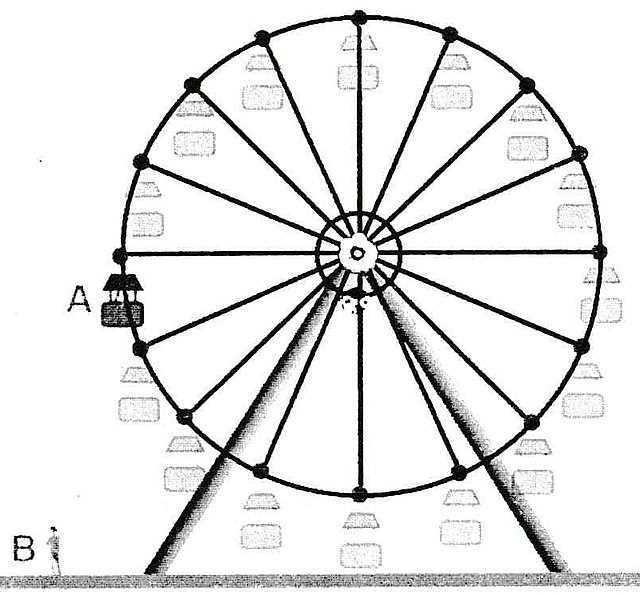
The magnificent structure that captures the imagination of visitors around the world stands as a symbol of joy and wonder. This towering installation, often found in amusement parks and city skylines, consists of various elements that work harmoniously together to create a captivating experience. Exploring its intricacies reveals how design and engineering come together to support both functionality and delight.
Each segment of this enchanting attraction plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and safety. From the towering supports to the rotating cabins, every piece is meticulously crafted to withstand the forces of nature and provide a thrilling journey for passengers. Understanding these essential components helps to appreciate the artistry and skill involved in bringing this experience to life.
By delving into the specifics of each segment, one gains insight into the balance of aesthetics and engineering. The interplay between structural integrity and visual appeal showcases the innovation behind such a beloved amusement feature. Join us as we uncover the intricacies that make this spectacular attraction not just a ride, but a marvel of modern engineering.
Understanding the Structure of Ferris Wheels
The design of a giant rotating structure combines artistry and engineering, creating a captivating experience for visitors. At its core, this mechanism relies on a carefully balanced framework that supports movement and safety. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring stability and functionality, allowing for smooth operation while offering breathtaking views.
Central to the construction is the main support, which acts as the backbone of the entire apparatus. This towering element distributes weight evenly, enabling the entire system to withstand varying forces during operation. Surrounding this core are the intricate connections that form the overall shape, designed to enhance both aesthetics and structural integrity.
The passenger cabins, often suspended from the outer rim, are engineered for comfort and safety. These compartments provide an inviting space for individuals to enjoy the ascent and descent, showcasing the surrounding landscape. The arrangement and design of these cabins are critical for maintaining balance and ensuring an enjoyable experience.
Additionally, the mechanics involved in the rotation include gears and motors that facilitate movement. These elements are precisely calibrated to control speed and enhance the ride’s safety features. The synergy between the various components creates an enchanting spectacle that draws crowds and offers a memorable adventure.
Main Components of a Ferris Wheel
The design of this towering amusement structure encompasses several essential elements that work harmoniously to create a thrilling experience. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring both functionality and safety while providing passengers with breathtaking views.
Support Structure: The foundation of this attraction is its robust frame, typically made from steel, which provides stability and strength. This skeleton supports the entire apparatus, allowing it to reach impressive heights while withstanding various weather conditions.
Rotation Mechanism: At the heart of the experience lies the rotating system, which enables the circular motion. This mechanism is often powered by electric motors and ensures a smooth and controlled ascent and descent, allowing riders to enjoy the scenery at a leisurely pace.
Passenger Baskets: The individual compartments are designed to accommodate riders comfortably. These are securely attached to the main structure and often feature safety harnesses or bars to protect passengers during their journey.
Control System: A sophisticated control system governs the entire operation. It allows the operator to manage the speed and rotation, ensuring a seamless experience for riders. Additionally, emergency protocols are in place to address any unforeseen circumstances.
Lighting and Aesthetics: Visual appeal is a significant aspect, with vibrant lights and decorations enhancing the overall experience. These elements not only attract visitors but also create a festive atmosphere, especially during evening operations.
Mechanisms Behind Wheel Rotation
The rotation of large circular structures is an intricate process driven by several key components working in harmony. Understanding these mechanisms reveals the engineering marvel behind their smooth and efficient movement, essential for the overall experience.
At the core of this functionality are several fundamental elements:
- Drive System: This includes motors and gears that provide the necessary torque to initiate and sustain movement.
- Support Structure: A robust framework that ensures stability and balance during operation.
- Control Mechanisms: Systems that allow operators to manage speed and direction, ensuring a safe ride.
- Rotation Axis: A central pivot around which the entire assembly turns, crucial for maintaining equilibrium.
Each component plays a vital role in achieving the desired motion:
- Energy Input: Electrical or mechanical energy is transformed into kinetic energy.
- Transmission: Gears and pulleys efficiently transfer power from the motor to the rotating assembly.
- Friction Reduction: Bearings and lubricants minimize resistance, facilitating smoother rotations.
Through this intricate interplay of mechanics, large circular attractions can offer exhilarating experiences, captivating riders with their graceful and steady movement.
Types of Ferris Wheel Designs
Various configurations of these iconic amusement structures reflect both aesthetic appeal and engineering innovation. Each design not only enhances the experience for riders but also contributes to the visual landscape of parks and fairs. Understanding the different styles helps to appreciate their unique characteristics and the ingenuity behind their construction.
Classic Models
Traditional designs often feature a circular structure with evenly spaced cabins, providing riders with a straightforward view of their surroundings. These classic variants prioritize stability and ease of access, making them popular in amusement parks worldwide. Their familiar silhouette evokes nostalgia and remains a favorite among visitors of all ages.
Modern Innovations
Contemporary iterations incorporate advanced technology and creative aesthetics. Some utilize cable systems or incorporate dynamic lighting to enhance the visual experience, while others boast transparent cabins for an unobstructed view. These innovative designs not only attract thrill-seekers but also serve as landmarks in urban environments, blending entertainment with architectural artistry.
Materials Used in Construction
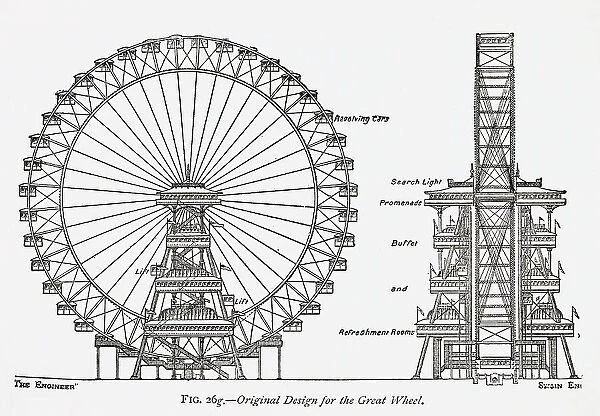
In the creation of large amusement structures, the selection of appropriate resources plays a crucial role in ensuring both safety and longevity. Various elements contribute to the overall integrity and functionality of these attractions, making it essential to choose wisely among available options.
Steel is one of the primary materials utilized, valued for its strength and durability. Its ability to withstand significant loads makes it an ideal choice for the framework, providing stability during operation. Additionally, aluminum is often employed for components that require lightweight characteristics, enhancing mobility without compromising on sturdiness.
Concrete serves as a foundational material, offering a robust base that supports the entire structure. Its resilience against environmental factors ensures that the attraction remains secure over time. Furthermore, glass can be integrated into the design for aesthetic purposes, allowing for panoramic views while ensuring passenger safety.
Lastly, advanced composite materials are increasingly being adopted due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. This modern approach not only enhances performance but also contributes to innovative design possibilities, pushing the boundaries of traditional construction techniques.
Safety Features in Ferris Wheels
When it comes to amusement rides, ensuring the well-being of passengers is of utmost importance. A well-designed structure incorporates various safety mechanisms that work together to create a secure experience for all riders. These elements not only enhance rider confidence but also mitigate potential risks associated with height and movement.
Structural Integrity and Materials
The framework of these attractions is engineered to withstand significant forces and environmental conditions. Manufacturers often use high-strength steel and reinforced materials that provide stability and durability. Regular inspections and maintenance schedules are crucial, allowing for timely identification of wear and tear, ensuring that the structure remains safe for use.
Passenger Restraints and Emergency Protocols
To further protect individuals, robust restraint systems are installed in each cabin. These mechanisms secure riders during the ascent and descent, minimizing the risk of accidental falls. In addition, emergency protocols are in place, including manual operation systems and evacuation procedures, which are practiced by staff to ensure quick and effective responses during unforeseen situations.
How Ferris Wheels Are Maintained
Ensuring the longevity and safety of amusement structures involves a series of meticulous procedures. Regular upkeep is essential to maintain their functionality and provide a secure experience for riders.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Daily | Check for any visible wear or damage to the components. |
| Lubrication | Weekly | Apply grease to moving parts to ensure smooth operation. |
| Structural Integrity Check | Monthly | Examine the framework for any signs of stress or fatigue. |
| Electrical Systems Review | Quarterly | Inspect wiring and connections for safety and functionality. |
| Annual Overhaul | Yearly | Complete disassembly and thorough inspection of all major components. |
Historical Evolution of Ferris Wheels
The journey of giant rotating structures has captivated the imagination of people for over a century. These impressive constructions, often found at amusement parks, have transformed from simple attractions into intricate marvels of engineering. Their evolution reflects advancements in design, technology, and cultural significance, showcasing how they have adapted to changing societal tastes and technological capabilities.
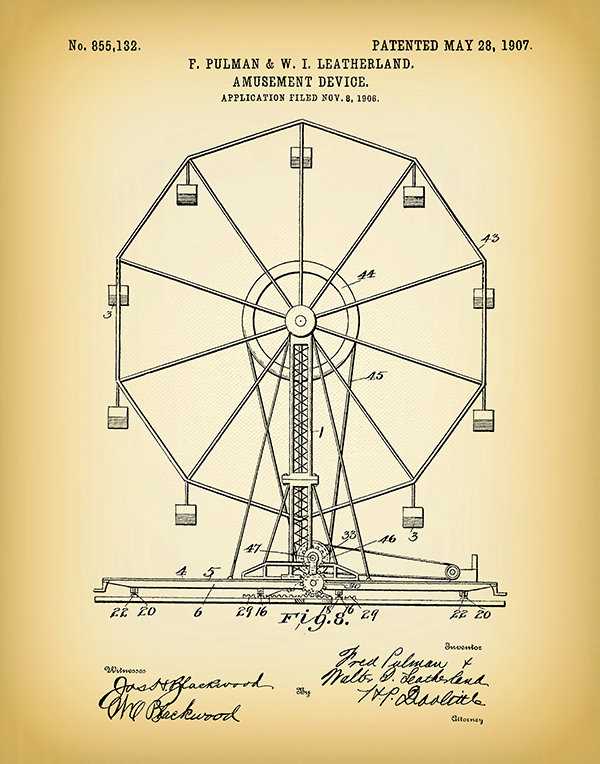
Early Innovations
The concept of large circular structures dates back to ancient civilizations, but the modern version began to take shape in the late 19th century. Here are some key milestones:
- Ancient Origins: Early instances of rotating structures can be traced back to ancient Greece and Rome, where simple designs were used for entertainment.
- Industrial Revolution: The rise of industrialization in the 18th and 19th centuries paved the way for more sophisticated engineering techniques, enabling larger and more stable structures.
- Chicago’s World Fair (1893): The iconic attraction designed by George Ferris marked a significant turning point, showcasing both engineering prowess and a new era of amusement rides.
Modern Developments
Throughout the 20th and 21st centuries, these attractions have continued to evolve, driven by innovation and the desire for new experiences. Notable developments include:
- Technological Advancements: Modern materials and construction techniques have allowed for taller and more complex designs, enhancing both safety and aesthetics.
- Global Spread: These structures have become popular worldwide, often serving as iconic symbols of cities and cultural landmarks.
- Interactive Experiences: Contemporary designs often incorporate advanced lighting, sound, and immersive experiences, appealing to a broader audience.
The historical trajectory of these rotating giants illustrates a blend of artistry and engineering, reflecting societal changes and technological progress. As they continue to evolve, they remain a testament to human creativity and ingenuity.
Cultural Significance of Ferris Wheels
The towering structures that offer breathtaking views have become iconic symbols in various cultures around the globe. They embody the spirit of celebration, joy, and community, often serving as central attractions at fairs and amusement parks. These colossal constructions are not merely entertainment devices; they represent the intersection of innovation and leisure, showcasing human creativity and engineering prowess.
Throughout history, these grand installations have played significant roles in festivals and public gatherings, marking milestones and communal experiences. They often evoke nostalgia, reminding people of simpler times spent with loved ones. Additionally, they have been featured in numerous artistic expressions, from literature to cinema, further solidifying their place in the collective cultural consciousness.
In many cities, these attractions symbolize progress and modernity, becoming landmarks that define the skyline and attract tourism. They serve as a backdrop for personal moments, such as proposals and family reunions, embedding them deeply into the fabric of social traditions. Ultimately, their presence fosters a sense of wonder and connection, transcending generations and cultural boundaries.