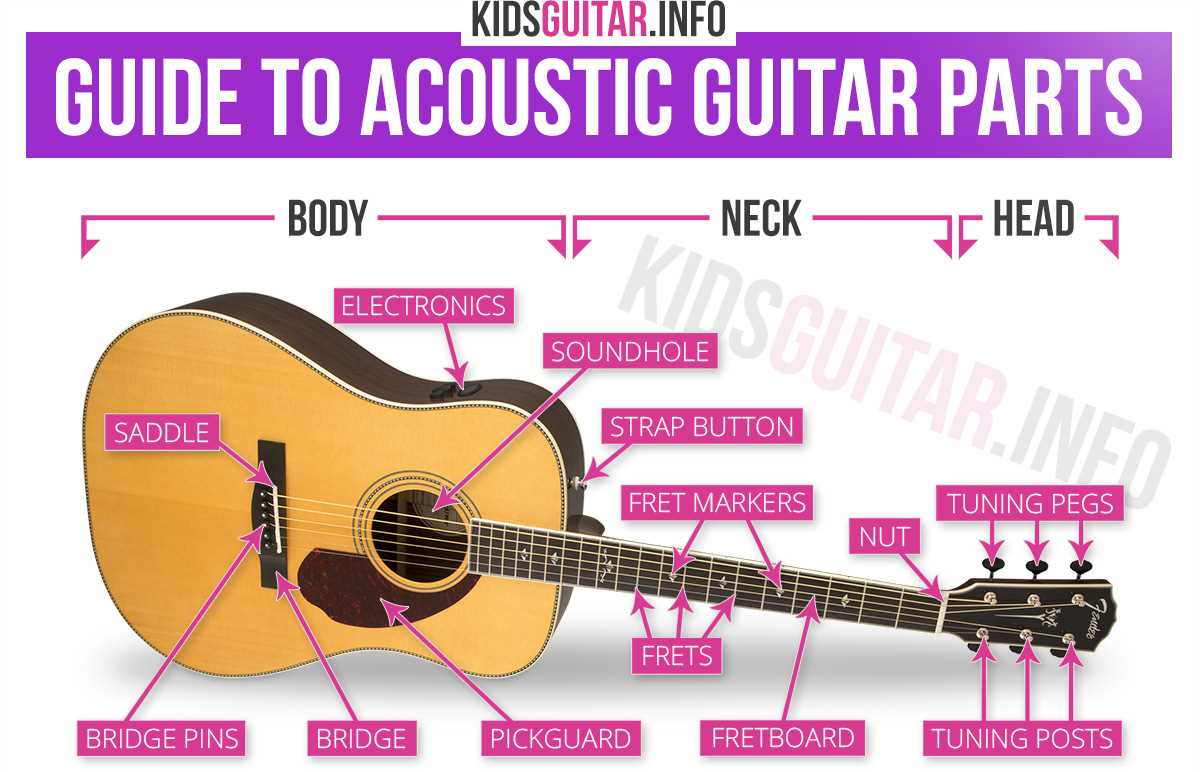
Understanding the structure of a stringed musical tool is essential for both musicians and enthusiasts. Each component serves a vital role in shaping the sound and playability, making it important to familiarize oneself with their functions and interactions. By breaking down these elements, one can better appreciate how they contribute to the overall performance.
This layout provides a comprehensive overview of the essential sections of the instrument, highlighting how each part influences tone, resonance, and ease of use. From the resonance chamber to the tuning mechanisms, the intricate design is a perfect blend of function and form, optimized for sound production.
Whether you’re an experienced player or just starting, gaining a deeper understanding of this musical tool’s blueprint can significantly enhance your ability to maintain, modify, or play it with confidence. This exploration offers valuable insights into how the unique arrangement of elements affects the musical experience.
Parts of a Guitar Diagram
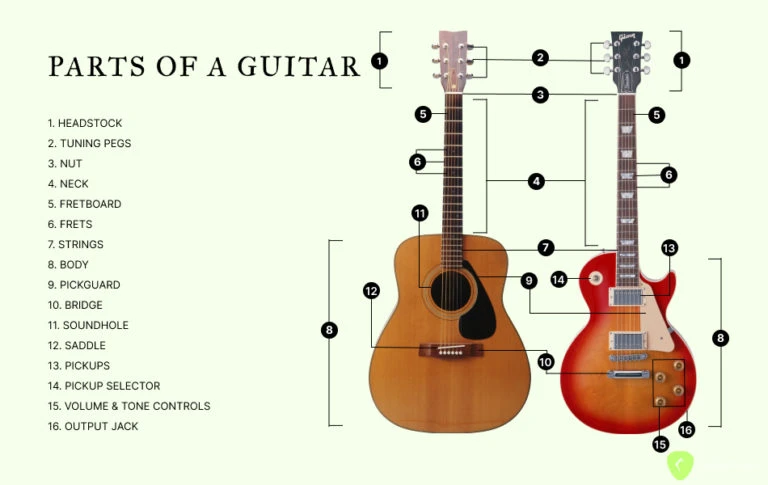
When exploring this intricate musical instrument, it becomes essential to understand the various components that work together to produce its signature sound. Each section, no matter how small, contributes to the overall playability and tone of the instrument, influencing the experience of musicians and listeners alike.
Understanding Key Components
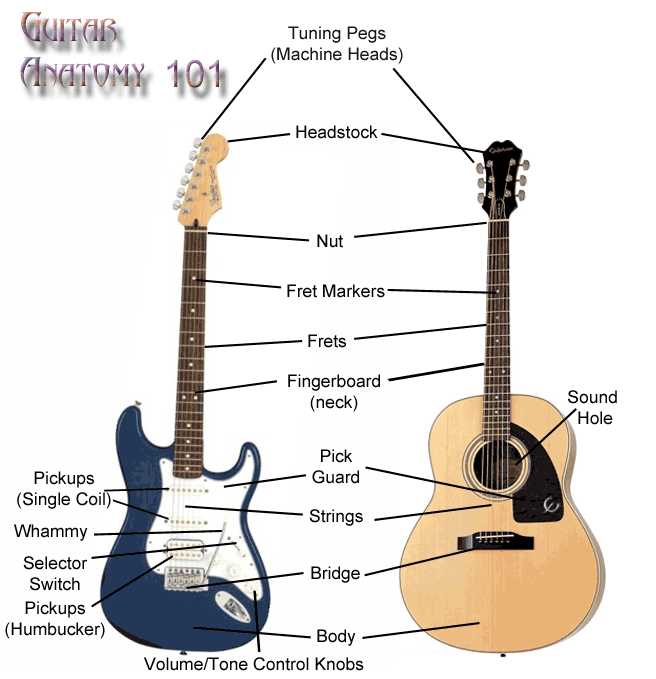
The various elements are designed with purpose and precision, offering control over pitch, volume, and resonance. From the long wooden structure that holds everything together to the sensitive mechanism used for adjusting tension, each piece serves a unique function.
How the Elements Interact
Each component is connected, creating a seamless flow of sound. When all parts are in harmony, the instrument performs at its best, allowing players to express their creativity through diverse musical styles. This interaction between the elements is vital to maintaining the balance and tone quality.
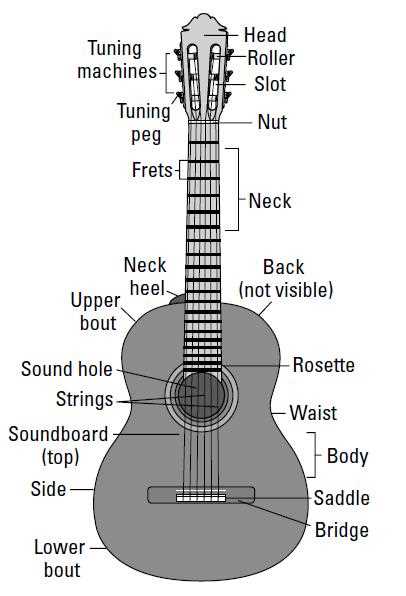
Anatomy of Acoustic Guitar Components
Understanding the various elements of this musical instrument is essential for anyone looking to master its use or appreciate its craftsmanship. Each section plays a vital role in producing sound, resonance, and overall performance. By breaking down these elements, we can gain a clearer picture of how the instrument operates and delivers its distinctive tones.
Main Structural Elements
The body of the instrument is designed to enhance the sound quality by amplifying vibrations. Its specific shape and internal bracing define the resonance and projection. The neck provides a surface for playing, with an arrangement of divisions that allow for changing pitch.
Sound Production Components
Key areas responsible for sound production include the strings, which, when plucked or strummed, create vibrations. These vibrations travel through various surfaces, contributing to the unique tone. The bridge and its supporting elements anchor the strings, maintaining
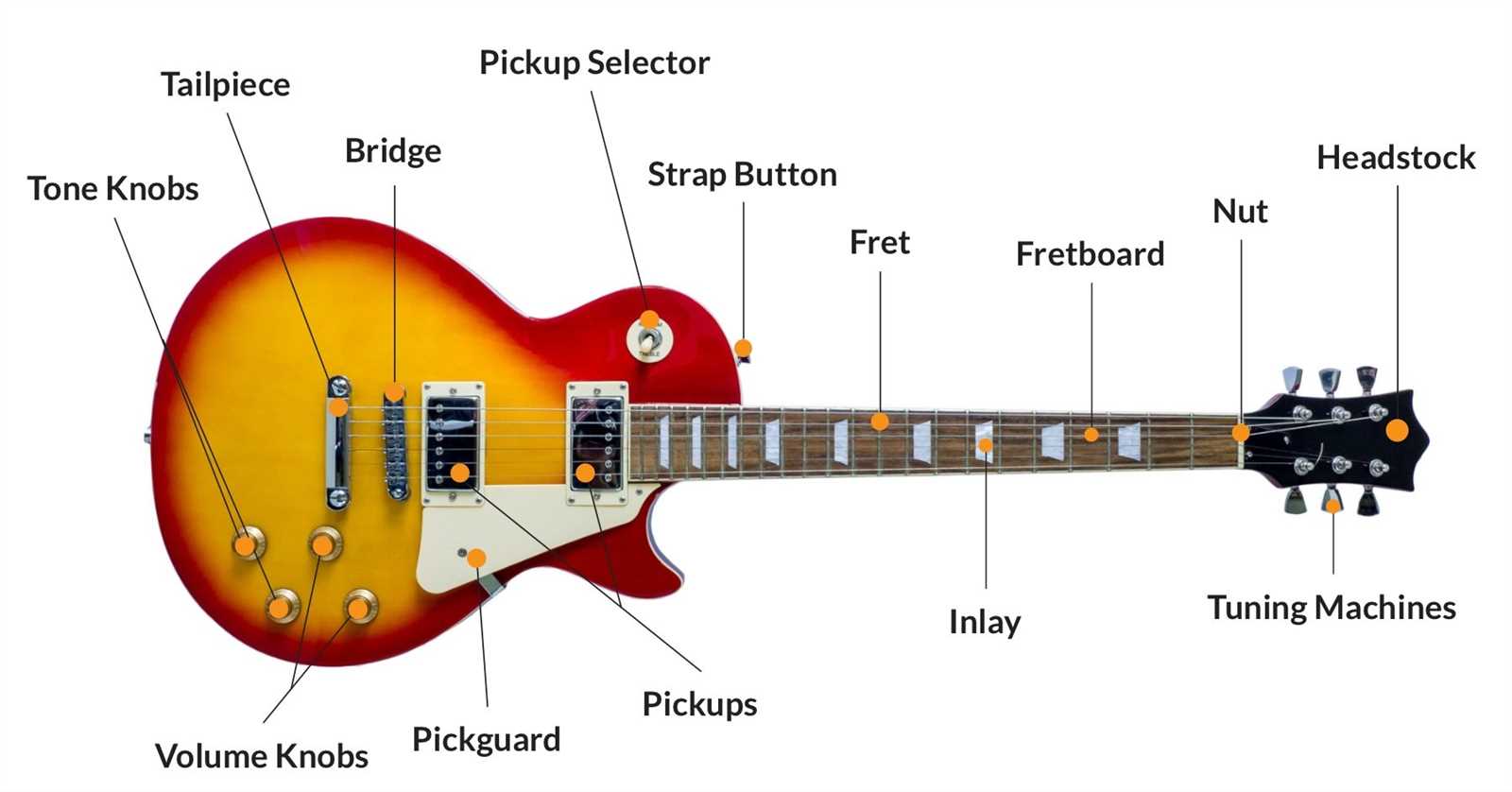
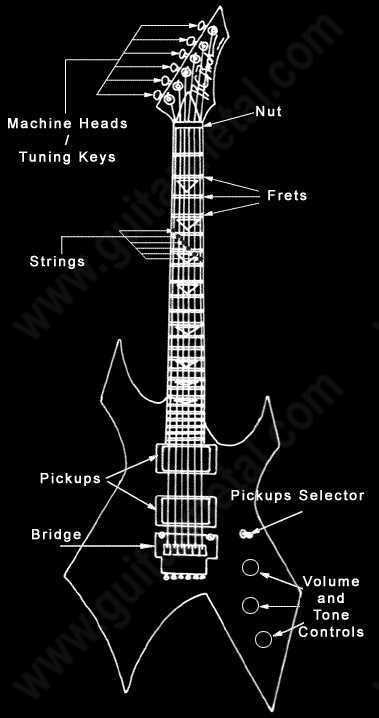
Electric Guitar Structure and Functions
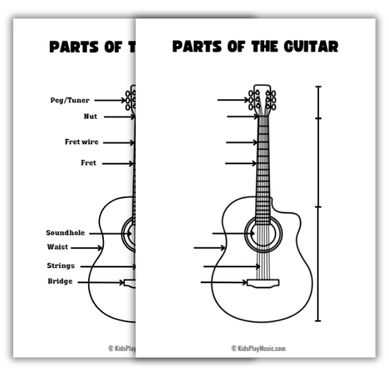
The configuration of this musical instrument consists of several interconnected components that together produce its signature sound. Each section contributes to both the tonal quality and playability, ensuring a smooth performance. Understanding these elements is essential for optimizing sound and enhancing play techniques.
The body serves as the primary platform, responsible for the resonance and amplification of sound. On the other hand, the neck plays a critical role in pitch variation, where strings are pressed to create different notes. Connecting these two areas is vital for controlling sound dynamics and sustain.
The electronic system embedded within manages the modulation and transmission of sound to external amplifiers. Additionally, specific controls allow players to adjust volume, tone, and other characteristics, providing flexibility in sound customization.
Exploring the Fretboard Layout
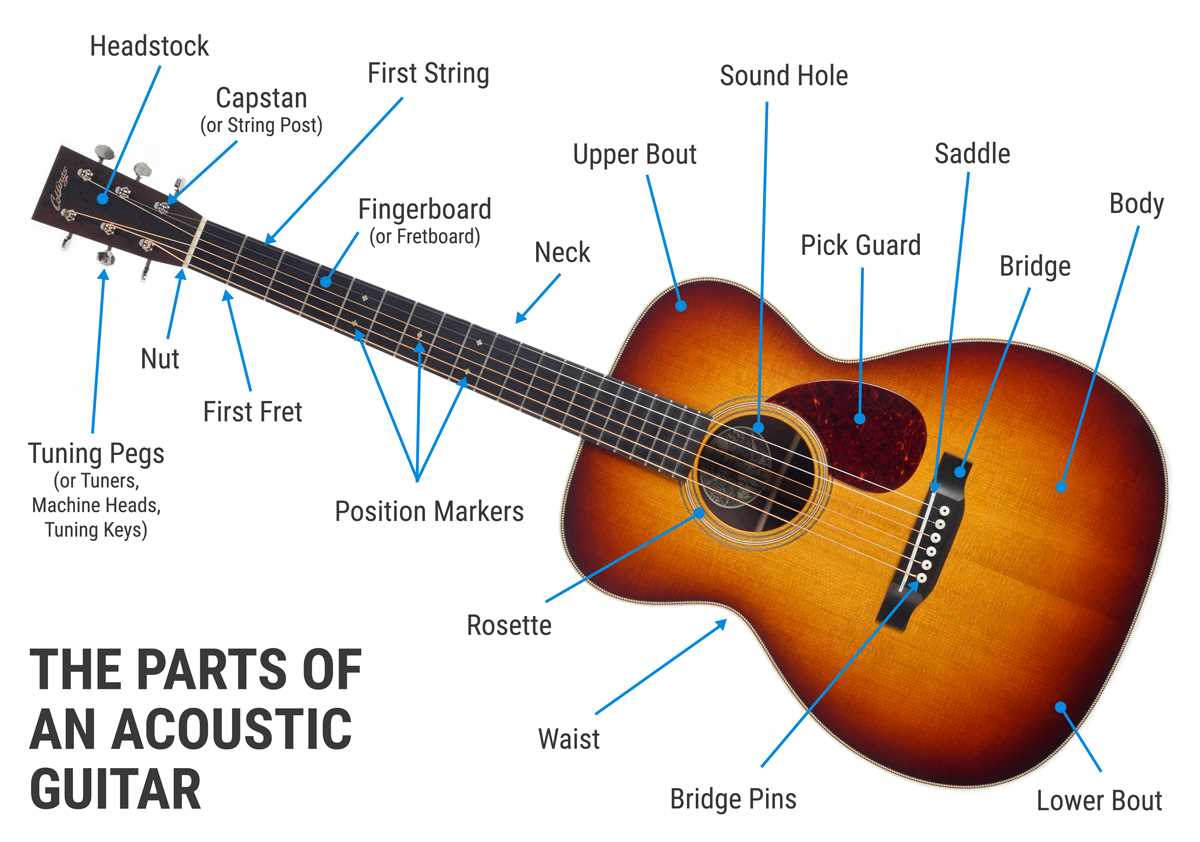
The structure of this essential section plays a vital role in the sound and feel of stringed instruments. Understanding its arrangement allows players to navigate different tones and patterns, offering a variety of musical possibilities.
Positioning and Numbering
The layout is organized by a series of evenly spaced markers that help identify various intervals and positions along the neck. These markers are often found in specific spots and assist in locating important musical notes.
- Frets are numbered sequentially, starting from the base of the neck.
- Markers, often placed on specific positions like the third, fifth, and seventh intervals, guide players during performance.
- Each interval represents a step in musical pitch, allowing for seamless transitions between notes.
Mastering the Layout

Becoming familiar with this layout is crucial for improvisation and performance across various musical genres. By memorizing the positions of important notes and their relationships, players can more easily transition between melodies and harmonies.
- Start by learning the positions of the most frequently used markers.
- Practice moving between intervals smoothly to enhance muscle memory.
The Role of Guitar Pickups
In any stringed instrument with electrical amplification, one of the key components that shape the overall sound is the device responsible for converting vibrations into electronic signals. These small, yet vital pieces of hardware allow the instrument to be connected to amplifiers and external equipment, transforming the acoustic qualities into a powerful, amplified output.
These elements are placed strategically under the strings, detecting subtle movements and generating signals that vary depending on string tension and material. The configuration of these components can significantly influence the tonal characteristics and responsiveness, making them essential in defining the sonic identity of the instrument.
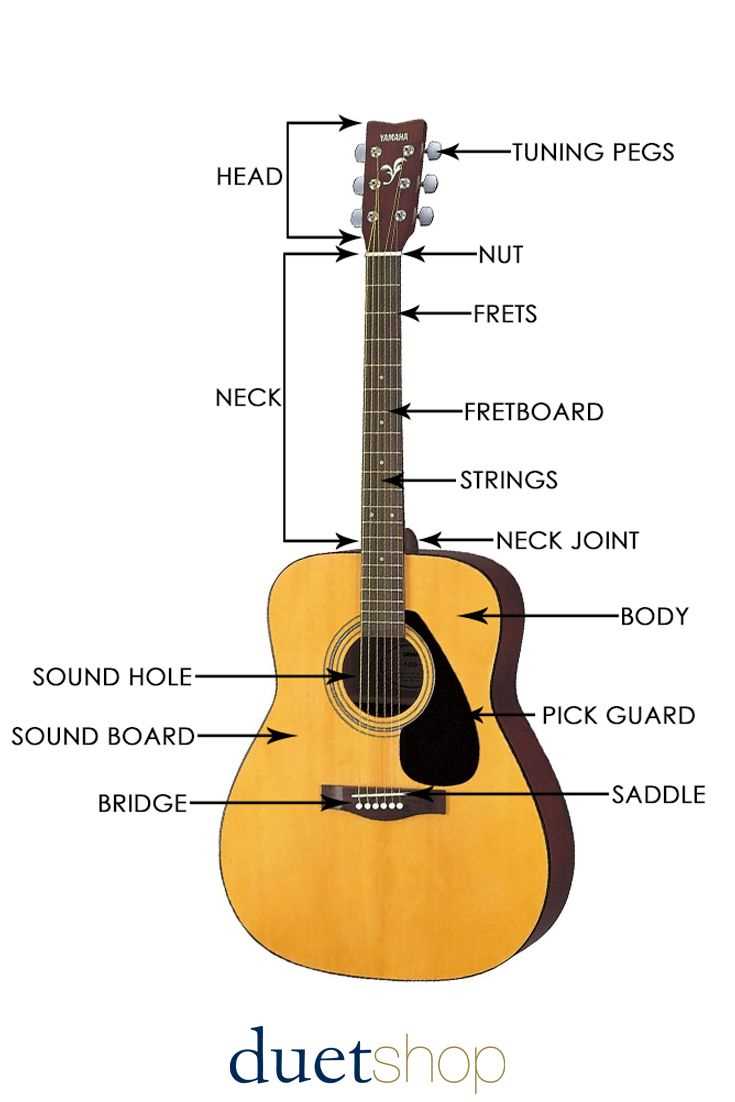
Bridge and Tuning Mechanisms
The connection between the strings and the body of a musical instrument is crucial for sound production and tuning accuracy. This section explores essential elements that contribute to the overall performance and stability of stringed instruments. Understanding these components allows musicians to optimize their instruments for better playability and tone.
One of the key features in this context is the bridge, which serves multiple purposes:
- Transfers string vibrations to the body, enhancing resonance.
- Holds the strings in place, maintaining proper tension.
- Affects action height, influencing playability.
In addition to the bridge, tuning mechanisms play a vital role in achieving precise pitch. These components are designed to facilitate easy adjustments and ensure stability:
- Tuning Pegs: Allow musicians to adjust string tension by winding or unwinding the strings.
- Nut: Guides strings from the tuning pegs to the bridge, affecting the instrument’s action.
- String Trees: Help maintain proper string angle, particularly for instruments with staggered tuning pegs.
By comprehensively understanding these elements, players can enhance their instrument’s functionality and achieve a more satisfying musical experience.
Understanding the Neck and Headstock
The neck and headstock are essential components that play a crucial role in the functionality and playability of string instruments. They serve as the backbone for creating melodies and harmonies, allowing musicians to navigate through various notes and chords with precision. This section explores their significance and structure, shedding light on how they contribute to the overall sound and performance.
The Structure of the Neck
The neck is the elongated section that extends from the body towards the headstock. It typically features a fingerboard where the player presses down on the strings to produce different pitches. The construction of this section often includes a truss rod, which allows for adjustments in curvature, ensuring optimal string action and playability. The choice of materials, such as wood types, can also affect the instrument’s tone and resonance.
The Role of the Headstock
At the upper end of the neck lies the headstock, which houses the tuning mechanisms that hold the strings in place. This area is crucial for achieving the correct tension and pitch. The design can vary widely among different instruments, impacting aesthetics and functionality. A well-crafted headstock not only enhances tuning stability but also contributes to the overall balance and comfort while playing.
The Importance of the Guitar Body Shape

The configuration of the instrument’s main structure significantly influences its overall sound and playability. Variations in design can affect resonance, tonal quality, and comfort for the musician. This section explores how different forms can cater to diverse playing styles and preferences, making them crucial for both performance and enjoyment.
Impact on Sound Quality
The shape of the instrument’s body plays a vital role in sound projection and tonal characteristics. A wider and deeper frame may enhance bass responses, while a shallower design often produces brighter tones. Musicians often select their instrument based on the sound they wish to achieve, making the body shape a fundamental aspect of their choice.
Comfort and Playability

Aside from acoustics, the physical outline directly affects how easily a performer can navigate the fretboard. Shapes designed with ergonomics in mind can facilitate extended playing sessions without discomfort. As such, a well-designed structure not only enhances musical expression but also contributes to the overall playing experience.
Controls and Switches on Electric Guitars
Understanding the components that manage sound output is essential for any enthusiast of stringed instruments. These elements play a crucial role in shaping the tonal characteristics and overall performance of the instrument. From altering volume levels to selecting different sound profiles, these features offer musicians a wide range of creative possibilities.
Types of Controls

Several types of controls are commonly found on electric instruments, each serving a unique function. Below is a brief overview of these elements:
| Control Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Volume Control | Adjusts the loudness of the sound produced by the instrument. |
| Tone Control | Modifies the tonal quality, allowing for brighter or warmer sound profiles. |
| Pickup Selector | Switches between different pickups, affecting the sound texture. |
Switch Functionality
Switches play an integral role in defining how different controls interact with the output. They provide the musician with options to modify sound characteristics dynamically during performance, enhancing versatility and expression.