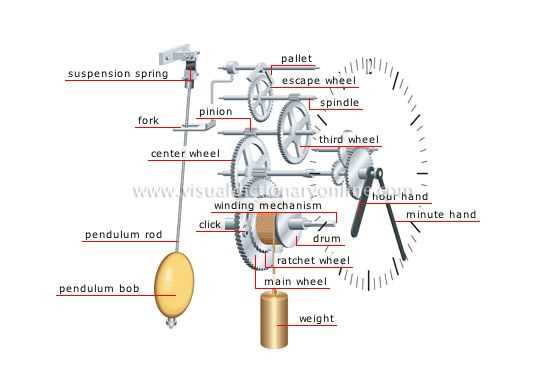
The intricate design of traditional timekeeping devices encompasses a variety of essential components that work harmoniously to ensure accurate measurement of time. Each element, from the driving force to the regulating mechanism, plays a critical role in the overall functionality of these elegant creations. A comprehensive overview of these mechanisms offers insights into the craftsmanship and engineering that define these classic artifacts.
In this section, we will explore the specific elements involved in the operation of these remarkable timekeeping instruments. The interaction between gears, weights, and pendulums creates a symphony of movement that not only serves a practical purpose but also contributes to the aesthetic appeal of the device. Understanding these components enhances appreciation for the artistry and precision involved in their construction.
By examining the arrangement and function of each constituent, one can gain a deeper knowledge of how these devices measure the passage of time. This exploration serves as an invitation to delve into the world of horology, revealing the beauty and complexity that lies within each mechanism. As we uncover the secrets of these exquisite creations, we celebrate the legacy of craftsmanship that has endured through generations.
The intricate design of a traditional timekeeping instrument involves several essential elements that work together harmoniously. Understanding these components is vital for appreciating the craftsmanship and functionality that characterize such a remarkable piece.
Essential Elements

- Movement: This is the heart of the device, responsible for regulating time and powering the mechanism.
- Pendulum: A swinging element that helps maintain accurate timing through its steady motion.
- Weights: These provide the necessary energy to keep the movement running smoothly, typically suspended from chains or cables.
- Dial: The face of the instrument, where the time is displayed, often adorned with decorative features.
- Case: The outer structure that houses and protects the internal components, often crafted from wood with intricate designs.
Additional Features
- Chimes: Many models include a musical feature that chimes at regular intervals, enhancing the ambiance.
- Escapement: A mechanism that controls the release of energy from the movement, ensuring consistent ticking.
- Glass Panels: These not only protect the face but also allow visibility of the inner workings and elegance of the design.
Functionality of Pendulum and Weights

The intricate relationship between the swinging element and the heavy components is fundamental to the operation of these timekeeping mechanisms. This system not only regulates the passage of time but also enhances the accuracy and stability of the entire mechanism.
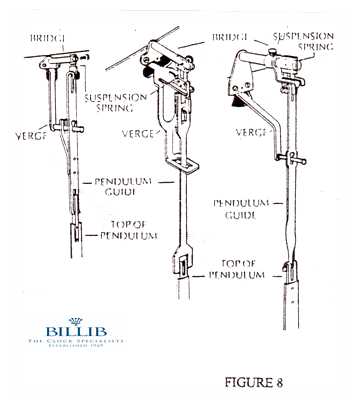
Role of the Swinging Element
The swinging element is crucial for maintaining a consistent rhythm. As it moves back and forth, it creates a predictable interval that dictates how the gears and other components interact. This oscillation serves as a timekeeping reference, ensuring that the entire assembly operates smoothly and accurately.
Impact of the Heavy Components
The weighted elements provide the necessary force to keep the mechanism in motion. Their gravitational pull ensures that the swinging element maintains its rhythm, while also driving the gears that control the overall timing. This balance of weight and motion is essential for precise operation, allowing the device to function reliably over extended periods.
Identifying the Escapement Mechanism

The escapement mechanism is a critical component that regulates the movement within timekeeping devices, ensuring accurate and consistent operation. It plays a vital role in controlling the release of energy, allowing for the measured passage of time. Understanding its structure and function can enhance appreciation for the intricacies of these intricate mechanisms.
This mechanism typically consists of several key elements, including a pallet fork and a gear wheel. The interaction between these components enables the mechanism to halt the wheel’s movement momentarily, allowing a pendulum or balance wheel to maintain its rhythm. Observing how these parts work together offers insight into the overall functioning of the system.
When identifying the escapement mechanism, one should examine the movement of the gear wheel and the action of the pallet fork. Any irregularities or wear can significantly affect the accuracy and performance of the timekeeping device. Therefore, recognizing the signs of deterioration or malfunction is crucial for maintenance and repair.
Types of Clock Movements Explained
Understanding the mechanisms behind timekeeping devices is essential for enthusiasts and collectors. These mechanisms, which drive the hands and provide precision, can vary significantly in design and operation. Here, we explore the different categories of movements commonly found in these timekeeping instruments.
There are primarily three main types of movements:
- Mechanical Movements: These rely on intricate gears and springs to function. They can be wound manually or can operate via a pendulum for added accuracy. The craftsmanship in mechanical movements is often highly regarded.
- Quartz Movements: These utilize a battery to power a small quartz crystal, which oscillates at a precise frequency. Quartz movements are known for their accuracy and low maintenance, making them a popular choice.
- Smart Movements: Incorporating technology, these movements can connect to smartphones or other devices. They often offer features like alarms, timers, and synchronization with time zones, appealing to modern users.
Each type of movement has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, catering to various preferences and purposes. Mechanical movements offer traditional craftsmanship, while quartz options provide reliability and ease of use. Smart mechanisms, on the other hand, appeal to tech-savvy individuals looking for multifunctional devices.
In conclusion, the choice of movement can greatly influence the functionality and aesthetic appeal of these timekeeping devices. Understanding these differences is key for anyone interested in acquiring or maintaining these instruments.
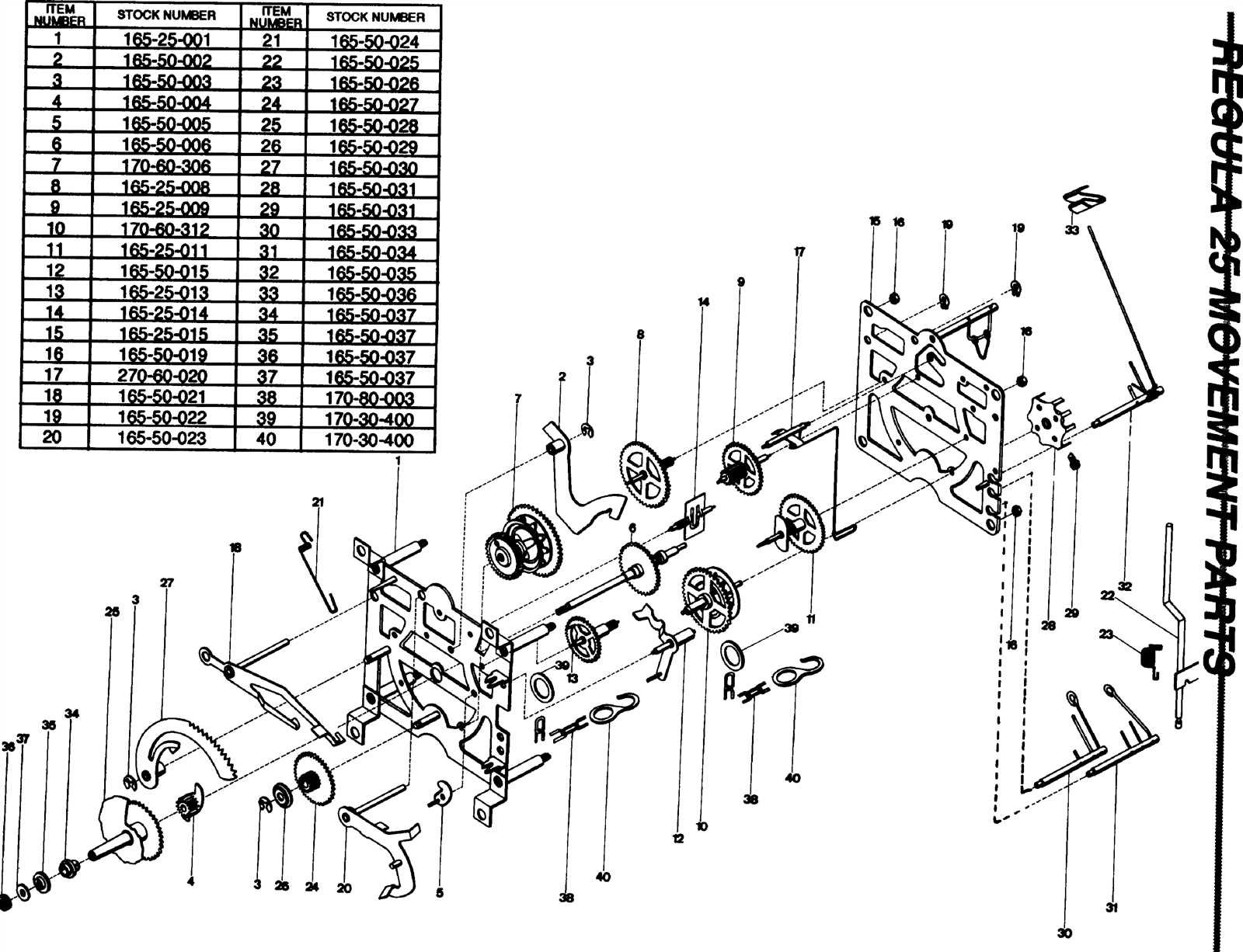
Assembly Process of Clock Parts
Creating a timekeeping device involves a meticulous sequence of tasks to ensure each component fits seamlessly. This process requires precision and attention to detail, allowing for the smooth operation of the mechanism. Each element plays a vital role in maintaining accurate time measurement.
Steps for Assembly
The following stages outline the assembly sequence:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Begin by laying out all necessary components to ensure easy access during assembly. |
| 2 | Connect the movement mechanism, ensuring that gears align properly for optimal function. |
| 3 | Attach the pendulum or alternative timing element, which regulates the device’s timing accuracy. |
| 4 | Incorporate the casing, ensuring that all internal parts are secured and positioned correctly. |
| 5 | Finalize the assembly by adding the face and hands, making sure they move freely and accurately indicate time. |
Final Adjustments
Once assembled, it’s essential to calibrate the device to ensure precise operation. This involves adjusting the timing mechanism and ensuring all elements are functioning harmoniously. Regular maintenance will help preserve accuracy and longevity.
Maintenance Tips for Clock Longevity

To ensure the lasting performance of your timepiece, regular upkeep is essential. Implementing proper care practices can significantly enhance its durability and functionality over the years.
Regular Cleaning: Dust and grime can accumulate over time, affecting the internal mechanisms. It is advisable to gently clean the exterior using a soft cloth, avoiding harsh chemicals that may damage the finish.
Lubrication: Adequate lubrication of moving components is crucial for smooth operation. Consider applying suitable oil to the gears and pivots periodically, following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Temperature Control: Keeping your timepiece in a stable environment is vital. Extreme temperatures and humidity can adversely affect its performance. Aim to place it in a climate-controlled room away from direct sunlight.
Professional Servicing: Engaging a skilled technician for routine inspections and maintenance can prevent potential issues. They can identify wear and tear early, ensuring that everything functions as intended.
Careful Handling: When relocating or adjusting the timepiece, handle it with care to avoid unnecessary jolts or falls. Proper handling minimizes the risk of damaging delicate components.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Antique timepieces can exhibit a variety of challenges over time, often resulting from mechanical wear or environmental factors. Understanding these common problems and how to address them can help maintain functionality and extend the lifespan of the mechanism.
Here are some frequent issues you might encounter along with suggested solutions:
| Issue | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Irregular ticking | The mechanism may not tick evenly due to misalignment or friction. | Check for any obstructions and ensure all components are properly aligned. |
| Stoppage | The timekeeping device may stop entirely due to a power failure or blockage. | Examine for any dirt or debris that may be causing a jam and clean the internal parts. |
| Incorrect time | The timepiece may run too fast or too slow. | Adjust the regulating mechanism to synchronize with the correct time. |
| Chiming issues | The chiming feature may not activate or may be out of sync. | Inspect the chiming mechanism and adjust it according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. |