
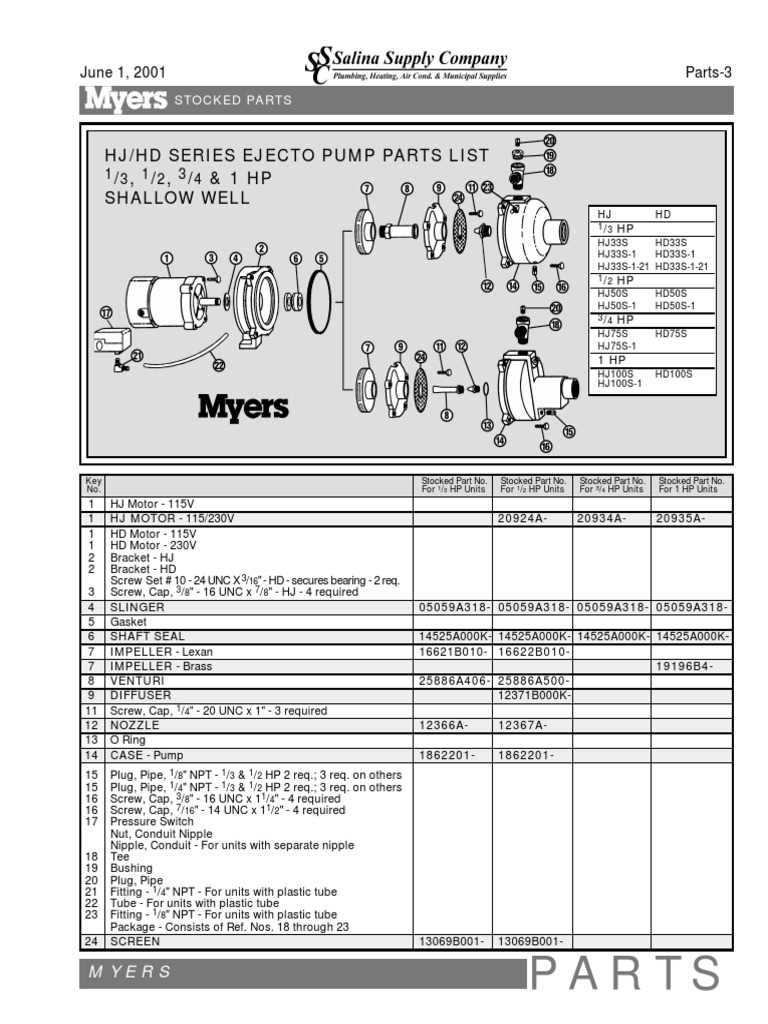
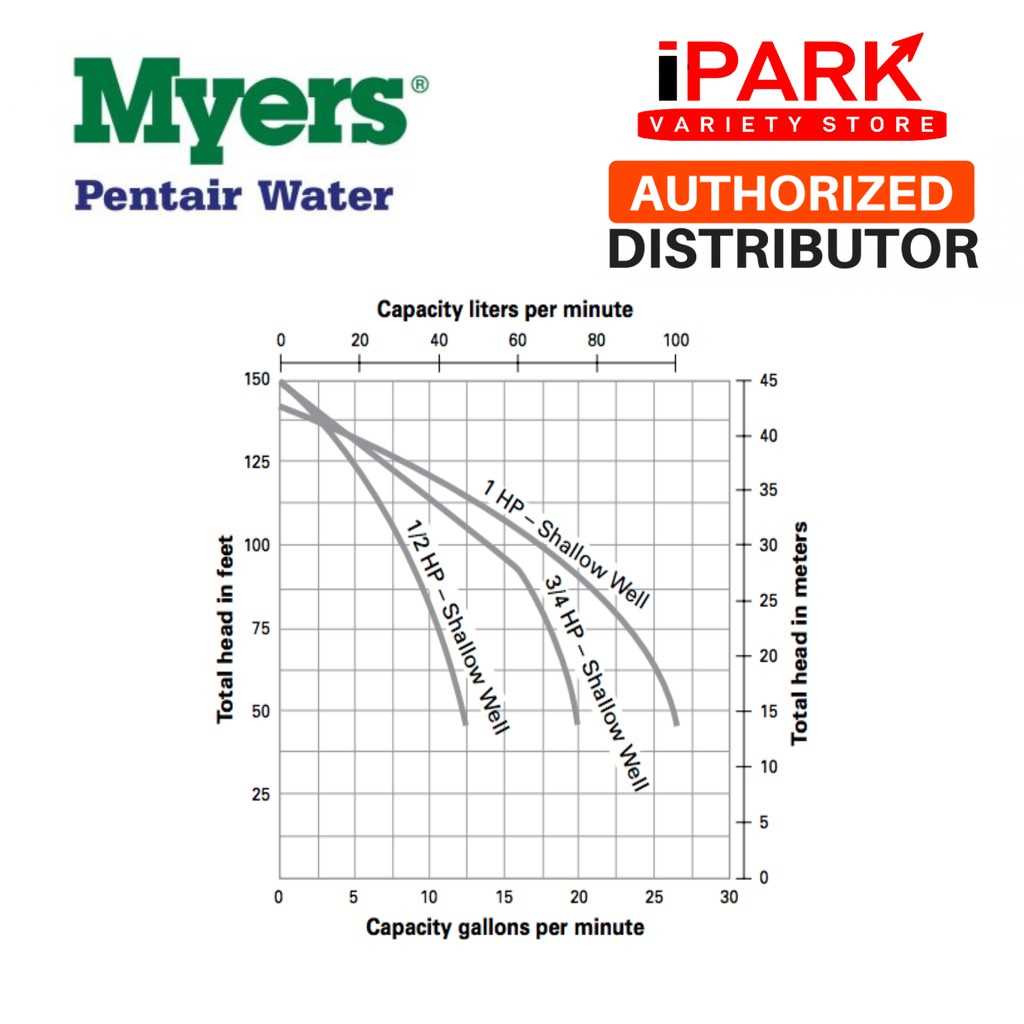
In the realm of fluid management, the efficiency and reliability of machinery play a pivotal role. Grasping the intricate details of the elements involved can significantly enhance performance and maintenance. This section delves into the essential components that make up these systems, providing a visual representation to clarify their interrelations and functionalities.
Exploring the intricate workings of these mechanisms reveals a network of interconnected units, each serving a specific purpose. By comprehensively understanding how these elements interact, one can better appreciate their contributions to overall system efficiency. The following insights will help illuminate the crucial roles played by each component.
With a clear representation of the various segments involved, operators and technicians can more effectively diagnose issues and implement solutions. Knowledge of these configurations not only fosters smoother operations but also aids in preventive maintenance, ensuring longevity and optimal performance of the equipment in question.
Understanding Myers Pump Functionality

The mechanism in question plays a crucial role in various applications, facilitating the movement of fluids efficiently. Grasping its operational principles is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity. This section delves into the core functions and components that contribute to its effectiveness in fluid transfer tasks.
At its core, this system consists of several interconnected elements working in harmony. Each component serves a distinct purpose, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the operation. Understanding these roles helps in troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring that the unit functions smoothly over time.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Motor | Provides the necessary power to initiate movement. |
| Impeller | Creates flow by converting rotational energy into fluid motion. |
| Housing | Encases the mechanism, protecting it from external elements. |
| Seal | Prevents leaks and maintains pressure within the system. |
By familiarizing oneself with these components, users can enhance their understanding of how the assembly operates, leading to more informed decisions regarding installation and maintenance. A thorough comprehension of these systems contributes to more effective management and utilization in various settings.
Key Components of Myers Pumps
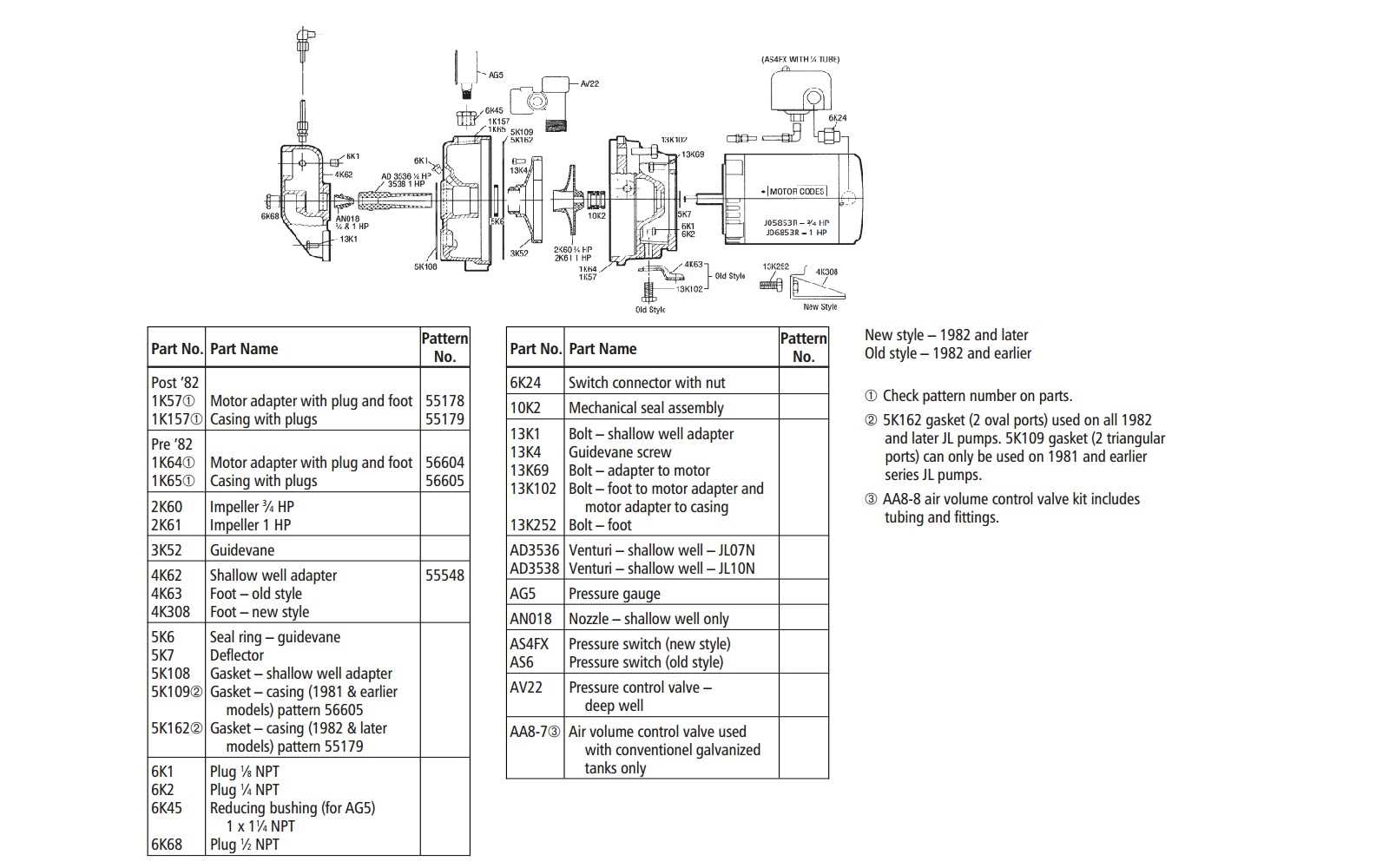
The efficient operation of hydraulic machinery relies on various essential elements, each playing a crucial role in overall functionality. Understanding these components is vital for optimal performance, maintenance, and troubleshooting. This section explores the main parts that contribute to the seamless operation of these systems.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Impeller | Drives the fluid movement through the assembly, converting rotational energy into fluid energy. |
| Motor | Provides the necessary power to drive the impeller, typically electric or diesel-driven. |
| Volute | Houses the impeller and directs the flow of fluid, allowing for efficient discharge. |
| Seal | Prevents leakage of fluids and protects internal components from contamination. |
| Suction Strainer | Filters debris from the incoming fluid, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the machinery. |
Recognizing the significance of these elements aids in understanding their interplay and the impact they have on performance. Proper maintenance and timely replacements of these components can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of hydraulic systems.
Importance of Diagrams in Maintenance
Visual representations play a crucial role in the upkeep and repair of complex machinery. They serve as essential tools that facilitate understanding, enhance communication, and streamline troubleshooting processes.
Here are several key reasons why these illustrations are invaluable in maintenance:
- Enhanced Understanding: Visual aids help technicians quickly grasp the structure and function of various components, reducing the time spent deciphering text-based instructions.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: Clear representations allow for quicker identification of issues, enabling a more effective approach to problem-solving.
- Standardized Communication: Illustrations provide a common reference point for teams, minimizing misunderstandings and improving collaborative efforts.
- Training and Onboarding: New personnel can benefit significantly from visual aids, allowing them to familiarize themselves with systems and processes faster.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Accurate visuals can serve as a historical reference, helping track changes and maintenance over time.
In conclusion, incorporating visual representations into maintenance practices not only boosts efficiency but also enhances overall safety and reliability in operations.
Common Issues with Pump Parts
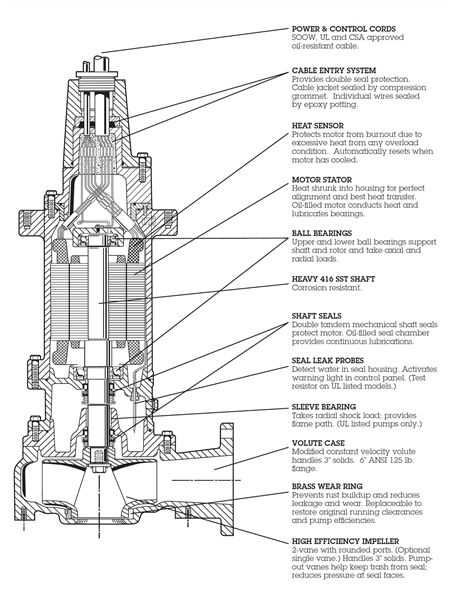
In any mechanical system, various components may encounter problems that can hinder performance. Identifying these issues early is crucial to maintaining efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
Wear and Tear: Over time, components may suffer from deterioration due to continuous use. Regular inspection is vital to catch these issues before they lead to significant failures.
Leaking Seals: One of the most prevalent concerns is the deterioration of seals, which can lead to fluid loss. Ensuring seals are in good condition is essential for optimal operation.
Clogged Filters: Accumulation of debris in filters can restrict flow, reducing efficiency. Routine cleaning or replacement can prevent this issue from escalating.
Misalignment: Improper alignment of components can cause excessive vibration and wear. Correct alignment is necessary to ensure smooth functioning and prevent further damage.
Corrosion: Exposure to harsh environments can lead to rust and degradation. Protective coatings and regular maintenance can mitigate this risk.
Addressing these common challenges promptly can help ensure the ultimate reliability and efficiency of your mechanical systems.
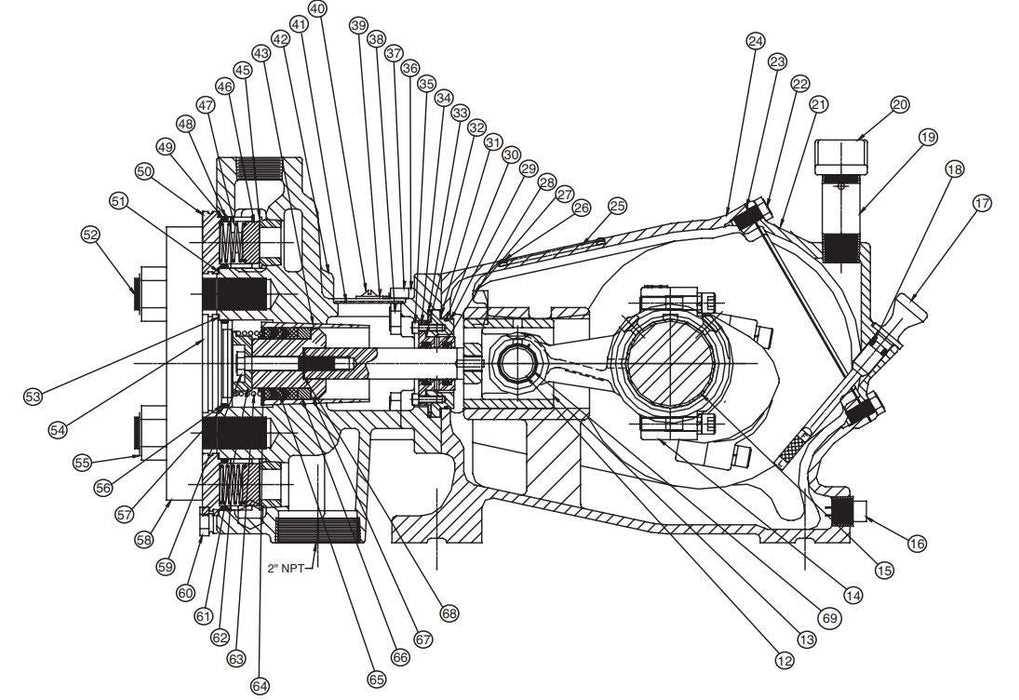
Step-by-Step Diagram Analysis
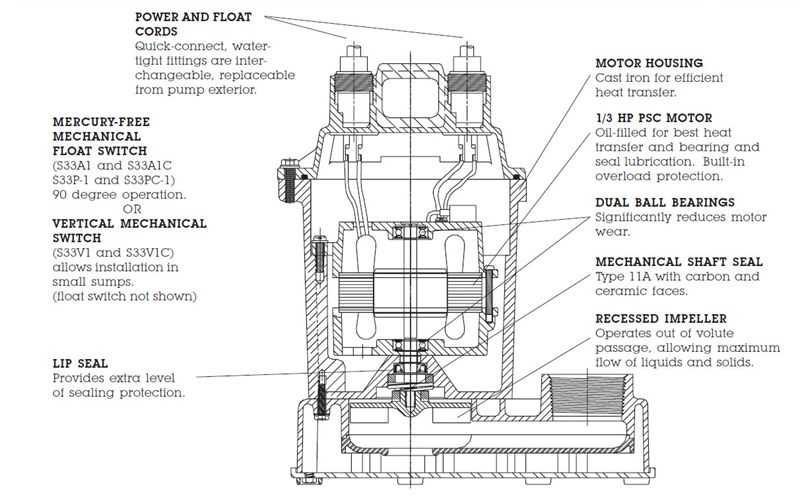
This section aims to provide a comprehensive breakdown of the visual representation that illustrates the various components and their interconnections within the system. By dissecting each element, we can enhance our understanding of functionality and improve maintenance practices.
Understanding Each Component

Begin by identifying the key elements illustrated in the representation. Each component plays a vital role in the overall operation, and recognizing their specific functions is essential. For instance, some parts may be responsible for movement, while others ensure stability or fluid flow. Analyzing these roles can lead to better troubleshooting techniques.
Connecting the Dots
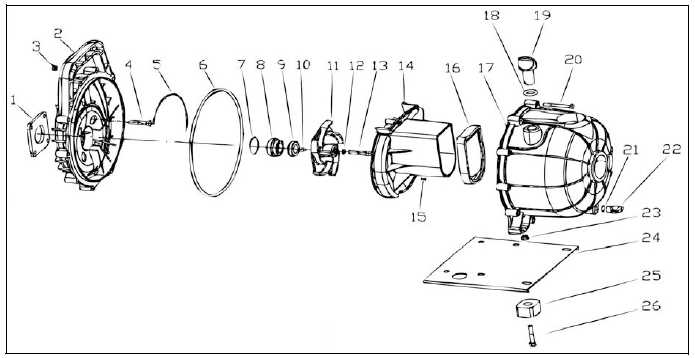
Once the individual elements are understood, focus on how they interact with one another. This interconnectedness is crucial, as it often determines the efficiency of the entire system. Pay attention to any arrows or lines that indicate flow direction or mechanical linkage. Understanding these relationships can help in diagnosing potential issues or planning upgrades.
Replacing Myers Pump Components
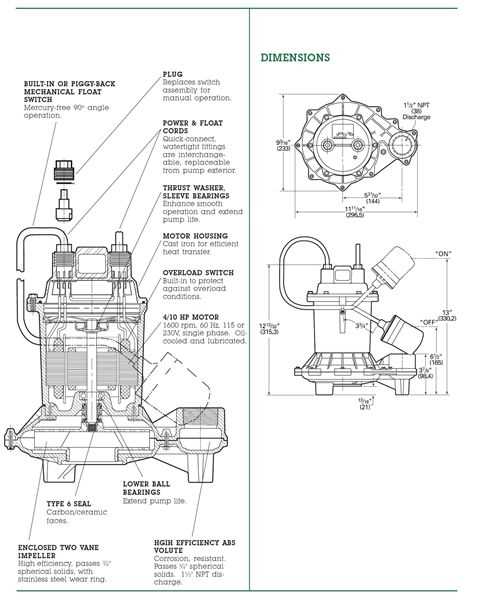
Maintaining optimal performance in machinery often necessitates the replacement of various components over time. Understanding the process and key elements involved is essential for ensuring that the equipment operates efficiently and reliably. This section will provide guidance on how to effectively replace essential elements of the system to restore functionality and longevity.
Identifying Components for Replacement

Before initiating the replacement process, it is crucial to identify the specific components that require attention. Regular inspections can help in diagnosing wear and tear. Here are some common elements that may need to be replaced:
| Component | Signs of Wear | Replacement Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Seals | Leaking fluid | Ensure correct sizing and material compatibility. |
| Impeller | Reduced flow rate | Check for damage and replace with an identical model. |
| Motor | Unusual noises or overheating | Test electrical connections before replacement. |
Steps for Replacement
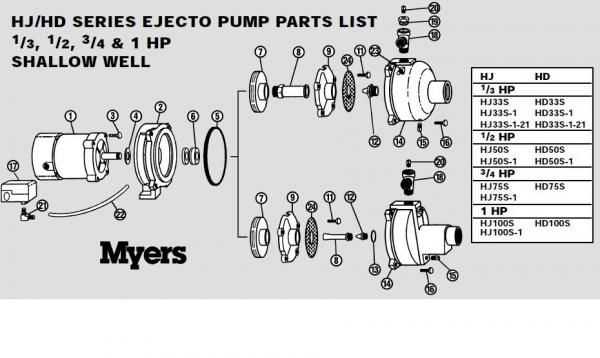
Once the components to be replaced have been identified, follow these steps for a successful replacement:
- Ensure the equipment is turned off and disconnected from power sources.
- Carefully disassemble the necessary sections to access the components.
- Remove the worn or damaged components with appropriate tools.
- Install new components, ensuring a secure and proper fit.
- Reassemble the equipment and conduct a test run to verify functionality.
Tools Needed for Pump Repair

Effective maintenance of hydraulic systems requires a specific set of instruments to ensure efficiency and reliability. Utilizing the right tools not only streamlines the repair process but also enhances safety and longevity of the equipment. Below are essential items that will facilitate the repair tasks and contribute to a successful outcome.
Basic Hand Tools
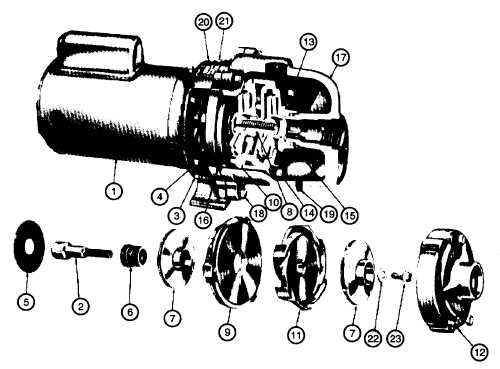
Having a good selection of hand tools is crucial. This includes wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. These fundamental implements allow for the disassembly and reassembly of components with precision. It’s advisable to have both metric and standard sizes to accommodate various fittings.
Specialized Equipment
In addition to basic tools, certain specialized equipment may be necessary. Torque wrenches ensure that fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications, preventing leaks. Calipers can be used for precise measurements, while cleaning supplies such as solvents and brushes are important for maintaining cleanliness during repairs. A reliable multimeter is also essential for electrical diagnostics, ensuring all systems function optimally.
Safety Precautions When Working

Ensuring safety in any mechanical environment is paramount to preventing accidents and injuries. Proper precautions not only protect individuals but also enhance efficiency and productivity. Understanding potential hazards and adopting appropriate measures can significantly reduce risks associated with maintenance and repair tasks.
Personal Protective Equipment
Wearing appropriate gear is essential. Always use gloves, goggles, and ear protection to safeguard against potential hazards. Make sure that clothing is suitable for the task, avoiding loose items that may get caught in machinery.
Work Environment
Maintain a clean and organized workspace. Ensure all tools are in good condition and stored correctly after use. Regularly inspect the area for any obstructions or hazards that could lead to accidents, and address them promptly to create a safer environment.