Exploring the intricate structure of these gentle creatures reveals a wealth of knowledge essential for both enthusiasts and professionals alike. A comprehensive analysis not only enhances our appreciation for their biological makeup but also serves practical purposes in various fields, from agriculture to veterinary science.
By examining the various components that make up their physique, one can delve into how each segment contributes to overall function and health. This exploration offers insights into breeding practices, nutritional needs, and management techniques that are crucial for optimal care.
Ultimately, grasping the nuances of their anatomy empowers individuals to make informed decisions, fostering a deeper connection with these remarkable animals and improving their welfare in diverse environments.
Understanding Sheep Anatomy Basics

Exploring the structure of these gentle animals reveals a fascinating interplay of systems that support their survival and functionality. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining health and well-being, contributing to their unique characteristics.
The skeletal framework provides essential support and shape, allowing for movement and protection of vital organs. Muscles, in conjunction with bones, enable locomotion and various physical activities necessary for grazing and social interactions.
Internally, various organs collaborate to facilitate digestion, circulation, and respiration, showcasing the intricate balance required for life. Understanding these elements is crucial for those involved in husbandry or veterinary care, as it informs practices that promote optimal health and productivity.
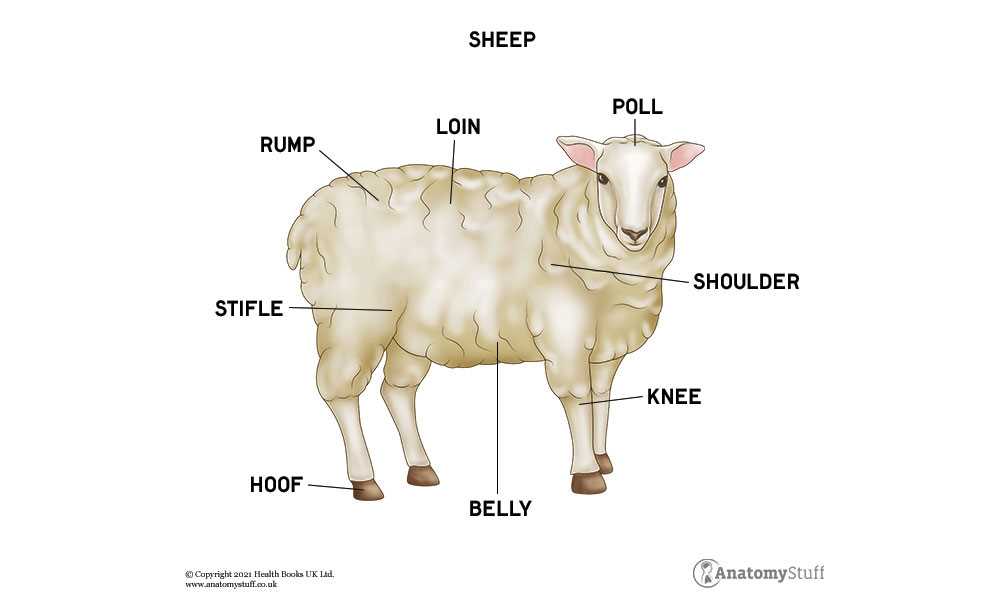
Key Functions of Sheep Body Parts
The anatomy of these animals is intricately designed to support various essential functions vital for their survival and overall well-being. Each segment contributes uniquely to physiological processes, enabling efficient movement, feeding, reproduction, and sensory perception.
Locomotion is primarily facilitated by the limbs, which provide stability and agility, allowing them to navigate diverse terrains. The muscular structure works in harmony with skeletal elements to ensure fluid movement, essential for evading predators and exploring their environment.
The digestive system plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption. Specialized organs break down fibrous plant material, ensuring optimal energy extraction. This complex system enables these creatures to thrive on a herbivorous diet, transforming tough vegetation into vital nutrients.
Another vital function is reproductive health. The reproductive organs are adapted for successful mating and nurturing of offspring. This biological design ensures species continuity, enhancing genetic diversity within populations.
Finally, senses such as sight and smell are critical for environmental awareness. The arrangement of sensory organs allows for effective detection of food sources and potential threats, promoting both survival and social interaction within groups.
Common Terms in Sheep Anatomy
Understanding the structure of these animals requires familiarity with various anatomical terms. Each component plays a crucial role in their overall functionality and health. Knowledge of these terms aids in effective communication within veterinary and agricultural contexts.
Head: This region houses vital sensory organs and is essential for feeding and social interaction.
Limbs: These appendages are key for mobility and support, allowing for movement across diverse terrains.
Torso: The central part contains critical organs for digestion and respiration, crucial for sustaining life.
Pelvic Area: This section is important for reproductive health and the support of various systems.
Fleece: The covering not only provides insulation but also plays a role in protection from environmental elements.
Each term represents a fundamental aspect of the animal’s anatomy, helping to promote better care and management practices.
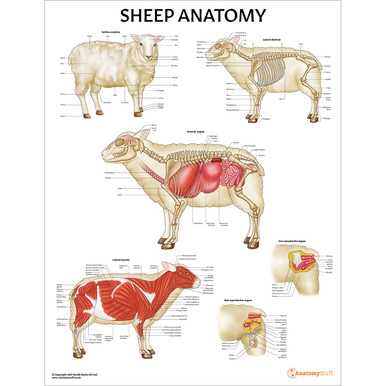
Visual Guide to Sheep Organs

This section provides an informative overview of the essential internal structures found within the animal. Understanding these components is crucial for various fields, including veterinary science, agriculture, and anatomy education. Each element plays a significant role in the overall functioning of the organism, contributing to its health and vitality.
Anatomical Overview
The internal systems are complex and intricately organized. From the circulatory network that ensures nutrient distribution to the respiratory structures that facilitate gas exchange, each aspect serves a vital purpose. By exploring these systems, one can gain insight into the physiological processes that sustain life.
Every internal feature has specific functions that are critical for maintaining the organism’s well-being. For instance, certain structures are responsible for digestion, while others play roles in excretion and reproduction. A detailed understanding of these functions can enhance knowledge in related scientific and agricultural practices.
Importance of Sheep Body Systems
The various biological systems of these animals play a crucial role in their overall health and productivity. Understanding how these systems function together allows for better management practices and enhances the well-being of the flock. Each system contributes to vital processes that ensure survival, growth, and reproduction, ultimately impacting the quality of livestock products.
Key Functions of Biological Systems
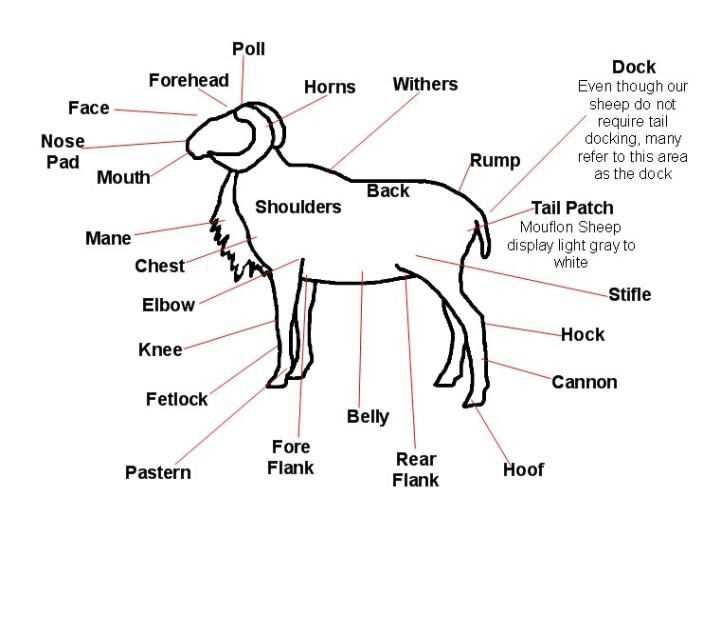
The circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems work in harmony to support metabolic activities. The efficient circulation of nutrients and oxygen is essential for maintaining energy levels and promoting growth. Similarly, the respiratory system facilitates the exchange of gases, which is vital for sustaining life. The digestive apparatus breaks down feed, allowing for nutrient absorption, which is critical for overall health.
Impact on Productivity and Welfare
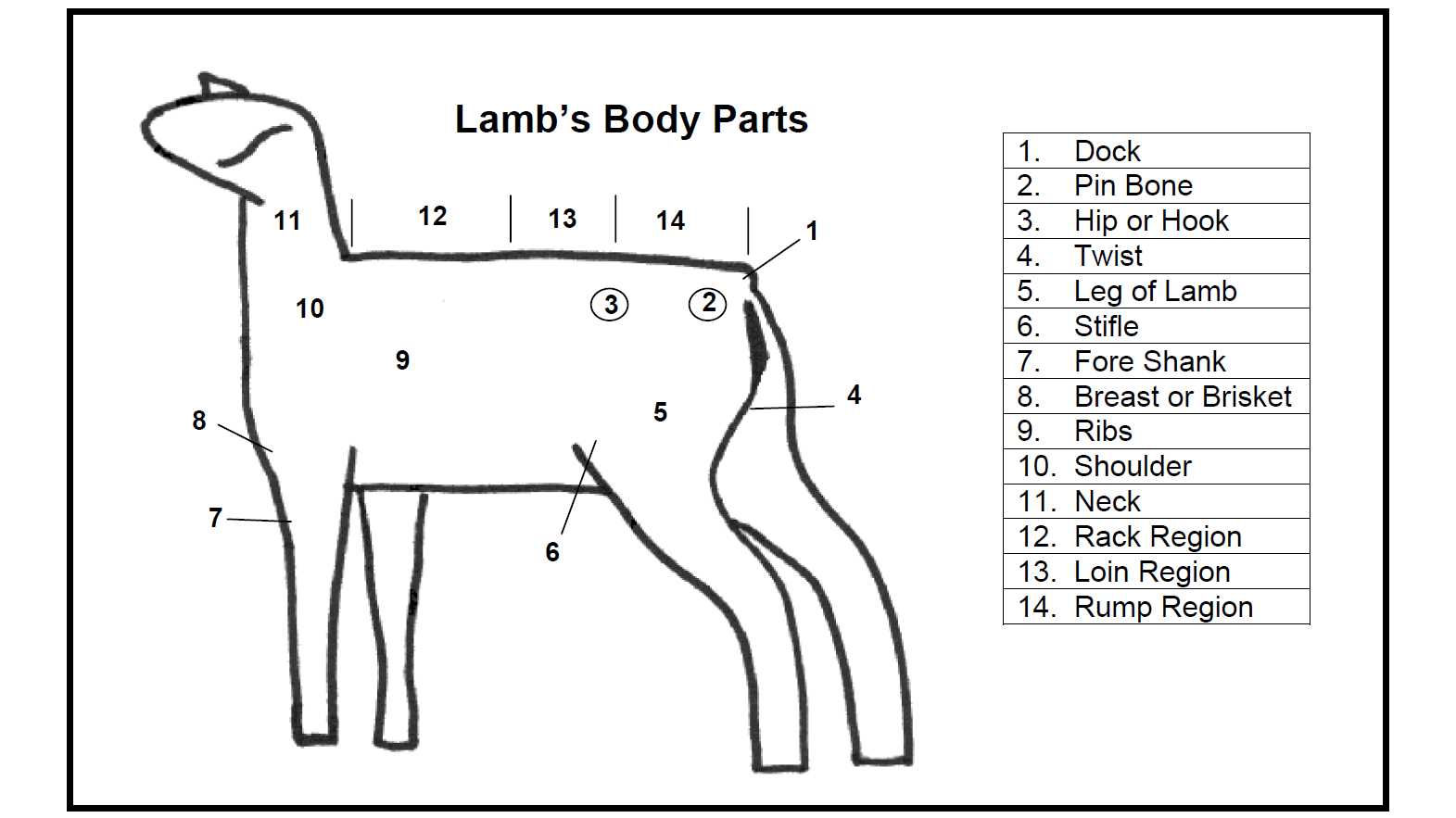
The functionality of these systems directly affects productivity metrics such as weight gain, wool quality, and reproductive success. A well-functioning system not only enhances yield but also ensures the animals are resilient to diseases and environmental stressors. Prioritizing the health of these systems leads to improved welfare and more sustainable farming practices.
Comparative Anatomy of Domestic Sheep
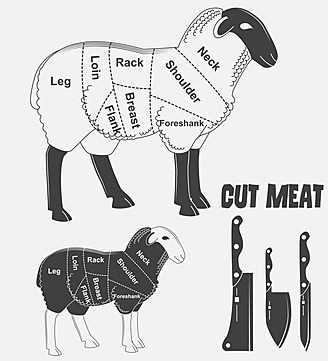
This section explores the structural characteristics and physiological features of domesticated ovines, emphasizing their unique adaptations and variations across breeds. Understanding these differences is essential for improving breeding practices and management strategies.
- Skeletal Structure:
- Distinct skull shape influencing grazing behavior.
- Variations in limb proportions enhancing mobility.
- Musculature:
- Differences in muscle distribution affecting meat quality.
- Adaptations for endurance in various environments.
- Digestive System:
- Ruminant features enabling efficient foraging.
- Variability in stomach compartments among breeds.
- Skin and Wool:
- Variations in fleece types for climate adaptation.
- Differences in skin thickness affecting insulation.
By examining these aspects, one can gain insights into how domestication has shaped the physical attributes of these animals, ultimately influencing their utility in agriculture.
Identifying Breeds Through Body Features
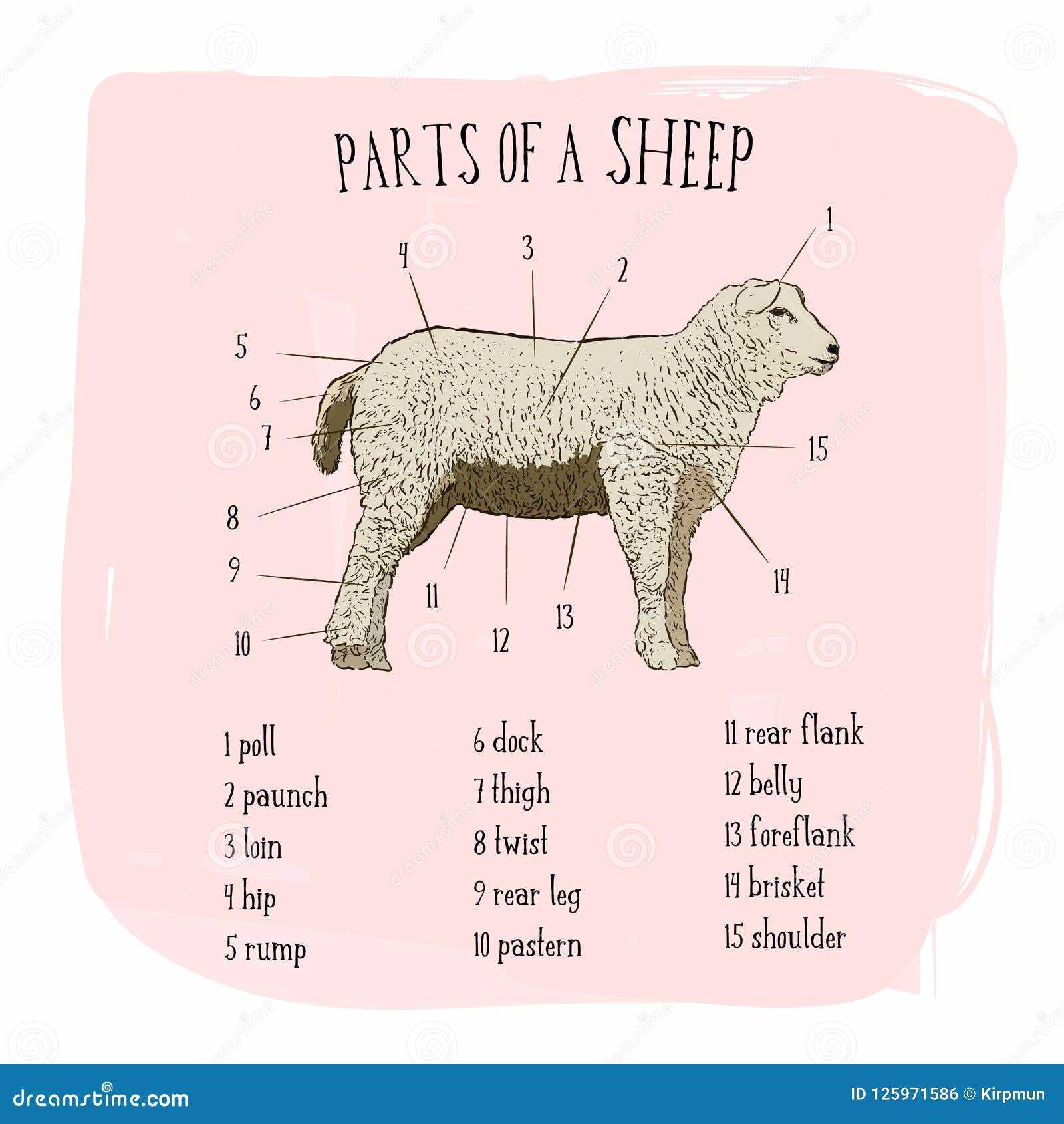
Recognizing various types of livestock can often be achieved by examining specific physical characteristics. These features not only reflect the animal’s breed but also offer insights into their history, adaptability, and purpose in agriculture. Understanding these traits is essential for effective breeding and management practices.
Key Physical Characteristics
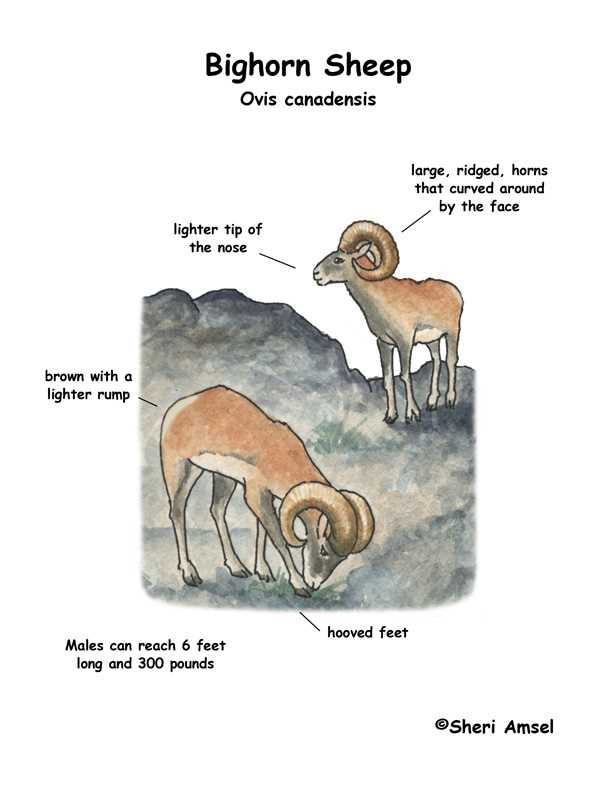
Several attributes serve as distinguishing markers among different breeds. For instance, the size and shape of the body can indicate whether the animal is suited for meat production or wool harvesting. Additionally, the coloration of the coat and the structure of the head play significant roles in breed identification. Ear shape and tail length are also critical elements that help differentiate between breeds.
Behavioral Indicators

In addition to physical traits, behavior can provide clues to breed identification. Some types exhibit more docile temperaments, while others may display heightened alertness or adaptability. Understanding these behavioral tendencies can assist farmers and breeders in selecting the right animals for specific environments or purposes, ensuring optimal productivity and welfare.
Applications of Anatomy in Sheep Farming
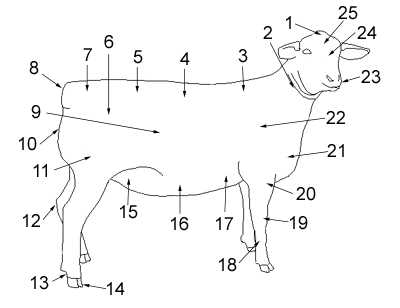
Understanding the structure and function of livestock is essential for optimizing their health and productivity. By exploring the biological systems, farmers can implement better management practices that enhance overall performance.
- Health Monitoring: Regular assessments help identify potential issues early.
- Breeding Programs: Knowledge of genetic traits aids in selecting optimal breeding pairs.
- Nutritional Management: Understanding digestive systems informs feed formulations that promote growth.
- Welfare Practices: Awareness of anatomical features contributes to humane handling and care.
Ultimately, applying anatomical insights allows for informed decisions that can significantly improve livestock quality and farm sustainability.