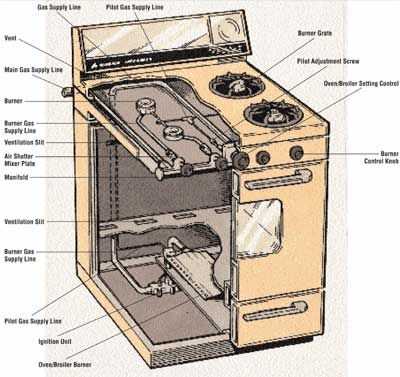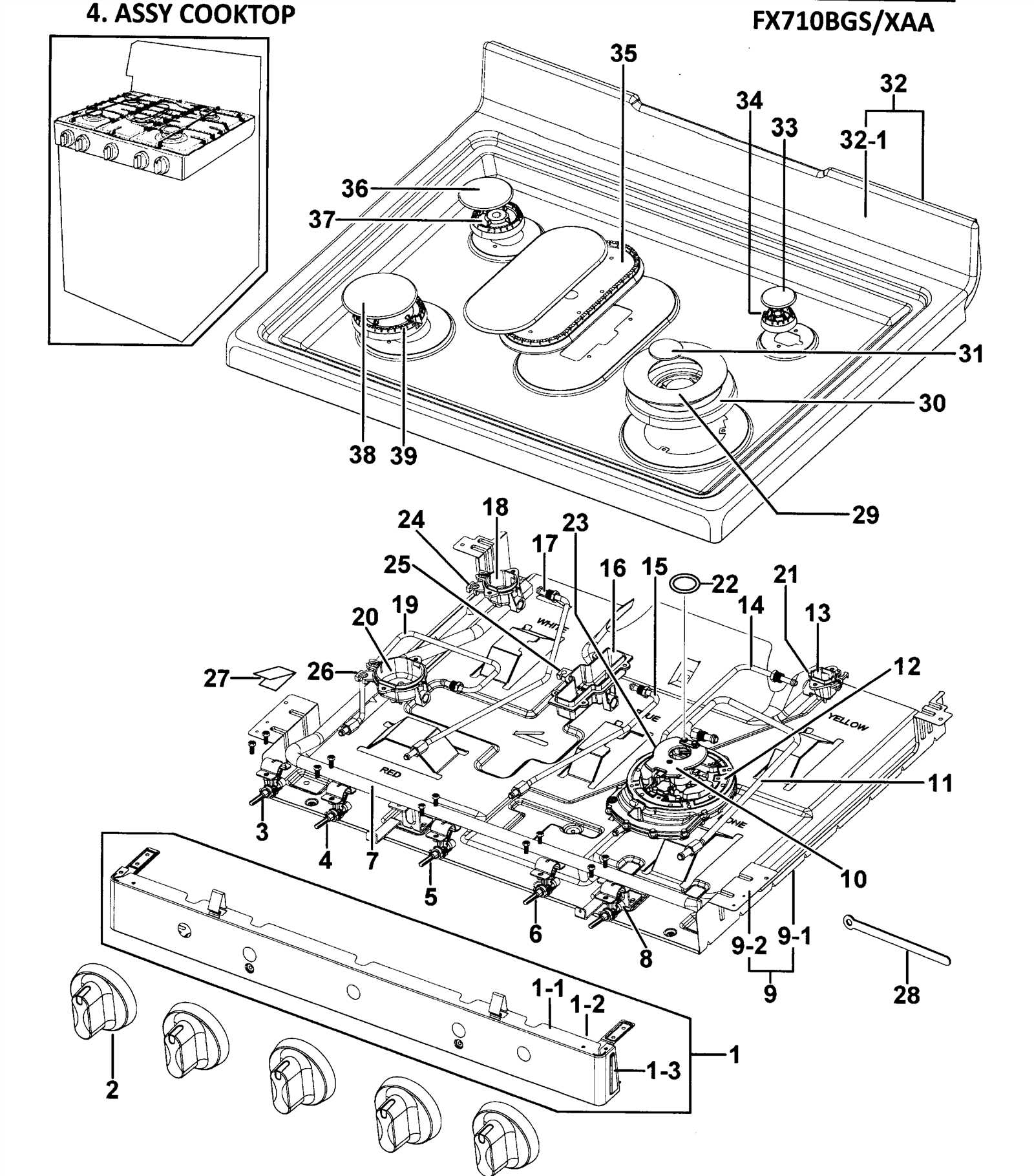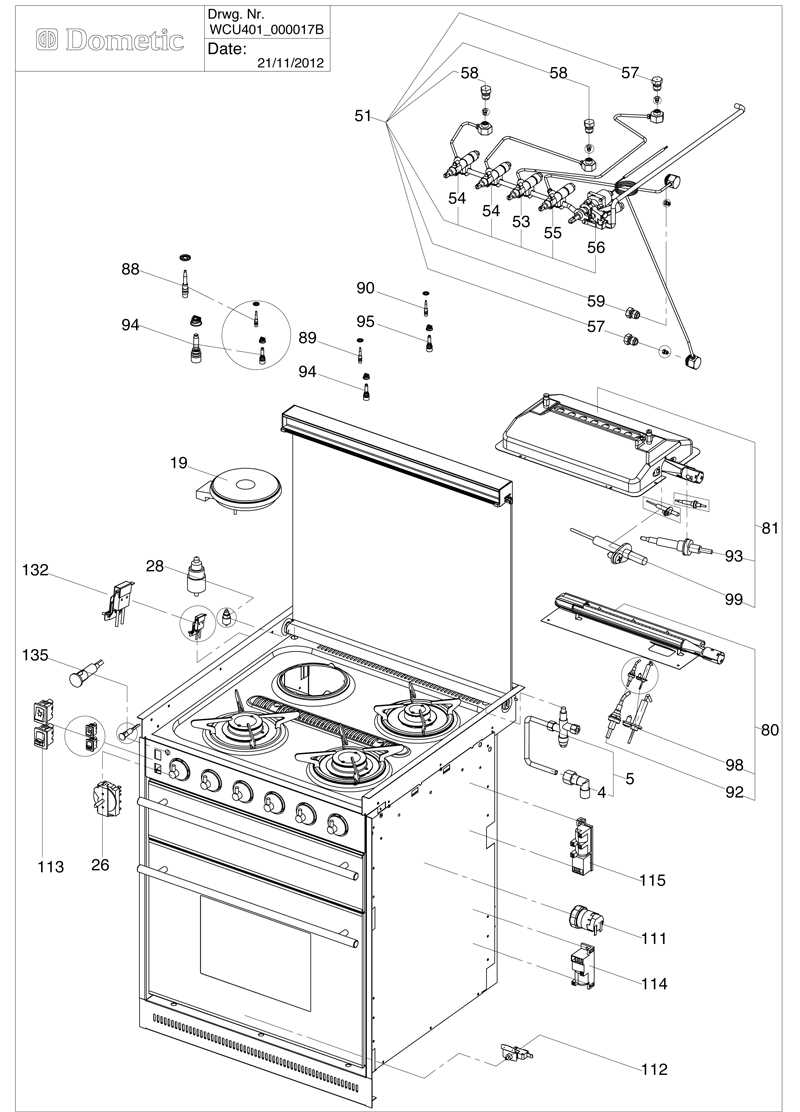
The functionality of a kitchen heat appliance relies on several essential components that work together to deliver efficient cooking performance. By recognizing the roles of each element, one can better appreciate how this everyday tool serves its purpose in various cooking methods, from baking to frying.
Each section of the appliance plays a unique role, contributing to the overall efficiency, safety, and ease of use. Whether managing temperature, providing fuel, or ensuring user control, these elements are carefully designed to work in harmony. Understanding their roles is key to maintaining the appliance and ensuring long-lasting use.
Exploring the individual features not only helps with maintenance but also ensures that users can operate it effectively. Proper knowledge of these components allows for safer and more efficient use, making every cooking experience smoother and more enjoyable.
Understanding the Structure of a Stove
Every cooking appliance designed for heat generation consists of several interconnected components, each serving a specific purpose in transforming energy into heat. By examining how these elements work together, one can gain insight into the core mechanics behind thermal appliances.
The key sections of this device involve components responsible for fuel supply, heat distribution, and temperature regulation. Below is a breakdown of these areas and their respective functions.
| Component | Function | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burner | Generates heat through combustion or electric resistance. | |||||||||||||
| Control Panel | Allows users to adjust temperature settings and other functionalities. | |||||||||||||
| Ignition System | Initiates the heating process by providing a spark or electrical current. | |||||||||||||
| Element | Function | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Knob | Adjusts the heating level to achieve the desired intensity. | |||||||||
| Timer Display |
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Consistent Results | Achieves uniform cooking by maintaining steady temperatures. |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces energy consumption by optimizing heat usage. |
| Extended Lifespan | Prevents overheating, which can damage the appliance. |
| Enhanced Safety | Minimizes risks of burns or fire hazards due to overheating. |
Safety Features Built into Stoves
Modern cooking appliances incorporate a range of safety mechanisms designed to prevent accidents and ensure user protection. These features play a crucial role in minimizing risks associated with high temperatures, flammable materials, and gas leaks, ultimately enhancing the overall cooking experience.
Automatic Shut-off Mechanism
One of the key innovations is the automatic shut-off system, which activates when a device is left unattended for an extended period. This feature significantly reduces the likelihood of overheating or potential fires, providing peace of mind to users. Additionally, many units now include timers that alert individuals when cooking is complete, further contributing to kitchen safety.
Temperature Regulation
Temperature control mechanisms are essential for maintaining safe heat levels during cooking. Many advanced appliances utilize sensors to monitor heat output, automatically adjusting as necessary to prevent overheating. Furthermore, non-slip surfaces and sturdy bases help to stabilize the appliance, minimizing the risk of accidental tipping or spills.
How the Ignition System Works
The ignition mechanism is a critical component in ensuring efficient operation and safety. It functions by producing a spark or heat source that ignites the fuel, initiating the combustion process. This system is designed to respond quickly, providing reliable ignition every time the appliance is activated.
Typically, the mechanism consists of an electrical source that generates a high-voltage spark. When the device is engaged, this electrical current flows to the ignitor, creating a spark that ignites the fuel mixture present in the combustion chamber. This process is essential for achieving optimal performance and reducing the risk of unburned fuel accumulation.
Moreover, safety features are integrated into the ignition system to prevent hazards. These may include automatic shutoff valves and fail-safes that ensure the flow of fuel is halted if ignition does not occur within a specified timeframe. Such mechanisms enhance user safety and contribute to the overall efficiency of the combustion process.
In summary, the ignition mechanism plays a vital role in the functioning of combustion appliances. Its ability to produce a reliable spark not only ensures effective operation but also promotes safety by minimizing potential risks associated with fuel ignition.
Common Stove Maintenance Parts
Regular upkeep of kitchen appliances is essential for ensuring their longevity and efficiency. Understanding the components that require attention helps to maintain optimal performance and prevent unexpected failures. This section explores the vital elements involved in routine care, focusing on their functions and significance in maintaining a smooth operation.
Heating Elements
Heating elements play a crucial role in delivering heat for cooking. Whether they are electric coils or gas burners, these components are responsible for transferring energy to cookware. Inspecting these elements regularly for signs of wear or damage can prevent cooking inefficiencies and potential safety hazards. Ensuring they are clean and functioning properly is key to effective meal preparation.
Control Knobs
The control knobs facilitate the regulation of temperature and settings, allowing users to tailor their cooking experiences. Over time, these knobs can become loose or unresponsive due to daily use. Ensuring they operate smoothly enhances both safety and usability. Regular cleaning and occasional tightening can prolong their functionality, making cooking more convenient and enjoyable.