
Exploring the internal design and connections of vintage agricultural machines can reveal much about their efficiency and performance. By examining how each element is positioned and connected, we gain insights into the system’s functionality and how it supports daily operations in the field. This approach ensures that even the oldest machinery continues to operate smoothly with proper maintenance and care.
When analyzing mechanical blueprints, one must focus on the structure of key elements, ensuring that everything is in its place for optimal performance. Understanding the relationship between various components is essential for addressing malfunctions or upgrading systems to meet modern standards. By doing so, you can maximize the lifespan and effectiveness of essential equipment.
By identifying specific areas where improvements can be made, owners can not only keep their equipment running longer but also enhance its performance. Detailed knowledge of the inner workings helps maintain reliability, ensuring that these powerful machines remain an indispensable tool for farming and related industries.
Ford 1910 Tractor Parts Diagram
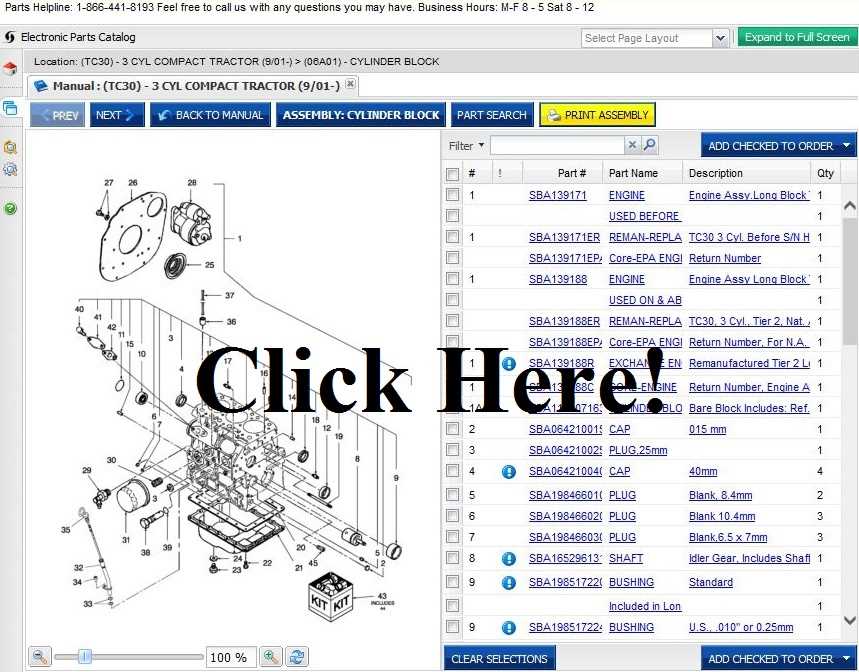
Understanding the layout and connections within mechanical systems is crucial for efficient maintenance and repairs. By analyzing the structure and identifying each key element, you can ensure smooth operation and prolonged equipment life.
Component Overview
Each system consists of various elements working together to create a cohesive unit. These include essential mechanisms responsible for movement, power transmission, and functional support. Proper identification and understanding of these individual components are vital for seamless operation.
Interconnectivity of Systems
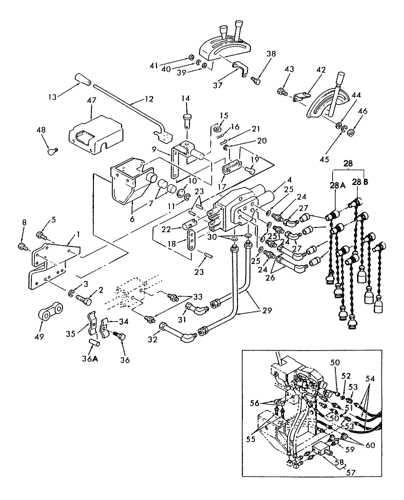
In any machinery, the relationship between different assemblies plays a pivotal role. These interconnected systems ensure that energy flows correctly, moving through a series of mechanisms to deliver power where needed. Maintaining this flow is fundamental for optimal performance.
Overview of Key Tractor Components

The intricate machinery that powers agricultural vehicles relies on several essential elements working together. These mechanical parts are designed to ensure smooth operation, enhancing both efficiency and durability in the field. Understanding the role each component plays is vital for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity.
Engine system: The core of any vehicle, the engine converts energy into motion, providing the necessary power to drive various functions. Proper maintenance and timely inspections are crucial to keeping this system running effectively.
Hydraulic system: This crucial mechanism allows for the control of lifting and lowering attachments, ensuring precise movements during tasks. Its reliability depends on well-maintained fluid levels and functioning seals.
Transmission: Responsible for transferring the engine’s power to the wheels, the transmission is vital for adjusting speed and torque. It plays a key role in enabling smooth transitions between different gears for a variety of terrain types.
Electrical components: These systems control essential functions, such as lighting and ignition, ensuring that all operations run smoothly and efficiently. Regular checks can prevent malfunctions and improve overall reliability.
Understanding the Engine Assembly Layout
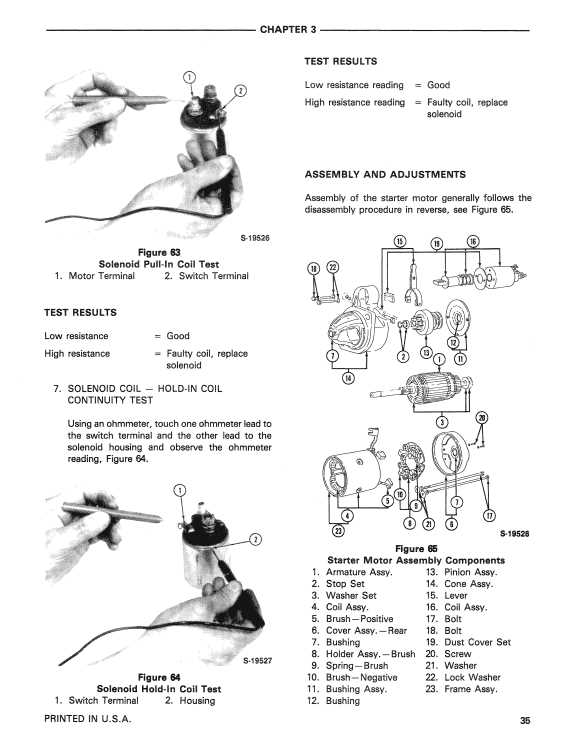
The layout of the engine components is critical for ensuring smooth operation and long-term performance. Each element plays a vital role in facilitating energy conversion, cooling, and movement within the system. Understanding how these components are positioned can help identify potential issues and improve maintenance strategies.
The core arrangement of mechanical elements is designed to optimize efficiency, allowing energy to be transferred with minimal friction and heat loss. Key elements such as pistons, valves, and cylinders are strategically placed to enable precise control over the system’s internal processes.
Proper alignment of these components ensures that the engine runs efficiently, reducing the likelihood of mechanical failures. A clear understanding of this arrangement allows for easier troubleshooting and improved performance adjustments.
Transmission System: Structure and Function
The transmission mechanism plays a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and operational efficiency within the overall machinery. By managing how energy is transferred from the engine to the wheels, this system ensures optimal performance under varying conditions.
Main Components of the System

- Clutch assembly: Allows the operator to disconnect power from the engine temporarily, enabling shifts between gears.
- Gearbox: Contains different gears that adjust the power output and speed of the machine according to operational needs.
- Shafts: Transmit power from one component to another within the system, ensuring energy flows effectively.
Functionality and Operation
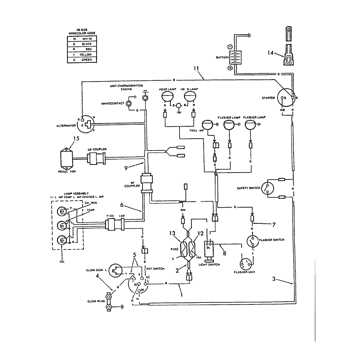
The transmission system’s primary function is to regulate speed and torque. This is achieved by selecting the appropriate gear ratio depending on the terrain and task at hand. By shifting gears, the machine can operate efficiently, whether under heavy load or in lighter conditions.
Hydraulic System Parts and Connections
The hydraulic mechanism plays a critical role in enhancing the overall functionality of various equipment by ensuring smooth movement and control of different components. Understanding the key elements involved in this system is essential for maintaining proper operation and ensuring longevity. Below, we explore the essential components and connections within this setup.
Key Components of the Hydraulic Mechanism

- Pumps: These are responsible for generating the flow of fluid that powers the system.
- Valves: These control the direction and amount of fluid movement, enabling precise operations.
- Cylinders: These convert the hydraulic fluid pressure into mechanical force to move various components.
- Filters: Designed to keep the fluid clean and free of contaminants that could damage other parts.
Connections and Fluid Flow
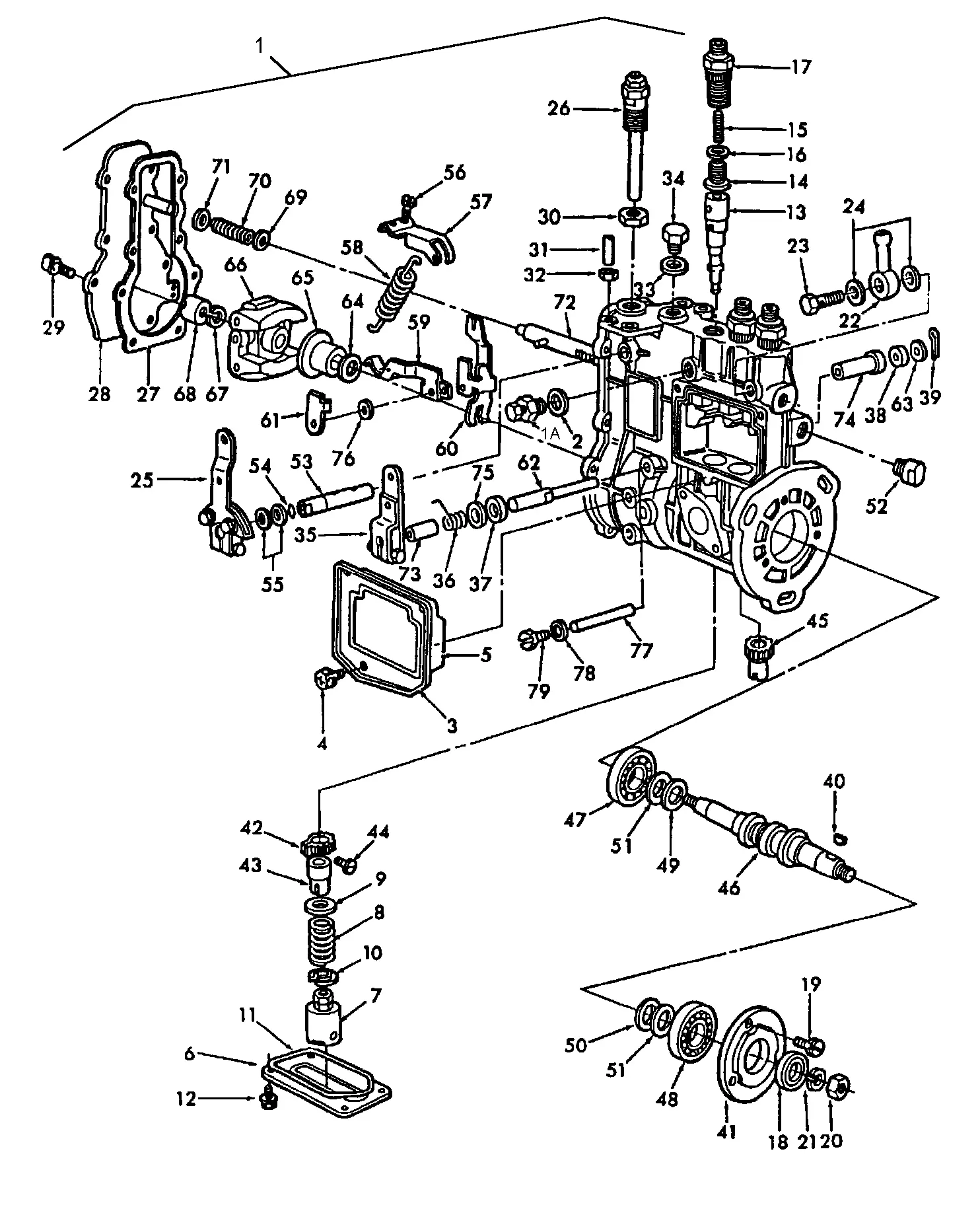
- Hoses and Tubes: These flexible lines carry fluid between different sections, ensuring a continuous flow.
- Fittings: Secure and connect various pipes and hoses, preventing leaks and ensuring efficient operation.
- Reservoir: This holds the hydraulic fluid, allowing the system to draw the necessary amount for operation.
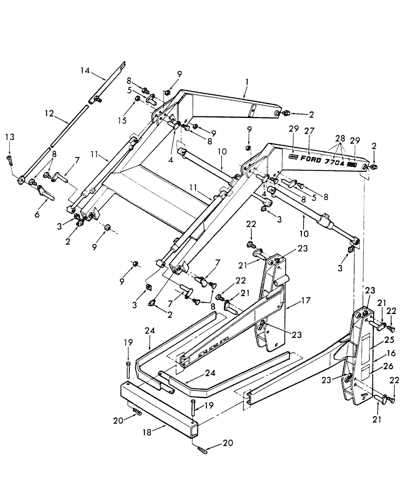
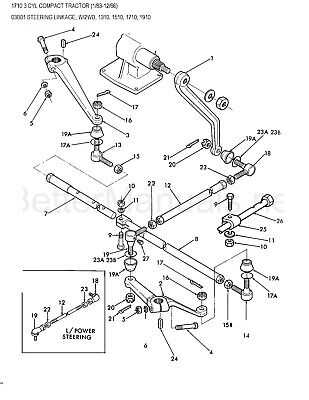
Detailed View of the Steering Mechanism
The steering system is a critical component in ensuring precise control and maneuverability of heavy machinery. This intricate assembly facilitates directional changes while maintaining stability, allowing operators to navigate various terrains with confidence. Understanding the elements that comprise this mechanism is essential for effective maintenance and operation.
At the core of the steering assembly lies the steering wheel, which is connected to a series of linkages and gears. These components translate the rotational motion of the wheel into linear movement, guiding the vehicle’s front wheels. Key parts include the steering column, which supports the wheel and houses essential controls, as well as the pitman arm and drag link, which play pivotal roles in the overall functionality. Proper inspection and adjustment of these elements are vital for optimal performance.
Brake System Components and Diagram
The braking mechanism is a crucial aspect of any agricultural machinery, ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding the various elements involved in this system is essential for maintaining optimal functionality. This section will explore the key components and their arrangement within the braking assembly, providing a comprehensive overview.
Each part plays a significant role in the overall performance, and knowledge of their interactions can aid in effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Pedal | The lever that the operator presses to activate the braking system. |
| Master Cylinder | Converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. |
| Brake Lines | Flexible tubes that carry hydraulic fluid to the brake assembly. |
| Brake Shoes | Friction components that engage with the drum to slow down or stop motion. |
| Brake Drum | A cylindrical part that houses the brake shoes and allows for braking action. |
| Adjuster | Device that maintains the correct distance between the brake shoes and drum. |
Electrical System: Wiring and Components

The electrical framework of agricultural machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and reliable functionality. This section delves into the essential wiring configurations and integral elements that compose the electrical network, facilitating seamless communication between various components.
Key Wiring Elements
A comprehensive understanding of the wiring elements is fundamental for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Below are the primary components that comprise the electrical system:
- Battery: The energy source for starting the engine and powering electrical accessories.
- Alternator: Responsible for generating electrical power while the engine runs, maintaining battery charge.
- Wiring Harness: A collection of wires that distribute electrical power to various parts.
- Fuses: Protect the electrical system from overloads by breaking the circuit when current exceeds safe levels.
- Switches: Control the flow of electricity, enabling or disabling circuits as needed.
Understanding Circuit Connections
Proper circuit connections are vital for optimal performance and safety. Here are some key considerations:
- Ensure all connections are secure to prevent power loss.
- Regularly inspect for wear or damage to wiring insulation.
- Follow the wiring schematics for accurate assembly and repairs.
- Use the correct gauge of wire for each application to prevent overheating.
Maintenance Tips for Ford 1910 Parts
Regular upkeep of machinery components is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Implementing effective maintenance strategies can prevent unexpected breakdowns and ensure smooth operation. Below are some essential recommendations to enhance the reliability of these vital elements.
Firstly, it is crucial to conduct routine inspections. Checking for wear, tear, and any irregularities allows for early detection of potential issues. This proactive approach can save time and resources in the long run.
Secondly, ensure that all connections are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or corroded connections can lead to inefficient operation and safety hazards. Regularly cleaning and tightening these connections is advisable.
Lastly, maintain a clean environment around the equipment. Debris and dirt can impede performance and lead to premature wear. Regular cleaning not only protects components but also promotes a safer working space.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Weekly | Look for signs of wear and damage. |
| Connection Tightening | Monthly | Check for corrosion and secure connections. |
| Cleaning | As needed | Remove dirt and debris from the surrounding area. |