
Understanding how different elements come together to create beautiful melodies is essential for anyone looking to delve deeper into the world of musical craftsmanship. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned player, learning about the core elements of this instrument helps enhance your playing experience and appreciation for the intricate design that makes it all possible.
Each section of this musical device plays a unique role, contributing to the overall sound, comfort, and playability. From the framework to the smaller details, every piece is crafted with precision, ensuring the harmony of tones and ease of handling. Knowing the function of these various elements allows players to understand how they affect performance, maintenance, and sound quality.
In this overview, we’ll break down the major features, offering insights into their significance and how they interact with one another. This knowledge will not only improve your ability to use the instrument effectively but also deepen your connection to the music it produces.
Acoustic Guitar Structure Overview
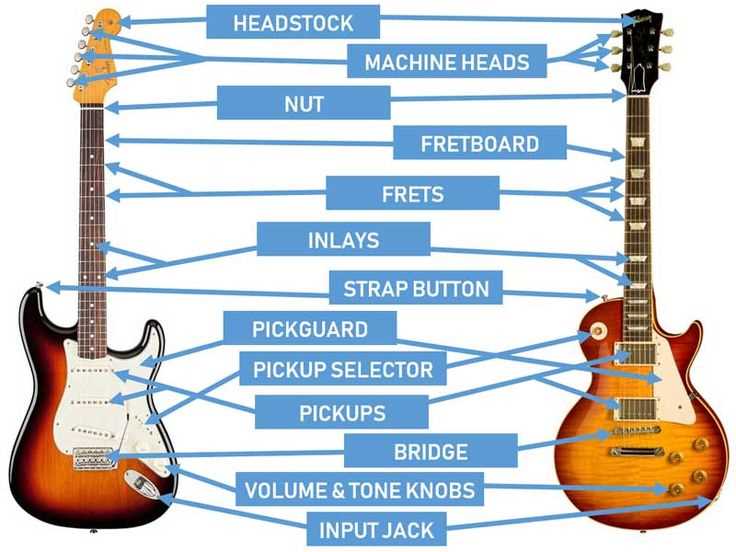
The design of this instrument combines craftsmanship and engineering to create a resonant and harmonious experience. Its architecture allows for rich tones, blending various elements seamlessly to enhance sound production. Understanding the overall build is essential for appreciating how each section contributes to the overall performance and resonance.
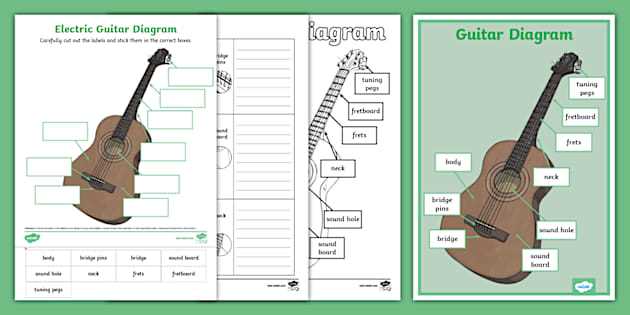
Main Components and Their Roles
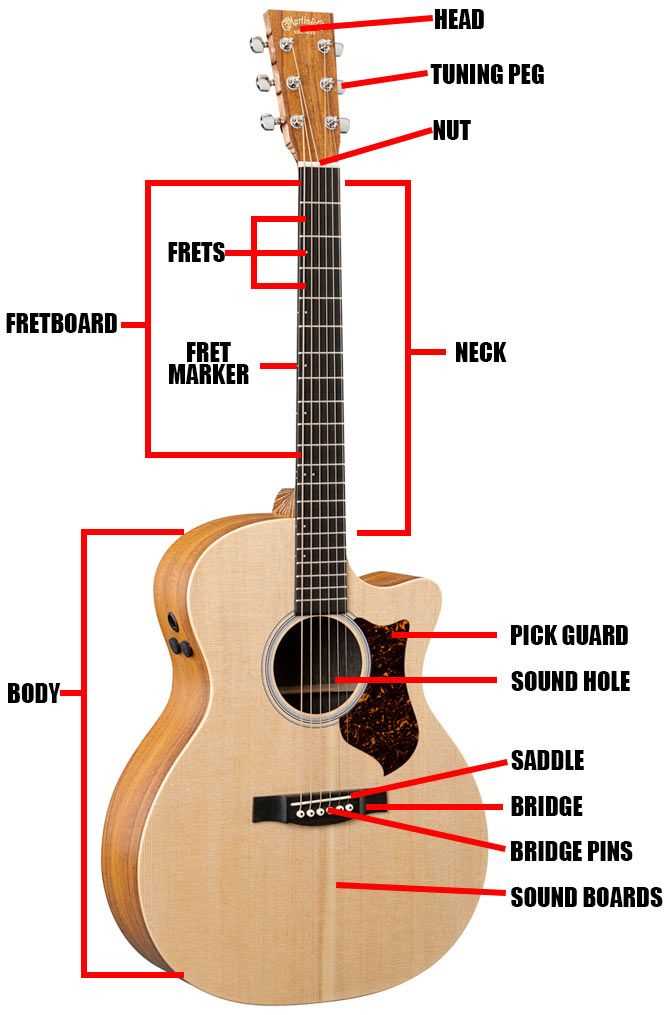
Several key elements work together to shape the tonal output. Each section has its own purpose, impacting the sound, comfort, and playability. Let’s take a closer look at how these pieces function within the whole.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Body | The main section responsible for resonance and volume projection. |
| Neck | Provides a surface for playing notes and chords, influencing tuning and intonation. |
| Bridge | Anchors the strings and transfers vibration to the soundboard for amplification. |
| Tuning Pegs | Used to adjust the tension of the strings, affecting pitch accuracy. |
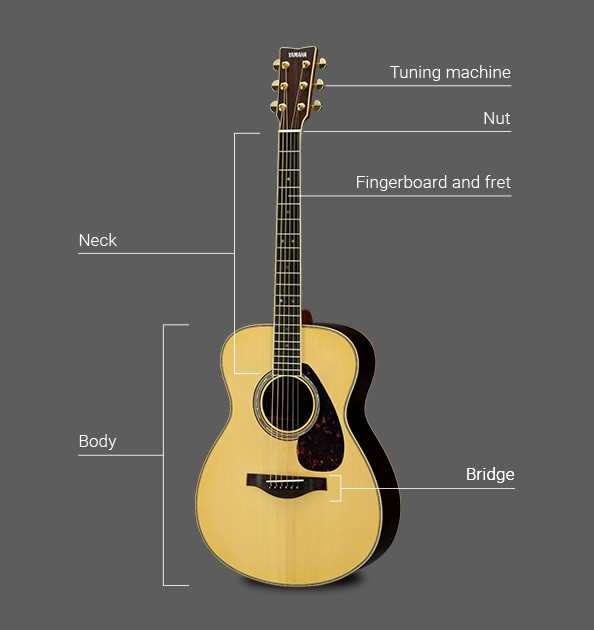
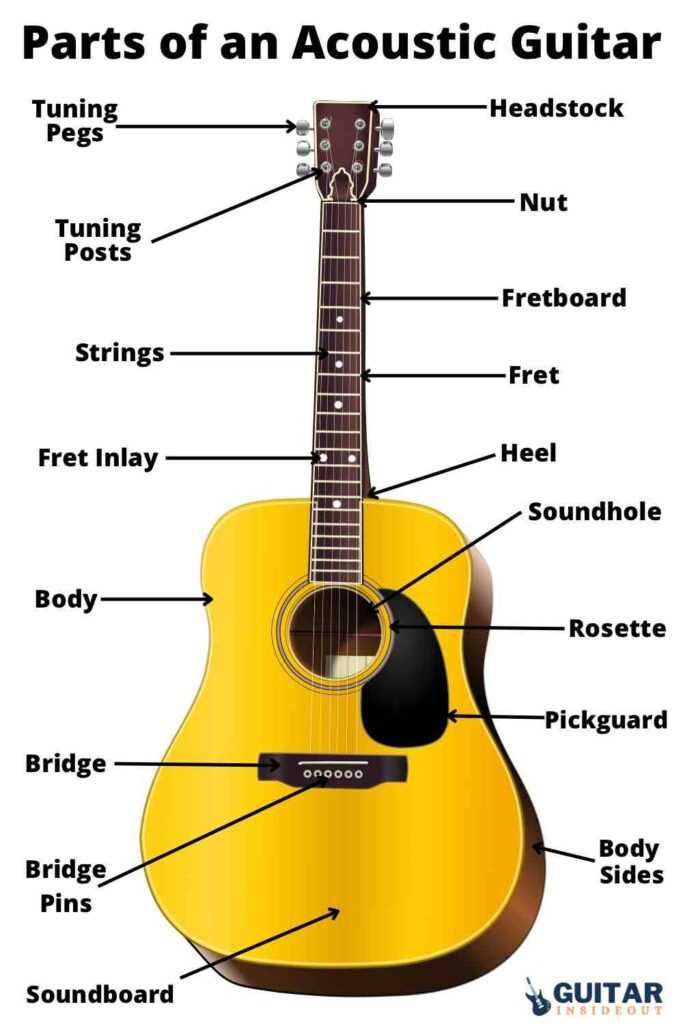
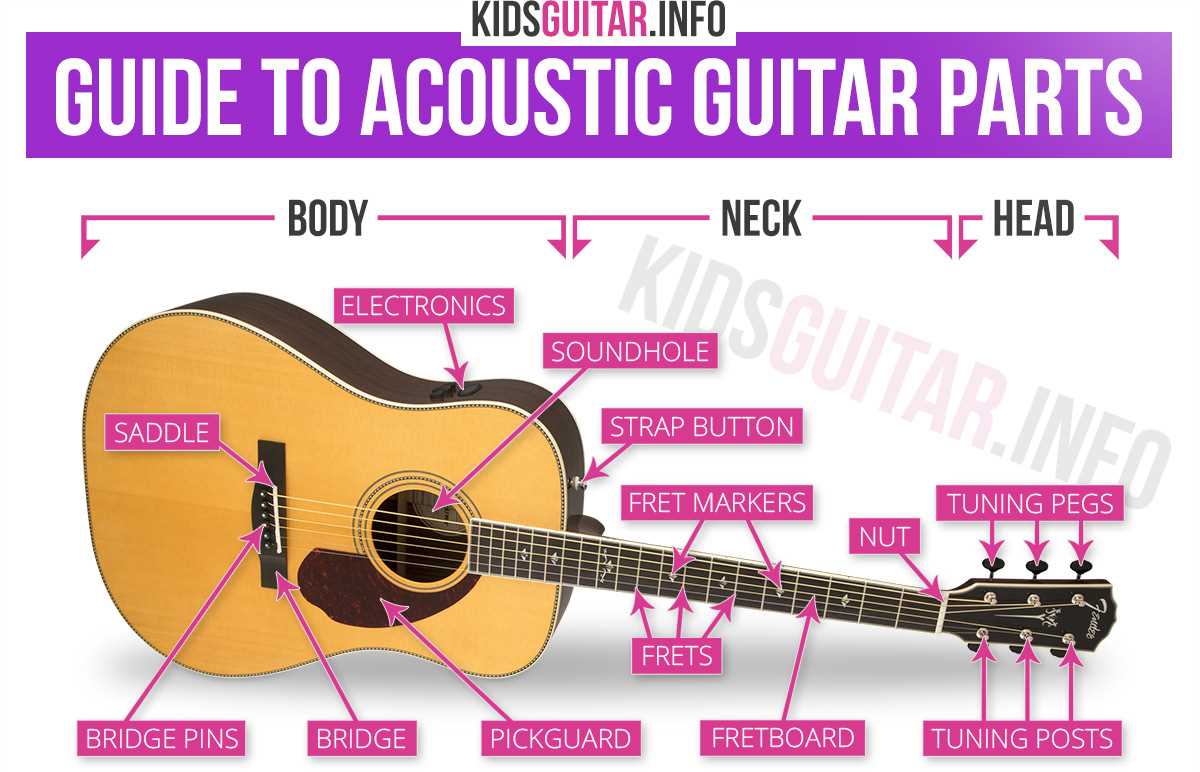
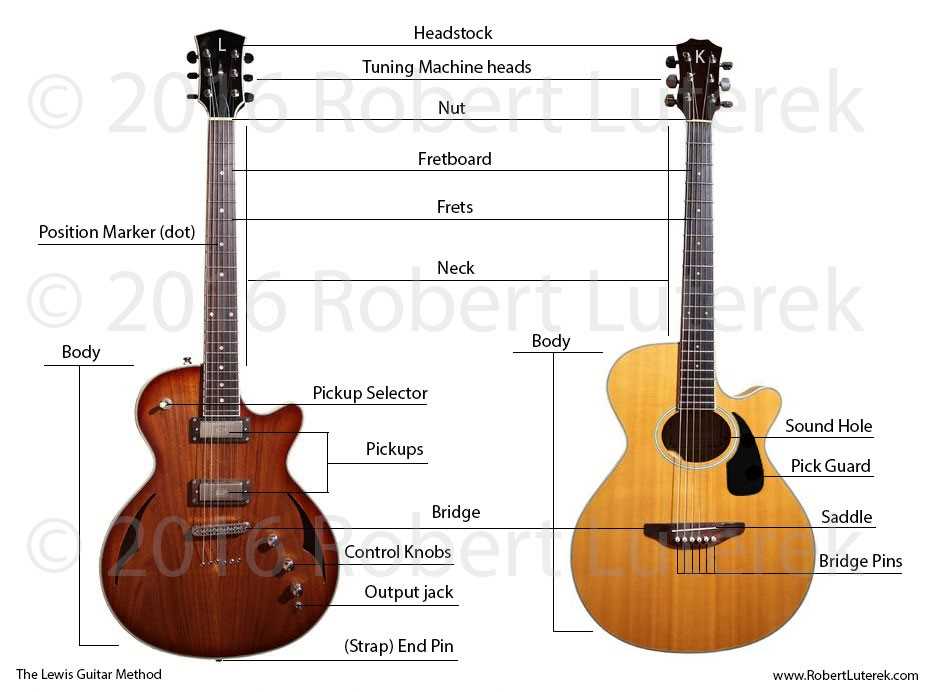
Main Components of an Acoustic Guitar
Understanding the essential elements of a traditional string instrument helps one appreciate its structure and functionality. Each part works together to produce rich sound and maintain the instrument’s balance and resonance. Let’s explore the critical pieces that define its performance.
The Soundboard and Its Importance
The top surface of the instrument plays a significant role in projecting the sound. This panel is designed to vibrate, amplifying the notes created by the strings. Typically made from specific types of wood, it contributes directly to the tonal quality and volume.
The Neck and Its Role in Playability
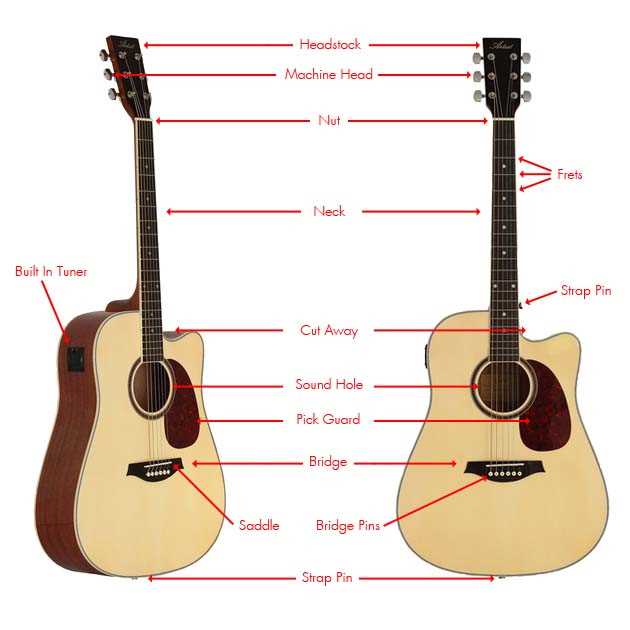
The long section connecting the body and head is essential for control and precision. It houses the fretboard, where players press down the strings to create different pitches. A smooth neck ensures ease of movement, making it easier to switch between chords and melodies.
These core components are intricately designed to work in harmony, delivering the warm, resonant sounds typical of this type of stringed instrument.
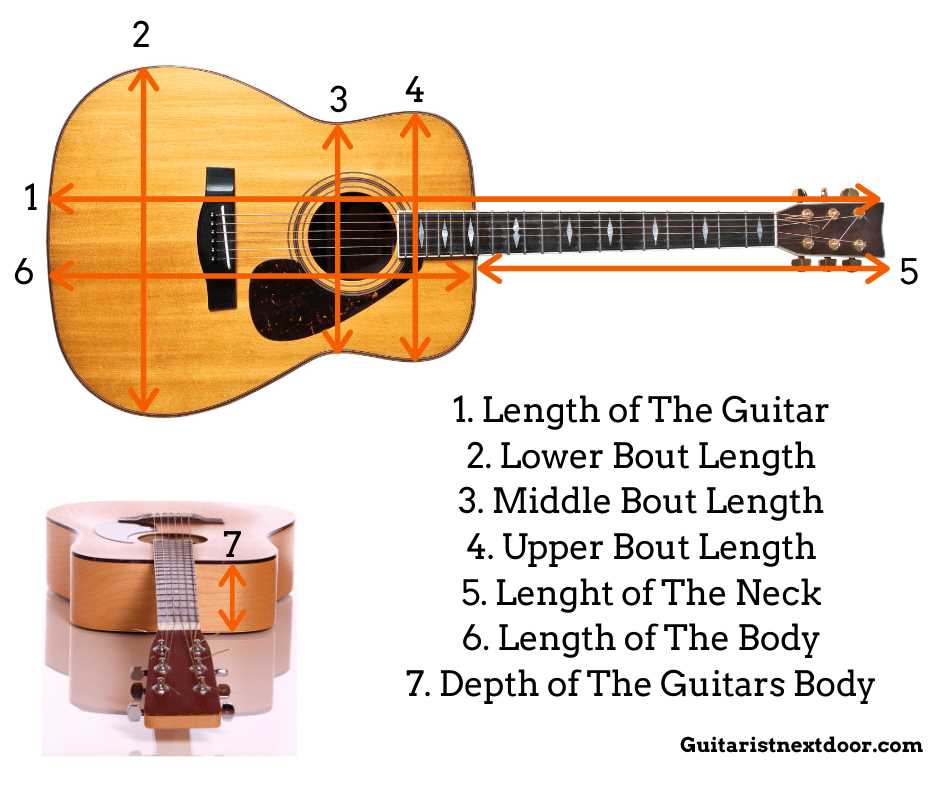
Understanding the Body of a Guitar
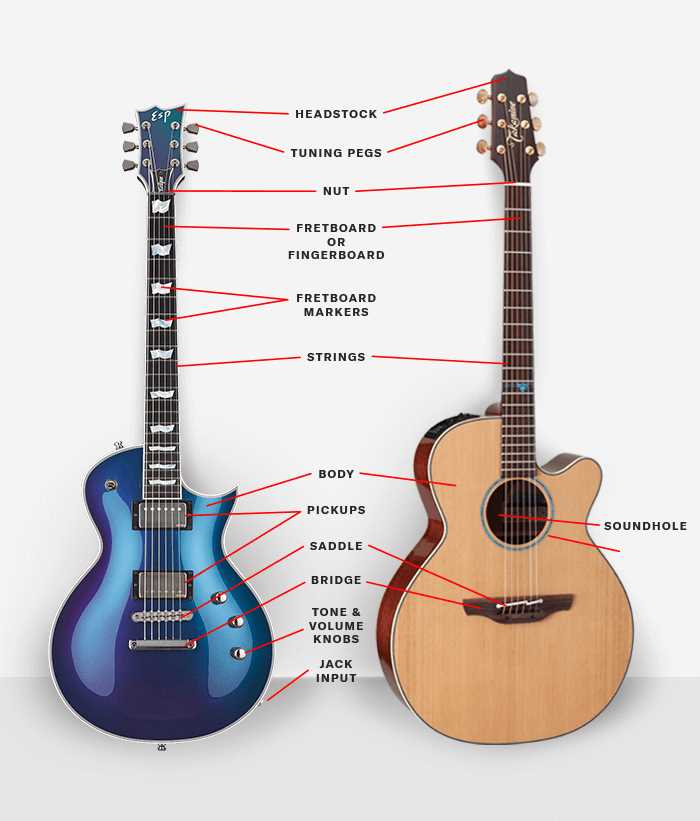
The structure of this musical instrument’s main component plays a crucial role in shaping its overall sound and resonance. Its craftsmanship, along with the materials used, directly influences the tones it produces, making each instrument unique. The design, curvature, and hollow cavity create an acoustic space that amplifies the vibrations and delivers rich sound.
Shape and Form
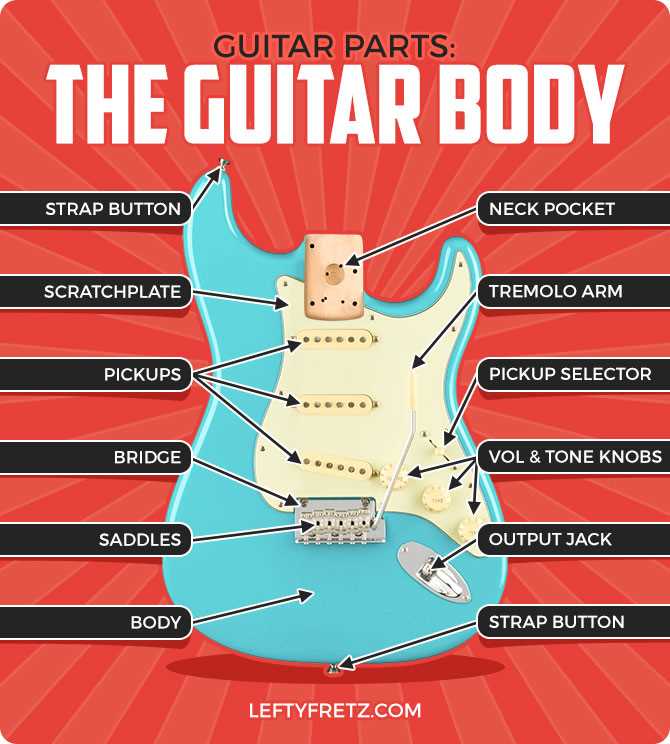
The outline and curves of this section contribute to the feel and balance while playing. Different models can have variations in width, depth, and overall design, which in turn affect comfort during performance. This physical form is carefully designed to ensure optimal resonance while allowing the player a comfortable grip.
Materials and Construction
The type of wood and the way it’s constructed are significant factors in sound quality. Lighter materials tend to produce brighter tones, while denser ones give a deeper, fuller sound. Each layer and joint is meticulously crafted, ensuring that the vibrations produced by the strings resonate clearly and harmoniously.
How the Soundhole Affects Tone
The central opening plays a significant role in shaping the resonance and overall sound quality. It allows air to move freely, which impacts the vibration of the body and the balance between high and low frequencies. Without this feature, the sound would be muffled, lacking projection and clarity.
When sound waves travel through the opening, they create a blend of harmonics that influence the richness of the sound. The size and placement of this feature also affect how warm or bright the sound becomes, giving it a unique character.
By enhancing airflow, the opening contributes to the instrument’s loudness and resonance, making it essential for achieving a well-rounded sound. Every detail in its design can alter the tonal balance, from soft and mellow to sharp and articulate.
Fretboard Layout and Its Role
The design of the fingerboard plays a crucial role in the overall experience of playing, impacting both sound and technique. Its structure allows for easy navigation across different notes, influencing the harmony and precision of the sound produced. Understanding its layout is key to mastering various melodies and progressions.
- Positioning: The arrangement of the frets creates distinct intervals, helping define musical tones.
- Note Placement: Each section of the fingerboard corresponds to specific notes, which can be accessed by pressing on the frets.
- Octave Patterns: The layout features repeating patterns that help musicians easily recognize notes across different sections.
- Playing Techniques: The spacing between the frets directly affects how smoothly transitions between chords and notes can be executed.
The well-organized structure of the fingerboard ensures that musicians can efficiently move between notes and develop precise control over their technique.
The Importance of the Bridge
The bridge plays a vital role in the overall functionality and sound quality of stringed instruments. This essential component not only supports the strings but also transfers their vibrations to the body, influencing tonal characteristics. Its design and materials significantly affect the instrument’s resonance and sustain, making it a crucial element for achieving the desired sound.
A well-crafted bridge can enhance the instrument’s projection and clarity. The positioning and height of the bridge are critical in determining string action and playability. Musicians often choose specific shapes and materials to tailor their instruments to personal preferences, further emphasizing the bridge’s impact on performance and sound output.
Ultimately, the bridge serves as a connection between the player and the instrument, affecting how notes are produced and perceived. Understanding its significance enables musicians to make informed decisions when selecting or modifying their instrument, ensuring an optimal musical experience.
What You Need to Know About the Neck
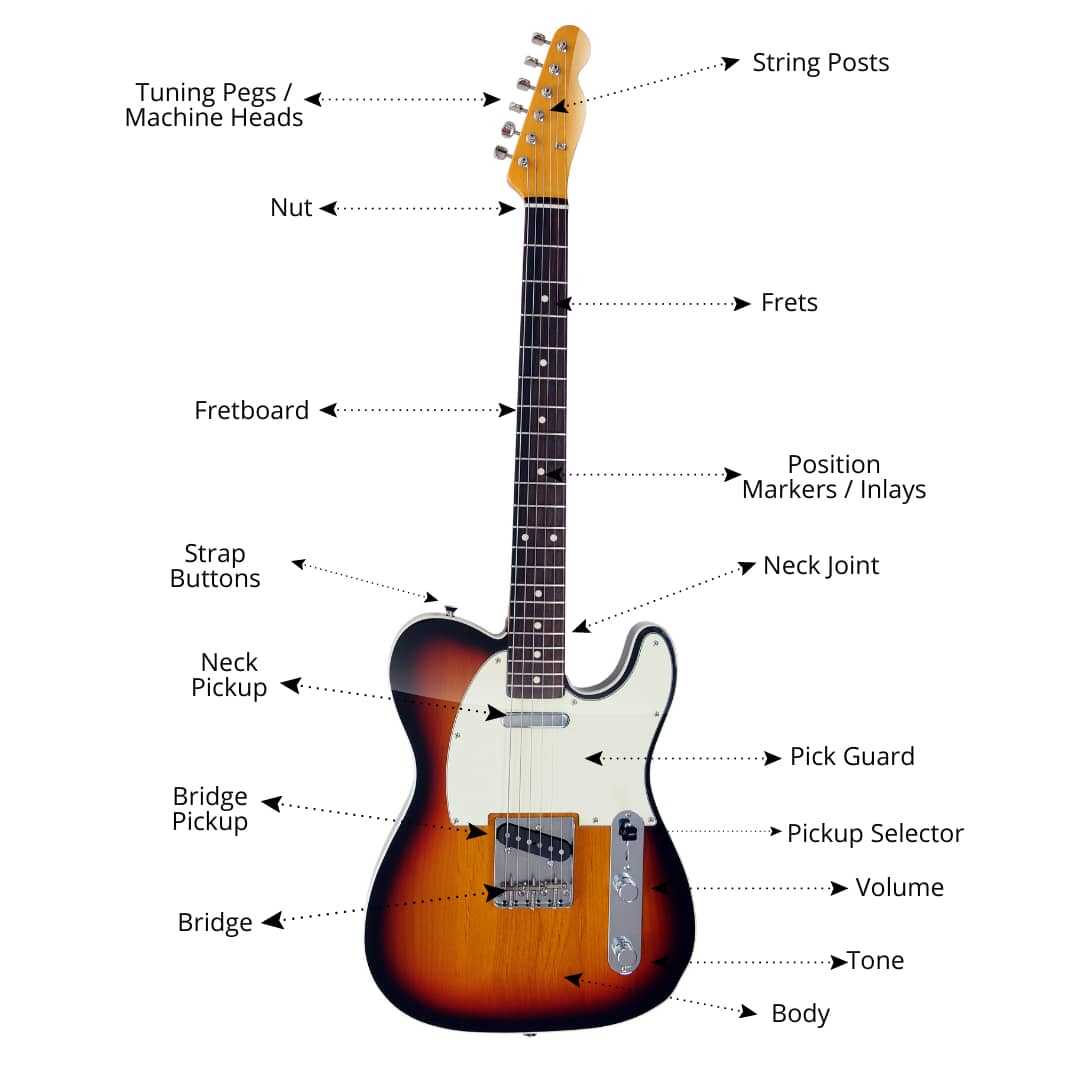
The long, slender component of stringed instruments plays a crucial role in the overall performance and playability. This section delves into the significance of this feature, highlighting its influence on tone production and the musician’s comfort. Understanding its structure and function is essential for anyone looking to enhance their skills or knowledge about these instruments.
Structure and Function
This elongated section typically comprises several distinct sections, each serving a unique purpose. The frets allow players to create various notes by pressing down on the strings, while the curvature and width can greatly affect how easy or difficult it is to play different styles. The quality of materials used in construction also influences the sound and feel, making it an important consideration for musicians.
Maintenance and Care
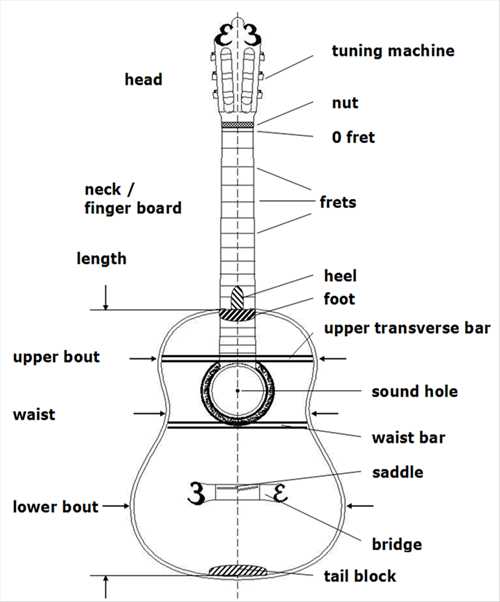
The Function of the Guitar’s Headstock
The headstock serves as a crucial component that plays a significant role in the overall performance and tuning stability of stringed instruments. It is strategically positioned at the end of the neck, providing essential support for the strings and housing important mechanisms for pitch adjustment.
String Tension Management

One of the primary functions of this section is to maintain proper tension in the strings. By anchoring the strings securely, it ensures that they remain in the correct position and can vibrate freely. This contributes to the instrument’s tonal quality and helps musicians achieve precise notes during play.
Tuning Mechanism

The headstock also features tuning pegs that allow for quick adjustments. These pegs enable the player to fine-tune each string, ensuring optimal sound. The ability to adjust tension easily is vital for performances, as it allows artists to adapt to different musical styles or environmental conditions.
Tuning Pegs and Their Adjustment Process
The mechanism responsible for controlling the pitch of strings plays a crucial role in the overall sound quality and playability of stringed instruments. Understanding how to adjust this mechanism is essential for musicians who seek to achieve accurate tuning and maintain the instrument’s performance over time.
To effectively manage the tension of the strings, follow these essential steps:
- Identify the correct peg: Each string is associated with a specific tuning peg, usually located on the headstock. Ensure you are adjusting the correct one to avoid confusion.
- Loosen the string: If you need to make significant adjustments, start by gently loosening the string to relieve tension. This makes it easier to turn the peg without causing strain.
- Turn the peg: Rotate the tuning peg clockwise to raise the pitch and counterclockwise to lower it. Make small adjustments to ensure precise tuning.
- Check the pitch: Use a reliable tuner or an app to monitor the pitch as you adjust. Stop turning the peg when the desired note is reached.
- Re-tension the string: Once you achieve the correct pitch, carefully tighten the string to its original tension. This step is crucial for maintaining stability.
- Repeat as necessary: Go through the process for each string until all are accurately tuned.
Regular adjustments and maintenance of this mechanism ensure that the instrument remains in optimal condition, allowing musicians to deliver their best performances.