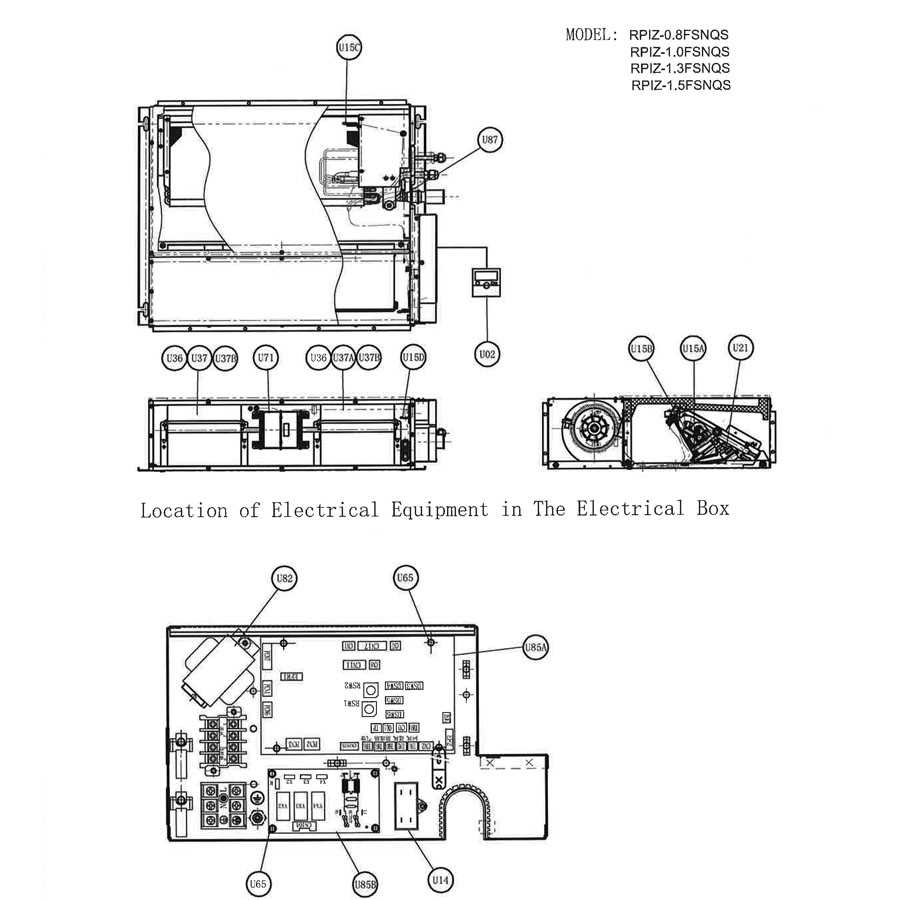
In today’s world, having a reliable solution for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures is essential. Various systems exist to provide relief during warmer months, each comprising multiple elements that work together to create a conducive environment. Understanding how these components function is key to optimizing performance and ensuring longevity.
Whether it’s for residential use or commercial spaces, familiarity with the individual elements enhances your ability to troubleshoot issues effectively. Recognizing how these components interact can lead to better maintenance practices and improved energy efficiency. This section aims to elucidate the roles of each segment within these cooling systems, offering insights into their design and functionality.
From the fundamental mechanisms that facilitate temperature regulation to the more intricate details that support efficient operation, a comprehensive overview of these components is invaluable. Gaining knowledge about these crucial segments not only aids in effective usage but also empowers users to make informed decisions regarding their maintenance and care.
The functionality of compact cooling systems relies on several essential elements that work together to create a comfortable indoor environment. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and operation.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Compressor | This device compresses refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature, which is vital for heat exchange. |
| Evaporator | The evaporator absorbs heat from the surrounding air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the environment. |
| Condenser | Located within the unit, this component releases absorbed heat outside, allowing the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid state. |
| Fan | Essential for circulation, the fan helps distribute cool air into the room and assists in the heat exchange process. |
| Drain Pan | This collects condensation produced during the cooling process, ensuring efficient operation and preventing water buildup. |
How Cooling Mechanism Works
The process of temperature reduction in a compact cooling unit relies on the principles of thermodynamics and the behavior of refrigerants. Understanding this mechanism reveals how heat is absorbed from the surrounding environment and dissipated effectively, ensuring a comfortable indoor atmosphere. This section delves into the critical components and their roles in facilitating efficient cooling.
Key Components Involved
The primary elements that contribute to the cooling process include the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve. The compressor circulates the refrigerant, compressing it to increase its pressure and temperature. As the high-pressure refrigerant gas moves to the condenser, it releases heat to the outside, transforming into a liquid state. This liquid then travels to the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air, thereby cooling the environment. Finally, the expansion valve regulates the refrigerant flow, allowing it to evaporate and complete the cycle.
The Role of Refrigerants
Refrigerants play a crucial role in the cooling mechanism, as they undergo phase changes to absorb and release heat. These substances are designed to have low boiling points, enabling them to evaporate at low temperatures. This property allows the refrigerant to absorb significant amounts of heat from the indoor environment, effectively lowering the ambient temperature. As the cycle continues, the refrigerant circulates back to the compressor, ready to repeat the process.
Importance of Air Filters
Filters play a crucial role in maintaining indoor climate control systems. Their primary function is to trap unwanted particles, ensuring that the circulated atmosphere remains clean and free from pollutants. Regular maintenance of these components is essential for optimal performance and efficiency.
Incorporating high-quality filtration systems not only enhances the quality of the environment but also contributes to the longevity of the overall mechanism. Clean filters allow for better airflow, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills. Furthermore, they help in minimizing wear and tear on the equipment, preventing costly repairs down the line.
| Type of Filter | Benefits |
|---|---|
| HEPA Filters | Traps 99.97% of particles, including dust, pollen, and pet dander. |
| Activated Carbon Filters | Reduces odors and harmful gases, improving overall air quality. |
| Electrostatic Filters | Uses static electricity to capture smaller particles, enhancing efficiency. |
Role of the Compressor Explained
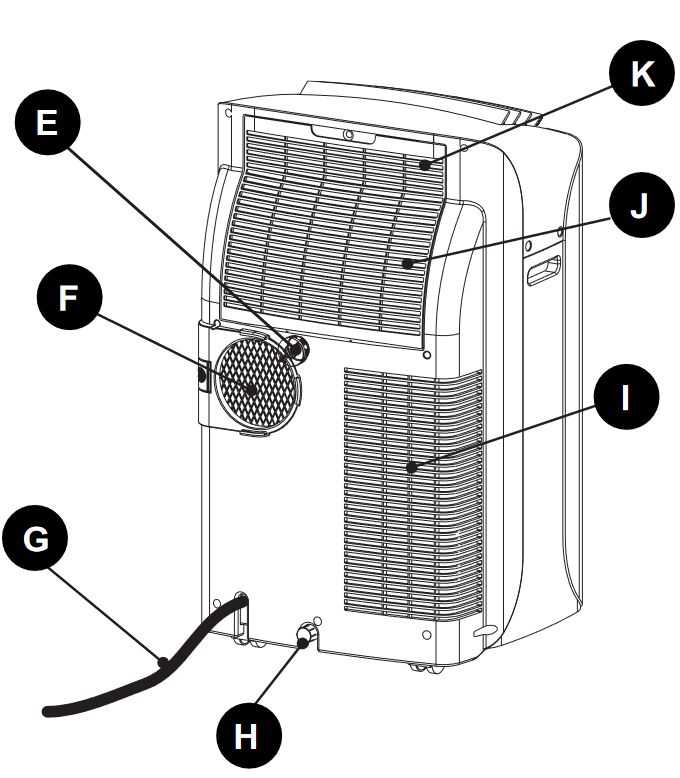
The compressor serves as a vital component within a cooling system, playing a crucial part in the refrigeration cycle. It is responsible for pressurizing the refrigerant, enabling its transformation into a gaseous state. This process not only facilitates the movement of the refrigerant but also enhances its ability to absorb heat, ultimately leading to effective temperature regulation in the surrounding environment.
Understanding the Functionality
At its core, the compressor operates by drawing in low-pressure refrigerant gas and compressing it into a high-pressure vapor. This increase in pressure raises the temperature of the refrigerant, preparing it for subsequent stages of the cooling cycle. The high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser, where it releases heat and changes back into a liquid form, ready to continue the cycle.
Impact on System Efficiency
A well-functioning compressor is essential for optimal performance and energy efficiency. When the compressor operates efficiently, it minimizes energy consumption while maximizing cooling output. Conversely, any issues within the compressor can lead to decreased efficiency, resulting in increased energy costs and reduced overall effectiveness of the cooling system. Regular maintenance and monitoring are therefore crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of this key component.
Water Drainage System Overview

The water drainage mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining efficiency and comfort in cooling units. It effectively removes excess moisture produced during the cooling process, ensuring optimal performance and preventing potential damage.
Understanding the components of this system is essential for proper maintenance and operation. The key elements include:
- Drain Pan: This component collects the condensed water from the cooling process.
- Drain Line: A pipe that transports the collected water away from the unit.
- Pump (if applicable): An optional feature that aids in moving water to a designated drainage point when gravity is insufficient.
- Filters: These prevent debris from clogging the drainage system, ensuring smooth water flow.
Proper maintenance of the drainage system is vital to avoid issues such as leaks or water buildup. Regular cleaning and inspection of the drain pan, lines, and filters help ensure efficient operation and longevity of the unit.
Fan Types and Their Functions
Different varieties of fans play crucial roles in enhancing comfort and promoting airflow within various systems. Each type serves distinct purposes, catering to specific needs and environments. Understanding these differences allows for better decision-making when it comes to selecting the right type for optimal performance.
One common type is the axial fan, characterized by its ability to move air parallel to the axis of rotation. These fans are highly efficient for cooling and ventilation, often found in settings requiring high airflow with minimal pressure loss. Conversely, centrifugal fans, which draw air into the center and expel it at right angles, excel in generating higher pressure, making them ideal for systems that need to overcome resistance or direct airflow through ducts.
Moreover, mixed-flow fans combine elements of both axial and centrifugal designs, offering versatility for applications needing a balance of airflow and pressure. Additionally, special-purpose fans, such as blower fans, focus on directing airflow to specific areas, often used in appliances and compact spaces.
Understanding these different varieties ensures that users can select the most effective option for their cooling and ventilation needs, ultimately enhancing system efficiency and user comfort.
Electrical Wiring and Safety Features
Ensuring proper connectivity and safety in cooling devices is crucial for their efficient operation and user protection. This section outlines essential aspects of electrical configurations and the safety mechanisms integrated within these systems.
Understanding the electrical components is vital for maintaining optimal functionality:
- Power Supply: The primary source providing necessary voltage for the unit’s operation.
- Control Board: Manages the device’s settings and operations, receiving input from user controls.
- Fan Motor: Responsible for circulating air within the unit to facilitate temperature regulation.
- Compressor: Compresses refrigerant to enable heat exchange processes.
To enhance safety, several features are commonly included:
- Overload Protection: Prevents the unit from overheating by disconnecting power when excessive current is detected.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI): Shuts off electricity in case of a ground fault, minimizing shock hazards.
- Thermal Fuse: Acts as a safeguard by cutting off power if internal temperatures exceed safe levels.
- Insulated Wiring: Reduces the risk of electrical shorts and enhances overall safety.
By adhering to recommended wiring practices and safety protocols, users can ensure both efficiency and protection while operating their cooling systems.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and efficiency of your cooling unit involves regular upkeep and attention. By following specific maintenance practices, you can enhance the performance of your system while extending its lifespan. This section provides essential guidelines to keep your equipment in optimal condition.
Regular Cleaning: Accumulated dust and debris can hinder performance. Periodically clean the filters and other accessible components to ensure proper airflow. A clean unit operates more efficiently, reducing energy consumption.
Check for Leaks: Inspecting for any refrigerant leaks is crucial. If you notice any signs of leakage, it’s essential to address them promptly to prevent damage to the unit and maintain effective cooling capabilities.
Monitor Thermostat Settings: Ensure your thermostat is set at an appropriate level. Frequent adjustments or extreme settings can strain the system. Maintaining a consistent temperature can lead to improved efficiency and reduced wear.
Professional Servicing: Schedule annual inspections with a qualified technician. Professional maintenance can identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring your system runs smoothly throughout its lifespan.
Storage Tips: If you plan to store your unit during off-seasons, ensure it is cleaned and dried thoroughly. Proper storage prevents mold growth and preserves the integrity of the components.