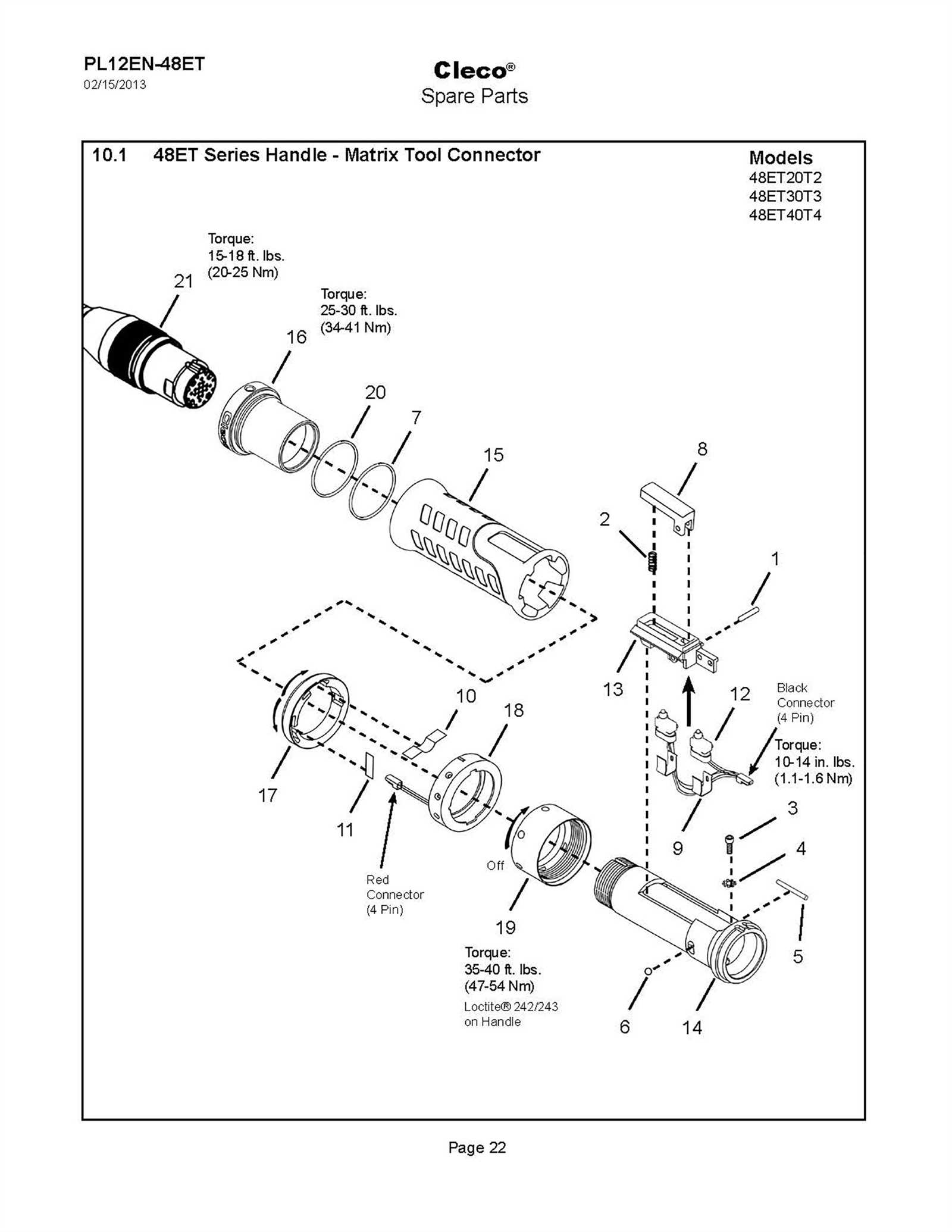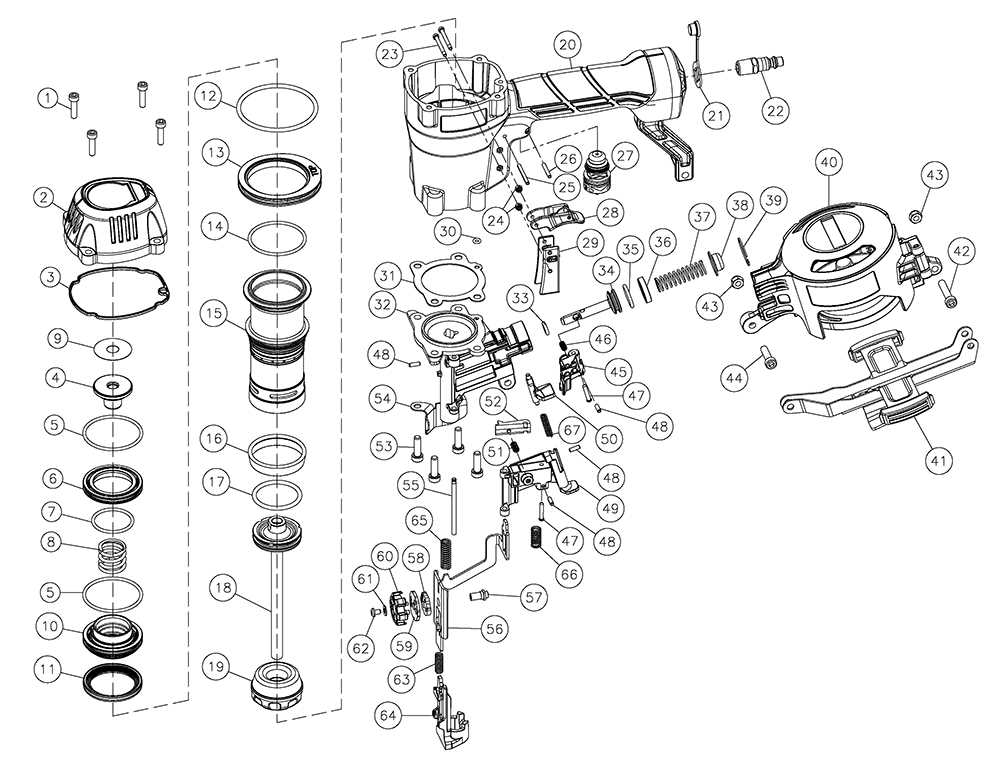
Understanding how various elements come together in mechanical devices is essential for maintenance and efficient operation. Visual representations of equipment structures provide valuable insights into how different sections are assembled, making it easier to identify specific areas in need of attention. By grasping the overall configuration, one can improve the tool’s performance and prolong its lifespan.
Detailed breakdowns of each section enable users to navigate complex assemblies with confidence. These schematics serve as a guide for those looking to address issues, replace worn-out sections, or optimize the tool’s operation. In-depth knowledge of the equipment’s layout aids in effective troubleshooting and ensures smooth functionality.
Overview of Key Components

Understanding the essential elements of this tool helps in maintaining its performance and ensuring long-lasting functionality. Each piece plays a crucial role in the overall operation, making it important to familiarize yourself with their functions and connections.
- Drive Mechanism: This is the core element that powers the tool, providing the necessary force to complete tasks efficiently.
- Trigger Assembly: Responsible for initiating the tool’s action, the trigger assembly ensures precise control over the operation.
- Magazine: The section that holds and feeds the material, enabling continuous use without frequent reloads.
- Safety Features: Built-in safeguards that prevent accidental activation and ensure secure handling during use.
- Exhaust System: Directs airflow away from the user, ensuring a clean and safe working environment.
By understanding these components and their roles, you can easily
Understanding the Nail Gun Mechanism
A nail gun is a powerful tool designed to drive nails into various materials with precision and speed. Its operation relies on a combination of mechanical and pneumatic systems, which work together to deliver consistent force with minimal effort. This tool simplifies tasks that would otherwise require manual hammering, offering accuracy and efficiency, especially in large projects.
At its core, the tool’s mechanism consists of a few key components that handle nail loading, positioning, and firing. The trigger controls air or mechanical pressure, propelling the fastener into the material. A magazine holds the nails in place, feeding them into the chamber, while the safety system ensures that the tool operates only when properly aligned with the surface.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trigger | Initiates the firing process by releasing stored pressure. | ||||||||||
| Magazine | Holds and feeds nails into the chamber. | ||||||||||
| Material | Temperature Resistance | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrile Rubber | -40°C to 120°C | Hydraulic systems, automotive |
| Silicone | -55°C to 200°C | Food and medical equipment |
| Fluoroelastomer | -20°C to 250°C | Chemical resistance applications |
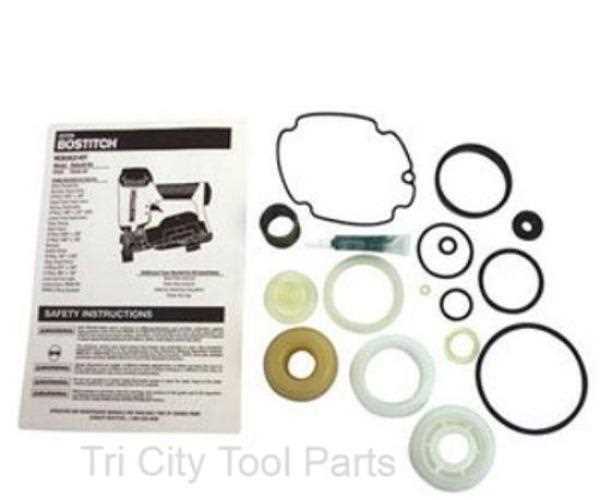
Regular inspection and replacement of these components are crucial to prevent wear and tear that can lead to performance issues. By ensuring the integrity of rings and seals, users can extend the service life of their equipment, reduce maintenance costs, and improve reliability in demanding environments.
Tips for Replacing Worn-Out Components
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. Over time, certain elements may wear out and require replacement. This guide provides valuable tips to help you effectively replace these components, restoring your tool’s functionality.
- Identify the Worn Parts: Before proceeding, thoroughly inspect your equipment to determine which components are damaged or degraded. Look for signs of wear, such as cracks, discoloration, or reduced performance.
- Consult the Manual: Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific information on the components used in your model. This resource can provide guidance on the types of replacements needed and the correct procedures for installation.
- Gather Necessary Tools: Prepare all the tools required for the replacement process. Having everything on hand will make the task more efficient and prevent interruptions.
- Follow Safety Protocols: Prioritize safety by wearing appropriate protective gear and ensuring the equipment is powered off before starting any work. This reduces the risk of injury during the replacement process.
- Use Quality Replacement Parts: When selecting new components, opt for high-quality or original parts. This helps maintain the performance and reliability of your equipment.
- Test After Replacement: Once the worn parts have been replaced, conduct a thorough test of the equipment. This step ensures everything is functioning correctly and helps identify any potential issues early.
Troubleshooting Common Part Failures
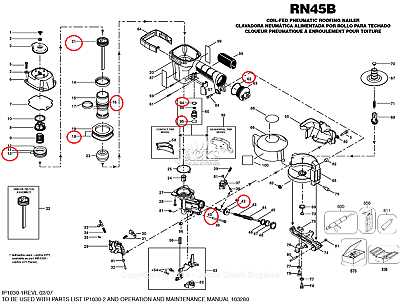
Understanding and addressing frequent component malfunctions can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of your equipment. This section provides guidance on identifying typical issues that may arise and offers practical solutions for resolving them.
Loss of Power: A common issue encountered is the sudden loss of power during operation. This may be caused by a faulty electrical connection or a depleted power source. To troubleshoot, check all connections for tightness and inspect the power supply for any signs of wear or damage.
Inconsistent Performance: If the equipment operates inconsistently, it may indicate that certain components are worn or damaged. Examine the mechanism for any obstructions and ensure that all moving parts are lubricated adequately. Regular maintenance can prevent such issues from escalating.
Jamming: Jamming can occur when debris accumulates or when components are not aligned correctly. To resolve this, inspect the interior for any foreign objects and clear them away. Additionally, verify that all parts are properly seated and aligned to ensure smooth operation.
Noisy Operation: Unusual noises during operation can signal underlying problems, such as worn bearings or loose components. Investigate the source of the noise and consider lubricating any moving parts. If the noise persists, further examination of the affected components may be necessary.