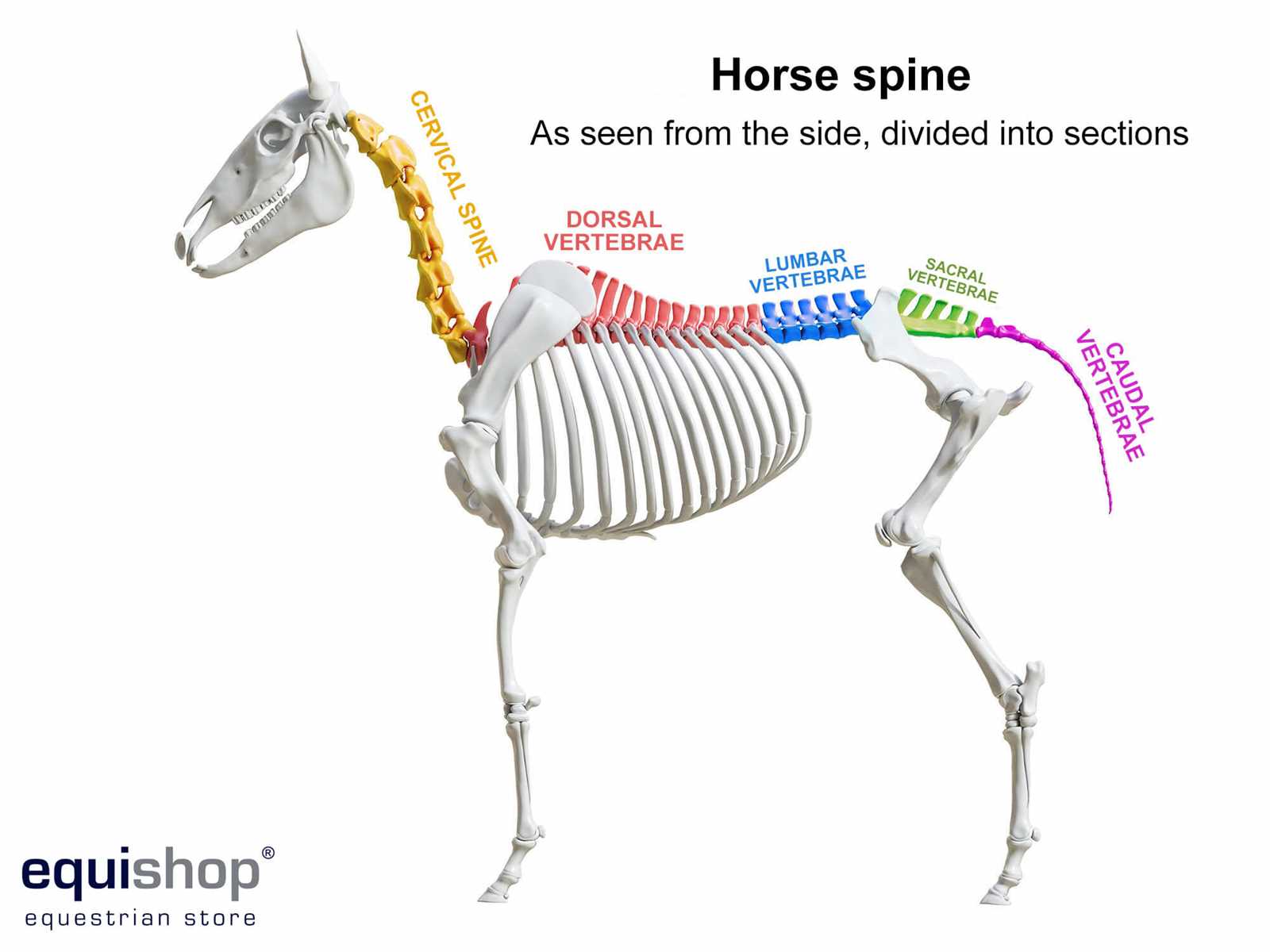
Exploring the intricate structure of these magnificent creatures offers valuable insights into their health and functionality. A comprehensive understanding of the various components that make up their physique can enhance both care practices and training methods. This knowledge is essential for anyone involved in equine management or veterinary care.
In this section, we will delve into the essential elements that contribute to the overall makeup of these animals. Each segment plays a vital role in their movement, agility, and well-being. By familiarizing ourselves with these key regions, we can better appreciate the complexities of their physiology.
The examination of the various sections not only fosters a deeper connection with equines but also equips enthusiasts and professionals alike with the necessary tools to promote optimal health. Understanding how these areas interrelate can lead to improved care strategies and performance outcomes.
Overview of Horse Anatomy
The structure of equines is a fascinating study, revealing the intricacies that contribute to their grace and power. Understanding this framework is essential for appreciating their movement, behavior, and overall health. Each section serves a specific function, working in harmony to support their majestic form.
Musculoskeletal System: The framework consists of bones and muscles that enable agility and strength. The skeletal system supports the animal’s weight and provides attachment points for muscles, which facilitate movement. This synergy allows for the impressive speed and endurance that equines are known for.
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems: Vital for sustaining life, these systems work tirelessly to deliver oxygen and nutrients. The heart pumps blood efficiently, while the respiratory organs ensure adequate intake of air, optimizing performance during physical exertion.
Digestive System: Adapted for a herbivorous diet, the digestive tract processes fibrous materials, converting them into energy. This efficient system is crucial for maintaining overall health and supporting the high energy demands of these animals.
Nervous System: This complex network controls all bodily functions and responses to the environment. It plays a key role in communication, allowing for rapid reactions and coordination during various activities, from grazing to competing.
Overall, the anatomical makeup of equines showcases a remarkable design, reflecting their evolution and adaptability. A thorough understanding of this design is invaluable for anyone involved in their care and management.
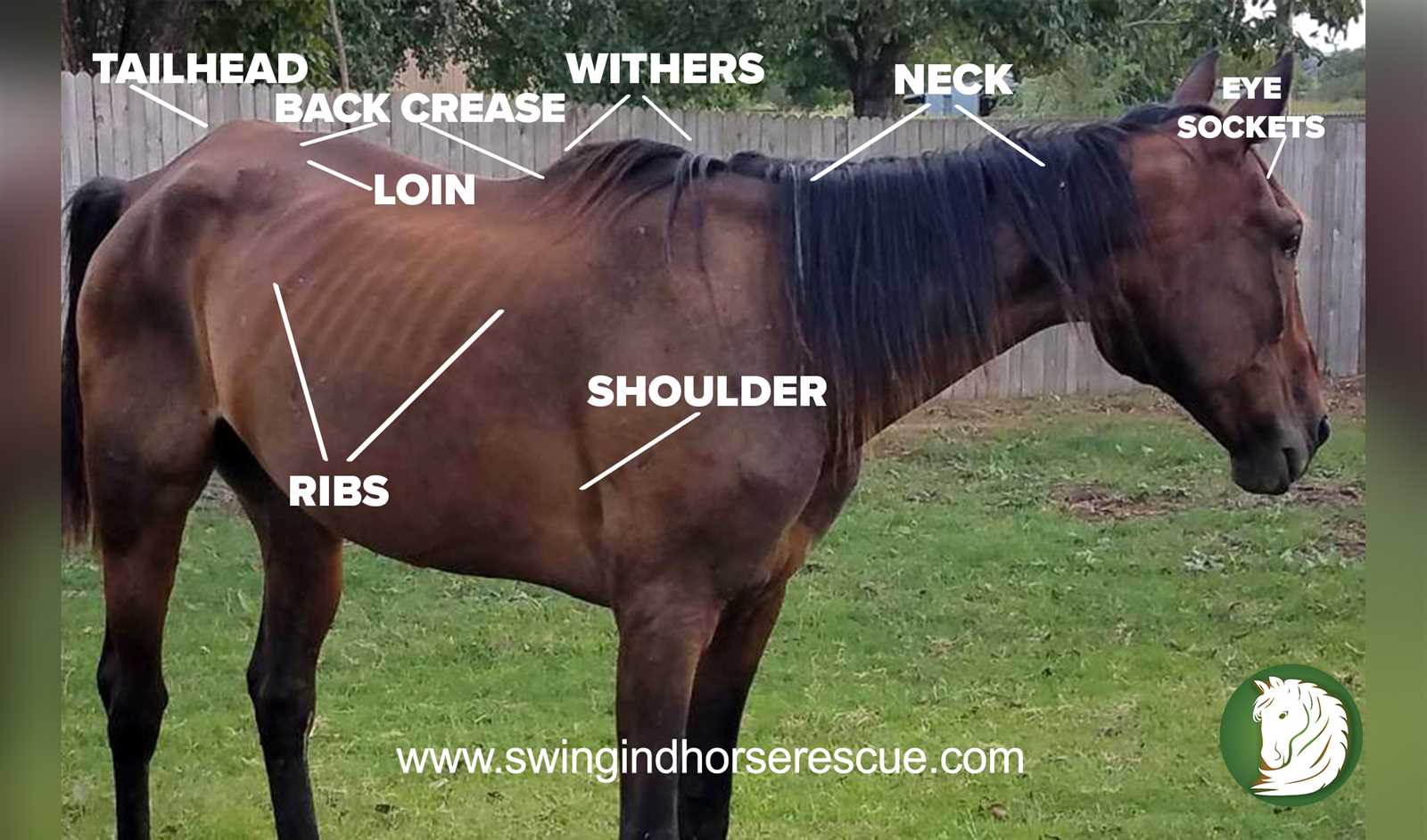
Major Body Regions Explained
This section delves into the primary anatomical areas of equines, highlighting their significance and function. Understanding these regions is crucial for effective care, training, and overall management.
- Head: The head houses vital sensory organs and is essential for communication and interaction.
- Neck: A crucial connector, the neck supports the head and allows for a range of movement, impacting balance and posture.
- Chest: This area contains important respiratory and circulatory organs, contributing to stamina and overall health.
- Back: The back serves as a support structure, enabling movement and weight distribution during various activities.
- Abdomen: Home to digestive organs, the abdomen plays a key role in nutrition and energy supply.
- Limbs: The forelimbs and hindlimbs provide mobility and strength, crucial for performance and agility.
Each region has its own unique attributes and roles, collectively contributing to the creature’s well-being and performance capabilities. A thorough understanding of these areas enhances both management practices and training techniques.
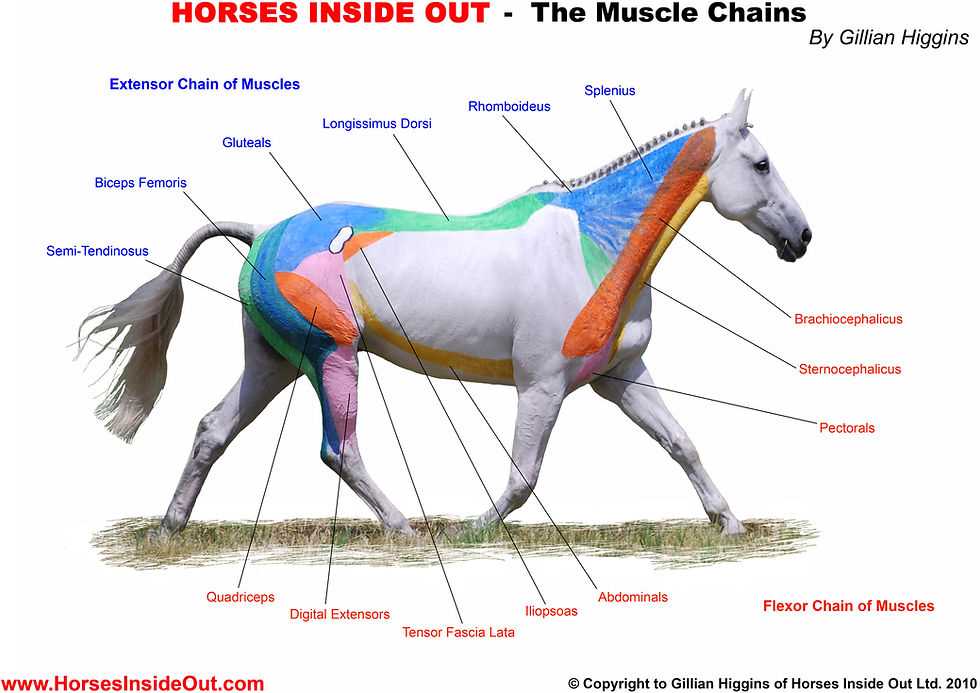
Importance of Muscular Structure
The muscular framework plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of an animal. It not only supports movement but also contributes to stability and agility, allowing for various activities ranging from running to jumping. A well-developed system of muscles is essential for maintaining balance and executing precise maneuvers.
Strength and Endurance: Muscles provide the necessary strength to perform demanding tasks and sustain prolonged activity. This endurance is vital for both daily functions and competitive scenarios, where stamina can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Coordination and Flexibility: A robust muscular arrangement enhances coordination between different movements, allowing for seamless transitions and quick adjustments. Flexibility within this structure ensures that the body can adapt to different terrains and obstacles effectively.
Overall, the significance of a strong and well-coordinated muscular system cannot be overstated; it is fundamental to both the health and performance capabilities of the creature.
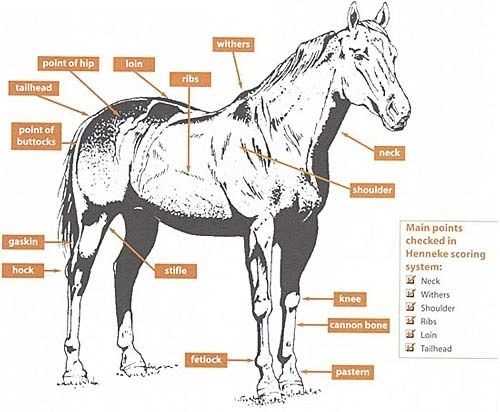
Understanding the Skeletal Framework
The skeletal structure serves as a crucial foundation for movement, support, and protection in living beings. This intricate network of bones and joints not only provides shape but also plays a vital role in various physiological functions. Understanding this framework is essential for appreciating the complexity and elegance of these creatures.
Key Components
The framework consists of numerous components, each with specific roles and characteristics:
- Bones: The rigid elements that form the primary structure.
- Joints: The connections between bones that allow for movement.
- Cartilage: The flexible tissue that cushions joints and provides support.
- Ligaments: The fibrous tissues that connect bones and stabilize joints.
Functions of the Skeletal Framework
This structure performs several essential functions:
- Support: It provides the necessary support for the body’s shape and form.
- Protection: Vital organs are shielded by the surrounding bony elements.
- Movement: It facilitates locomotion through joint articulation.
- Mineral Storage: Bones serve as reservoirs for minerals such as calcium and phosphorus.
- Blood Cell Production: Certain bones are involved in the production of blood cells within the marrow.
In summary, the skeletal framework is a remarkable system that not only provides structural integrity but also supports various life-sustaining processes. Understanding its intricacies enhances our appreciation for the mechanics of movement and the overall functionality of these beings.
Functions of the Digestive System
The digestive system plays a crucial role in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients essential for life. Its intricate processes ensure that the organism can efficiently utilize energy and maintain overall health. Understanding these functions reveals the importance of nutrition and the body’s ability to transform sustenance into vital resources.
Breaking Down Food
One of the primary functions involves the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller, absorbable components. This process starts in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed with saliva. As it travels through the digestive tract, enzymes and acids further decompose it, preparing it for nutrient extraction.
Nutrient Absorption
Following the breakdown, the next vital function is the absorption of nutrients. The small intestine, lined with tiny projections called villi, maximizes surface area for effective nutrient uptake. These nutrients are then transported into the bloodstream, where they are distributed to cells and tissues throughout the body. Proper absorption is essential for energy production, growth, and overall functionality.
Circulatory System in Horses
The circulatory framework in equines plays a crucial role in maintaining their overall health and performance. This intricate system is responsible for the transportation of vital nutrients, oxygen, and waste products throughout the organism, ensuring that every cell receives what it needs to function optimally.
Key Components
- Heart: The central pump that drives blood throughout the system.
- Blood Vessels: Includes arteries, veins, and capillaries that facilitate circulation.
- Blood: The fluid that carries essential elements and aids in temperature regulation.
Functions of the Circulatory Framework
- Transporting oxygen from the lungs to various tissues.
- Delivering nutrients absorbed from the digestive tract.
- Removing metabolic waste products for excretion.
- Regulating body temperature through blood flow adjustments.
Understanding this complex system is vital for equine caretakers, as it directly impacts the animal’s performance and well-being.
Respiratory Mechanisms and Health
The respiratory system plays a vital role in maintaining overall well-being and vitality. Efficient oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion are crucial for sustaining life. Understanding how these processes function and their impact on health is essential for promoting optimal performance and longevity in equines.
Functionality of the Respiratory System
In mammals, the respiratory apparatus consists of various structures that facilitate the exchange of gases. Air enters through the nasal passages, where it is filtered and warmed before reaching the lungs. Within the lungs, specialized units called alveoli enable the crucial exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. This intricate system relies on muscular contractions and relaxation, allowing for effective ventilation and gas exchange.
Factors Affecting Respiratory Health
Several elements can influence the efficiency of the respiratory system. Environmental conditions, such as air quality and temperature, significantly impact respiratory performance. Infections or inflammatory conditions can impair lung function, leading to reduced exercise capacity and overall health deterioration. Regular monitoring and proactive management are essential to ensure optimal respiratory function and to address any emerging concerns promptly.
Role of Sensory Organs
The sensory structures of equines play a crucial role in their interaction with the environment, allowing them to perceive stimuli and respond appropriately. These organs are finely tuned to help these animals navigate their surroundings, ensuring survival and enhancing their quality of life.
Furthermore, the efficiency of these sensory mechanisms influences their behavior and overall adaptability in various habitats. Understanding how these organs function ultimately sheds light on the animal’s interactions within its ecosystem.
Common Injuries and Care Tips
Understanding typical injuries that can affect equines is crucial for any caretaker. Knowledge of these issues not only aids in early detection but also in providing the best possible care. Here are some prevalent conditions and suggestions for effective management.
- Soft Tissue Injuries:
- Common in athletic activities, these include strains and sprains.
- Signs: swelling, heat, and limping.
- Care tips: Rest, ice application, and veterinary evaluation are essential.
- Hoof Problems:
- Issues like abscesses or laminitis are frequent among these animals.
- Signs: lameness, sensitivity in the feet, and changes in stance.
- Care tips: Regular hoof care and prompt veterinary assistance are vital.
- Wounds:
- Injuries from fencing or other sharp objects can occur easily.
- Signs: bleeding, swelling, and potential infection.
- Care tips: Clean the area, apply antiseptic, and monitor for signs of infection.
- Colic:
- This condition refers to abdominal pain, often requiring urgent attention.
- Signs: restlessness, rolling, and lack of appetite.
- Care tips: Monitor dietary changes and consult a veterinarian if symptoms persist.
lessCopy code
By staying informed about these common issues and implementing proper care strategies, you can help ensure a healthier and happier life for your equine companion.