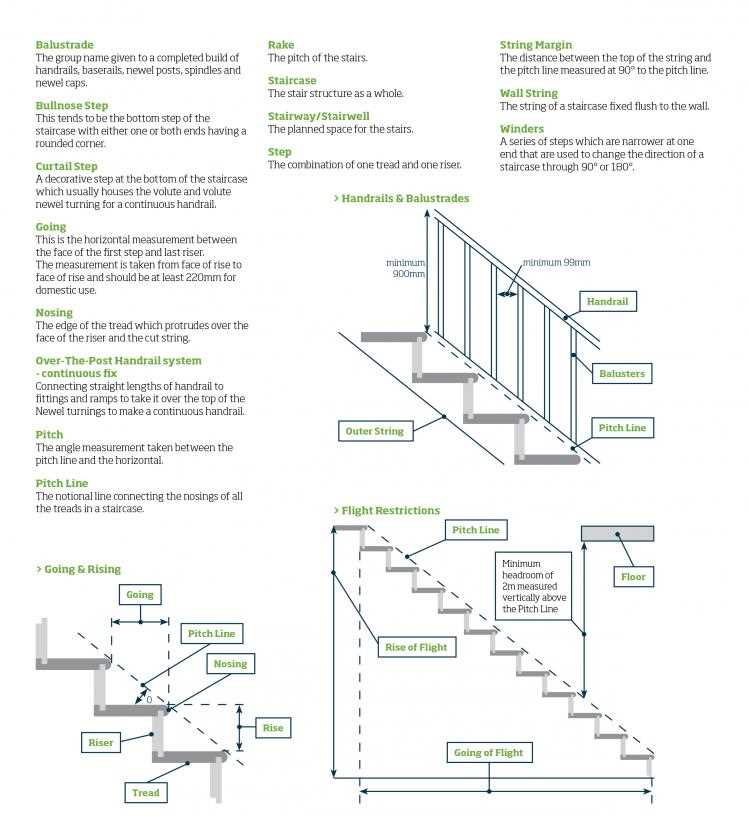
In the construction of a multi-level structure, certain components play a vital role in ensuring safety and accessibility. These elements, integral to the functionality of the elevation system, contribute to the overall design and usability of the structure. Understanding their characteristics and relationships can greatly enhance the experience of navigating between different levels.
The component that provides the surface upon which individuals step is crucial for stability and comfort. It is essential to ensure that this surface is designed to withstand frequent use and to offer adequate traction. The vertical portion connecting each step serves to define the height and creates a transition between different levels.
- Treads: This element is the horizontal surface that users step on, which is typically wider than it is deep. Proper dimensions can significantly affect ease of movement.
- Risers: The vertical section between each tread, which adds height to the elevation. A well-calibrated height contributes to user comfort and safety.
When designing these components, various factors should be taken into account:
- Dimensions: The measurements of both the tread and riser are critical. Standard dimensions can improve usability and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
- Material: The choice of materials affects durability, maintenance, and aesthetics. Selecting appropriate materials enhances the longevity of these components.
- Finish: Surface treatments can improve traction, especially in high-traffic areas or environments prone to moisture.
Understanding the interplay between these elements not only ensures compliance with safety standards but also enhances the overall aesthetic appeal of the construction.
Handrails: Importance and Design
Railings play a vital role in enhancing both the safety and aesthetics of any vertical structure. Their presence not only prevents accidental falls but also adds a finishing touch to the overall appearance of the environment. The careful consideration of their design can significantly impact functionality and visual appeal.
Incorporating well-designed railings offers numerous benefits:
- Safety: A sturdy railing provides essential support for individuals navigating inclines or declines.
- Aesthetics: The style and material of railings can elevate the visual character of a space.
- Accessibility: Properly positioned railings assist those with mobility challenges, ensuring inclusivity.
- Durability: Quality materials enhance longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
When considering the design of railings, several factors should be taken into account:
- Material Selection: Common choices include wood, metal, and glass, each offering unique benefits and aesthetics.
- Height and Width: Railings should meet safety standards while ensuring comfortable use for all individuals.
- Style and Finish: The choice of style should harmonize with the overall theme of the structure, contributing to a cohesive look.
- Installation: Proper installation techniques are crucial to maintain both functionality and safety.
Ultimately, the thoughtful design of railings is essential for creating secure, attractive environments. A blend of practicality and style ensures that they fulfill their purpose while enhancing the overall experience of the space.
Common Materials Used in Stairs
When designing a structure for elevation changes, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. Various substances are utilized in the creation of these essential components, each offering distinct benefits and characteristics. Understanding the most prevalent options can aid in making informed decisions for construction or renovation projects.
Wood is one of the most traditional choices, valued for its natural beauty and warmth. It can be easily shaped and finished, providing a classic appearance that complements various interior styles. Hardwoods such as oak, maple, and cherry are often preferred for their durability and resistance to wear.
Metal is another popular option, frequently used for its strength and modern appeal. Steel and aluminum provide robust support and can be incorporated into contemporary designs, enhancing the overall industrial look. Additionally, metal components can be powder-coated or painted to match any color scheme.
Concrete is increasingly favored for its versatility and longevity. This material can be molded into various shapes and finishes, allowing for creative expressions while maintaining structural integrity. Often used in both indoor and outdoor applications, concrete is known for its resistance to the elements and minimal maintenance requirements.
Finally, composite materials have gained traction in recent years, combining the best attributes of wood and plastic. These substances are engineered to be durable and resistant to moisture, making them ideal for environments where traditional materials may falter. Their low maintenance and eco-friendly options appeal to many modern homeowners.
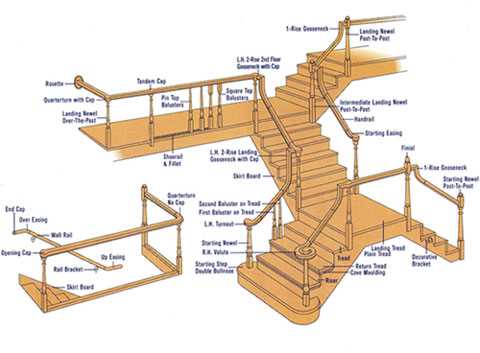
Visual Representation of Stair Diagrams
The effective illustration of structures related to vertical access systems is essential for understanding their components and functionality. This visual approach enhances comprehension and allows for an easier grasp of design elements and their interrelations. By employing various graphical techniques, one can effectively communicate the intricate details that define these constructions.
Different types of illustrations serve distinct purposes, catering to diverse audiences, from architects to homeowners. For instance, detailed drawings can showcase the intricate connections and materials, while simplified representations highlight overall layouts. Each style offers valuable insights into the construction process and helps identify essential elements.
Incorporating colors, labels, and dimensions into these visuals further enriches the information presented. Clear markings can guide viewers through the arrangement and spatial relationships, ensuring that even those unfamiliar with technical terminology can navigate the complexities of design. Ultimately, these graphical representations play a crucial role in making construction concepts accessible and understandable.
Safety Features in Stair Construction
Ensuring security in the construction of elevation transitions is crucial for preventing accidents and enhancing usability. Various elements contribute to the overall safety of these structures, from design considerations to materials used. The integration of these features not only protects users but also complies with regulatory standards.
Key Considerations for Safety
- Handrails: Adequate support on both sides provides stability and confidence to users.
- Non-slip Surfaces: Textured finishes can significantly reduce the risk of slips, especially in high-traffic areas.
- Consistent Tread Depth: Uniform steps help users maintain a steady rhythm while ascending or descending.
- Proper Lighting: Sufficient illumination aids visibility, reducing the likelihood of missteps.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
- Familiarity with local building codes ensures that structures meet minimum safety requirements.
- Regular inspections can identify wear and tear, allowing for timely maintenance and upgrades.
- Utilizing quality materials enhances durability and safety over time.
Tips for Designing Efficient Stairs
Creating an effective climbing solution requires careful consideration of various factors that contribute to safety, accessibility, and aesthetics. A well-planned approach can enhance user experience while minimizing potential hazards. This section explores essential guidelines to ensure optimal functionality and comfort in your design.
Key Considerations
When embarking on the design process, it’s vital to keep in mind the overall layout and flow of movement. Factors such as width, rise, and run play a crucial role in determining the usability of the ascent. Additionally, integrating appropriate materials can enhance both durability and visual appeal.
Design Elements
Incorporating elements like handrails, landings, and lighting is essential for safety and ease of use. Properly placed handholds can provide support, while well-lit areas reduce the risk of accidents during use. The following table summarizes essential elements to consider:
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Width | Ensures sufficient space for movement |
| Rise and Run | Affects comfort and ease of ascent |
| Handrails | Provides support and stability |
| Lighting | Enhances visibility and safety |
| Landings | Offers resting points and direction changes |