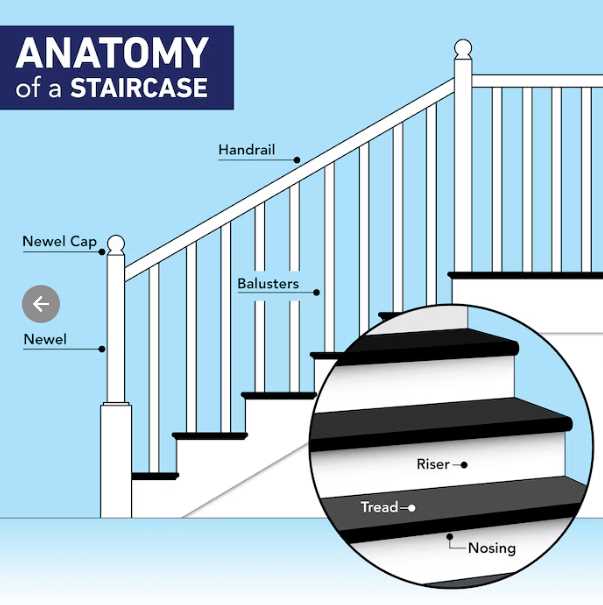
The intricate design of an elevation framework is essential for both functionality and aesthetics. Each element plays a crucial role, contributing to the overall stability and accessibility of the construction. A thorough comprehension of these individual segments is vital for anyone involved in architectural planning or renovation.
Exploring the various sections reveals how they interconnect to form a cohesive unit. From the foundational elements that provide support to the finishing touches that enhance appearance, every aspect is designed with a specific purpose in mind. This knowledge not only aids in construction but also helps in ensuring safety and compliance with regulations.
Additionally, understanding these components can inspire innovative designs and improvements in existing structures. Whether for residential or commercial purposes, a deep dive into the framework’s makeup fosters creativity and practical solutions. Recognizing the significance of each segment allows architects and builders to elevate their projects to new heights.
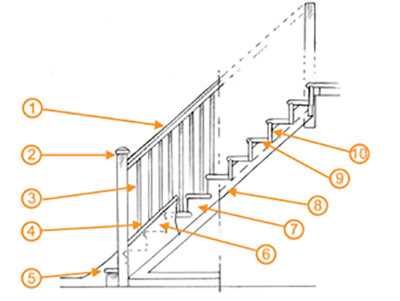
Understanding Stair Components
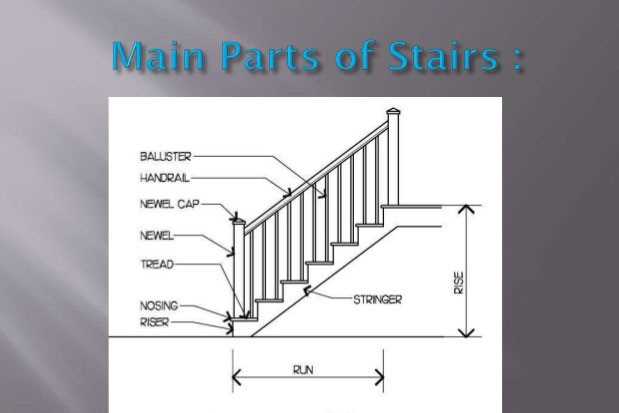
When considering the structure that facilitates movement between different levels of a building, it is essential to recognize the various elements that contribute to its functionality and safety. Each component plays a vital role in the overall design, ensuring both aesthetic appeal and practical use.
Main Elements
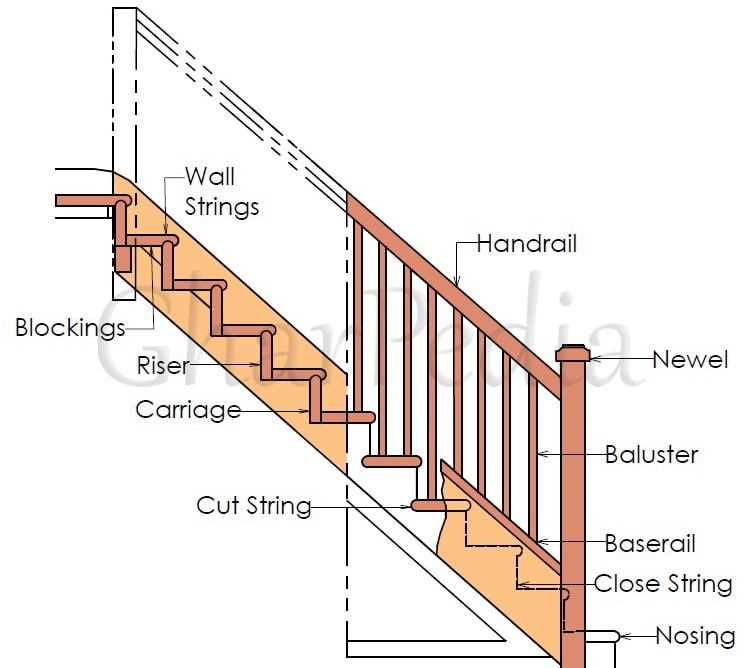
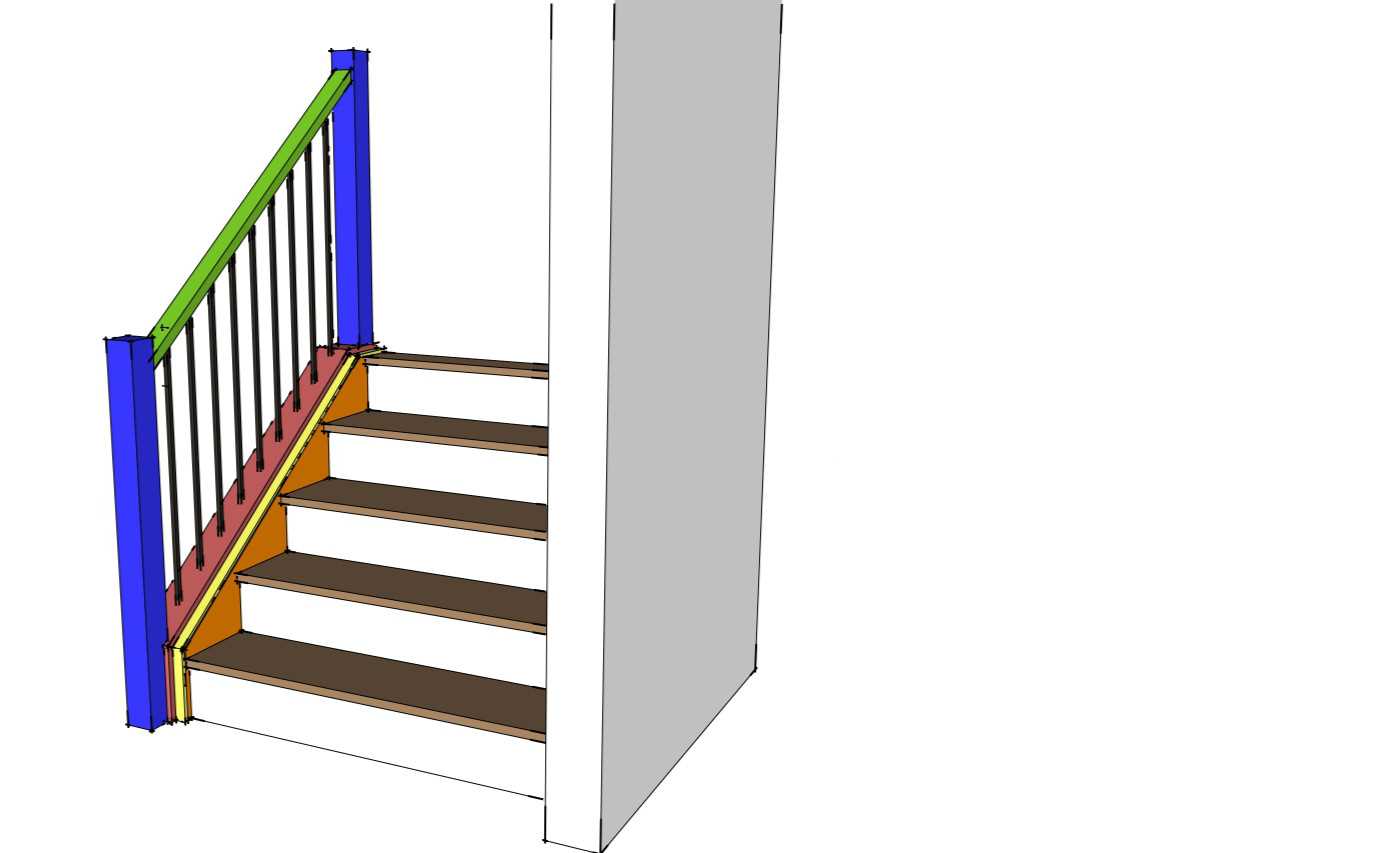
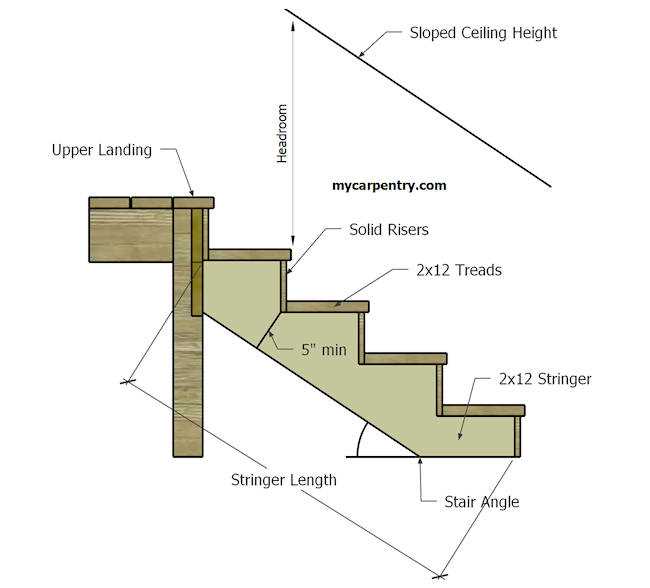
- Riser: The vertical part that connects one step to another.
- Tread: The horizontal surface where one places their foot.
- Stringer: The supporting framework that holds the treads and risers in place.
- Landing: A flat area at the top or bottom that provides a resting point.
- Handrail: A safety feature designed for support while ascending or descending.
Functionality and Safety
Understanding these components is crucial for ensuring safety and comfort. Proper design and construction can prevent accidents and enhance accessibility. Furthermore, the selection of materials and finishes can significantly influence the overall ambiance of the space.
- Consider the weight-bearing capacity of each element.
- Evaluate slip resistance for enhanced safety.
- Choose durable materials that withstand wear and tear.
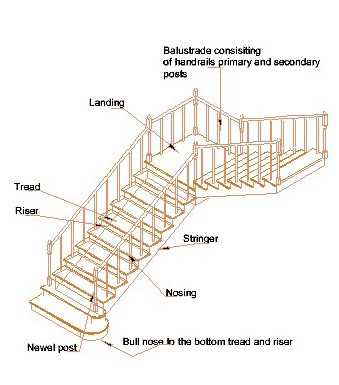
Basic Structure of Staircases
The design of elevated pathways involves several fundamental components that ensure safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these key elements is essential for effective construction and use, whether in residential or commercial settings.
Key Elements of Elevation Systems
- Riser: The vertical portion that connects one step to the next, providing height.
- Tread: The horizontal surface where one steps, crucial for stability.
- Stringer: The support framework running along the sides, holding the entire structure together.
- Landing: A flat area at the top or bottom, serving as a transition space.
Construction Considerations
- Ensure proper measurements for risers and treads to maintain comfort and safety.
- Choose durable materials to withstand wear and provide adequate support.
- Incorporate handrails where necessary to enhance safety and accessibility.
By paying attention to these vital components and considerations, the effectiveness and safety of an elevated pathway can be significantly improved, allowing for both practical use and aesthetic enhancement in various environments.
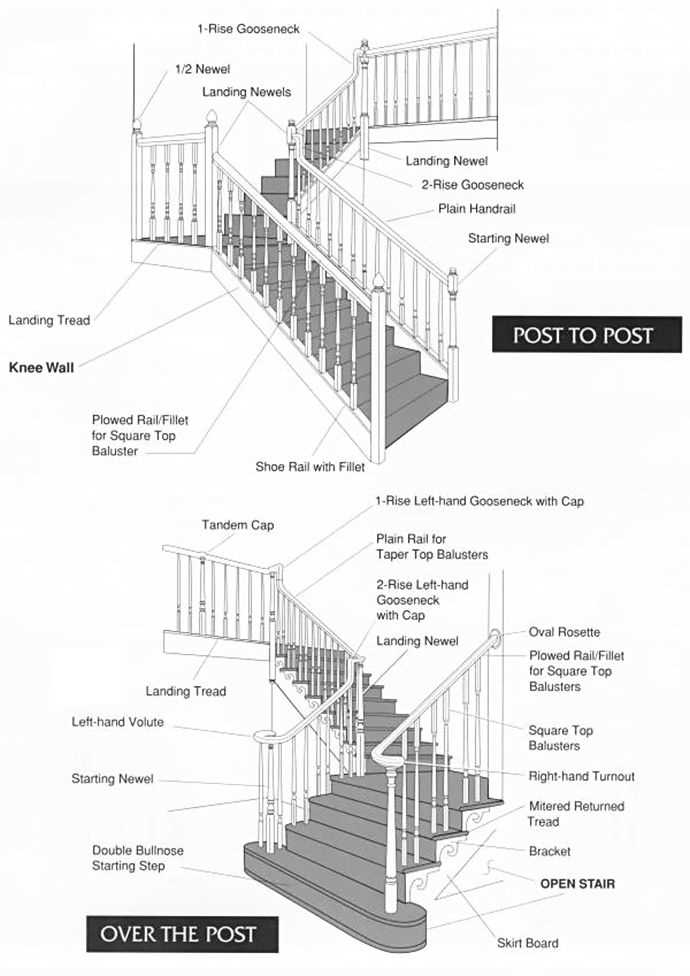
Types of Staircase Designs
The selection of various ascent structures can significantly influence both functionality and aesthetics within a space. Each design not only serves a practical purpose but also contributes to the overall character of an environment. Understanding the diversity of available styles allows for tailored choices that align with personal preferences and architectural demands.
Spiral configurations are characterized by their elegant, compact form, making them ideal for limited spaces. These designs often create a visually striking centerpiece, drawing the eye upward and enhancing the sense of height in a room.
Straight designs are the most straightforward and common, featuring a linear path from one level to another. Their simplicity offers ease of construction and accessibility, making them a reliable choice for many settings.
L-shaped variants introduce a turn in the ascent, adding visual interest and functionality. This style can effectively separate areas within a home while still providing a smooth transition between levels.
U-shaped models, with their double turn, offer a more dramatic and spacious experience. They can serve as a grand feature in larger residences, providing ample room for movement and interaction.
Floating options showcase individual steps that appear to ‘hover’ without visible support, creating a modern, minimalist aesthetic. This innovative design emphasizes lightness and space, appealing to contemporary tastes.
Ultimately, the choice of ascent structure depends on a myriad of factors, including space constraints, style preferences, and practical requirements. Each design brings its own unique qualities, ensuring that there is a perfect option for every environment.
Common Materials Used in Stairs
When it comes to designing elevated pathways, the choice of substances is crucial for both aesthetics and functionality. Various materials can greatly influence the overall look and durability, allowing for a personalized touch while meeting safety standards. Understanding the different options available can help in making informed decisions for any construction project.
Wood
Wood is a classic choice, appreciated for its warmth and versatility. It can be crafted into various styles, from rustic to contemporary, and is available in numerous species, each with its unique grain and color. While it offers a comfortable feel underfoot, it requires regular maintenance to prevent wear and damage from moisture.
Metal
Metal options, such as steel and aluminum, are favored for their strength and modern appeal. These materials provide excellent durability and can be designed to fit both industrial and minimalist aesthetics. Additionally, they often allow for creative designs and can be combined with other materials to enhance visual interest.
Safety Features for Staircases
Ensuring the well-being of individuals navigating elevated structures is paramount. Effective design and thoughtful enhancements play a crucial role in preventing accidents and fostering a secure environment. Various elements contribute to a safer experience, addressing common risks associated with elevation changes.
One of the primary considerations is the use of non-slip materials on surfaces, which significantly reduces the likelihood of slips and falls. Additionally, proper illumination enhances visibility, making it easier for users to perceive their surroundings. Handrails are another vital feature, providing support and stability, especially for those with mobility challenges.
Moreover, the dimensions of each step should adhere to recommended standards, ensuring uniformity and predictability. Clear markings can also aid in distinguishing edges, helping individuals navigate safely. Incorporating these features not only promotes safety but also instills confidence in users as they traverse elevated paths.
Measuring Stair Dimensions Accurately
Accurate measurement is crucial for ensuring safety and functionality in elevated structures. Whether constructing a new design or renovating an existing one, precise calculations are essential for achieving optimal performance and comfort.
Essential Tools for Measurement
- Tape Measure: A flexible measuring tool for capturing length and width.
- Level: Ensures even surfaces for consistent height across various points.
- Square: A tool to check right angles, important for accurate corners.
- Laser Distance Measurer: Provides quick and precise measurements over long distances.
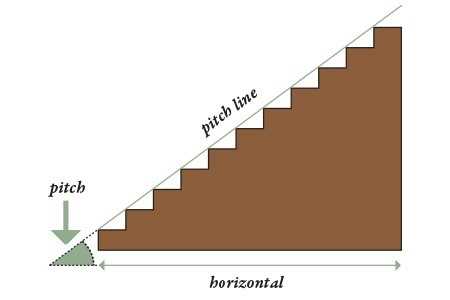
Steps for Accurate Measurement
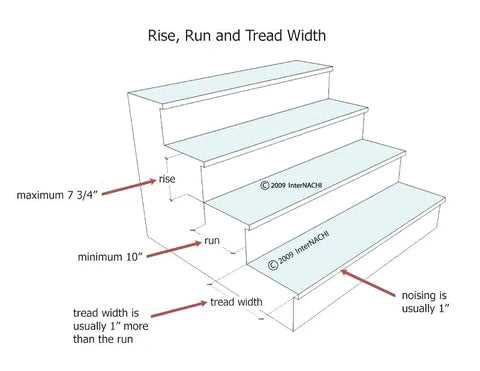
- Determine the total height to be covered.
- Measure the horizontal distance available for the ascent.
- Calculate the rise and run to ensure proper ratios.
- Verify all measurements multiple times to eliminate errors.
Following these steps will lead to a safe and comfortable ascent or descent, allowing for successful design implementation.
Maintenance Tips for Stair Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your elevated surfaces requires a thoughtful approach to upkeep. Regular maintenance not only enhances safety but also prolongs the lifespan of your structure. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind for effective preservation.
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the area free of dust, debris, and moisture. Use appropriate cleaning solutions to prevent stains and deterioration.
- Inspect for Damage: Periodically check for cracks, loose elements, or signs of wear. Early detection allows for timely repairs.
- Check for Proper Lighting: Adequate illumination can prevent accidents. Ensure that all areas are well-lit and consider adding lights in darker spots.
Implementing the following practices can further enhance stability:
- Sealants: Apply sealants to protect the surface from moisture and other damaging elements.
- Reinforce Structure: Ensure that supports are secure and consider reinforcing weak areas to handle weight more effectively.
- Use Non-Slip Treatments: Apply anti-slip coatings to minimize the risk of slips and falls, particularly in high-traffic areas.
By adhering to these strategies, you can maintain the integrity and safety of your elevated surfaces for years to come.
Designing Accessible Stair Solutions
Creating environments that promote inclusivity requires thoughtful consideration of elevation transitions. These structures play a crucial role in facilitating movement and ensuring that everyone can navigate their surroundings with ease and safety. By prioritizing universal design principles, we can enhance usability and comfort for individuals of all abilities.
One essential aspect is the incorporation of features that reduce physical barriers. This includes implementing gradual inclines, appropriate handrails, and non-slip surfaces. Each of these elements contributes to a safer experience, especially for those who may have mobility challenges or are carrying items.
Additionally, visual cues such as contrasting colors and clear signage can significantly improve navigation. These enhancements not only assist individuals with visual impairments but also aid all users in understanding their environment more intuitively.
Collaboration with accessibility experts during the planning phase is vital. Their insights can help identify potential obstacles and recommend solutions tailored to the specific needs of a diverse user group. This cooperative approach fosters an inclusive atmosphere that values every individual’s experience.
Ultimately, the goal is to design systems that allow for seamless movement, ensuring that all individuals feel welcome and supported in their endeavors. By embracing these principles, we create spaces that uplift and empower, bridging gaps and connecting communities.
Innovative Staircase Trends Today

In recent years, the design of vertical transitions has evolved dramatically, reflecting both aesthetic desires and functional needs. Contemporary innovations focus on blending style with safety, creating features that not only enhance the interior but also serve practical purposes. Designers are exploring new materials, forms, and technologies to redefine how these structures interact with their surroundings.
Materials and Sustainability
Modern designs often prioritize eco-friendly materials that reduce environmental impact while adding a unique touch. From reclaimed wood to recycled metals, the choices reflect a commitment to sustainability without sacrificing elegance. This trend not only promotes responsible consumption but also offers homeowners the opportunity to showcase distinctive, handcrafted elements.
Smart Technology Integration
Another exciting development is the incorporation of smart technology. Innovations such as motion sensors for lighting and automated safety features enhance usability and convenience. These advancements make navigating vertical transitions safer, especially in homes with children or elderly residents. The integration of technology provides a seamless blend of function and contemporary flair.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Sustainable Materials | Use of eco-friendly and reclaimed resources to create stylish transitions. |
| Smart Features | Integration of motion sensors and automated safety systems for enhanced functionality. |
| Artistic Designs | Unique shapes and bold aesthetics that serve as focal points in spaces. |
| Space-Saving Solutions | Innovative designs that maximize space efficiency in compact environments. |