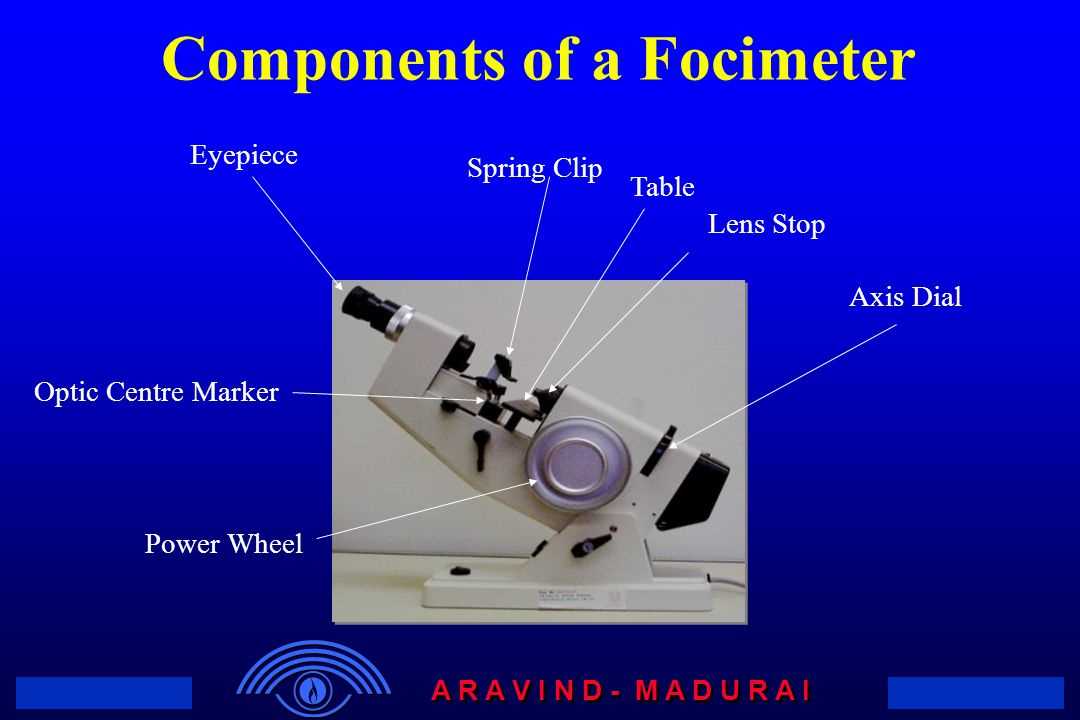
The precision instruments used for evaluating optical prescriptions are essential in the field of vision care. These sophisticated devices play a critical role in ensuring that lenses are crafted with the utmost accuracy, directly impacting the quality of vision for users. A closer examination of these tools reveals a variety of interconnected elements that work in harmony to achieve precise measurements.
Each segment of these measurement tools serves a unique purpose, contributing to the overall functionality and effectiveness of the device. From optical alignments to calibration mechanisms, understanding how these various components interact provides valuable insights into their operational efficiency. This knowledge not only aids technicians in their work but also enhances the overall user experience.
Delving into the specific characteristics and arrangements of these elements allows professionals to optimize their use and maintenance. Recognizing the importance of each individual piece fosters a deeper appreciation for the technology that underpins modern optical practices. As we explore the intricacies of these measurement instruments, the significance of their construction becomes increasingly evident.
Understanding the Lensometer Functionality
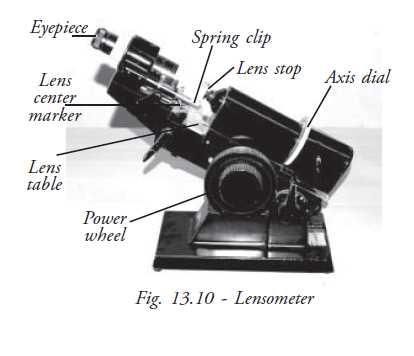
The ability to assess and measure optical prescriptions is essential in the field of vision care. This specialized equipment facilitates the evaluation of lenses, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications for effective visual correction. By employing various components, it enables practitioners to gain precise insights into the refractive qualities of optical elements.
Key aspects of this equipment include its capacity to determine focal lengths, assess alignment, and evaluate curvature. Each function plays a vital role in delivering accurate results, which are crucial for crafting tailor-made visual aids. Moreover, understanding how these features interact allows for enhanced diagnosis and treatment planning.
Ultimately, a comprehensive grasp of this instrument’s functionality is indispensable for professionals in optometry and ophthalmology, contributing to improved patient outcomes and overall satisfaction in vision correction. Delving into its operation reveals the intricate balance between technology and eye care expertise.
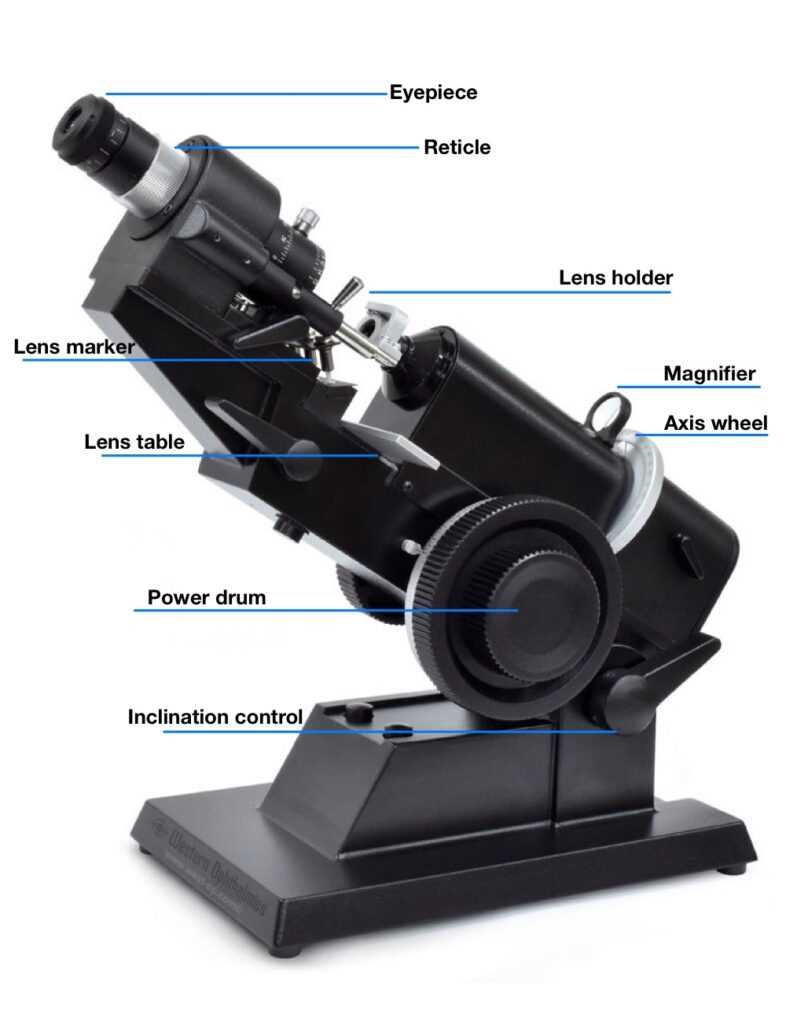
Key Components of a Lensometer
A precision optical instrument is essential for determining the characteristics of corrective eyewear. Understanding its fundamental elements is crucial for accurate measurement and calibration. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring the device functions effectively, allowing professionals to assess lenses with high precision.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Light Source | Provides illumination to facilitate visibility of the lens characteristics. |
| Crosshair | Aiming guide used for aligning the optical center of the lens during measurements. |
| Diopter Adjustment | Allows users to calibrate the device according to their individual visual needs. |
| Viewing Lens | Magnifies the lens image, making it easier to analyze various parameters. |
| Scale | Graduated markings that indicate the specific measurements and values obtained. |
| Stage | Platform where the lens is securely placed for precise evaluation. |
How to Read a Lensometer Diagram

Understanding the layout of an optical measuring device is essential for accurate interpretation and effective use. This guide focuses on the essential elements that make up the schematic representation of such a device, highlighting the key components and their functions.
Begin by identifying the main sections within the illustration. Each component plays a critical role in the overall operation, from the calibration settings to the measurement scales. Familiarize yourself with symbols and labels; they provide vital information about each element’s purpose.
Next, pay attention to the arrangement of various features. The configuration often indicates how to correctly align the optical instruments for precise readings. Take note of any directional arrows or indicators that guide the user in manipulating the device effectively.
Additionally, understand the relationship between the components. Some features work in tandem, and knowing how they interact can enhance your proficiency. Recognize how adjustments in one area may impact the readings from another.
Finally, practice interpreting different schematics to build confidence. With experience, reading these illustrations will become intuitive, enabling you to operate the device with greater accuracy and ease.
Importance of Calibration in Lensometers
Ensuring the precision of optical measurement devices is crucial for maintaining the quality of vision correction. Calibration plays a vital role in guaranteeing that these instruments provide accurate readings, which ultimately affects the effectiveness of corrective lenses.
Benefits of Regular Calibration

- Enhances measurement accuracy
- Improves patient satisfaction
- Reduces the risk of errors in prescriptions
Calibration Process

- Initial assessment of the device’s performance
- Adjustment of settings based on standards
- Documentation of results for future reference
By prioritizing this practice, practitioners can ensure their tools deliver the ultimate precision necessary for optimal patient care.
Common Issues with Lensometer Parts

When it comes to optical measuring devices, various complications can arise, affecting their performance and accuracy. Understanding these challenges is essential for ensuring optimal functionality and longevity. Below are some frequent problems encountered with components of these sophisticated instruments.
Calibration Errors: One of the most common difficulties involves misalignment or incorrect calibration, leading to inaccurate readings. Regular checks are necessary to maintain precision.
Wear and Tear: Over time, mechanical elements can experience wear, resulting in decreased reliability. Frequent usage without proper maintenance can exacerbate these issues.
Optical Obstructions: Dust, smudges, or other debris on lenses can significantly impair visibility and accuracy. Regular cleaning and care are crucial to prevent this.
Electrical Malfunctions: In devices that incorporate electronic components, power issues or software glitches can arise, disrupting operations. Proper troubleshooting techniques are essential for resolution.
Component Compatibility: Using mismatched or incompatible elements can lead to functionality problems. Ensuring that each component is designed to work together is vital for performance.
Maintenance Tips for Lensometer Components

Ensuring the longevity and accuracy of optical measuring devices is crucial for optimal performance. Regular upkeep not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also enhances measurement precision. Below are essential recommendations for maintaining various components effectively.
1. Regular Cleaning: Keeping surfaces free from dust and smudges is vital. Use a microfiber cloth and suitable cleaning solution to gently wipe down the lenses and other optical surfaces. Avoid abrasive materials that can scratch delicate components.
2. Calibration Checks: Periodically verify the calibration of your equipment. This involves using standardized tools to ensure that measurements remain accurate over time. If discrepancies are found, recalibration may be necessary.
3. Inspecting Moving Parts: Regularly check any mechanical components for signs of wear or misalignment. Lubricate moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain smooth operation and prevent damage.
4. Safe Storage: When not in use, store the device in a protective case to shield it from dust, moisture, and physical impact. Ensure that the storage environment is stable and free from extreme temperatures.
5. Software Updates: If your device utilizes software for operation, keep it updated. Regular updates can enhance functionality, improve accuracy, and fix any bugs that may arise.
6. Professional Servicing: Schedule routine maintenance with qualified technicians who can conduct thorough inspections and repairs. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Advanced Features in Modern Lensometers

The evolution of optical measurement devices has introduced a range of sophisticated functionalities that enhance accuracy and user experience. These innovations cater to the increasing demands for precision in vision correction and facilitate seamless integration into various clinical settings.
One of the standout advancements is the incorporation of digital technology, which allows for real-time data analysis and display. This feature significantly reduces the time required for assessments, enabling practitioners to serve patients more efficiently. Additionally, automated alignment systems ensure optimal positioning, minimizing human error and improving the reliability of results.
Furthermore, modern instruments often come equipped with enhanced connectivity options, allowing for easy integration with electronic health record systems. This capability streamlines workflow and facilitates better data management, ensuring that patient histories are accurately maintained and easily accessible.
Moreover, many contemporary devices offer customizable settings, enabling practitioners to tailor measurements to individual patient needs. This adaptability is crucial for providing personalized care, particularly in complex cases where standard measurements may not suffice.
In summary, the latest advancements in optical measurement tools not only improve the accuracy and efficiency of assessments but also enhance the overall quality of patient care through innovative features and seamless integration with modern healthcare practices.
Applications of Lensometers in Optometry
In the field of vision care, precise measurement tools are essential for ensuring optimal eyewear fitting and vision correction. These instruments play a critical role in evaluating optical prescriptions, enabling practitioners to deliver tailored solutions to their patients. Their applications extend beyond basic assessments, encompassing a variety of functions that enhance both diagnosis and treatment.
One primary application involves the verification of prescription lenses. By accurately measuring the focal properties, professionals can confirm that the manufactured eyewear matches the specifications provided by the optometrist. This process not only minimizes errors but also ensures that patients receive the correct vision correction needed for their daily activities.
Another important use is the assessment of lens characteristics, such as power and orientation. Understanding these elements is crucial when determining the best options for multifocal or specialized lenses. Such evaluations help in recommending the most suitable eyewear, enhancing visual comfort and clarity for various tasks.
Additionally, these devices assist in the fitting process by evaluating the alignment and positioning of lenses within frames. Proper alignment is vital for effective vision correction, particularly for patients requiring advanced optical solutions. Ensuring that lenses are optimally positioned can greatly improve the overall effectiveness of the eyewear.
In summary, the implementation of these precise instruments in optometry not only facilitates accurate measurements but also elevates the standard of care provided to patients. Their diverse applications underscore their significance in the overall vision health landscape.