| Camshaft |
Regulates the opening and closing of valves, ensuring the right timing for fuel intake and exhaust release
Understanding the G35 Suspension System
The suspension system plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It is designed to absorb shocks from uneven roads, enhance handling, and maintain vehicle balance during various driving conditions. The structure and components work together to provide comfort while also maintaining control over the vehicle’s movement.
Core Components of the Suspension
The suspension system consists of several interconnected elements. These include springs, which help absorb the force from bumps, and dampers that control the rebound of the springs. Control arms and bushings are responsible for connecting the wheels to the frame, allowing controlled movement. Sway bars reduce body roll when turning corners, offering more stability.
How the System Improves Ride Quality
A well-functioning suspension system helps reduce the impact felt by the driver and passengers, improving the overall comfort of the ride. By maintaining the vehicle’s alignment and supporting weight distribution, the system contributes to both performance and safety, especially when driving on uneven terrain or at higher speeds.
Transmission Components Breakdown
The transmission system is crucial for ensuring a smooth driving experience, transferring power from the engine to the wheels. A detailed understanding of the main elements involved in this process helps with maintenance and repair tasks. This section outlines the key components and their functions within the overall system.
Main Components
- Torque Converter: Responsible for transmitting power from the engine, allowing the vehicle to stop without stalling the engine.
- Valve Body: Directs the flow of hydraulic fluid, controlling gear shifts within the system.
- Clutch Packs: Engage and disengage various gears, ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently at different speeds.
- Planetary Gear Set: Provides different gear ratios, enabling the vehicle to adapt to various driving conditions.
Supporting Elements
- Transmission Fluid
Exhaust System Components of the G35
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in maintaining engine performance and reducing emissions. This system efficiently directs waste gases away from the engine, contributing to smoother vehicle operation and compliance with environmental standards.
Main Elements of the Exhaust Assembly
- Muffler: This component dampens the noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases, ensuring a quieter driving experience.
- Catalytic Converter: A key element that reduces harmful pollutants, converting them into less harmful emissions before they exit the vehicle.
- Exhaust Manifold: Attached to the engine, this component collects exhaust gases from the cylinders and channels them through the exhaust pipes.
Supporting Components
- Oxygen Sensors: These sensors monitor the levels of oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing feedback to optimize engine efficiency.
- Resonator: This part works alongside the muffler to further reduce sound and improve the vehicle’s acoustics.
- Exhaust Pipes: These pipes connect various parts of th
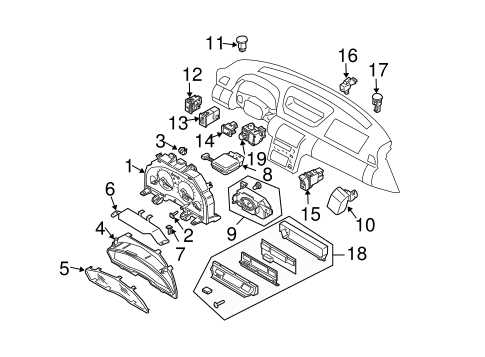
Electrical Systems and Wiring Layout
This section explores the intricacies of the electrical systems and their wiring configurations found in modern vehicles. Understanding these components is crucial for troubleshooting issues and ensuring optimal performance. The electrical setup encompasses various systems, including lighting, ignition, and instrumentation, all of which play vital roles in the overall functionality of the automobile.
Key Electrical Components
- Battery
- Alternator
- Fuses and Relay Boxes
- Wiring Harness
- ECU (Engine Control Unit)
Wiring Layout Overview
The wiring layout serves as a blueprint for the electrical systems, detailing how components are interconnected. A well-organized wiring harness is essential for minimizing electrical interference and ensuring reliable operation.
- Color Coding: Wires are typically color-coded for easy identification and troubleshooting.
- Connector Types: Various connectors are used throughout the system to facilitate secure connections.
- Grounding: Proper grounding is critical to prevent electrical faults and ensure safety.
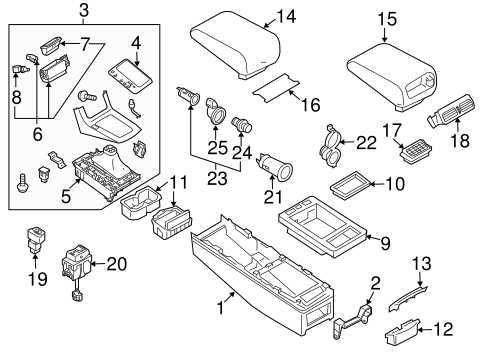
Interior Parts and Controls Diagram

This section provides an overview of the various components and control mechanisms found within the vehicle’s cabin. Understanding the arrangement and function of these elements is crucial for both maintenance and operational efficiency.
Key Interior Features
The interior layout includes several essential features designed for comfort and usability. These components work together to enhance the driving experience and ensure convenient access to controls and storage.
| Component |
Description |
| Dashboard |
The central control panel displaying instruments and controls for the vehicle. |
| Center Console |
A central unit housing various controls, storage compartments, and infotainment system. |
| Door Panels |
Sections of the doors that contain switches for windows and locks. |
| Steering Wheel |
Control device for steering, often equipped with additional controls for convenience. |
| Seats |
Chairs designed for driver and passengers, often adjustable for comfort. |
Control Mechanisms Overview
The operation of the vehicle relies on various control mechanisms that allow the driver to interact effectively with the vehicle’s systems. Familiarity with these controls contributes to a safer and more enjoyable driving experience.
Body Panels and Exterior Components
The outer structure and surface elements of a vehicle play a crucial role in its aesthetics, aerodynamics, and protection. These components not only contribute to the overall visual appeal but also ensure safety and functionality. Understanding the various exterior elements helps in maintaining and customizing a vehicle effectively.
Types of Body Panels
Body panels encompass a variety of elements that form the exterior of a vehicle. Each panel serves specific purposes, from enhancing the look to providing structural integrity. Below is a summary of common types of panels found in modern automobiles:
| Component |
Description |
| Fenders |
Panels located above the wheels, protecting the body from debris and enhancing aerodynamics. |
| Hood |
The cover over the engine compartment, allowing access for maintenance and contributing to aerodynamics. |
| Doors |
Movable panels that provide access to the interior, available in various styles such as sedan, coupe, or hatchback. |
| Trunk Lid |
The rear cover that encloses the cargo area, often featuring a design that complements the vehicle’s aesthetics. |
| Bumpers |
Protective components at the front and rear, designed to absorb impact and minimize damage in collisions. |
Exterior Accessories
In addition to the main panels, various accessories enhance functionality and style. These include mirrors, light assemblies, and spoilers, which can improve visibility and aerodynamics while offering personalization options for vehicle owners.
Brake System Layout
The braking mechanism in a vehicle is essential for ensuring safety and control while driving. This system comprises various components that work together to provide effective stopping power. Understanding the configuration and function of these elements is crucial for both maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Braking Mechanism
The braking setup includes several key elements, such as calipers, rotors, and pads. Calipers house the brake pads and apply pressure to the rotors, while rotors are circular discs that the pads grip to slow down or stop the wheels. The pads are friction materials that make contact with the rotors, converting kinetic energy into heat, which is dissipated through the components.
Hydraulic System Functionality
The hydraulic system plays a vital role in the overall effectiveness of the braking system. It operates using fluid to transmit force from the brake pedal to the calipers. When the pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure is generated, causing the calipers to clamp down on the rotors, resulting in deceleration. Regular inspection of the hydraulic components is necessary to ensure optimal performance and safety.
|