The art of creating warmth and ambiance in a living space is deeply rooted in the intricate design of a traditional heating structure. Each element plays a crucial role, contributing not only to the aesthetic appeal but also to the functionality and safety of the entire assembly. A well-designed unit is both an engineering marvel and a focal point of the home, reflecting the craftsmanship and intention behind its creation.
In exploring this topic, we will delve into the various sections that comprise these essential installations. From the base that supports the entire structure to the chimney that ensures proper ventilation, each segment is integral to its overall performance. Understanding these elements can enhance appreciation for the craftsmanship involved and inform better choices for those looking to incorporate such features into their own spaces.
As we break down these individual components, it becomes evident how they interact and support one another, creating a harmonious system. Whether considering the materials used or the design choices made, each facet contributes to the warmth and comfort experienced in the home, making the study of these installations both practical and fascinating.
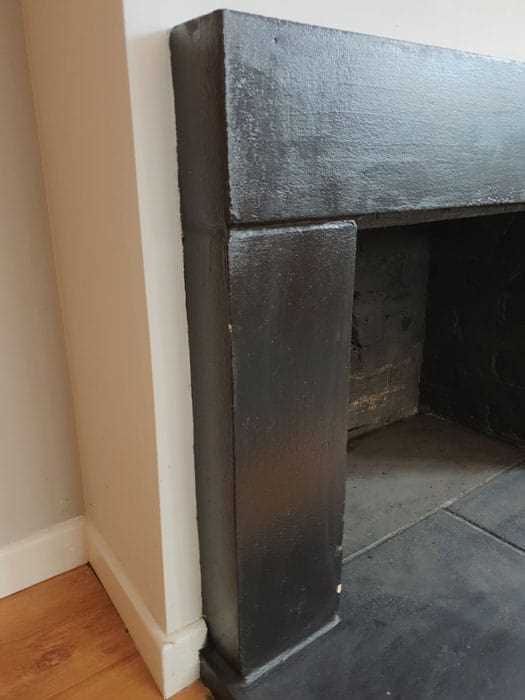
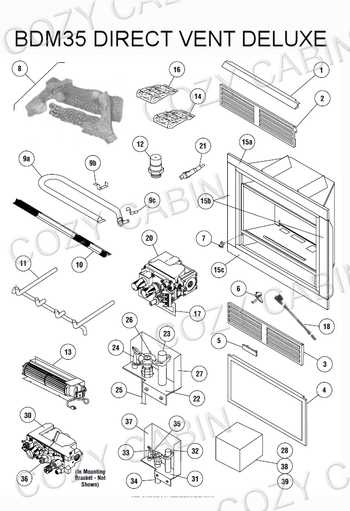
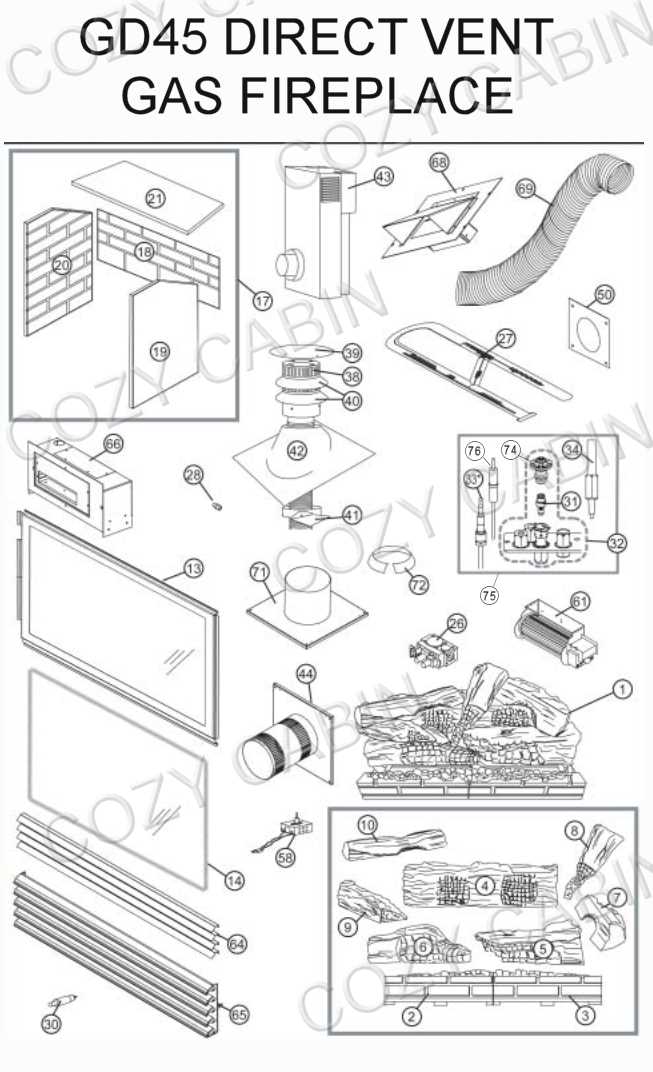
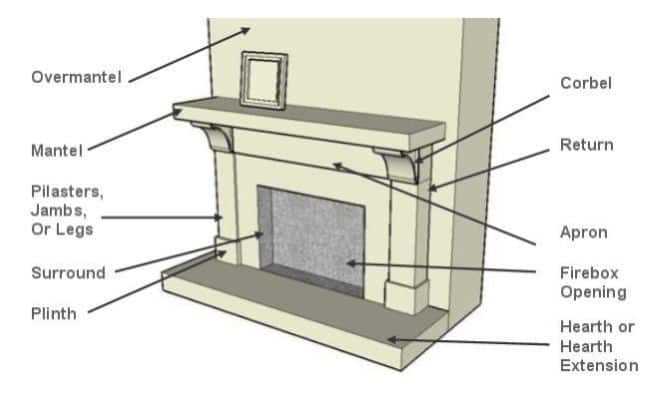
Understanding Fireplace Components
Grasping the essential elements of a heating structure is crucial for both functionality and safety. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring efficient operation, aesthetic appeal, and the overall experience of warmth and ambiance. A thorough comprehension of these elements allows for better maintenance and informed decisions regarding installation and upgrades.
Key Elements of a Heating Structure
The main components include the combustion chamber, which is responsible for burning fuel; the chimney, essential for venting smoke and gases; and the hearth, providing a safe surface for the fire. Each of these plays a unique part in the overall system, contributing to the effectiveness and safety of the entire setup.
Importance of Proper Installation
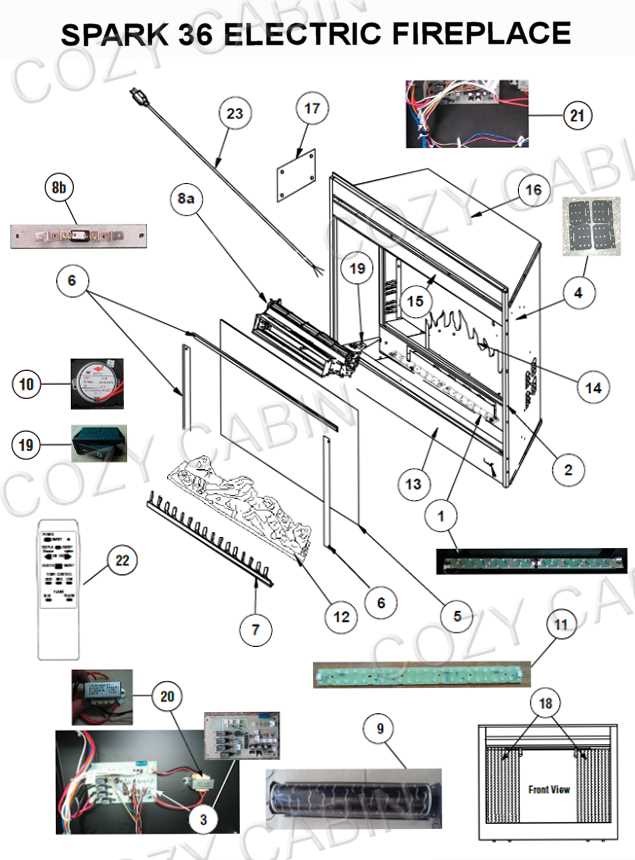
Correct installation of each element is vital to prevent hazards such as carbon monoxide buildup or structural damage. Engaging professionals for setup and maintenance ensures compliance with safety standards and enhances the longevity of the system. Regular inspections help in identifying potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions.
Key Elements of a Fireplace System
This section explores the essential components that contribute to the functionality and safety of a heating structure. Understanding these elements is crucial for both design and maintenance, ensuring an efficient and enjoyable experience.
Primary Components
- Chimney: Directs smoke outside and ensures proper ventilation.
- Firebox: The chamber where combustion occurs, designed to withstand high temperatures.
- Hearth: The area in front of the firebox, providing protection against embers and heat.
Supporting Features
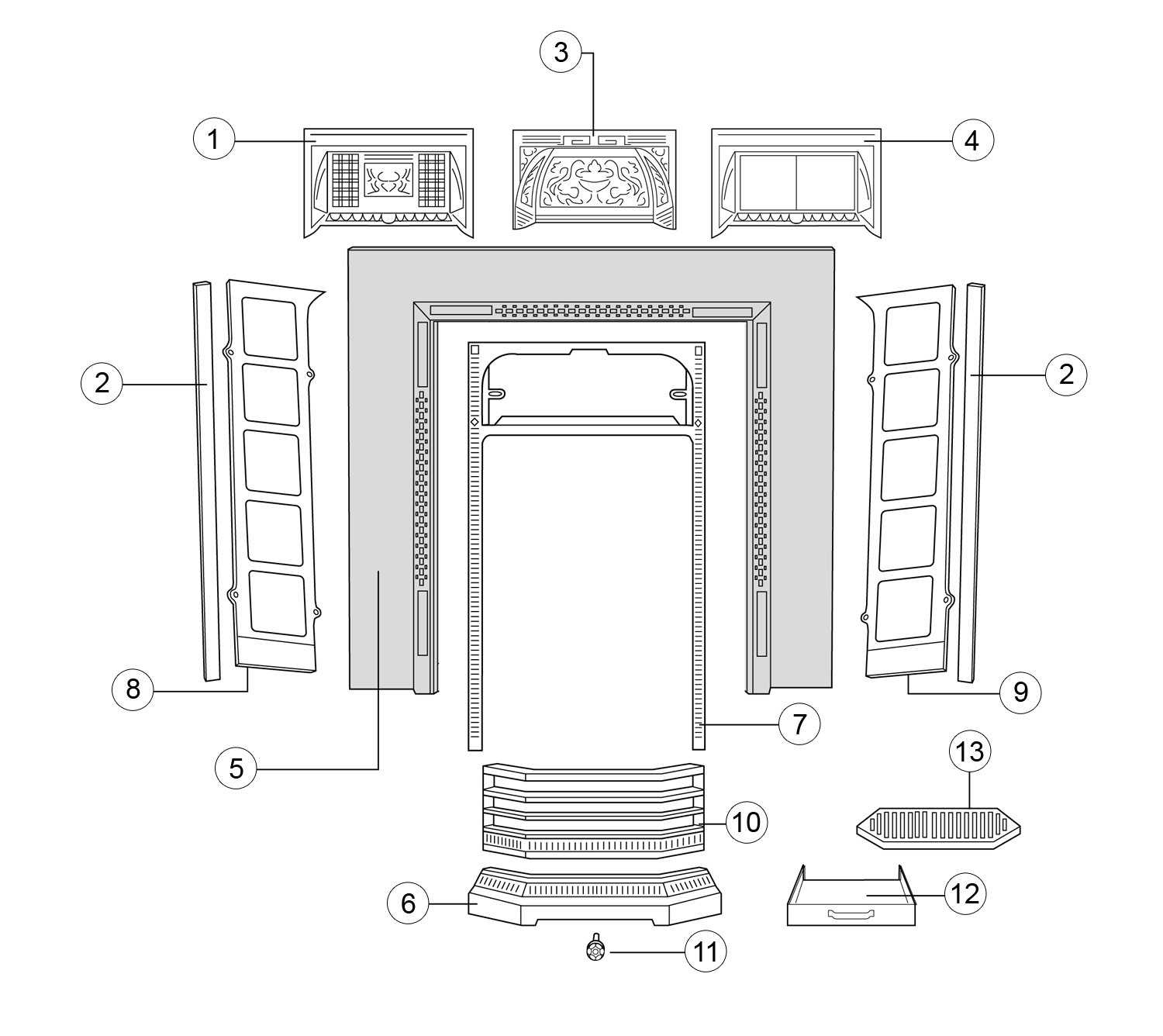
- Dampers: Regulate airflow and help control the intensity of the fire.
- Flue: The passage that channels smoke and gases from the firebox to the chimney.
- Grate: Supports burning materials, allowing airflow for efficient combustion.
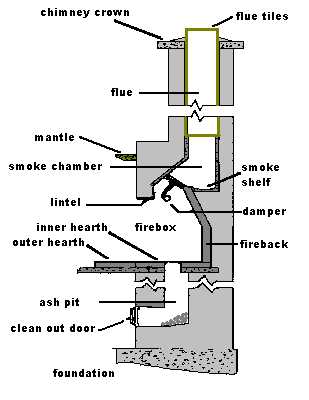
Functionality of a Chimney Structure
The design of a chimney plays a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient operation of heating systems. Its primary purpose revolves around directing smoke and gases away from living spaces, thereby maintaining air quality and preventing the buildup of harmful substances indoors. Understanding its functionality helps in appreciating the importance of proper installation and maintenance.
Key Functions
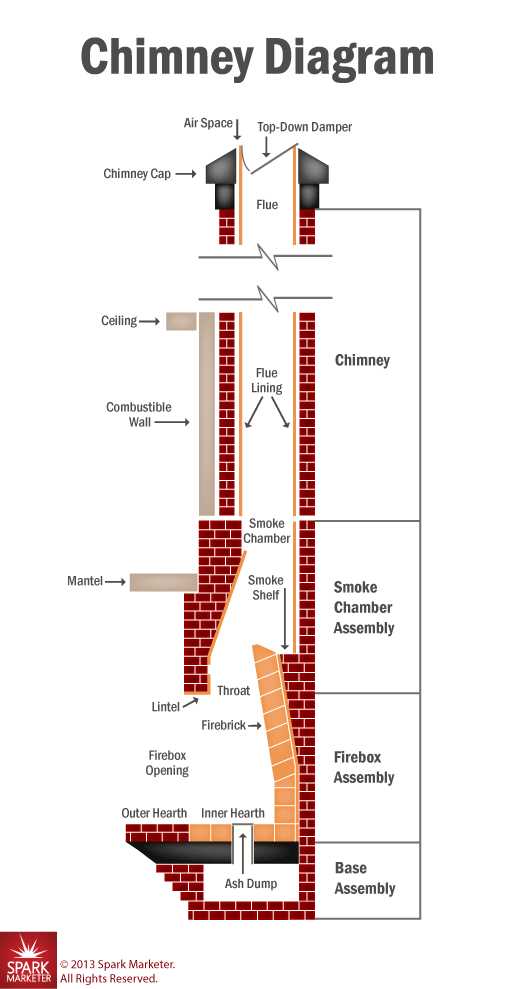
- Ventilation: A well-constructed chimney allows for the proper expulsion of combustion byproducts, facilitating efficient airflow.
- Draft Creation: The structure helps create a draft that draws air into the combustion area, supporting consistent burning and reducing smoke emissions.
- Temperature Regulation: It aids in managing temperature differences, which is vital for preventing overheating and reducing the risk of fire hazards.
- Protection Against Elements: A chimney shields the interior from rain, snow, and debris, minimizing the risk of blockage and structural damage.
Importance of Maintenance
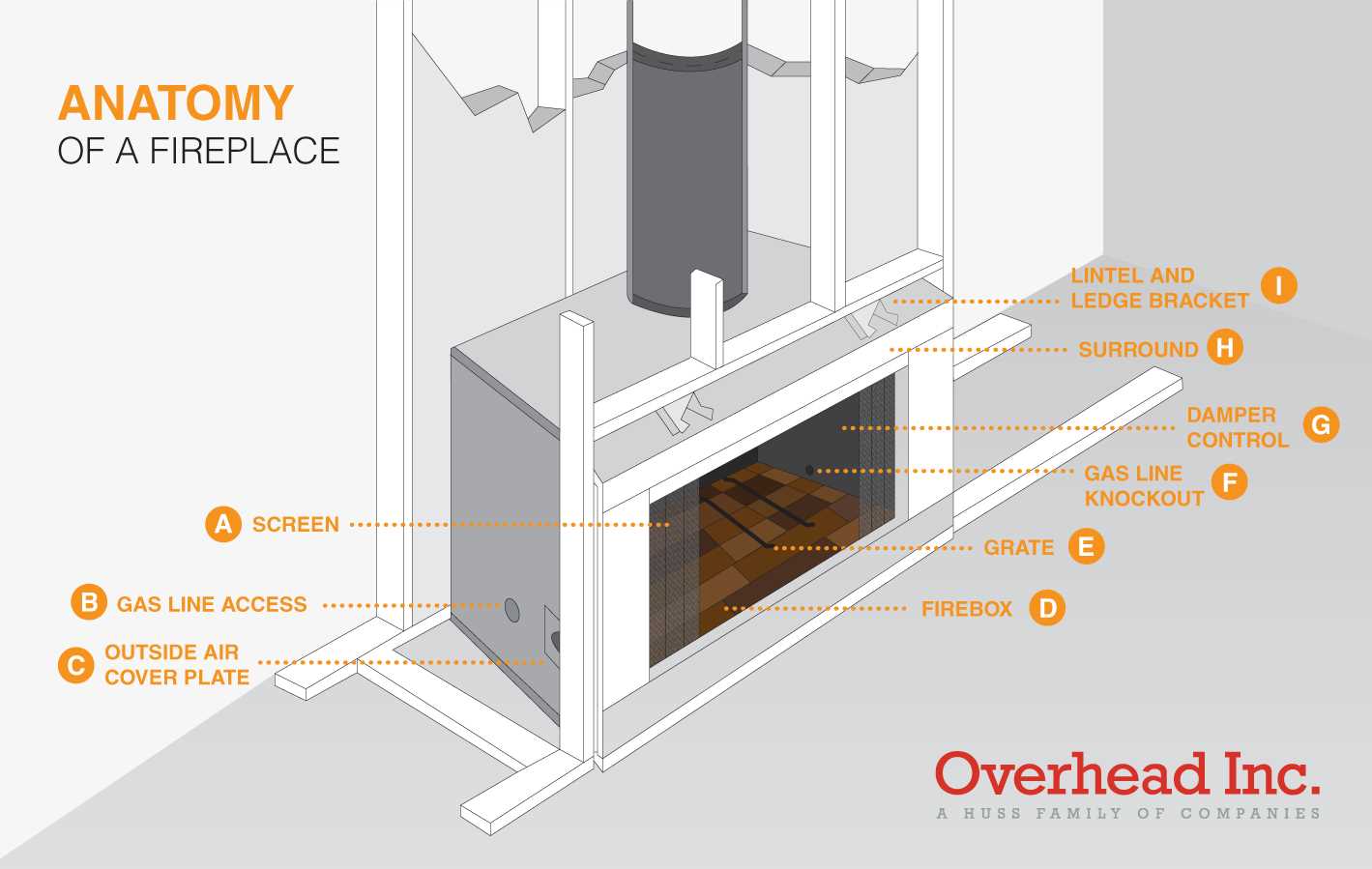
Regular upkeep of the chimney is essential to ensure its functionality. Neglecting maintenance can lead to:
- Blockages caused by soot or creosote buildup.
- Increased risk of chimney fires.
- Potential damage to the home from leaks or structural failure.
Investing time and resources in the maintenance of this structure ultimately contributes to the safety and efficiency of heating systems.
Types of Fireplace Fuel Sources
Choosing the right energy source for your heating system is crucial for efficiency and ambiance. Various options are available, each with distinct characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Understanding these sources can help you make an informed decision that best suits your needs and preferences.
Traditional Fuels

Wood has been a favored choice for centuries, offering a classic aesthetic and comforting aroma. However, it requires regular maintenance and may produce smoke and ash. Pellets, made from compressed wood byproducts, provide a cleaner alternative, with automated feeding systems that enhance convenience.
Modern Alternatives
For those seeking a more contemporary solution, natural gas and propane are popular due to their ease of use and clean-burning properties. They eliminate the need for physical fuel storage and reduce emissions. Electric options also offer a hassle-free experience, providing instant heat without the mess associated with traditional materials.
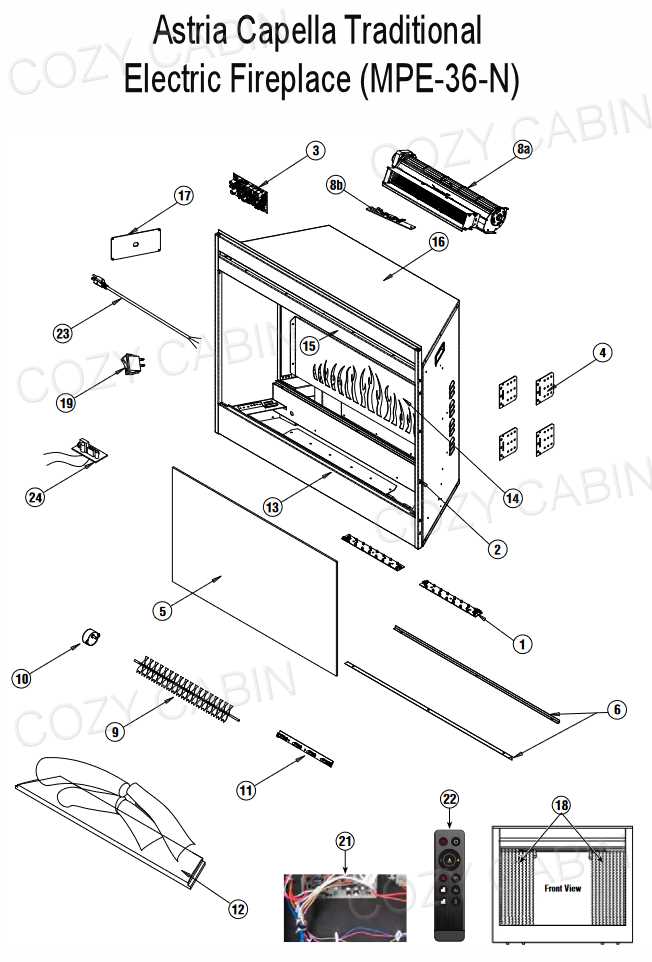
Importance of Firebox Design
The structure of the firebox plays a crucial role in determining the overall efficiency and safety of a heating system. A well-designed firebox ensures that heat is distributed evenly while minimizing the risks associated with improper ventilation. It directly impacts the performance, longevity, and environmental footprint of the system.
Efficiency and Heat Distribution
The design of the firebox is essential for achieving optimal heat output. Its dimensions, materials, and airflow dynamics all contribute to how effectively the system can generate and retain heat. Properly calculated proportions prevent heat loss, allowing for better energy conservation and more consistent warmth.
Safety Considerations
Another critical aspect of firebox design is ensuring safety. A well-engineered firebox minimizes the risk of structural damage and the escape of harmful gases. Key features like appropriate ventilation, durable construction materials, and precise alignment of components help in maintaining a secure environment.
| Design Factor | Benefit |
|---|
| Material | Heat Resistance | Durability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fiber | High | Long-lasting | Moderate |
| Mineral Wool | Moderate | Resistant to moisture | Low |
Calcium Silicate
Common Fireplace Maintenance TipsEnsuring the longevity and safe operation of your heating installation requires regular attention and upkeep. A few key practices can help maintain the unit’s efficiency and keep it in top condition, contributing to a safer and more pleasant home environment. By performing routine checks and cleaning, you can avoid costly repairs and ensure consistent performance. Regular CleaningKeeping the heating unit clean is essential for proper air circulation and efficiency. Accumulation of dirt and debris can hinder performance, so regular sweeping or vacuuming of the interior area is recommended. Additionally, removing any buildup in the vent system ensures better airflow and safety. Annual InspectionTo ensure |