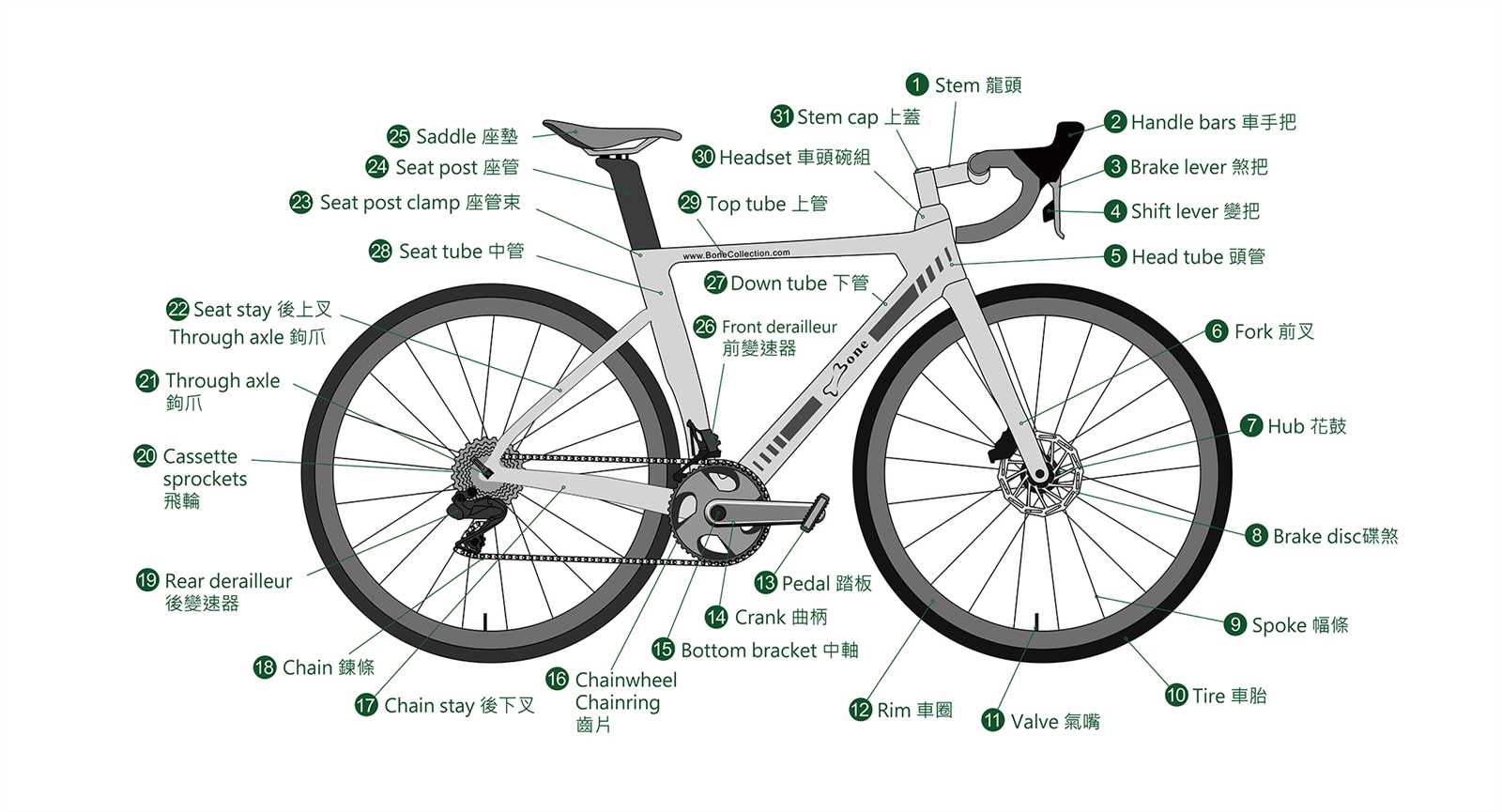
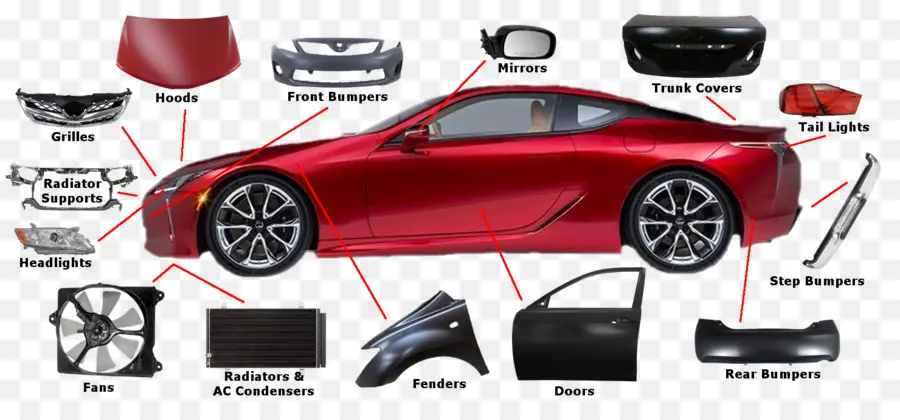
In the intricate world of automotive design, the assembly responsible for mobility plays a crucial role. This section aims to explore the various elements that contribute to the functionality and efficiency of the rolling system. By grasping these components, one can better appreciate their importance in ensuring a smooth driving experience.
Each individual element is integral to the overall operation, working in harmony to provide stability and performance. From the foundational structures to the intricate accessories, the synergy between these components defines the ultimate driving experience. Delving into their specific roles reveals a fascinating interplay of engineering and design.
By enhancing our understanding of these mechanisms, enthusiasts and professionals alike can make informed decisions regarding maintenance, upgrades, and innovations. As we proceed, let’s break down each segment to uncover its unique contributions and interdependencies.
Understanding Wheel Components

Grasping the essential elements that contribute to a vehicle’s motion is crucial for any enthusiast. Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring stability, performance, and safety while navigating various terrains. Familiarity with these elements enhances one’s ability to maintain and optimize functionality.
Key Elements of the Assembly
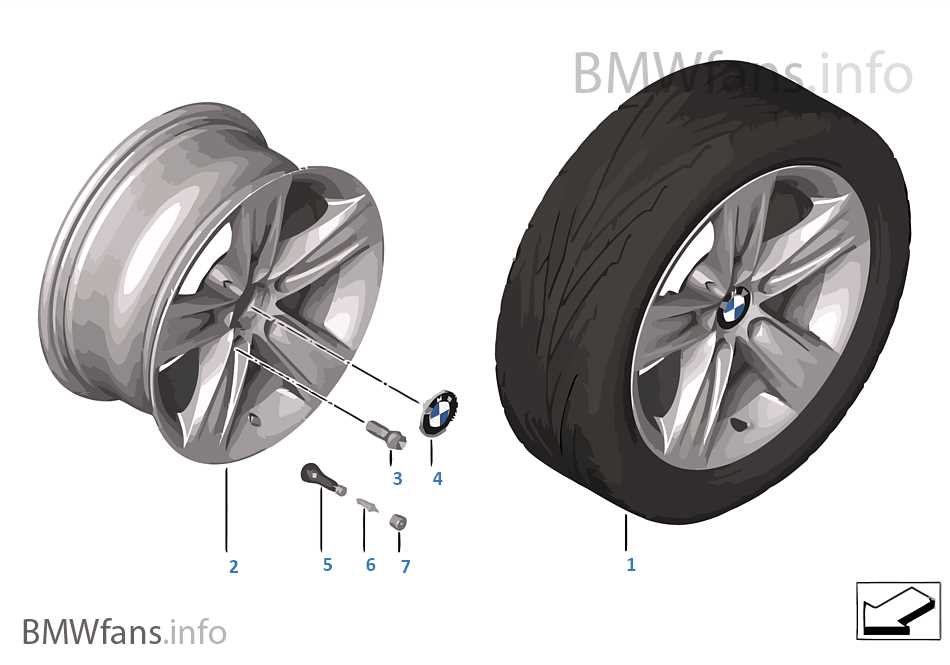
At the core of this assembly lies the hub, which connects the structure to the axle, allowing for smooth rotation. Surrounding this central piece are the spokes, providing strength and reducing weight. Understanding the interplay between these components is vital for effective maintenance.
Performance and Safety Considerations
Braking systems and suspension mechanisms are also integral to overall performance. These systems work together to ensure optimal handling and stability, particularly under demanding conditions. A thorough comprehension of these connections leads to informed decisions when it comes to upgrades or repairs.
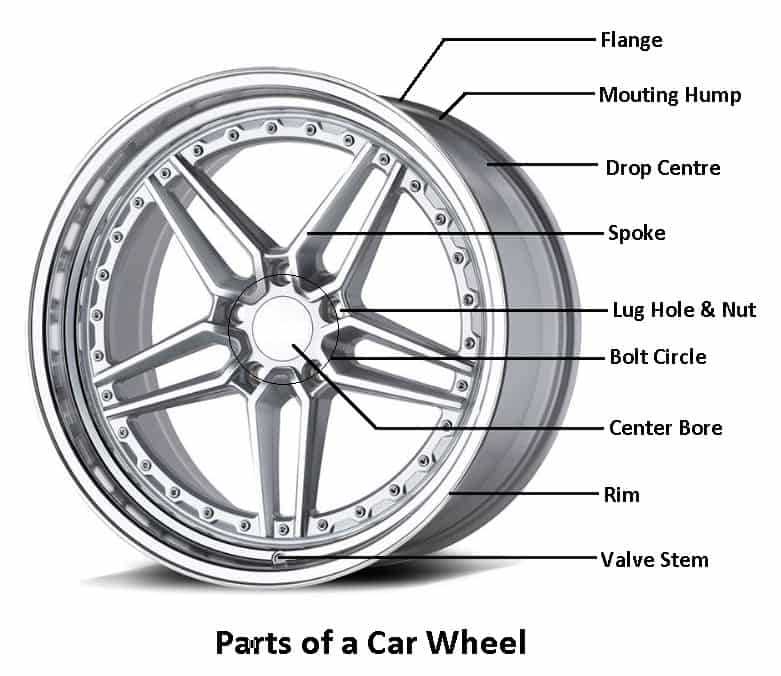
Basic Functions of Wheel Parts

The various components of a rolling mechanism play crucial roles in ensuring smooth operation and stability. Understanding their fundamental functions is essential for optimal performance and safety.
Support and Stability
- Rim: Provides structure and supports the tire, maintaining its shape.
- Hub: Connects the assembly to the axle, facilitating rotation.
- Spokes: Distribute weight evenly and enhance structural integrity.
Traction and Control
- Tread: Offers grip on surfaces, influencing handling and braking.
- Sidewall: Absorbs shock and contributes to overall resilience.
- Valves: Regulate air pressure, essential for maintaining proper performance.
Importance of Wheel Maintenance

Regular upkeep of essential components that connect a vehicle to the road is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Neglecting this aspect can lead to a range of issues, affecting both functionality and longevity. Proper maintenance ensures not only a smooth ride but also enhances the overall driving experience.
Benefits of Regular Maintenance
Ensuring that all elements are in good condition brings numerous advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Safety | Regular checks reduce the risk of failures, providing better control and stability. |
| Improved Performance | Well-maintained components contribute to better handling and fuel efficiency. |
| Cost Savings | Timely repairs can prevent more expensive issues from developing. |
Key Maintenance Practices
To maintain optimal functionality, consider the following practices:
- Regular inspections for wear and tear
- Proper inflation to ensure stability
- Timely replacement of any damaged components
Common Issues with Wheel Parts
When it comes to the components that facilitate movement, various challenges can arise, impacting overall performance and safety. Understanding these common issues can help in maintaining optimal functionality and extending the lifespan of these essential elements.
Wear and Tear: Over time, frequent use can lead to significant degradation. This can manifest as uneven surfaces or reduced effectiveness, necessitating regular inspections and timely replacements.
Alignment Problems: Misalignment can cause uneven distribution of weight, resulting in compromised handling and increased friction. It’s crucial to address alignment issues promptly to ensure a smooth experience.
Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and road salt can lead to rust formation, which weakens structures. Regular cleaning and protective treatments can mitigate this risk and preserve integrity.
Noise and Vibration: Unusual sounds or excessive vibration can indicate underlying issues, such as loose components or damage. Identifying and resolving these symptoms early can prevent more severe complications.
Brake Performance: Components associated with braking may also experience issues. Worn pads or faulty mechanisms can lead to decreased responsiveness, highlighting the importance of routine maintenance.
Being aware of these challenges allows for proactive measures, ensuring safety and efficiency in daily operations.
Types of Wheel Designs
In the realm of automotive engineering, the aesthetics and functionality of circular structures play a crucial role in performance and appearance. Various configurations not only influence the overall look but also impact handling, stability, and efficiency. Understanding the different styles can aid in making informed choices, whether for enhancements or replacements.
| Design Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Spoke | Characterized by multiple rods radiating from the center, this style promotes strength and lightweight construction. | Enhanced airflow, reduced weight, improved handling. |
| Mesh | A complex network of interwoven sections offering a unique visual appeal and structural integrity. | Stylish appearance, excellent brake cooling, good strength. |
| Solid | Featuring a single, unbroken surface, this design emphasizes durability and simplicity. | High strength, easy maintenance, better resistance to damage. |
| Multi-spoke | Combining numerous spokes, this design delivers a balance between aesthetics and functionality. | Visual dynamism, improved grip, good load distribution. |
| Deep Dish | With a pronounced inward curvature, this design creates a striking look and can enhance tire fitment. | Distinctive style, allows for wider tires, improved traction. |
Material Choices for Wheel Construction
The selection of materials for constructing circular supports plays a crucial role in performance, durability, and overall functionality. Different substances offer unique properties that cater to specific needs and preferences, influencing factors such as weight, strength, and cost.
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good heat dissipation | Can be more expensive, less strong than some alloys |
| Steel | High strength, cost-effective, excellent durability | Heavier, prone to rust without treatment |
| Carbon Fiber | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, aesthetic appeal | High cost, complex manufacturing process |
| Magnesium | Very lightweight, good thermal properties | More expensive, can be prone to corrosion |
How to Read a Wheel Diagram
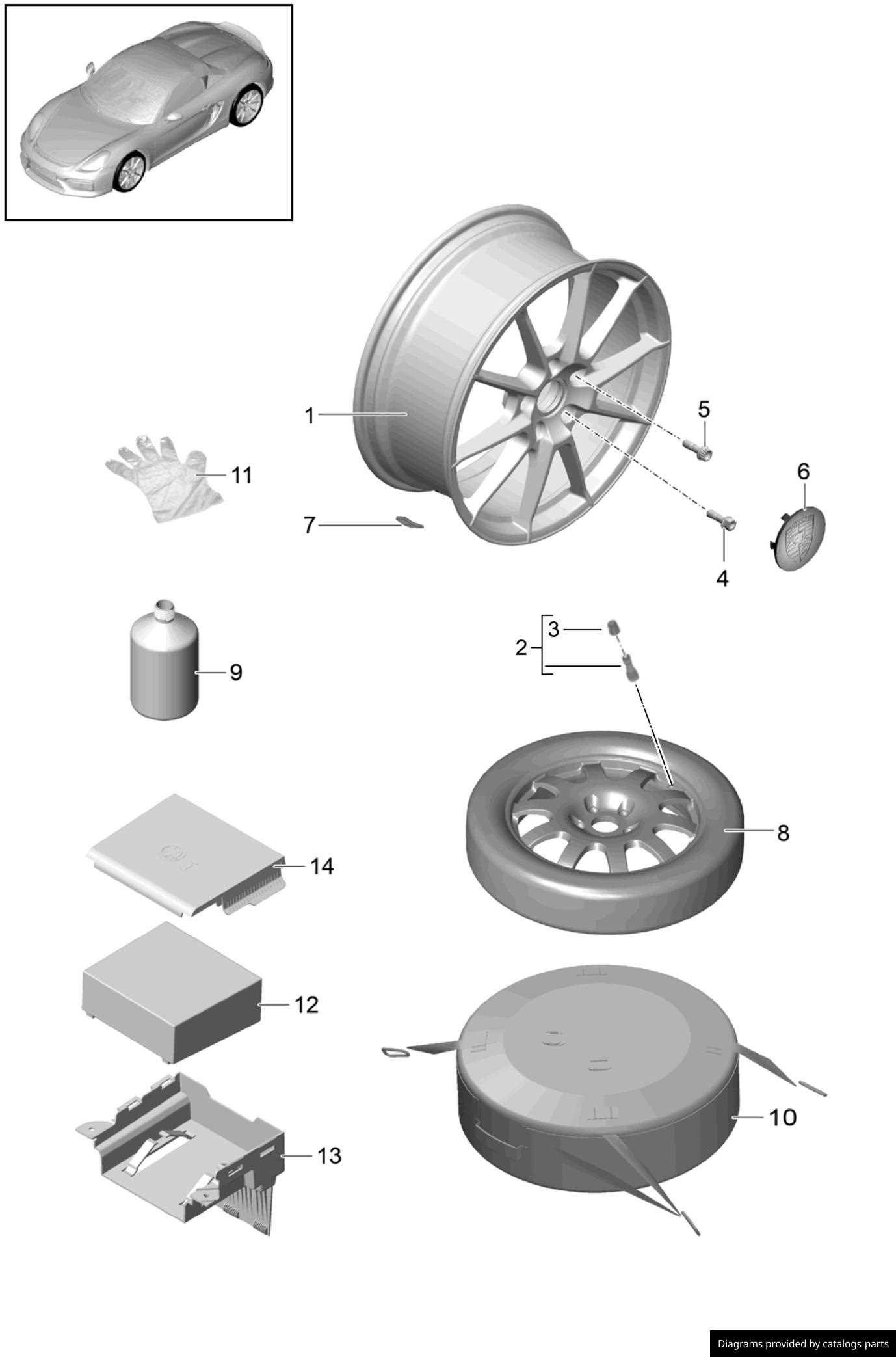
Understanding a visual representation of a circular component is essential for effective maintenance and repairs. By familiarizing yourself with the elements displayed, you can better assess functionality and identify any issues. Each symbol and line conveys specific information about the structure and mechanics involved.
Firstly, take note of the legend or key, which explains the symbols used. This will guide you through the various components and their relationships. Secondly, pay attention to the scale, as it provides insight into the actual size and proportions of the elements depicted.
Finally, practice interpreting different diagrams to enhance your understanding. With time, you’ll develop the ability to quickly and accurately decode these illustrations, leading to more informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades.
Tools for Wheel Inspection and Repair
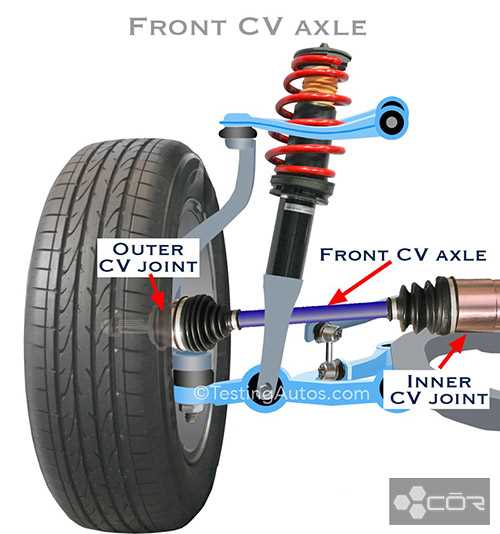
Ensuring the safety and performance of a vehicle requires regular examination and maintenance of its rolling components. Various instruments are essential for identifying issues and executing necessary repairs effectively. Utilizing the right tools not only streamlines the process but also enhances the longevity of the elements involved.
Essential Inspection Tools

- Tread Depth Gauge
- Pressure Gauge
- Visual Inspection Mirror
- Flashlight
- Brake Pad Thickness Tool
Repair Instruments
- Wrench Set
- Torque Wrench
- Jack and Jack Stands
- Pliers
- Sealant and Adhesives
Proper knowledge and application of these tools can significantly improve maintenance outcomes and ensure a smoother ride.