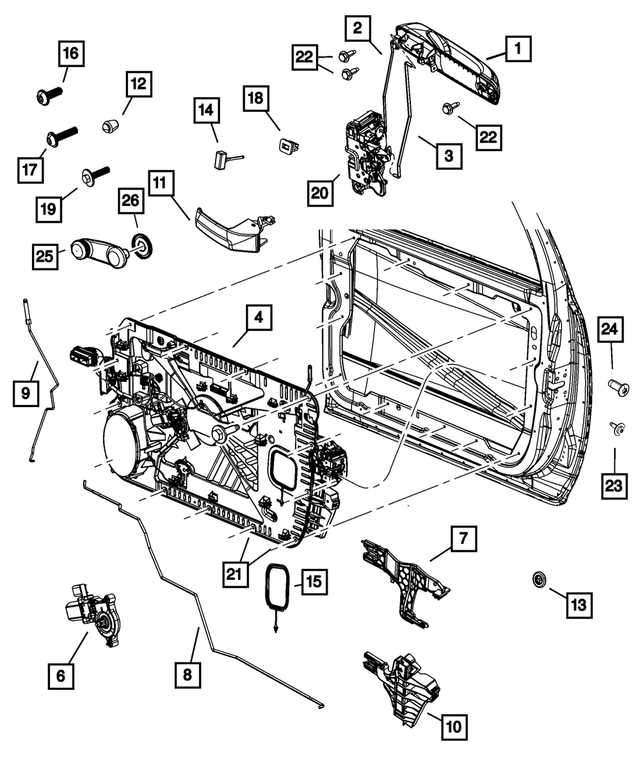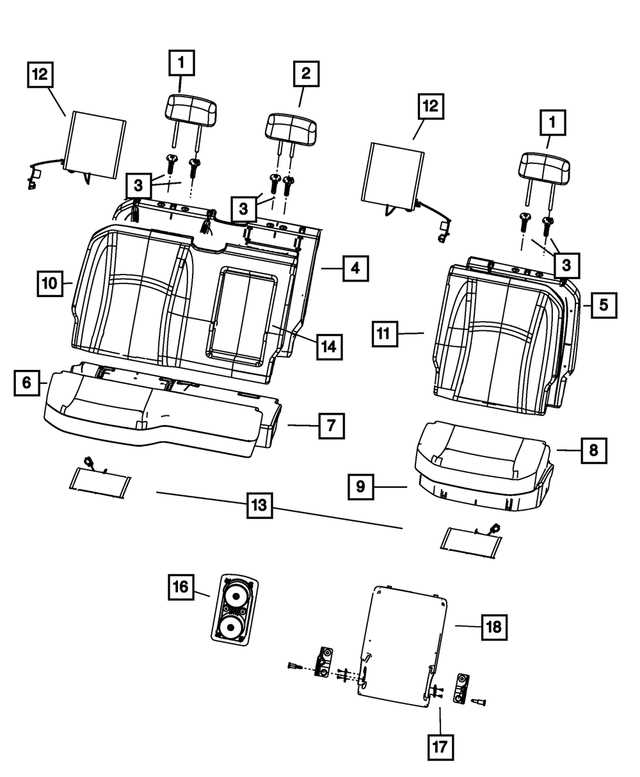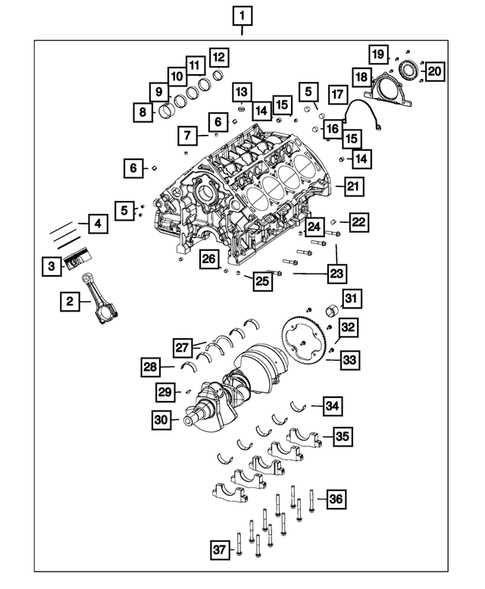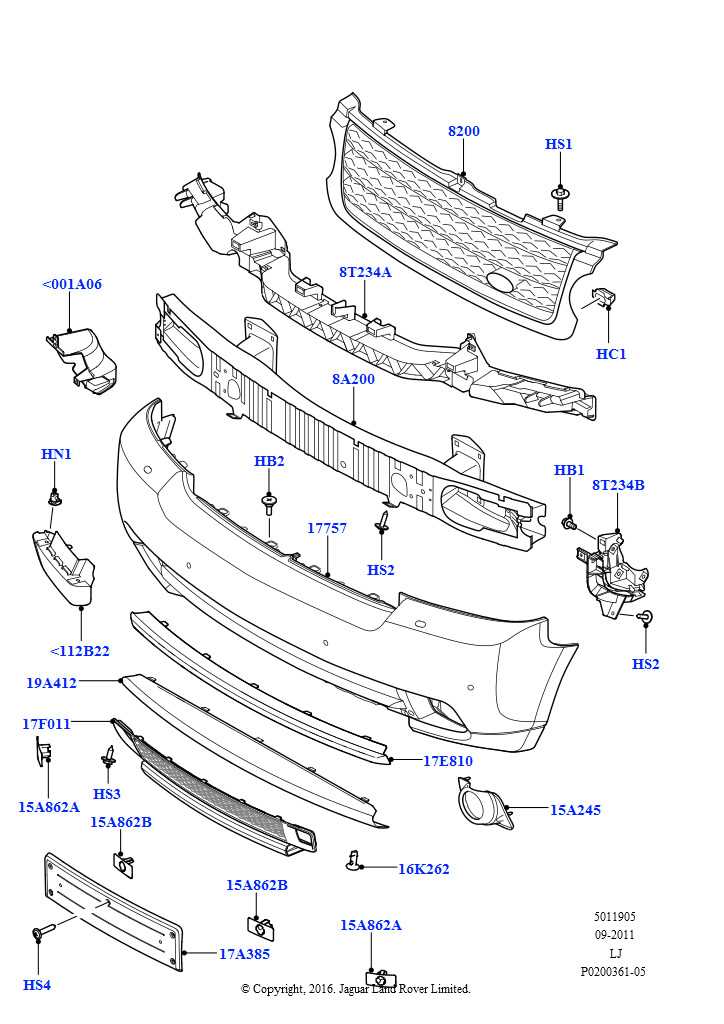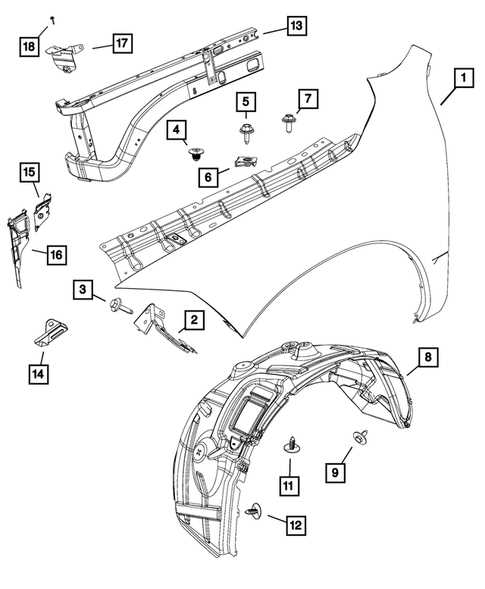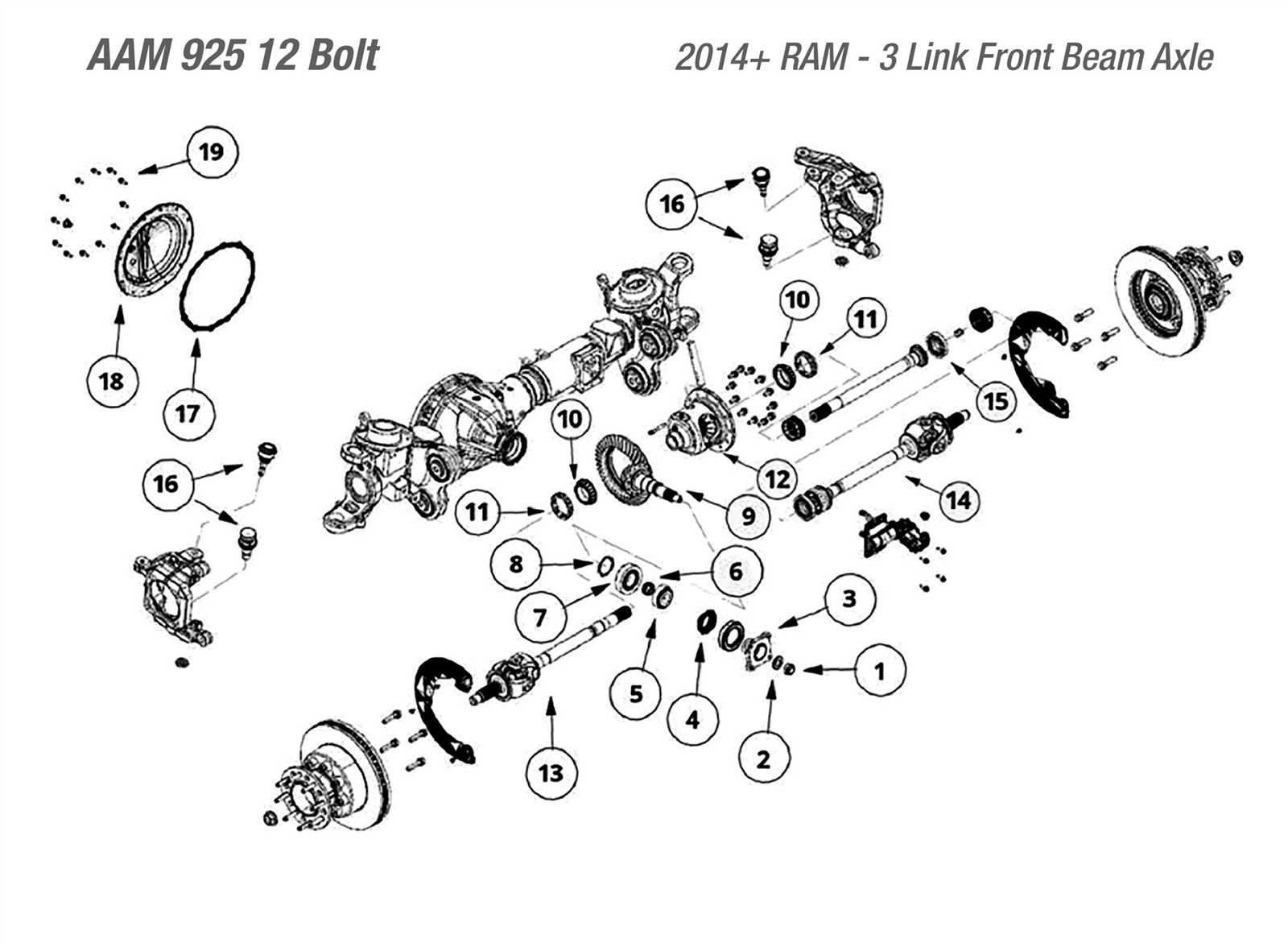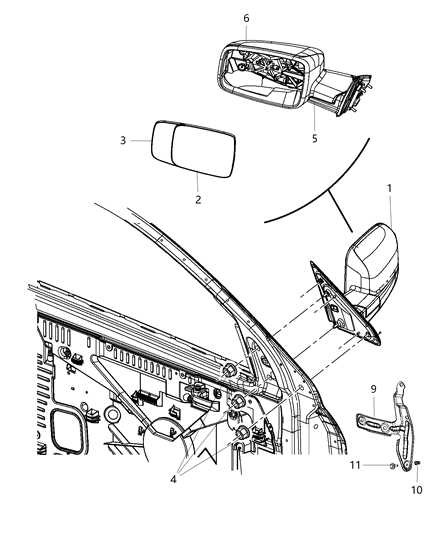
When working with any vehicle, understanding the layout of its individual components is crucial for both maintenance and repair. Each element is intricately connected to various systems, making it essential to have a clear visual representation of how these parts work together. This allows for more efficient troubleshooting, reducing the time and effort needed to locate specific elements during a service task.
By breaking down the arrangement into smaller sections, one can gain a deeper insight into how each component plays a role in the overall functionality of the vehicle. Whether you’re focusing on mechanical structures, electrical wiring, or internal systems, having an organized view of the setup simplifies the process of identifying key elements and understanding their respective roles within the system.
For those involved in vehicle maintenance, this structured information serves as a valuable resource, offering a straightforward path to tackling various tasks. It becomes especially important when dealing with more
Overview of Key Components
Understanding the main elements of a vehicle’s system is essential for maintaining and optimizing its performance. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring smooth operation and functionality. Below is an outline of some critical elements that contribute to the overall efficiency and durability.
- Engine System: The powerhouse that drives the vehicle forward, responsible for converting fuel into motion through a series of controlled explosions.
- Transmission: This system manages the vehicle’s speed and torque, ensuring smooth transitions between gears and adapting to driving conditions.
- Suspension: A critical element that enhances ride comfort and stability by absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces and keeping the vehicle grounded.
- Braking Mechanism: Ensures safe and effective stopping power, working in tandem with other safety systems to prevent accidents.
- Cooling System: Helps regulate the temperature of the engine, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance during extended use.
- Power source block – the central unit driving the vehicle’s operation.
- Cooling system – consisting of a radiator, coolant hoses, and related parts to manage heat dissipation.
- Air intake system – regulates airflow to ensure proper combustion.
- Electrical system – battery and fuse box, providing necessary energy and protection for the vehicle’s circuits.
- Fluid reservoirs – containers for vital fluids such as engine oil, coolant, and windshield washer fluid.
- Gearbox: Responsible for regulating power distribution and enabling different speed options.
- Clutch: Facilitates the engagement and disengagement of the gearbox with the engine.
- Torque Converter: Transfers power from the engine to the transmission in automatic setups.
- Driveshaft: Transmits power from the transmission to the axles.
- Axles: Connect the driveshaft to the wheels, enabling their rotation.
- Differential: Distributes power between the wheels, especially crucial for turns.
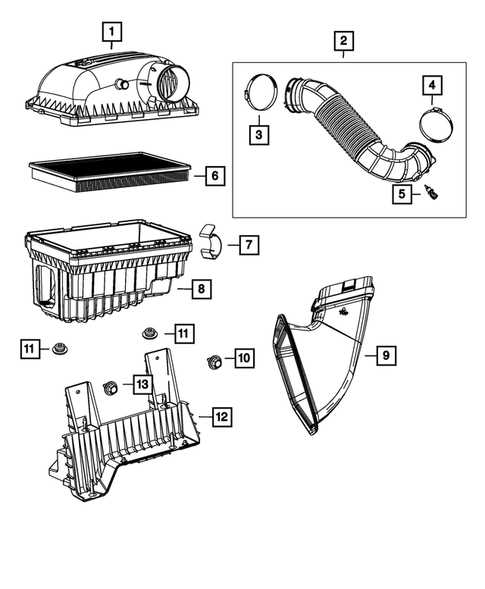
Engine Bay Components Layout
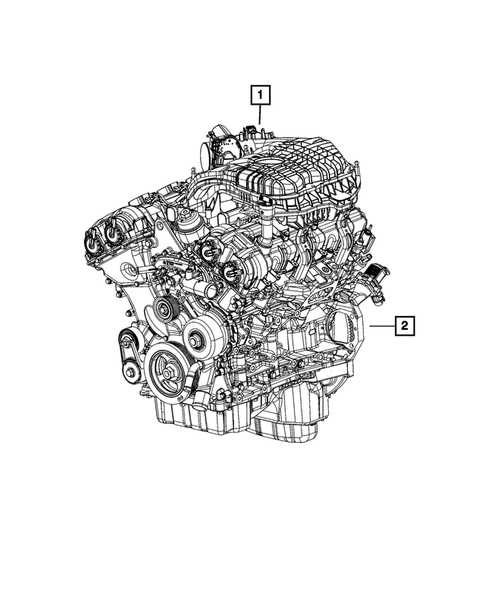
The arrangement under the hood is crucial for ensuring efficient performance and easy maintenance. This section provides an overview of the key elements found in the engine bay, focusing on the strategic positioning of each component to optimize space and accessibility.
Below is a breakdown of the essential elements located in this area:
The positioning of these components allows for streamlined functionality, contributing to the overall reliability and ease of service in this area.
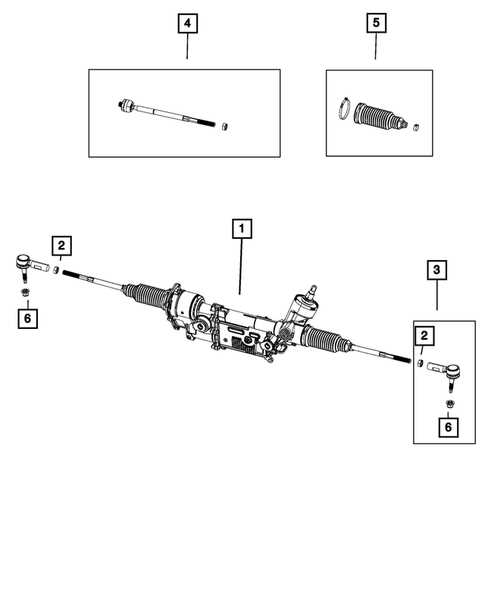
Suspension and Steering Parts Arrangement
The organization of components responsible for handling and ride comfort is crucial to maintaining the balance and control of a vehicle. Each element in the system works together to ensure stability, providing smooth steering and absorbing shocks from the road surface. Understanding how these elements interconnect allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting when adjustments or repairs are necessary.
| Component | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Arm | Connects the frame to the steering components, enabling up and down movement for the wheels. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shock Absorber | Reduces the impact of bumps and uneven surfaces, providing a smoother ride. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Steering Linkage | Transfers motion from the steering wheel to the wheels, allowing precise control and
Electrical System and Wiring Diagram
The electrical system is a vital component that powers various devices and ensures their proper functionality. Understanding the overall layout of the wiring connections helps in diagnosing potential issues and maintaining the system efficiently. This section provides a detailed look at how the different circuits are interlinked and how electrical power is distributed throughout the vehicle. Key elements of this setup include power sources, fuses, relays, and connectors, all of which contribute to the seamless operation of essential systems. Analyzing the wiring routes allows for pinpointing faults, making repairs easier, and ensuring reliable performance over time. Proper attention to wire routing and component connections is crucial for maintaining system integrity. Brake System Component Locations
The braking mechanism is a crucial part of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control. To understand how it functions, it is essential to identify the main areas where the key components are situated. Each element, from the master cylinder to the calipers, plays a vital role in the overall performance of the braking system. Primary Brake Components
The main components include the brake pedal, master cylinder, brake lines, and wheel cylinders or calipers. These parts are strategically placed to work in unison for efficient operation. The brake pedal transmits force to the master cylinder, which then distributes hydraulic pressure through the lines to the braking units located near the wheels. Detailed Location Overview
|