
Understanding how various components are organized within equipment is crucial for both troubleshooting and maintenance. A detailed visual representation of the internal and external systems can simplify the process of identifying and replacing specific elements, ensuring smooth operation and prolonging the machine’s lifespan.
In this guide, we will explore the general layout of mechanical assemblies, focusing on how different elements are interconnected. Whether you are maintaining or repairing, knowing the arrangement of the various parts can help streamline your work, saving time and effort.
We’ll cover the most common aspects, from key structural elements to smaller, often overlooked components. With clear explanations, this resource will assist both professionals and enthusiasts in gaining a deeper understanding of equipment functionality.
Key Components Overview
The equipment in question consists of several essential elements designed to ensure reliable functionality across a variety of demanding environments. Each element works in harmony to provide efficient operation and durability, supporting the machine’s overall performance and user needs.
Engine System: The power source is a vital component that drives the entire operation. This system is engineered for efficiency and longevity, allowing the unit to perform even in challenging conditions.
Control Panel: The interface provides easy access to adjustments, making it simple for operators to manage performance settings. It includes indicators and controls that enhance usability and precision in various applications.
Cooling Mechanism: To prevent overheating
Main Electrical System Parts
The electrical system in power equipment plays a critical role in ensuring smooth operation and consistent performance. This section focuses on the key elements that manage the flow of electricity, safeguarding both the equipment and the user. Understanding these components is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Alternator: This component is responsible for generating electrical power by converting mechanical energy. It supplies electricity to various systems while also charging the battery.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator ensures that the power output remains steady, preventing overvoltage or undervoltage situations, which could cause damage to sensitive electronics.
- Battery: The battery stores electrical energy and provides power during startup. It works in tandem with the alternator to ensure uninterrupted operation.
- Wiring Harness:
Engine and Power Supply Details
The engine and power supply are key elements that drive the functionality and efficiency of any portable welding and generator system. Understanding the structure and specifications of these components is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in various conditions.
- Engine Type: The machine is equipped with a durable internal combustion engine, designed to deliver consistent power output while maintaining fuel efficiency.
- Fuel System: The fuel delivery system ensures smooth operation by providing a steady flow of energy to the engine, enabling prolonged use without frequent refueling.
- Power Output: The generator is capable of delivering a stable electrical supply, suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including welding, powering tools, and backup power solutions.
- Cooling Mechanism: A built-in cooling system prevents overheating, enhancing longevity and ensuring that the equipme
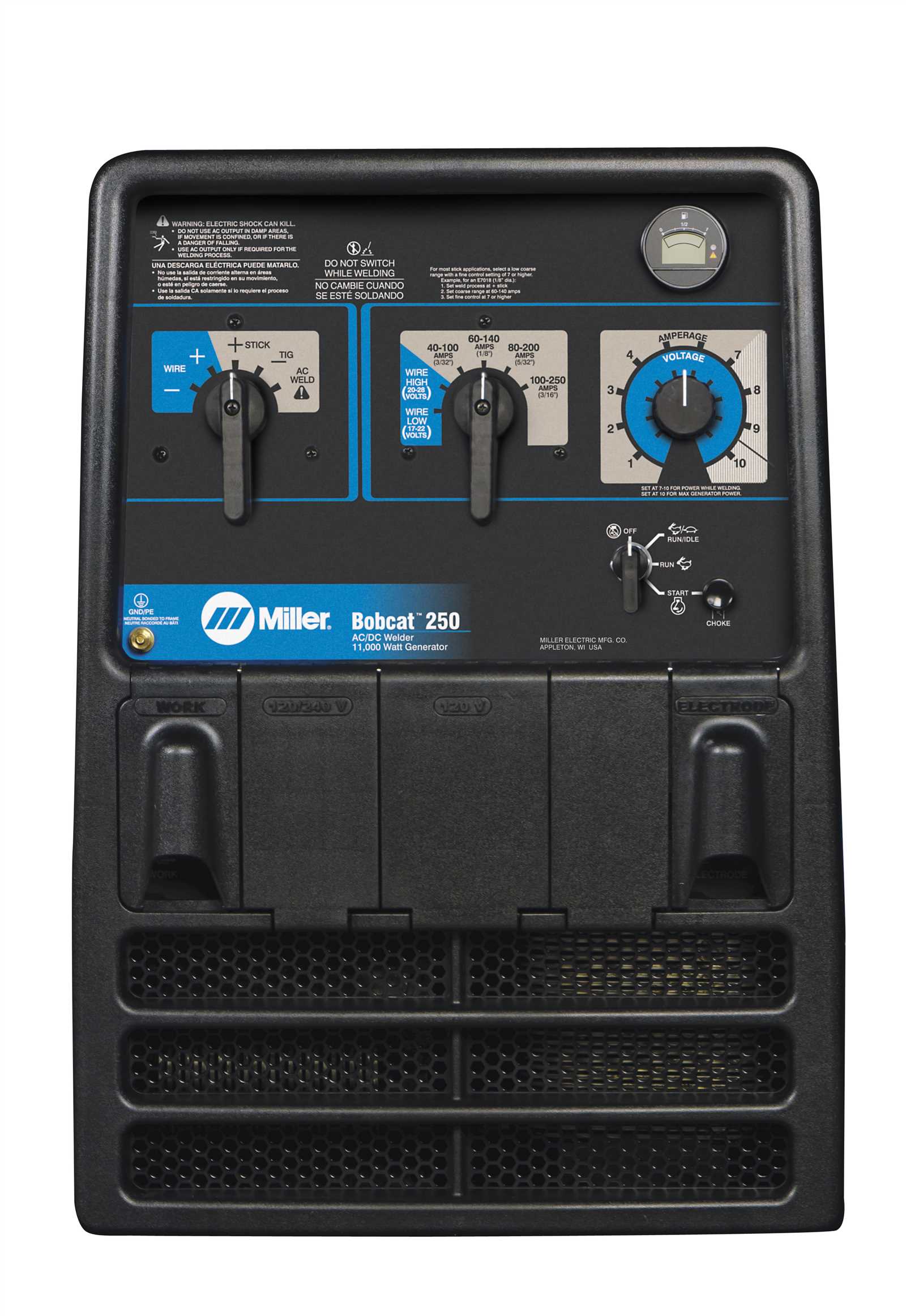
Control Panel Layout and Functions
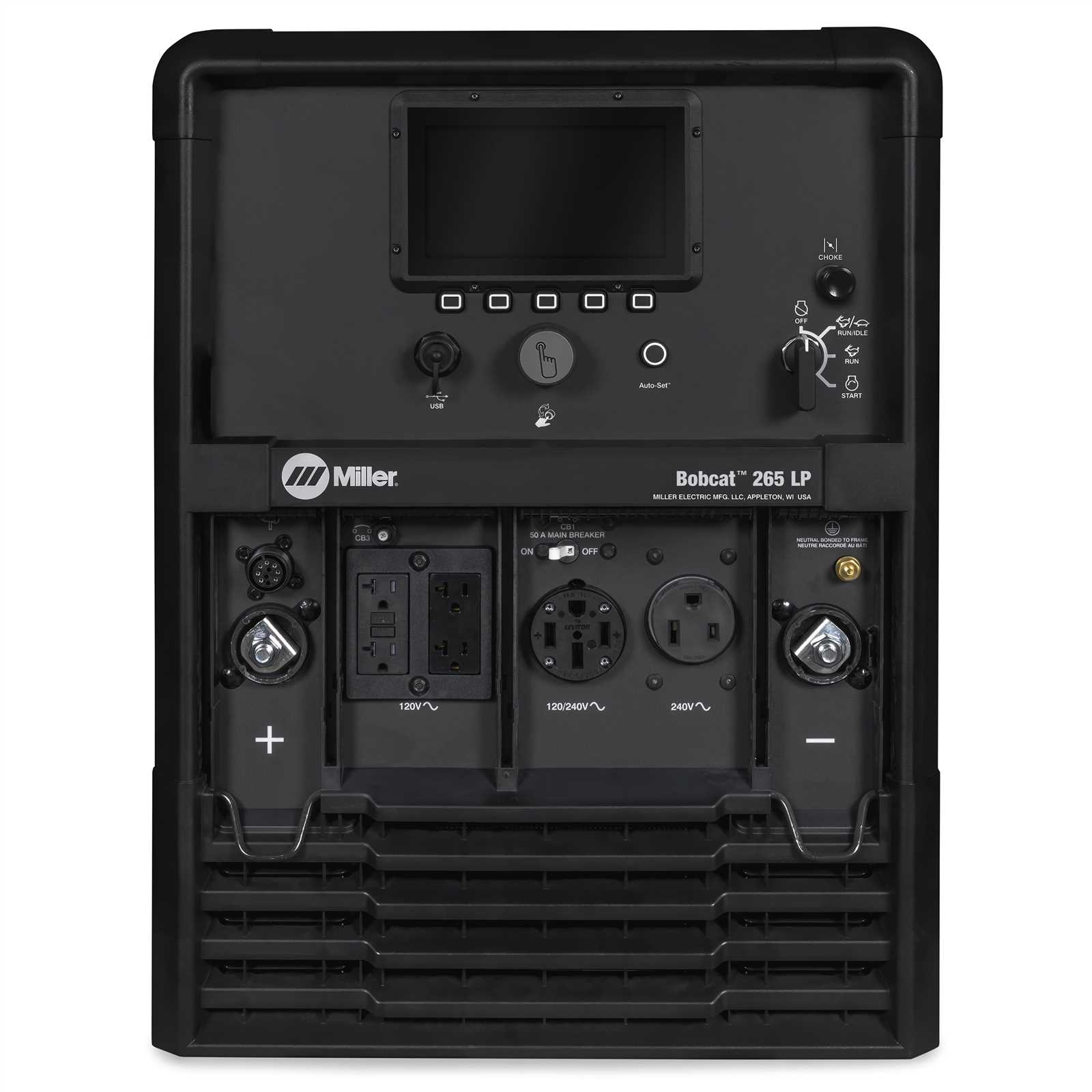

The control panel is the central interface that allows users to manage and monitor various operational settings and functions. Understanding the layout and functionality of this panel is essential for efficient operation. This section provides a detailed overview of the key features and controls available on the panel, ensuring clarity in their use.
Main Switches and Indicators

The control panel includes several critical switches and indicators, each designed to provide users with precise control over the system’s operations. These elements allow for adjustments, safety measures, and visual feedback on performance.
Component Function Power Switch Activates or deactivates the main power flow, enabling the system to start or stop. Output Control Adjusts the level of output to match the requirements of the current task. Welding Output Components

The welding output system is responsible for providing the necessary energy to carry out the welding process. It ensures that sufficient power is delivered to create a stable arc, enabling the fusion of materials. Various components work together to regulate and maintain this output, ensuring consistent performance across different welding tasks.
Power Delivery System

At the core of the welding output is the power delivery system. This component manages the flow of electricity, adjusting the output according to the specific welding requirements. It ensures that the correct amount of current reaches the welding torch or electrode, allowing precise control over the heat and arc stability.
Output Control Mechanism
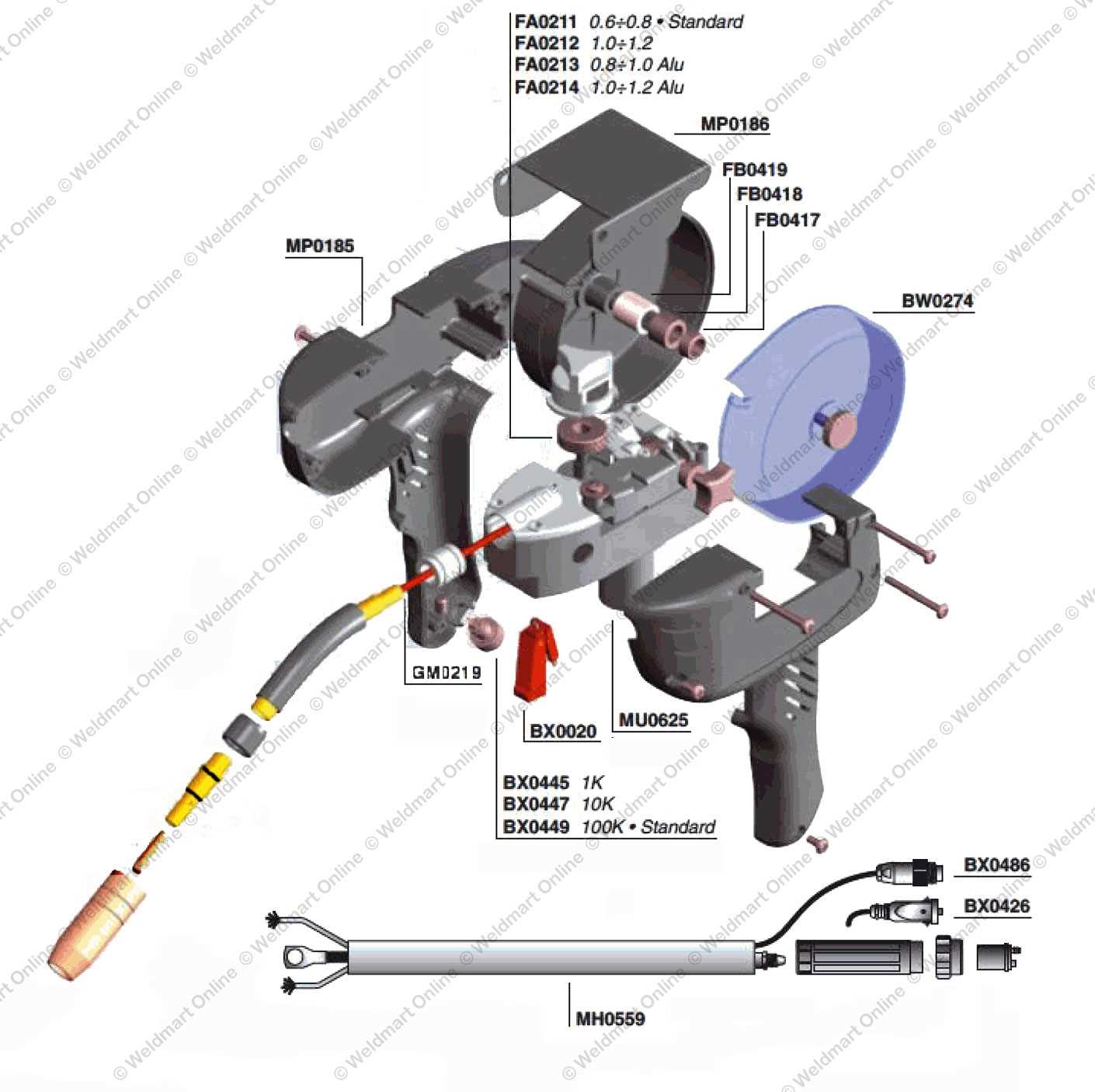
The output control mechanism allows operators to fine-tune the welding parameters, adjusting the amperage and voltage as needed. This ensures that the welder can handle different types of materials and thicknesses, optimizing performance for each specific task. The control system provides flexibility, enabling efficient and effective welding in various conditions.
Cooling and Ventilation System
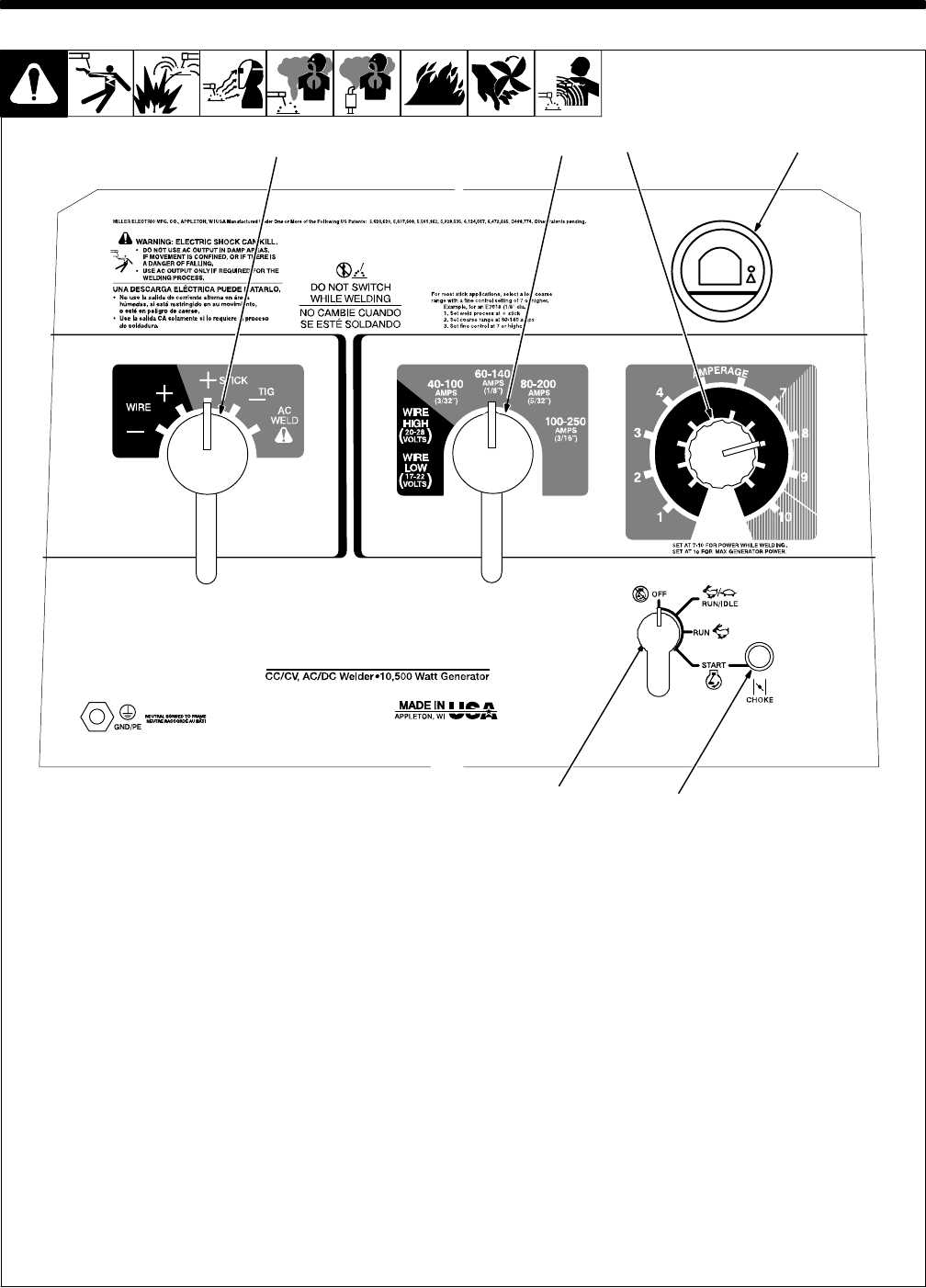
The effectiveness of any machine greatly relies on its cooling and ventilation setup. This essential component ensures optimal operating temperatures and prevents overheating, which can lead to significant performance issues and potential damage. Proper airflow and heat dissipation are vital for maintaining efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
In this context, the cooling and ventilation system encompasses various elements designed to facilitate heat management. Components such as radiators, fans, and ducts work together to regulate temperatures effectively. The circulation of air plays a crucial role in transferring heat away from critical areas, allowing the engine and other mechanical parts to function smoothly.
Regular maintenance of this system is imperative to ensure it operates at peak performance. Accumulation of dirt and debris can obstruct airflow, leading to insufficient cooling. Therefore, periodic inspections and cleanings are recommended to maintain efficiency. Additionally, understanding the layout of the ventilation system can help in troubleshooting any issues that may arise, ensuring the machinery remains operational and reliable.
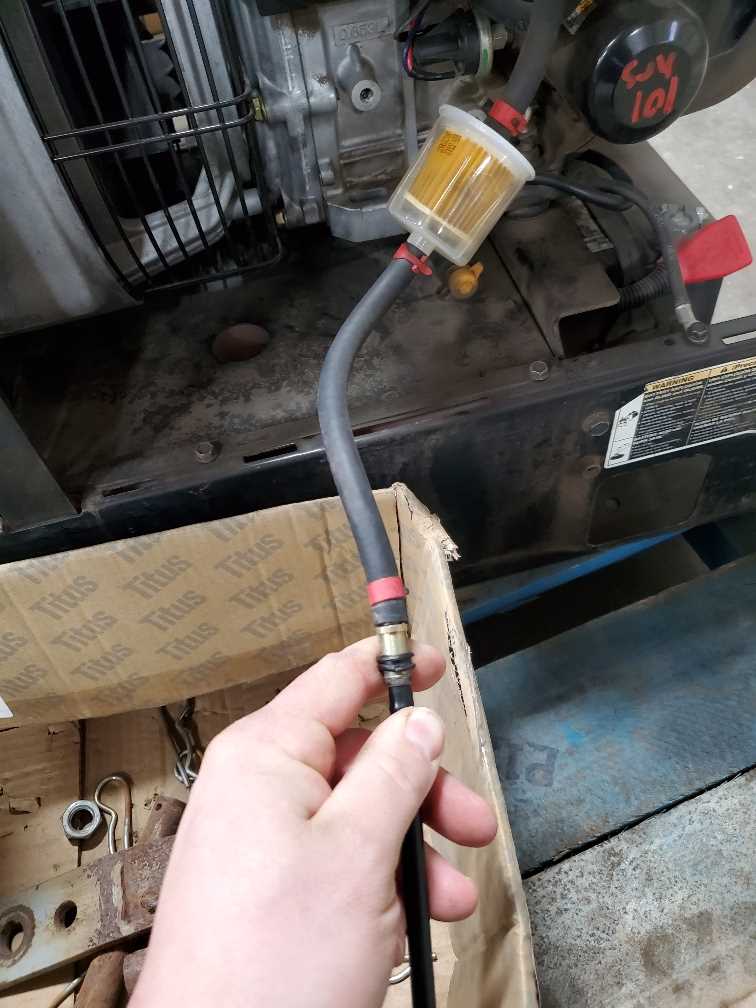
Fuel System Breakdown
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the operation of equipment, ensuring that the engine receives the necessary fuel for efficient performance. Understanding its components and functionality can help in diagnosing issues and maintaining optimal operation.
Key Components

- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel needed for the system.
- Fuel Pump: Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Connect various components, allowing the flow of fuel.
- Injectors: Atomize the fuel for better combustion within the engine.
Common Issues
- Clogged Fuel Filter: Can restrict fuel flow, leading to performance problems.
- Damaged Fuel Lines: May cause leaks and reduce fuel efficiency.
- Malfunctioning Fuel Pump: Can result in insufficient fuel delivery to the engine.
- Injector Problems: Poor atomization can lead to incomplete combustion and increased emissions.
Maintenance and Serviceable Parts
Regular upkeep and attention to serviceable components are essential for optimal performance and longevity of any equipment. Understanding which elements require periodic inspection and replacement can significantly enhance efficiency and reliability. By prioritizing maintenance, users can prevent unexpected failures and costly repairs.
Key Components: Various elements play a critical role in the overall functioning of machinery. These include filters, belts, and fluids, all of which should be routinely checked and replaced as necessary. Ensuring that these components are in good condition helps maintain smooth operation.
Maintenance Practices: Establishing a regular maintenance schedule is vital. Users should perform visual inspections, replace worn parts, and keep the equipment clean. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations will ensure that the machinery operates at its best, reducing downtime and extending its lifespan.
Troubleshooting Common Part Issues
When operating machinery, encountering malfunctions is a possibility that can disrupt workflow. Identifying and resolving common component-related problems can enhance efficiency and prolong the lifespan of the equipment. This section aims to provide insights into recognizing symptoms, diagnosing issues, and implementing effective solutions.
Identifying Symptoms
Recognizing early signs of malfunction is crucial. Users may notice unusual noises, decreased performance, or irregular vibrations. These indicators often suggest that certain components may require attention. Regular inspections can help in pinpointing these symptoms before they escalate into major issues.
Effective Solutions
Once problems are identified, it is essential to address them promptly. Common remedies include replacing worn-out elements, tightening loose connections, and ensuring proper lubrication of moving parts. Regular maintenance can significantly reduce the likelihood of recurring issues, thereby enhancing the overall reliability of the machinery.